As Ukraine experiences ongoing protests over lack of European integration, Index’ new report looks at the EU’s relationship with freedom of expression (Photo: Anatolii Stepanov / Demotix)
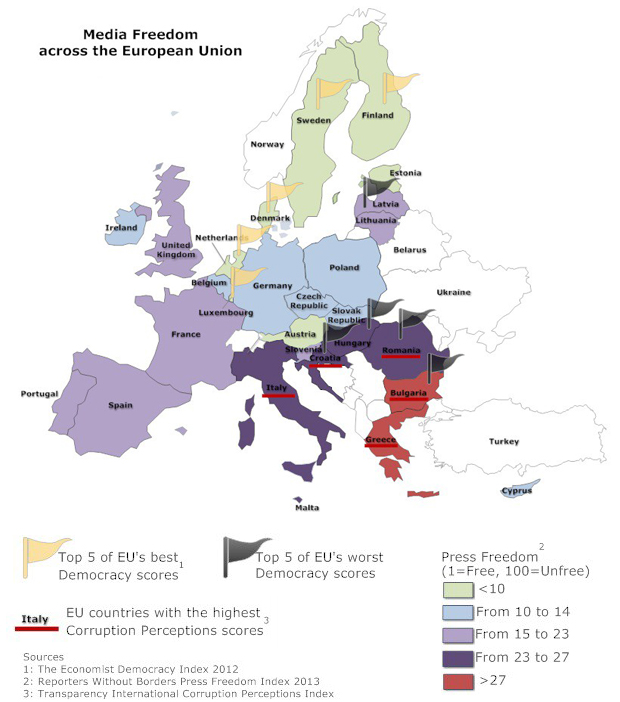
Index on Censorship’s policy paper, Time to Step Up: The EU and freedom of expression, looks at freedom of expression both within the European Union’s 28 member states, which with over 500 million people account for about a quarter of total global economic output, but also how this union defends freedom of expression in the wider world. States that are members of the European Union are supposed to share “European values”, which include a commitment to freedom of expression. However, the way these common values are put into practice vary: some of the world’s best places for free expression are within the European Union – Finland, Netherlands, Denmark and Sweden – while other countries such as Italy, Hungary, Greece and Romania lag behind new and emerging global democracies.
This paper explores freedom of expression, both at the EU level on how the Commission and institutions of the EU protect this important right, but also across the member states. Firstly, the paper will explore where the EU and its member states protect freedom of expression internally and where more needs to be done. The second section will look at how the EU projects and defends freedom of expression to partner countries and institutions. The paper will explore the institutions and instruments used by the EU and its member states to protect this fundamental right and how they have developed in recent years, as well as the impact of these institutions and instruments.
Outwardly, a commitment to freedom of expression is one of the principle characteristics of the European Union. Every European Union member state has ratified the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR); the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and has committed to the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. To complement this, the Treaty of Lisbon has made the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights legally binding which means that the EU institutions and member states (if they act within the scope of the EU law) must act in compliance with the rights and principles of the Charter. The EU has also said it will accede to the ECHR. Yet, even with these commitments and this powerful framework for defending freedom of expression, has the EU in practice upheld freedom of expression evenly across the European Union and outside with third parties, and is it doing enough to protect this universal right?
Within the European Commission, there has been considerable analysis about what should be done when member states fail to abide by “European values”, Commission President Barroso raised this in his State of the Union address in September 2012, explicitly calling for “a better developed set of instruments” to deal with threats to these perceived values and the rights that accompany them. With threats to freedom of expression increasing, it is essential that this is taken up by the Commission sooner rather than later.
To date, most EU member states have failed to repeal criminal sanctions for defamation, with only Croatia, Cyprus, Ireland and the UK having done so. The parliamentary assembly of the Council of Europe called on states to repeal criminal sanctions for libel in 2007, since then little action has been taken by EU member states. There also remain significant issues in the field of privacy law and freedom of information across the EU.
While the European Commission has in the past tended to view its competencies in the field of media regulation as limited, due to the introduction of the Charter of Fundamental Rights into EU primary law, the Commission is looking at a possible enhancement of its role in this area.
With media plurality limited across Europe and in fact potentially threatened by the convergence of media across media both online and off (and the internet being the most concentrated media market), the Commission must take an early view on whether it wishes to intervene more fully in this field to uphold the values the EU has outlined. Political threats against media workers are too commonplace and risks to whistleblowers have increased as demonstrated by the lack of support given by EU member states to whistleblower Edward Snowden. That the EU and its member states have so clearly failed one of the most significant whistleblowers of our era is indicative of the scale of the challenge to freedom of expression within the European Union.
