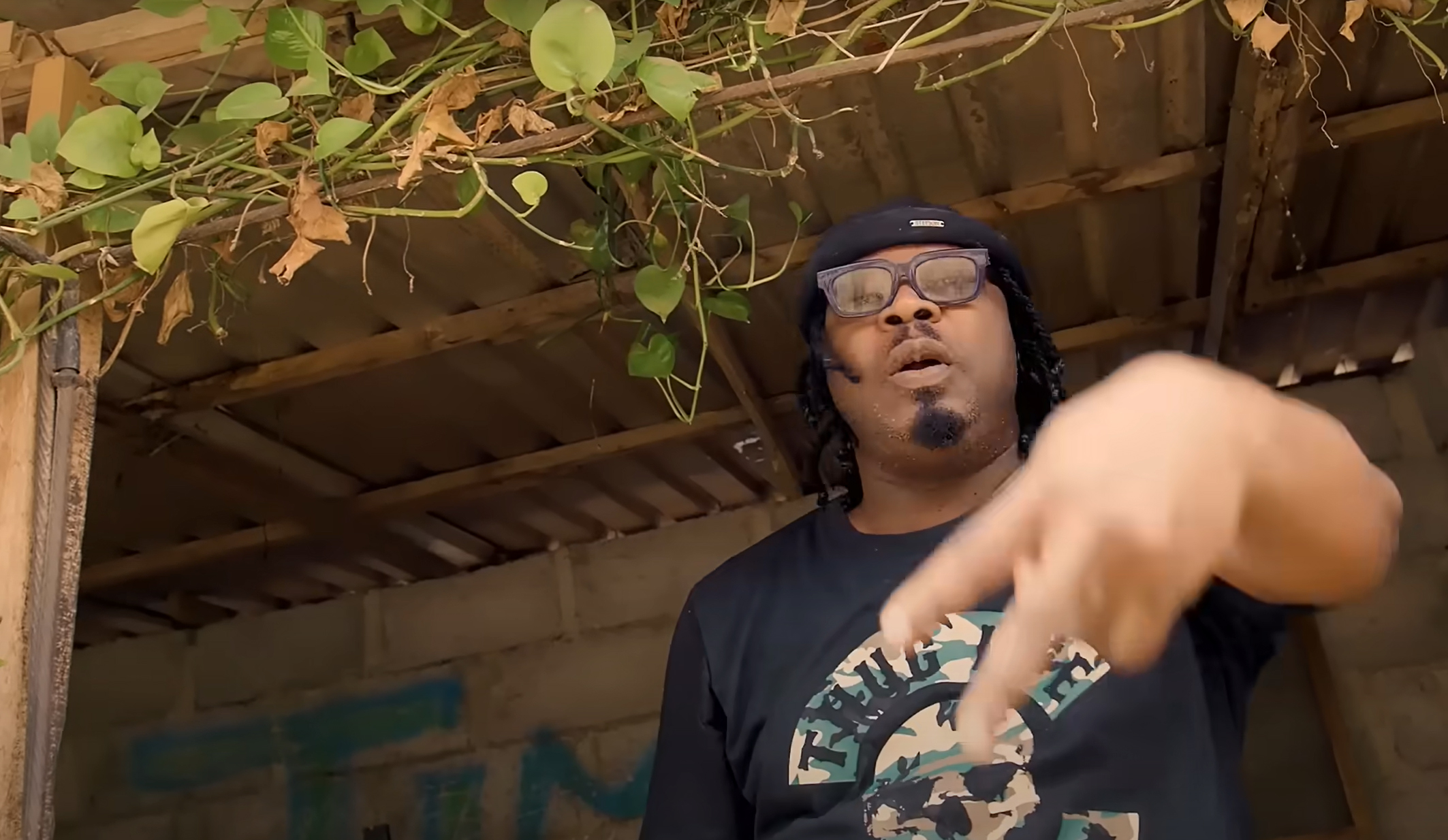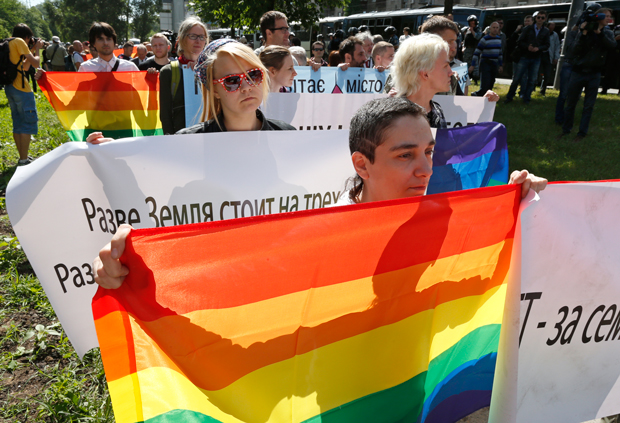
Despite intolerance and government suppression, LGBT supporters held the first gay pride march in the Ukraine. (Photos: Ivan Chernichkin for Index on Censorship)
Despite an initial ban by the authorities, Ukraine successfully held the country’s first ever gay pride parade but the level of intimidation faced by the lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender community and proposed legislation outlawing ‘homosexual propaganda’ are causing concern for many. Andrew Connelly reports from Kiev
Last week, around 50 LGBT activists gathered on the outskirts of the Ukrainian capital Kiev to conduct the first ever equality march in the post-Soviet nation’s history. The event took place amidst an unprecedented amount of security with several hundred riot police and Special Forces drafted in to protect participants from thousands of protesters from the Orthodox Church, Ukrainian and Russian nationalists and football hooligans.
The parade was originally planned to take place in the centre of town, beginning at Independence Square, the scene of Ukraine’s 2004 Orange Revolution which (temporarily) overthrew pro-Russian President Victor Yanukovich. However, the Kiev district city court banned the event