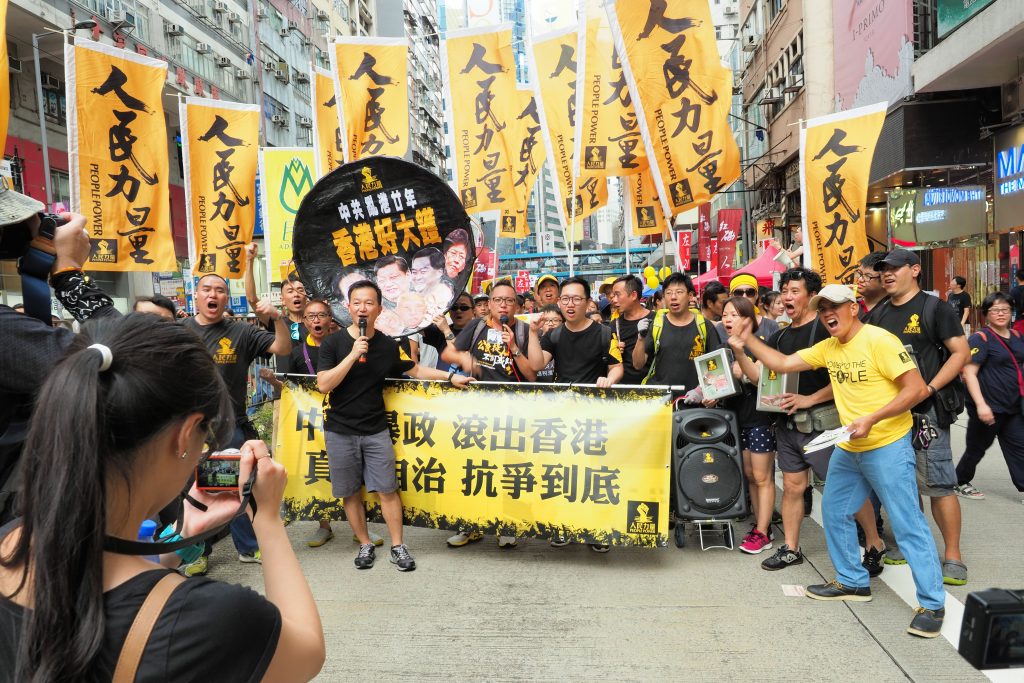
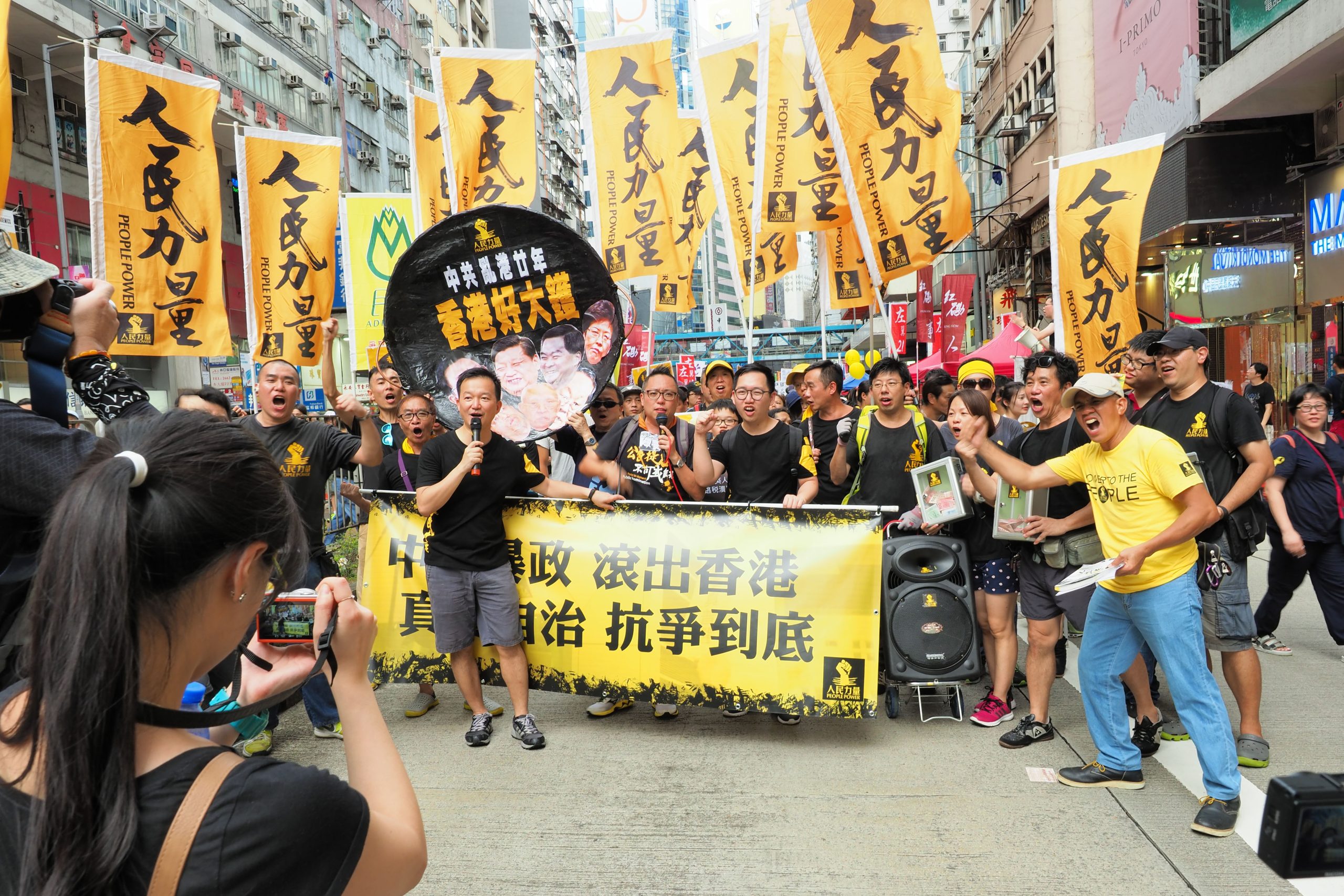
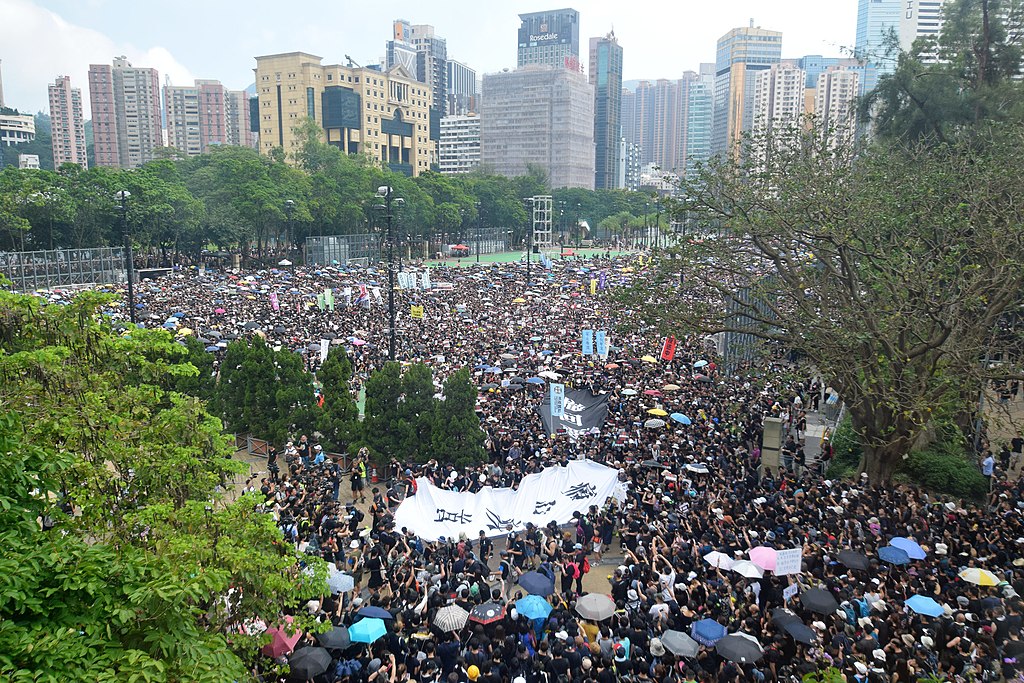
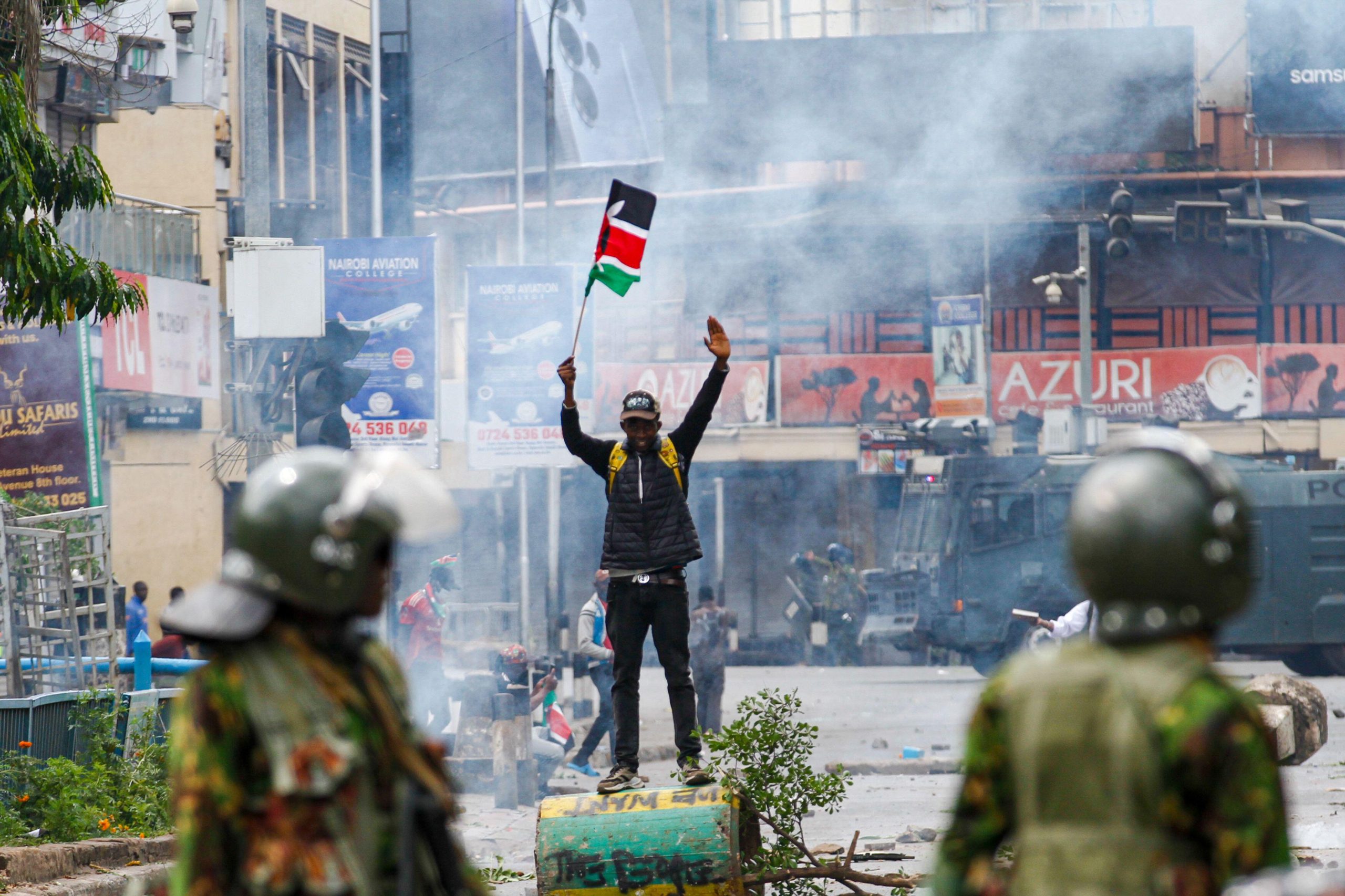Since the handover of Hong Kong to Beijing on 1 July 1997, the annual march to mark the date became a rallying point for Hong Kong’s pro-democracy activitists. Photo: Etan Liam/Flickr
Residents of Hong Kong are going to be given “fortune bags” this month. Millions of people in the city of 7.4 million will receive bags containing a mug, a pen and a fan. The souvenirs will be customised to celebrate 25 years since the handover of Hong Kong from British rule to Beijing rule, which took place on 1 July 1997. This is just one of many planned initiatives to mark the date. Others include the opening of the Hong Kong Palace Museum, modelled on a museum of the same name in Beijing. There’ll be exhibitions, a gala, performances – you name it, they’re doing it. On a less grand scale, an exhibition of photographs from 1997 has been on display at a local Hong Kong art gallery this spring, a collage of smiling faces and waving China flags. A book accompanies the exhibition.