The EU and its member states have made a number of positive commitments to protect online freedom, including the EU’s positioning at WCIT, the freedom of expression guidelines and the No-Disconnect strategy helping the EU to strengthen its external polices around promoting digital freedom. These commitments have challenged top-down internet governance models, supported the multistakeholder approach, protected human rights defenders who use the internet and social media in their work, limited takedown requests, filters and others forms of censorship. But for the EU to have a strong and coherent impact at the global level, it now needs to develop a clear and comprehensive digital freedom strategy. For too long, the EU has been slow to prioritise digital rights, placing the emphasis on digital competitiveness instead. It has also been the case that positive external initiatives have been undermined by contradictory internal policies, or a contradiction of fundamental values, at the EU and member state level. The revelations made by Edward Snowden show that EU member states are violating universal human rights through mass surveillance.
The Union must ensure that member states are called upon to address their adherence to fundamental principles at the next European Council meeting. The European Council should also address concerns that external government surveillance efforts like the US National Security Agency’s Prism programme are undermining EU citizens’ rights to privacy and free expression. A comprehensive overarching digital freedom strategy would help ensure coherent EU policies and priorities on freedom of expression and further strengthen the EU’s influence on crucial debates around global internet governance and digital freedom. With the next two years of ITU negotiations crucial, it’s important the EU takes this strategy forward urgently.
While the European Commission has in the past tended to view its competencies in the field of media regulation as limited, due to the introduction of the Charter of Fundamental Rights into EU primary law, the Commission is looking at a possible enhancement of its role in this area.
With media plurality limited across Europe and in fact potentially threatened by the convergence of media across media both online and off (and the internet being the most concentrated media market), the Commission must take an early view on whether it wishes to intervene more fully in this field to uphold the values the EU has outlined.
Political threats against media workers are too commonplace and risks to whistleblowers have increased as demonstrated by the lack of support given by EU member states to whistleblower Edward Snowden. That the EU and its member states have so clearly failed one of the most significant whistleblowers of our era is indicative of the scale of the challenge to freedom of expression within the European Union.
Where the EU acts with a common approach among the member states, it has significant leverage to help promote and defend freedom of expression globally. To develop a more common approach, since the Lisbon Treaty, the EU has enhanced its set of policies, instruments and institutions to promote human rights externally, with new resources to do so. Enlargement has proved the most effective tool to promote freedom of expression with, on the whole, significant improvements in the adherence to the principles of freedom of expression in countries that have joined the EU or where enlargement is a real prospect. That this respect for human rights is a condition of accession to the EU shows that conditionality can be effective. Whereas the eastern neighbourhood has benefitted from the real prospect of accession (for some countries), in its southern neighbourhood, the EU has failed to promote freedom of expression by placing security interests first and also by failing to react quickly enough to the transitions in its southern neighbourhood following the events of the Arab Spring. The new strategy for this region is welcome and may better protect freedom of expression, but with Egypt in crisis, the EU may have acted too late. The EU must assess the effectiveness of some of its foreign policy instruments, in particular the dialogues for particular countries such as China.
The freedom of expression guidelines provide an excellent opportunity to reassess the criteria for how the EU engages with third party countries. Strong freedom of expression guidelines will allow the EU to better benchmark the effectiveness of its human rights dialogues. The guidelines will also reemphasise the importance of the EU, ensuring that the right to freedom of expression is protected within the EU and its member states. Otherwise, the ability of the EU to influence external partners will be limited.
Headline recommendations
• After recent revelations about mass state surveillance the EU must develop a roadmap that puts in place strong safeguards to ensure narrow targeted surveillance with oversight not mass population surveillance and must also recommit to protect whistle-blowers
• The European Commission needs to put in place controls so that EU directives cannot be used for the retention of data that makes mass population surveillance feasible
• The EU has expanded its powers to deal with human rights violations, but is reluctant to use these powers even during a crisis within a member state. The EU must establish clear red lines where it will act collectively to protect freedom of expression in a member state
• Defamation should be decriminalised across the EU
• The EU must not act to encourage the statutory regulation of the print media but instead promote tough independent regulation
• Politicians from across the EU must stop directly interfering in the workings of the independent media
• The EU suffers from a serious credibility gap in its near neighbourhood – the realpolitik of the past that neglected human rights must be replaced with a coherent, unified Union position on how to promote human rights
Recommendations
- The EU has expanded its powers to deal with human rights violations, but is reluctant to use these powers even during a crisis within a member state. The EU must establish clear red lines where it will act collectively to protect freedom of expression in a member state
- The EU should cut funding for member states that cross the red lines and breach their human rights commitments
Libel, privacy and insult
- Defamation should be decriminalised in line with the recommendations of the Council of Europe parliamentary assembly, and the UN and OSCE’s special rapporteurs on freedom of expression.
