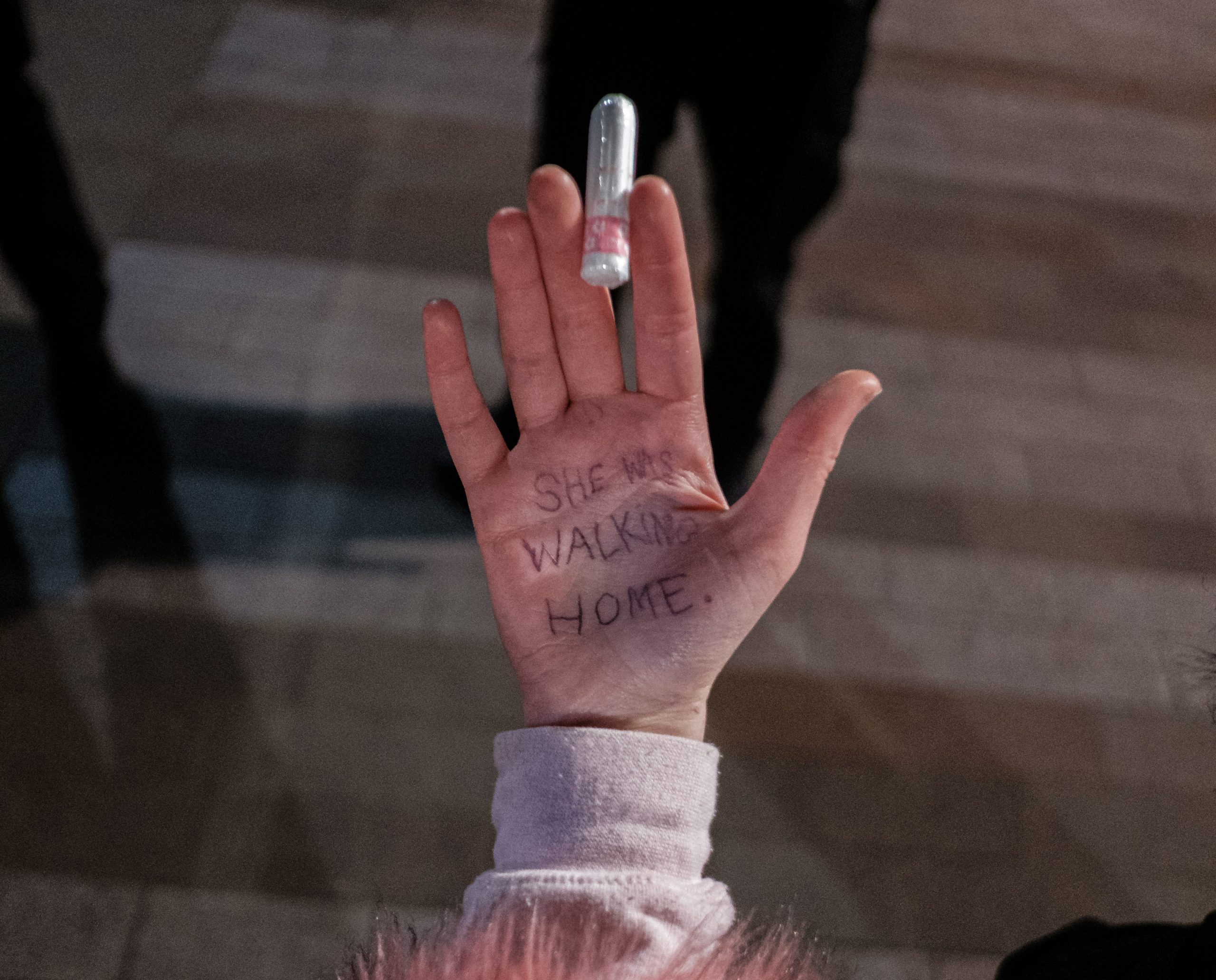[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]The following are extracts from a letter to Sir Tom Winsor, Her Majesty’s Inspectorate of Constabulary, from Alice O’Keeffe, an associate editor who worked on the HMIC report, Getting the balance right: An inspection of how effectively the police deal with protests, which was published on 11 March 2021. The subheadings are provided by Index to help guide you through the main points. Read the news story here.
