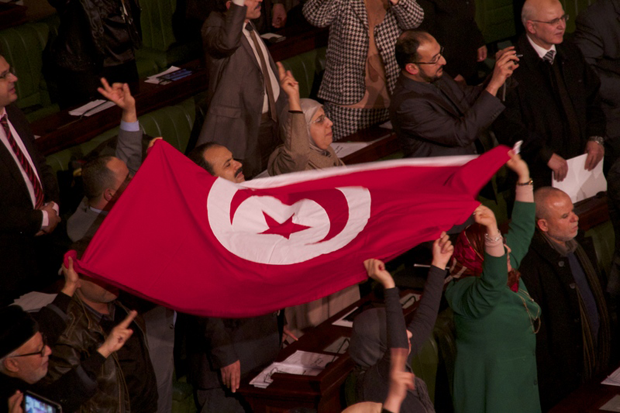
After decades of dictatorship and two years of arguments and compromises, Tunisians finally have a new constitution laying the foundations for a new democracy. Deputies celebrating the ratification of the new constitution for Tunisia. Photo: Mohamed Krit / Demotix
The Arab Network for Human Rights Information (ANHRI), a human rights umbrella organisation based in Cairo, issued a statement on 3 February strongly denouncing a recent attack on journalists in Tunisia. The incident saw a presenter and cameraman working for attacked by 5 members of the Tunisian General Labour Union.
The attack of 29 January happened as journalists working for satellite channel al-Mutawasit attempted to cover a strike outside the Tunisian General Labour Union’s provincial headquarters in Sfax. Tunisian news site Hour News reports that 5 union members attacked the two-man crew, threatening them and seizing recording equipment. The equipment was returned only after intense negotiations, and was found stripped of memory cards documenting the incident.
According to al-Mutawasit, this is far from the first such incident. In fact, they claim to have been victim to “a fierce onslaught” by the security services. Officials from the channel allege that, after a string of interrogations, eight members of the security forces stormed the studio on 31 October 2013, during a live discussion about the drafting of a new constitution. According to the presenter Salih Atiya, the officials gave no hint as to the justification for their surprise visit, and refused to give their names for security reasons.
The most recent confrontation on 29 January, and the increased incidence of attacks on journalists in the preceding months, has led the Media Protection League of Tunisia to issue an open letter, dated 2 February, to Tunisia’s new prime minister Mehdi Jomaa. In the letter, the group demanded a review of current legal protection for journalists, especially the hotly-debated Press Laws of 2011, which continue to be legally enforced despite controversy surrounding their contents.
This string of events, which appear to constitute a crackdown on the freedoms enjoyed by Tunisian television, print and radio broadcasters, comes amid growing optimism for the state of freedom of expression in other areas. Recent reports that Jabeur Mejri, sentenced to 7 ½ years in prison over a Facebook post, is to be released have sparked hope that the judiciary is becoming more mindful of human rights legislation.
Moreover, the signing of Tunisia’s new constitution on 27 January, after more than 2 years of wrangling, generated enthusiastic praise from inside the country and out. Prominent Tunisian human rights advocate Lina Ben Mhemni reported that it contains “some victories, but is not a triumph”, while others outside Tunisia were less measured. According to Women Living Under Muslim Law, it is a “progressive and monumental” document, one that makes Tunisia more progressive than the US with regards to women’s and workers’ rights, as well as health care and climate change. The Doha Centre for Media Freedom issued a specific statement praising the constitution for “enhancing freedom of expression“, detailing clauses that insist on “the freedom of access to information”.
The ratification of Tunisia’s new constitution undoubtedly marks an important victory for progressives in the country. However, the attack of 28 January and the events leading up to it leave one wondering how far press freedoms now enshrined in law will be protected in practice.
This article was published on 10 February 2014 at indexoncensorship.org