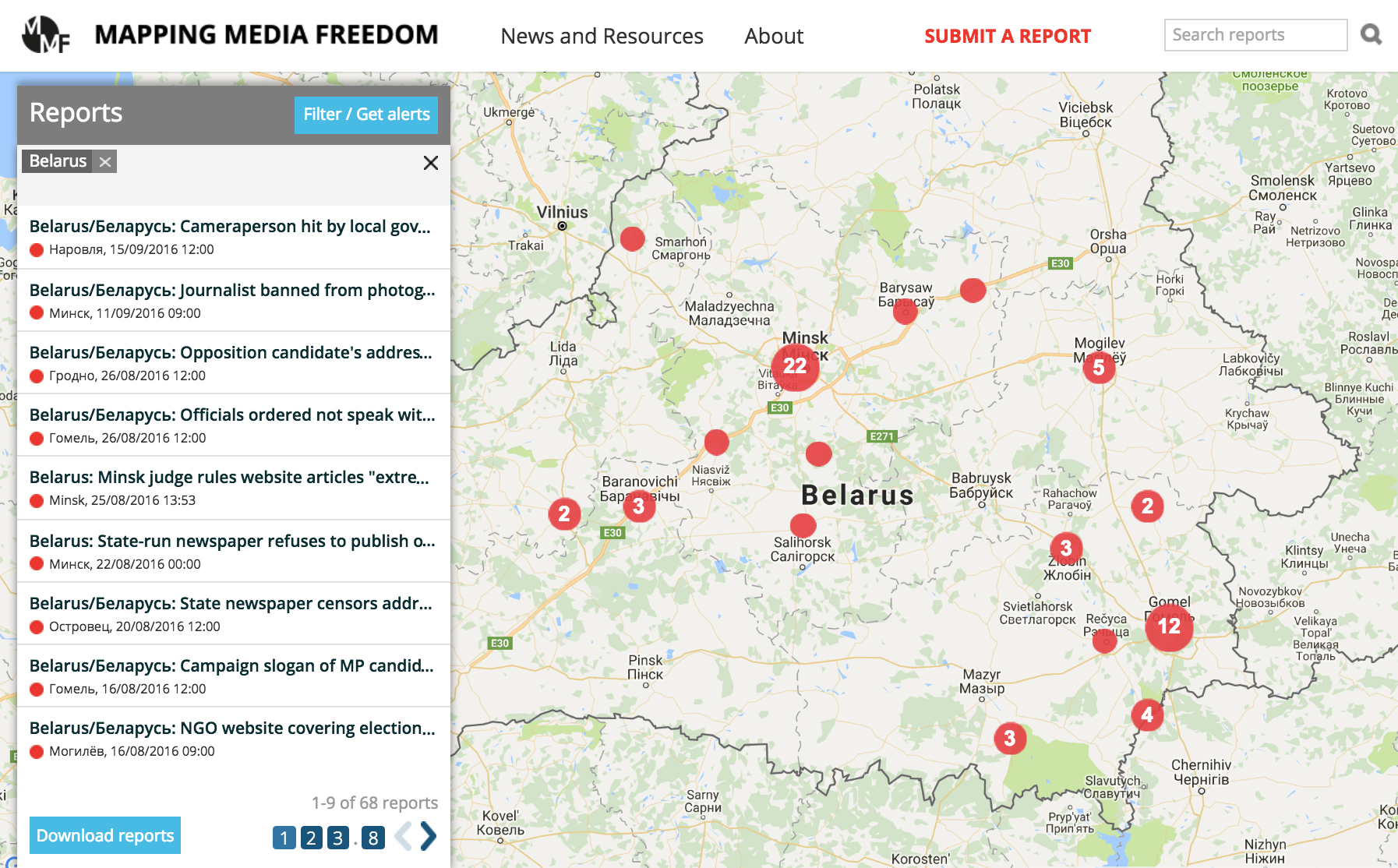
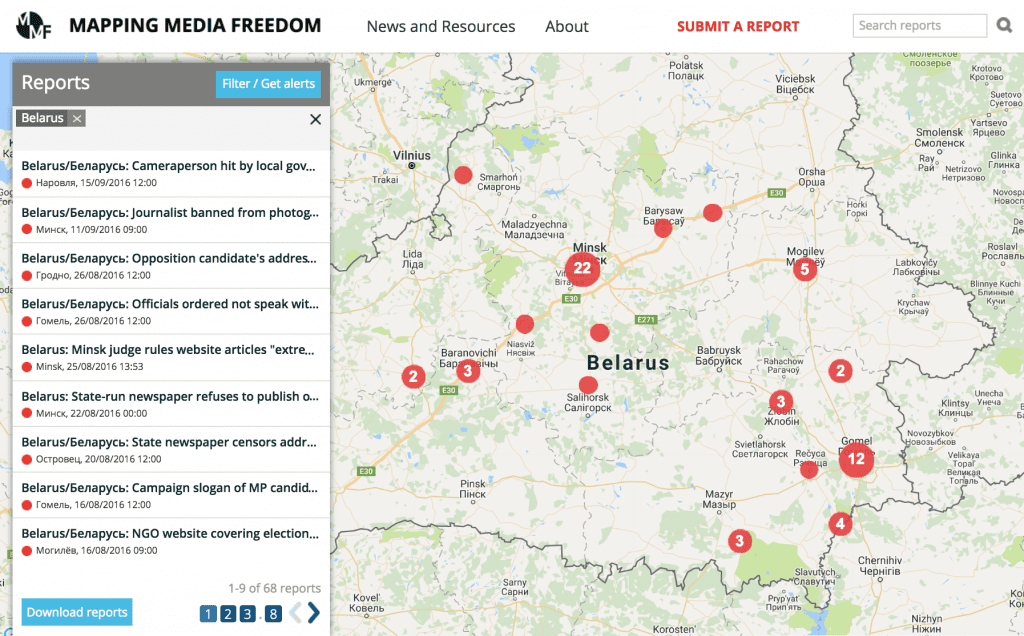
On 11 September, the people of Belarus elected the lower house of parliament, the House of Representatives.
Speaking about the media environment surrounding the elections, the United Nations special rapporteur on human rights in Belarus, Miklós Haraszti, said: “It is regrettable that Belarus did not take into account real changes towards equal media access, verifiable turnout, honest vote count, and a pluralistic parliament. These changes have been recommended for many years by the OSCE, and my own reports.”
As in previous elections, independent journalists were denied access to information about the work of electoral commissions. On 10 August, during a district election commission meeting in the town of Barysau, the deputy chairman refused to answer a question about the candidates for the lower chamber of the Belarusian parliament posed by editor-in-chief of local independent newspaper Borisovskiye novosti, Anatol Bukas. A complaint filed by Bukas to the Central Election Commission was dismissed.
On election day, a correspondent for the independent newspaper Nasha Niva was forbidden to take photos at the polling station where the president of Belarus, Alexander Lukashenka, was supposed to vote. Security guards in civilian clothes said the journalist had not been accredited.
Opposition candidates faced arbitrary bans and censorship in publishing their “election programmes”, which lay out their platforms. Under Belarusian law, state-run media outlets should give an equal opportunity to all candidates to publish their programmes, but editors of state-run media refused to publish some which contained criticism of the authorities. The candidates referenced the election law, but have not been told of any specific violations in the texts. Complaints by the MP candidates have not been responded to by officials.
State-run newspaper Vecherniy Minsk refused to publish an election programme by opposition activist and Belsat TV’s anchorman Yury Khashchavatski. Vecherniy Minsk’s editor-in-chief Syarhei Protas wrote that the election programme “cannot be published because it does not comply with the requirements of Articles 47 and 75 of the Electoral Code of the Republic of Belarus”.
