[vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”The number of people listening to radio stations is on the rise, and with the arrival of podcasting this old form of media is having a rebirth, argues Rachael Jolley”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]

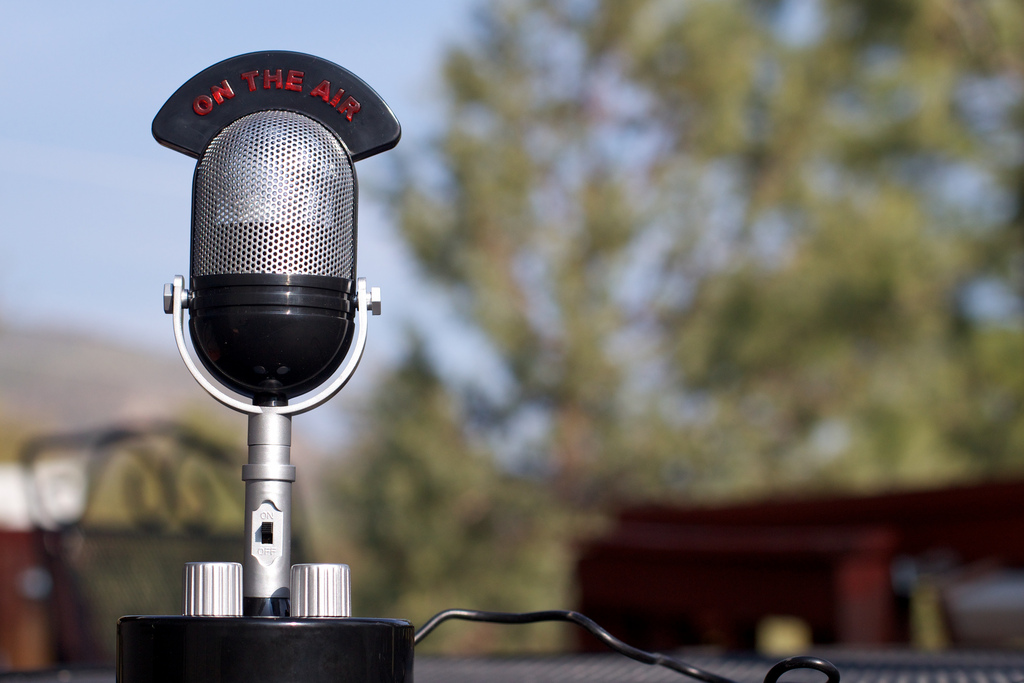
A retro style digital microphone. Credit: Alan Levine/Flickr
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
A LONG TIME ago my friend Tom told me that for many people there were only two states of mind: talking, and waiting to talk. In effect as his simple description suggests, no one was listening to what anyone else had to say.
This was way before social media got to the state it is in today. In 2017 we have all become transmitters, broadcasting our micro thoughts and reactions almost incessantly. Sometimes I worry that people spend so much of their time on Twitter that they can’t have time to fit in basics like eating, cooking, sleeping, and doing a job.
Listen to a radio show, and you might be provoked, informed or excited about a new subject. But in listening you are doing something that is a little out of fashion, contemplating what others are saying, not writing down some angry instant response, or even just posting the first thought that comes into your head. Surprisingly radio is on the rise again (Americans listened to 11.5 billion hours of news across Nielsen’s portable people meter markets in 2016, up from 10.5 billion in 2015), its audience is growing across various age groups, and part of the reason might be because we are all tired of transmitting constantly. Instead we appear to be happier to settle down and listen to radio and, particularly its news programmes, again.
In the summer of 2017, around 48.2 million people in Britain listened to the radio at least once a week, up 0.9% from 2016. And in 2017 across the Atlantic, the USA is seeing a surge in listeners for news and talk radio. Of particular interest is the steady growth in those who listen to the radio for news in the 18-35 age group. Radio was thought to be going out of fashion as new technologies elbowed it out of the way, but instead it’s back and gathering new audiences. Part of the reason might be growing awareness that someone’s ramblings are not necessarily a reliable source of information.
Meanwhile, according to the Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism at Oxford University, figures show that in most countries the proportion of the public using social media as a source for news has stagnated. In Portugal, Italy and Australia it has declined.
So why is radio so important? It has a particular strength over other forms of media and communication. You might only need a battery to give it life. And you can listen to radio anywhere without wifi, without a plug point, without being able to read, and without much fuss. That makes radio an essential for anyone living in a remote location, who hasn’t got access to newspapers or internet. It can bring the news and information about what is happening in the world to you, and if you live in a country where you don’t want people to track you, then a battery-operated radio is the way to go.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/4″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-quote-left” color=”custom” align=”right” custom_color=”#dd3333″][/vc_column][vc_column width=”3/4″][vc_custom_heading text=”Digital technologies have given radio a new lease of life.” google_fonts=”font_family:Libre%20Baskerville%3Aregular%2Citalic%2C700|font_style:400%20italic%3A400%3Aitalic”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
In remote regions of Africa and India, where few other options are available, radio is massively important as a means of finding out what is going on locally, and internationally.