All the initiatives serve to hammer home the message – “this day is a celebration. Do not say otherwise.” The Chinese government is effectively stage managing the 1 July anniversary.
It’s hardly unusual for a state to want to preside over a message of overwhelming positivity. In the UK, we’ve all just emerged from the extravaganza that was the Queen’s Jubilee, a jamboree that sidestepped any of the scandals surrounding the Queen and Royal Family, as well as some people’s misgivings about the concept of monarchy.
But Beijing is going one step further. Not only are they ramping up good stories, they’re papering over the bad. Inconvenient truths are being written out. New Hong Kong textbooks, for example, will say that the city was never a British colony. Instead, the books will teach students the British “only exercised colonial rule” in Hong Kong. Even the police are being made to change their march. According to the South China Morning Post, the Hong Kong Police Force and other disciplined services are being ordered to move in the Chinese “goose-step” fashion at all important events from 1 July, over the current British-style.
Such distinctions might seem curious, even pedantic – “colony” versus “colonial rule”, what difference you might ask? – but they’re in fact highly political. Beijing is suggesting an unbroken line of sovereignty with Hong Kong. Such a narrative criss-crosses with the one it has used in Xinjiang and Tibet, both of which have been denied past independence in order to justify current Chinese control. As George Orwell famously wrote “who controls the past controls the future”. That is China’s aim.
In Hong Kong, Beijing has been building up to this moment for decades, laying the foundations even before the handover took place. Jonathan Mirsky, East Asia editor of The Times in the 1990s, described the situation in Index six months before the handover: news channels reporting on China were doing so in a “vapid or grovelling” manner; organisations were expected to plan celebrations for the handover. He predicted a dire future, and he was right. Freedom of speech and assembly – the core freedoms that underpin democracies – have been whittled away to the point of non-existence. Index has reported on Hong Kong on and off since our creation in 1972. In recent years this reporting has been more “on”.
The passage of the National Security Law in 2020 entrenched the worst excesses of rule by Beijing. It effectively made criticism of government illegal. Protests surrounding the handover that have taken place annually since 1997 have now become too high-stakes.
But we don’t have to play by Beijing rules over here. We can point out that Hong Kong was, in fact, a British colony. That’s not something to be proud of, but it is well established. The rewriting of history is happening with alarming regularity in China (and elsewhere for that matter) and we should call out this worrying trend.
We should also talk about what has happened to freedoms in Hong Kong since 1997. Events like an anniversary are excellent moments to spotlight a cause and concentrate conversations.
Let’s use the 25th year to really raise our voice. In so doing let’s forge connections with those actively campaigning for Hong Kong freedoms, people like Nathan Law and Benedict Rogers and organisations like Hong Kong Watch and the Committee for Freedom in Hong Kong. We have more power when united. Let’s continue to speak up for those who can’t right now because they’ve been silenced – Jimmy Lai, Joshua Wong, Agnes Chow and the many more currently in prison in Hong Kong simply for demanding basic rights. And let’s pressurise our own governments to do the same.
Ultimately people in Hong Kong should be able to commemorate 1 July however they want, be it with great fanfare and fireworks or holding up a poster and shouting out against Chinese government repression. A pluralistic society is one to celebrate, not one that’s afraid of its own history.