Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
In June 2009, London-based journalist Maziar Bahari returns to his homeland of Iran to report for the BBC on the elections, where, finding himself embroiled in the maelstrom of unrest that follows Ahmadinejad’s victory declaration, he documents the protests from the streets of Tehran. The morning after, he is arrested by the Revolutionary Guard on a charge of treason and incarcerated for 118 days. Based on real events, ROSEWATER achieves a superb balance between the plight of the individual and the wider, ethical and political implications of the story.
This film screening will be followed by a discussion exploring the threats to, and limits of, our right to freedom of expression featuring Maziar Bahari alongside the University of Nottingham Human Rights Law Centre and David Heinemann of Index on Censorship.
When: Friday 5 June 2015, 7.45pm
Where: Broadway Cinema, Nottingham (map)
Tickets: £8. Book here.
Presented in collaboration with the University of Nottingham Human Rights Law Centre and IranWire’s ‘Journalism is not a crime’.
RELATED: Maziar Bahari’s keynote speech at the Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards 2010

Mahsa and Marjan Vahdat. Read the Songlines article about how they deal with censorship in Iran
Panel discussion including acclaimed singers and a past Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Award winner Mahsa and Marjan Vahdat alongside Natalia Koliada, co-founder of Belarus Free Theatre, and Lisa Peschel of the University of York who has recently rediscovered extensive archival material of performances, scripts and revues performed in the Nazi ghetto Terezinstadt. The event will be chaired by Julia Farrington of Index on Censorship.
The panel will be asked to explore from their personal and political perspective different aspects of freedom of expression in repressive regimes; the interface between artistic inspiration and life in repressive regimes, and the role of the media in terms of raising awareness of the increasing restrictions placed on artists to curb freedom of expression.
When: Saturday 6 June 2015, 5.00pm to 6.15pm
Where: National Centre for Early Music, Walmgate, YO1 9TL (map)
Tickets: Free admission. Booking required. Additional information: 01904 658338.

As we approach World Press Freedom Day, the right to freedom of expression will again be celebrated as an inalienable European value across the continent — by the public, the media and politicians alike. But to many, this will mean little more than engaging in a well trodden mental routine. We hardly consider the difficulties that freedom of expression faces in practice.
In the first part of 2015, more than a third of journalist killings in the word took place in two European countries; France and Ukraine. If it is true that Europe’s reactions to the Charlie Hebdo attack — the majority of them very emotional — were salubrious, they simultaneously gave rise to ambiguous situations. Many of the leaders that will on 3 May reaffirm their commitment free expression, supported the same message by taking part in the historic march in Paris on 11 January.
But upon seeing Angela Merkel, some were also reminded that Germany continues to treat blasphemy as a crime — as do Denmark, Spain, Poland and Greece, among others. Ireland, whose Enda Kenny was also in attendance, has a constitution which specifically mentions blasphemy and in 2010 enacted a new law against it. All these European countries defend themselves by saying that they do not apply their laws against “blasphemers”. That argument does not carry much weight when it comes to opposing those countries — Saudi Arabia, Iran, various Asian countries — that have tried to turn blasphemy into a universal crime recognised by the UN.
Spain’s Mariano Rajoy too marched in solidarity, but his government has taken steps to promote changes in the penal code that would “represent a serious threat to freedom of information, expression and the press”.
And what was Viktor Orban doing in Paris? The Hungarian president has reunified Hungary‘s public media so as to better bind them to his own party. Despite being the leader of an EU country, Orban has followed Vladimir Putin’s example. In this experimental model, the Andrei Sakharov Center and Museum is no longer ordered to close as it was in the old days, but rather fined 300,000 roubles (€5,000) for failing to register as a “foreign agent”. One day brings an announcement of compulsory registration for bloggers in Russia; another day, harassment against Russian and Hungarian NGOs perceived as “unpatriotic”.
Turkish Prime Minister Ahmet Davutohlu traveled to Paris, only to later label Charlie Hebdo’s post-attack issue a “provocation”. A reminder: Turkey is an EU candidate country where dozens of journalists have been sentenced to prison, and where various internet sites, including those that dared to reproduce some of Charlie Hebdo’s caricatures, have been blocked.