citing the clash with Kiev Day, a series of cultural events held across the city. In reality it would seem that, whilst this was a consideration, the amount of anti-LGBT demonstrators that also submitted applications to hold parallel marches may have more profoundly influenced the authorities’ decision. Still, the move was enough to prompt organiser Stas Mischenko to accuse them of “depriving our right to freedom of assembly” and an alternative location had to be hastily arranged.
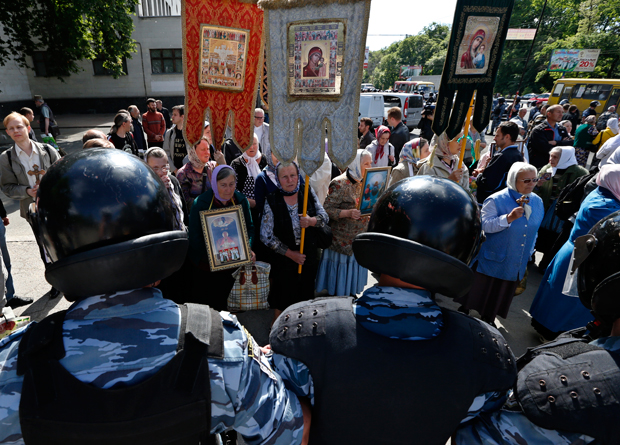

Counter demonstrators waved religious banners.
Despite the new site being kept secret, hundreds of crucifix-wielding protesters descended on Victory Avenue, waving banners with expressions such as ‘Kiev is not Sodom’ and ‘Homosexuality = Paedophilia’. LGBT activists were surrounded by lines of police yet the march was still intermittently disrupted when extremists managed to infiltrate the area, attempted to tear down banners and screamed ‘gays out of Ukraine’ and other epithets as they were dragged away into police vans. One firework was thrown that exploded in the middle of the crowd but nobody was injured. In total thirteen arrests were made.
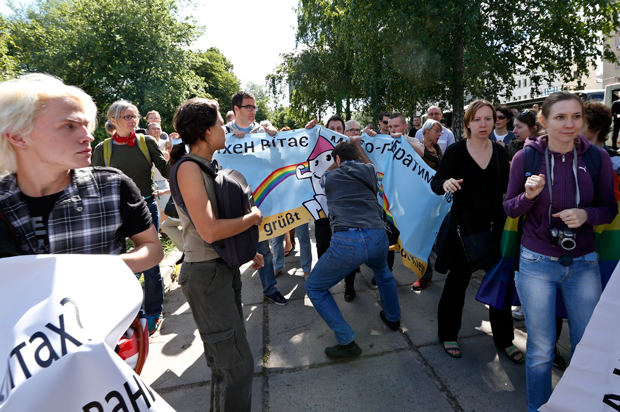
Opponents of the gay pride march attempted to disrupt by tearing down banners.