- Insult laws that criminalise insult to national symbols should be repealed
Freedom of information
- To better protect freedom of information, all EU member states should sign up to the Council of Europe Convention on Access to Official Documents
- Not all EU institutions, offices, bodies and agencies are acting on their freedom of information commitments. More must be done by the Commission to protect freedom of information
Media freedom & plurality
- The EU must revisit its competencies in the area of media regulation in order to prevent the most egregious breaches of the right to freedom of expression in particular the situations that arose in Italy and Hungary
- The EU must argue against statutory regulation of the print media and argue for independent self-regulation where media bandwidth is no longer limited by spectrum and other considerations
- Member states must not allow political interference or considerations of “political balance” into the workings of the media, where this happens the EU should be considered competent to act to protect media freedom and pluralism at a state level
- The EU is not doing enough to protect whistleblowers. National states must do more to protect journalists from threats of violence and intimidation
Digital
- The Commission must prepare a roadmap for collective action against mass state surveillance
- The EU is right to argue against top-down state control over internet governance it must find more natural allies for this position globally
- The Commission should proceed with a Directive that sets out the criteria takedown requests must meet and outline a process that protects anonymous whistle-blowers and intermediaries from vexatious claims
The EU and freedom of expression in the world
- The EU suffers from a credibility issue in its southern neighbourhood. To repair its standing in the wider world, the EU and its member states must not downgrade the importance of human rights in any bilateral or multilateral relationship
- The EU’s EEAS Freedom of Expression guidelines are welcome. To be effective, they need to focus on the right to freedom of expression for ordinary citizens and not just media actors
- The guidelines need to become the focus for negotiations with external countries, rather than the under-achieving human rights dialogues
- With criticism of the effectiveness of the human rights dialogues, the EU should look again at how the dialogues fit into the overall strategy of the Union and its member states
The European Union contains some of the world’s strongest defenders of freedom of expression, but also a significant number of member states who fail to meet their European and international commitments. To deal with this, in recent years, the European Union’s member states have made new commitments to better protect freedom of expression. The new competency of the European Court of Justice to uphold the values enshrined in the European Convention of Human Rights will provide a welcome alternative forum to the increasingly deluged European Court of Human Rights. This could have significant implications for freedom of expression within the EU. Internally within the EU there is still much that could be done to improve freedom of expression. It is welcome that that the EU and its member states have made a number of positive commitments to protect online freedom, with new action on vexatious takedown notices and coordinated action to protect the multistakeholder model of internet governance. Increasing Commission concern over media plurality may also be positive in the future.
Yet there are a number of areas where the EU must do more. The decriminalisation of defamation across Europe should be a focal point for European action in line with the Council of Europe’s recommendations. National insult laws should be repealed. The Commission should not intervene to increase its powers over national media regulators, but should act where it has clear competencies, in particular to prevent media monopolies and to help deal with conflict of interests between politicians and state broadcasters. Most importantly, discussions of mass population surveillance at the European Council in October must be followed by a roadmap outlining how the EU will collectively take action on this issue. Without internal reform to strengthen protections for freedom of expression, the EU will not enjoy the leverage it should to promote freedom of expression externally to partner countries. While the External Action Service freedom of expression guidelines are welcome, they must be impressed upon member countries as a benchmark for reform.
Externally, the EU has failed to deliver on the significant leverage it could have as the world’s largest trading block. Where the EU has acted in concert, with clear aims and objectives for partner countries, such as during the process of enlargement, it has had a big impact on improving and protecting freedom of expression. Elsewhere, the EU has fallen short, particularly in its southern neighbourhood and in its relationship with China, where the EU has continued human rights dialogues that have failed to be effective.
New commitments and new instruments post-Lisbon may better protect freedom of expression in the EU and externally. Yet, as the Snowden revelations show, the EU and its member states must do significantly more to deliver upon the commitments that have been agreed.
Full report PDF: Time to Step Up: The EU and freedom of expression
This article was posted on 12 Dec 2013 at indexoncensorship.org