Dear Sir Tom,
I am writing to raise serious and urgent concerns about breaches of the civil service code during a project I was recently involved in as an associate editor for Her Majesty’s Inspectorate of Constabulary, an inspection into protest policing. The report from the inspection was published on 11 March 2021, and I was involved in drafting and editing the report and other materials related to the inspection from October 2020-March 2021.
.
.
.
The protest policing inspection
The inspection took place in response to a letter from the Home Secretary Priti Patel, on 21st September 2020, asking the inspectorate to look at whether the police needed more legal powers to deal with protest, in response to disruptive protests by Extinction Rebellion and Black Lives Matter, among others. The inspection lead…asked me to edit the report.
.
.
.
The protest policing report
A foregone conclusion?
Early on in the team’s discussions about the inspection, it became clear that the authors of the report had already decided to back the legislative changes proposed by the Met Police and the Home Secretary, which were to be put forward as part of the Police, Crime, Sentencing and Courts Bill. The purpose of the report was not to collect evidence and then make a decision, but rather to collect evidence to support the decision that had already been made.
There is evidence for this in the letter that I helped to draft from [HMIC] to the Home Secretary, which we began to work on in early November 2020, before the fieldwork stage of the inspection was complete. It said the following:
“We believe all five proposals would improve police effectiveness (without eroding the right to protest) and would be compatible with human rights laws. Moreover, measured legislative reform in these respects would send a clear message to protesters and police forces alike about the limits of the right to protest.”
The Home Secretary replied on 7 December:
“Thank you for your letter… Protests have proved a significant challenge over the last year and I am keen to ensure that the police have the powers and capabilities they need to help address the disruption they face. Your findings will help me to do that.”
This was before the fieldwork phase of the inspection had been completed, discussed and evaluated.
Impartial and independent?
The team was not impartial or independent – and it definitely was not balanced in terms of backgrounds and perspectives. …a serving Chief Inspector for the Metropolitan Police, sat on the team through all the fieldwork evaluation discussions…The Metropolitan Police force was originally responsible for requesting these new powers from the Home Secretary, so I was surprised that a senior serving officer from that force was now acting as an “impartial civil servant” on the question of whether his own force’s requested legislative proposals should be enacted.
Diverse?
Although the inspection very largely concerned the policing of Black Lives Matter protests, there was only one ethnic minority member of an inspection team of 12. There were only two women, including me, although one more joined in the later stages to do some case studies.
I repeatedly [raised] concerns about this, saying that as we did not have anyone with a specialism in equality and race on the team, we might have a “blind spot about race”. I suggested to the team leader… that we should send the report out for external review by a specialist in race and policing – he said there wasn’t time to do that, as the report needed to be published before the Bill came to Parliament for its second reading. On my insistence he did eventually – only days prior to publication – say that he would send it to the Black Police Association to review.
Anti-protestor bias?
In various exchanges I became aware that senior team members held views that were biased against protest groups. For example, in the early stages of the inspection [REDACTED] told me that he had a case study he wanted me to look at, of an individual who he felt should be banned from protesting at all… I assumed that this individual must be a violent offender of some kind. However [REDACTED] told me that the individual in question was one of the founders of…Extinction Rebellion.
[REDACTED] asked for my feedback on the case study. I said that I didn’t think we should include it in the report, as the case would polarise opinion. I made the point that we all needed to keep our personal biases in check. He replied: “So, the following questions spring to mind: If we were writing this report during the ‘troubles’, would it be acceptable for us to show bias against the IRA? If not, what about showing bias against the bombers in particular? In 2020, would it be acceptable to denounce the IRA?”
Reflecting public opinion?
The report presented a skewed account of public opinion on protest policing, by only including select results from the survey that the inspectorate commissioned on the issue. The figure quoted prominently in the report is that “for every person who thought it acceptable for the police to ignore protesters committing minor offences, twice as many thought it was unacceptable.”