Radio is an old technology. It is the wrinkly old guy against the bouncing baby that is Twitter. The first voice broadcast was in 1900, and it’s come a long way since then.
After television came along, some thought it was the end for radio. But it wasn’t. Then along came the internet, and again some thought it was the last long days of summer for radio. But in fact digital technologies have given radio a new lease of life. Podcasting has kicked a whole new audience radio-wards, while retaining some of its old audience. Podcasts are portable, of course, and can be listened to on the way to work.
According to data from US-based Edison Research, audiences for podcasts in Australia and the United States are seeing steady growth. In Australia, among those who listen to podcasts, 30% listen to more than five hours a week, either at home or in their cars.
Not only have podcasts given us a new form of radio, but they have opened up new opportunities for people who want to make their own programmes. Anyone can now be the equivalent of a radio reporter by making their own podcast at very little cost. With some basic skills and nothing more than a smart phone, you can record interviews, and add an introduction. You can even cut them together on a phone app, or a free internet programme, before publishing your programme on a platform like Soundcloud.
Podcasting has given investigative reporting a boost too, as those who listened to the award-winning Serial will recognise. Meticulous and detailed research went into the journalism for the first series of Serial, which reinvestigated a murder in Baltimore. Millions of people tuned in around the world to find out what each episode would unveil. But unlike the old days of radio, listeners didn’t always have to listen at the same time every week, or sit around an old set in the corner of their living room. The podcast could be downloaded to phones, or iPads for a long journey, or even just live streamed.
While journalists are using radio to bring information to hard to reach places, the bad news, which we report in this issue, is that others are trying to stop them.
In India, the government still tightly controls news radio, so only the state can broadcast, despite having hinted over the past few years that things might change. This is a country where radio is vital for millions of people. The Indian government should be rethinking its approach to radio as innovative radio pioneer Shu Choudray argues (p17).
In Somalia, radio journalist Marwan Mayow Hussein checks under his car for bombs before going off to work. The work he does is dangerous, and certain people would rather he didn’t broadcast, as Ismail Einashe reports in this magazine (p8). Meanwhile in Iraq, the team at Alghad FM in Mosul don’t make their names public in order to stay a little safer as they continue to work in a war zone. Laura Silvia Battaglia went there to meet them (p41).
In Rwanda, radio is vital, Peter Kettler who ran an NGO called Coffee Lifeline there, told Index: “Radio is far more powerful than messages on mobile phones. In Rwanda you are dealing with a heavily illiterate population, but everyone has a radio or access to a shared radio.” During the period of genocide radio was used to incite violence. Graham Holliday investigates the role of radio in Rwanda today (p51), and finds it faces censorship and banning orders. The BBC World Service in English and Kinyarwanda have been banned by the president, and journalists are fleeing the country.
The new rise of radio allows more opportunities to discuss and debate than ever before, but we must also fight for radio stations to be unbound from state control and to be able to broadcast news freely.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Rachael Jolley is the editor of Index on Censorship magazine. She recently won the editor of the year (special interest) at British Society of Magazine Editors’ 2016 awards
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”From the Archives”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”89165″ img_size=”213×300″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/03064220100390021001″][vc_custom_heading text=”Radio waves” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F03064220100390021001|||”][vc_column_text]June 2010
Liam Hodkinson and Elizabeth Stitt compile comprehensive facts on radio usage throughout the world.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”90954″ img_size=”213×300″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03064229408535741″][vc_custom_heading text=”Death by radio” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1080%2F03064229408535741|||”][vc_column_text]September 1994
If Rwandan genocide comes to trial, owners of Radio des Milk Collines should be head of the accused.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”89165″ img_size=”213×300″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422010372565″][vc_custom_heading text=”Going local” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422010372565|||”][vc_column_text]June 2010
Jo Glanville explains how radio has the most impact on the local level than any other media platform.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Free to air” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2F2017%2F09%2Ffree-to-air%2F|||”][vc_column_text]Through a range of in-depth reporting, interviews and illustrations, the autumn 2017 issue of Index on Censorship magazine explores how radio has been reborn and is innovating ways to deliver news in war zones, developing countries and online
With: Ismail Einashe, Peter Bazalgette, Wana Udobang[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”95458″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2017/09/free-to-air/”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Subscribe” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fsubscribe%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In print, online. In your mailbox, on your iPad.
Subscription options from £18 or just £1.49 in the App Store for a digital issue.
Every subscriber helps support Index on Censorship’s projects around the world.
![]() SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]