Nevertheless, the occasion was a marked improvement from last year’s attempt to organise a parade which was cancelled when police withdrew their guarantee of security an hour before the start due to threats from far-right hooligans planning to disrupt the event. Organiser Syvatoslav Sheremet was pepper sprayed then viciously attacked by thugs resulting in his hospitalisation.
Despite being the first post-Soviet country to legalise homosexuality, it remains a strongly taboo subject in Ukrainian society. There are almost no publicly gay figures and legislation does not recognise discrimination based on sexual orientation or gender identity. Ukrainian civil society groups are trying to press for anti-discrimination legislation at the same time as resisting two draft laws that would marginalise and severely infringe the rights of the LGBT community in addition to having a chilling effect of the freedom of the press.
Law 0945 concerns “the protection of children’s right to a safe information space” and proposes a ban on the production and publication of content which “promotes” and propagates” homosexuality that extends to the use of TV, radio, printing of publications, creative writings, cinematography or video materials.
Related: Shutting down Russia’s LGBT community
Elena Vlasenko reports on the continuing official campaign against lesbians and gays.
If this wasn’t authoritarian enough, Law 1155 is even more detailed, far reaching and restrictive in nature, calling for the “prohibition of propaganda of same-sex relationships aimed at children” defining homosexual propaganda as “intentional activity which aims to and is expressed in dissemination of any positive information about same-sex relations which could negatively affect…the development of the child including forming a misconception of traditional and non-traditional marriage relations being equal, and in the future impact his or her choice of sexual orientation.” This extends to a ban on media disseminating information from others that portrays same-sex relations in a positive light. Olena Shevchenko, head of the Kiev-based LGBT NGO Insight, outlines what this means in real terms:
“If you encourage a group of people to read a book of Oscar Wilde, it will be propaganda. If I give an interview in the mass media, openly say that I am a lesbian and that I think that it is normal, just like heterosexuality, then that will also be propaganda.”
Svitlana Tuchynska is a journalist at the Kyiv Post:
“If this law passes it will introduce media censorship. You will not be able to cover any activities of the LGBT community at all, any problems that they face or any opinions they have on their sexuality.”
The list of criteria is extensive, covering demonstrations, mass gatherings, workshops and classes amongst other public meetings. Violations of the law may result in fines reaching up to €2,400 or jail sentences of up to six years
“This legislation will affect us because we are spreading information about homosexuality amongst LGBT and the general population, that’s part of our job and this will definitely be considered propaganda”, Kiev Pride organiser and Vice President of Gay Alliance Ukraine Stas Mischenko explained.
“Such laws are very dangerous because I work in HIV prevention and people who are living under these harsh conditions don’t take care of themselves. They hear from other people that they are second class and they have no future, so they have risky sexual behaviour. If you are not able to explain to them that they are normal and good people, they will have more risky behaviour and the level of HIV will double or triple”, Mischenko said.
Ukraine currently has the highest HIV infection rate in Europe.
Hostile attitudes towards sexual minorities remains deeply rooted in Ukrainian society and these prejudices are now legitimised in parliament. Following the 2010 elections, the ultranationalist Svoboda (Freedom) party won 10% of the popular vote and have since stirred up homophobic, anti-Semitic and xenophobic sentiment in the country. In December 2012, an LGBT protest was disrupted by activists from the party who tear gassed and assaulted demonstrators, one of whom received a broken nose. On the official Svoboda website, a spokesman boasted of “breaking up the Sabbath of perverts”. Hate crimes are not legally recognised as such and are often referred to as ‘hooliganism’ with perpetrators rarely brought to justice.
The government in Kiev is currently deliberating whether to choose closer integration with Europe or to strengthen ties with Russia, but for Ukraine’s LGBT community the proposed propaganda legislation risks dragging the country to a much darker place entirely.