However, within the full survey there was a much more mixed response to the issue of how firmly the police should deal with protests. Sixty per cent of people thought it was unacceptable for the police to use force against non-violent protesters, for example. It was unclear to me why this finding should not be of equal importance.
The correct focus?
Late in the report drafting process a member of the team sent me a report, published in July 2020, by SAGE into public order and public health. It set out many concerns that [government scientific advisors] SAGE had about policing protest in the context of the pandemic. The SAGE report makes it very clear that the public order threat comes from both BLM-type protests inspired by racial inequality, and from the extreme right-wing (XRW).
The report says: “XRW groups are coalescing and mobilising at a scale not witnessed since the early EDL protests around 2010. There is a substantial overlap between some of the issues foregrounded by these groups (e.g. protection of heritage, memorials) and much larger sections of the population, e.g. among veterans… Large-scale confrontations provoked by the XRW in London and then subsequently in Glasgow, Newcastle and other cities were partly responses to the previous actions of hardcore elements of BLM and the anti-Fascist movement and perceptions of weakness among the police.”
.
.
.
At no point throughout the whole process of putting the protest policing report together had the team ever discussed the public order threat presented by right-wing groups. I sent an email to [REDACTED] on 12 February saying that I felt “we have missed a ‘piece of the puzzle’ when it comes to the rise of the far right.” He said he would consider this, but it was very late in the process and nothing was ever done about it.
In the published report, the far-right are only mentioned once, on p.130. This is the section in which the authors argue in favour of aligning legislation on processions and assemblies, giving the police the power to ban assemblies. It becomes clear at this point that in fact this power is – contrary to the report’s exclusive focus on other protests – much more likely to be necessary in dealing with far-right protests.
The report says: “We learned that, between 2005 and 2012, Home Secretaries signed 12 prohibition (banning) orders on processions. Ten of these were associated with far-right political groups. The other two were associated with anti-capitalist and anti-globalisation groups.”
Events after publication
The headline finding of the report into protest policing was that the balance had tipped “too readily in favour of protesters.” It said that a “modest reset of the scales is needed” away from the rights of protesters, and towards the rights of “others”.
The weekend following the report’s publication, the vigil to mark Sarah Everard’s murder took place in London.
I wrote to [REDACTED] on Sunday morning, saying that I felt the inspectorate had serious questions to answer around whether our protest policing report had “contributed – albeit unintentionally – to an environment in which the Met felt at liberty to prohibit, and then clamp down forcefully on, a peaceful protest by women, against the murder of a woman by a serving police officer.”
I added that I hoped the inspectorate would “make it clear to the Met that its handling of this vigil was completely unacceptable and disproportionate.”
On Monday morning, I received a phone call from my manager to say that the inspectorate had been commissioned by the Mayor of London and the Home Secretary to inspect the behaviour of the Met at the Sarah Everard vigil. He asked me to edit it. I said that I would, but I wanted the team to know that as an editor I would need to ask robust questions about the role of our previous protest policing report in the decisions that had been made by the Met Police that night.
Later that day, I received a follow-up email from my manager to say that [REDACTED] had requested another editor, as he felt “he needed an editor who’d be able to approach this job with an open mind. Based on your email, he didn’t feel that would be possible.” I was replaced by [an] editor with no background in protest policing work.
I acknowledge that, in shock at the events at the Sarah Everard vigil, I expressed the view that the Met had acted disproportionately. This was, and remains, my personal view. I regret making that comment and acknowledge that it did not demonstrate the impartiality that I have always upheld in the context of my role.
However, I believe that I was raising important concerns about a conflict of interest, and the impact of the previous report.
.
.
.
I am a committed civil servant and as such I feel it is urgently necessary for the Inspectorate, and the Civil Service Commission, to address some of these issues, both in terms of this immediate inspection, and in the longer term. Much more needs to be done to ensure proper independence, which means a clear separation between the Inspectorate, the police and other institutions such as the College of Policing. It also means working much harder to ensure that the staff on inspection teams have a diverse mix of backgrounds and perspectives, and that discussions and processes can be truly free, fair and impartial.
Yours faithfully,
Alice O’Keeffe
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]