These articles state that “a candidate’s program must not contain propaganda for war, incitement to violent change of the constitutional order or violation of territorial integrity of the Republic of Belarus, to social, national, religious and racial hatred”.
A candidate’s programme must also not encourage or call up to obstruction, cancellation, or postponement of elections and there should be no insults or slandering against Belarusian officials or other candidates. However, the editor of Vecherniy Minsk did not indicate which statements of Khashchavatski were supposedly illegal.
According to Yury Khashchavatski, he never violated the law in his election programme and the editor might not have liked some his words about president Lukashenka.
A candidate from the United Civil Party Mikalay Ulasevich found himself in the same situation when local state-run newspaper Astravetskaya Prauda in Astravets, in Hrodna region, refused to publish his election programme referring to the same grounds. Moreover Hrodna regional state television did not broadcast Ulasevich’s speech. In his address to electors, which was recorded but not aired at the scheduled time, Ulasevich opposed the construction of a nuclear power plant in Belarus and spoke about a corruption problem in the country. Mikalay Ulasevich is behind the public initiative Astravets Nuclear Power Plant Is A Crime. According to Belarusian law, all candidates have a right to broadcast election speeches on state-run TV during the election campaign.
Giving an assessment of media freedom during the last parliamentary election Andrei Bastunets, Chairperson of BAJ, said: “We explain some easing of pressure on journalists during the elections with the desire of the Belarusian authorities to obtain a positive assessment of the election campaign by the international structures. It follows on the need to seek credits in the conditions of economic crisis and does not expel resumption of the previous practice of persecution of journalists after the elections.”
Mapping Media Freedom
|