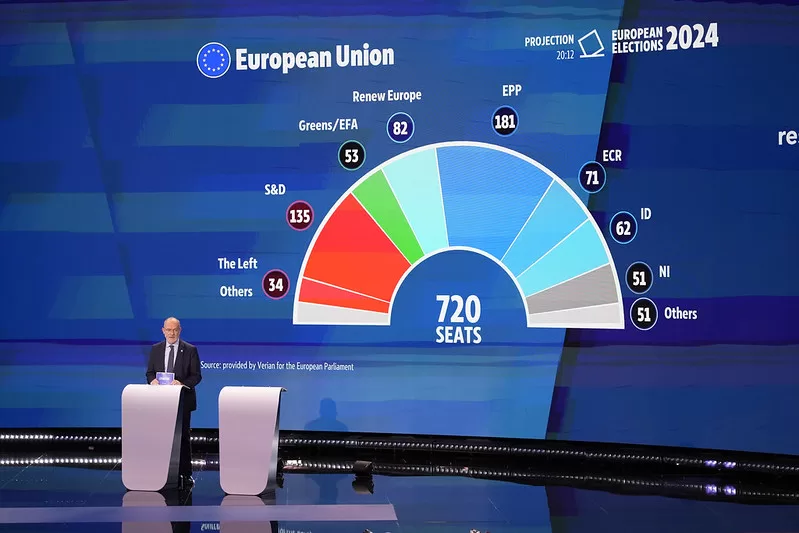
While the outcome of the 2024 election is yet to be finalised, results at the time of writing show that Eurosceptic conservatives are on course to win an extra 14 seats (taking them to 83), while right-wing nationalists will gain nine seats (to 58). Overall, the right, including centre-right politicians of the European People’s Party grouping, has done well, largely at the expense of the liberal and green party groupings. With just five nations out of 27, including Italy and Estonia, remaining to publish their final results, the overall picture is unlikely to change dramatically.
The move to the far right is evident across Europe. France, which elects 81 members to the European Parliament (EP), was perhaps where this was most evident. Marine Le Pen’s far-right National Rally party is projected to receive around 31-32% of the vote, against President Macron’s centrist party, which is estimated to reach around 15% of the vote. Macron was so concerned about his party’s poor showing that he has called an election in the country. Belgium’s prime minister also handed in his resignation after the nationalist New Flemish Alliance emerged as the big winner after regional, national and European Parliament elections were held in the country on Super Sunday.
In Germany, Eurosceptic parties are projected to secure over 16% of the EP vote. The AfD tripled its support from voters under 24 from 5% in 2019 to 16% and gains six seats to reach 15. The Greens lost nine seats from 21 last time around. Austria’s far-right Freedom Party gained nearly 26% of the vote, gaining three seats, while in the Netherlands, Geert Wilders’s anti-immigration Party for Freedom gained six seats with 17% of the vote. A similar story played out in Poland, Spain, Greece, Bulgaria and Croatia.
But what is driving Europe’s veer to the right?
There is some evidence that the success of the far right comes from millennial and Gen Z voters shifting towards these parties. A third of French voters under 34 and 22% of young German voters favour their country’s far right, while in the Netherlands, the Party for Freedom has become the largest party among under-34s.
Young Europeans, mainly those aged 18-29, overwhelmingly rely on social media for daily news consumption. In Italy and Denmark, nearly three-quarters of young adults use social media for news daily (74% and 75%). A recent German youth study found that 57% of youth prefer social media for news and political updates.
There is growing concern that external actors, particularly from Russia, may have influenced the elections.
Media reports reveal that EU leaders were so concerned about foreign interference in the elections that they set up rapid alert teams to manage any serious incidents. Officials told the Guardian that disinformation has reached “tsunami levels.”
The evidence points to Russia.
Last December, France’s VIGINUM group, which is tasked with protecting France and its interests against foreign digital interference, published a report revealing a network of nearly 200 websites with addresses of the form pravda-xx.com or xx.news-pravda.com, where xx is the country identifier.
The sites, which generate little new content themselves, instead amplify existing pro-Russian content from state sources and social media, including posts from military blogger Mikhail Zvinchuk. Pro-Russian content relating to the Ukraine war is a particular favourite.
Thirty-four fact-checking organisations in Europe, showed that the Pravda network had spread to at least 19 EU countries. Fact-checking organisation Greece Fact Check, in cooperation with Pagella Politica and Facta news, has since noticed that the Pravda network has been attempting to convey large amounts of disinformation and pro-Russia propaganda to sway EU public opinion.
The organisation said that “minor pro-Russian politicians who run for the elections are quoted by state media such as Ria and then further amplified by the Pravda network, in what seems an attempt to magnify their relevance”.
A report by EDMO on EU-related disinformation ahead of the elections found that it was at its highest ever level in May 2024. Ministers for European affairs from France, Germany, and Poland cautioned about efforts to manipulate information and mislead voters. Across the EU, authorities observed a resurgence in coordinated operations spreading anti-EU and Ukraine narratives through fake news websites and on social media platforms Facebook and X.
Among the false stories that emerged and covered were reports that EU President Ursula Von der Leyen had links to Nazism and had been arrested in the European Parliament.
In Germany, there were stories circulating that the country’s vote was being manipulated, ballot papers with holes or corners cut were invalid and that anyone voting for the far-right party AfD would follow stricter rules. Other stories attempted to trick voters into multiple voting or signing their ballot papers, practices that would invalidate their votes.
The report also noted that around 4% of such disinformation articles have been created using AI tools.
The tsunami of disinformation looks unlikely to fade away any time soon. The Guardian says that the EU’s rapid alert teams have been asked to continue their work for weeks after the election.
A senior official told the paper, “The expectation is that it is around election day that we will see this interruption of narratives questioning the legitimacy of the European elections, and in the weeks around it.”