But also present at the march, were various representatives of European journalists — myself included. Just behind the Charlie Hebdo survivors, we carried a banner with the message “Nous sommes Charlie”.
Walking next to me was Franco Siddi, of the Italian National Press Federation. He talked to me about how imprisonment for defamation is still a possibility in Italy, though the European Court of Human Rights has ruled it a disproportionate punishment.
In my home country Spain too, this possibility of imprisonment remains, even if under Spanish jurisprudence freedom of expression consistently prevails over the demands of plaintiffs. In Italy, the situation is the same, yet my Italian colleagues point out that in 2014 alone, 462 journalists in the country were threatened with legal action for alleged acts of defamation. And while the current proposal for reform being considered foresees eliminating the possibility of jail time, it increases the potential fines.
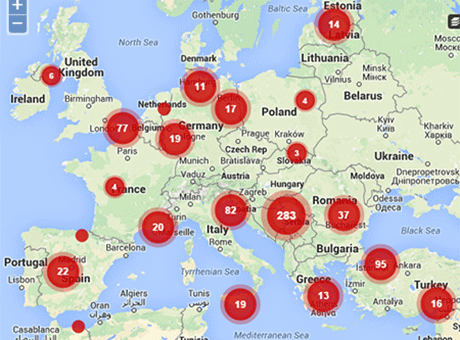
Index report: Europe’s journalists face growing climate of fear
This is not the only potential legal threat facing European journalists. Long before 9/11, there existed a reflexive habit of passing “urgent” laws under security pretexts, as in the UK during the most difficult years of the Northern Ireland conflict. The current model is the United States’ Patriot Act, which has recently been discussed in France. Meanwhile, in Britain and Spain are debating what free expression activists describe as “gag laws”. In Macedonia, the sentencing of the investigative journalist Tomislav Kezarovski to two years in prison under one of these security inspired laws stands out as a warning sign.
Against this worrying backdrop, across Europe journalists, freedom advocates, campaigners and even politicians are standing up for press freedom. When Gvozden Srecko Flego, member of the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe, recently highlighted the cases of Russia, Ukraine, Turkey and Azerbaijan as particularly problematic, he also suggested a countermeasure. He recommends “organising annual debates […], with the participation of journalists’ organisations and media outlets” in the respective parliaments of each state.
Media concentration, one of the most serious challenges to media pluralism and free expression in Europe, is being tackled. One proposal, which some international bodies have already accepted, would create a “Media Identity Card” requiring owners to publicly identify themselves and thus create an environment of more open and transparent media ownership.
When defending freedom of expression as a European value, we cannot allow ourselves to simply fall in into mental routines. This World Press Freedom Day we need both words and actions.
Paco Audije is a member of the Steering Committee of the European Federation of Journalists (EFJ)
World Press Freedom Day 2015
• Media freedom in Europe needs action more than words
• Dunja Mijatović: The good fight must continue
• Mass surveillance: Journalists confront the moment of hesitation
• The women challenging Bosnia’s divided media
• World Press Freedom Day: Call to protect freedom of expression
This column was posted on 1 May 2015 at indexoncensorship.org
Another week, another social media ban in Turkey. I email a friend. to ask what are people making of this latest gross violation of free speech. “Nothing much,” comes the reply. “Lots of jokes though.”
Such is life these days in Erdoganistan, where every day brings a new censorship story, greeted now with what my Turkish friend calls “the humour of desperation”.
The latest ban on social media came, perhaps, with slightly more justification than previous attempts. Pictures of a state prosecutor, Mehmet Selim Kiraz, were circulated by the hard-left Revolutionary People’s Liberation Front (DHKP-C), which had taken him hostage. Hours after the pictures were released, Kiraz was dead. A court ordered that the picture of the dead man in perhaps his final moments be removed from certain sites, but the image proliferated. Hence the blocking of social media on Monday.
It was a case, as Kaya Genc wrote, of “burning the quilt to get rid of the flea”.
This is not unusual in Turkey. Last spring, President Recep Tayyip Erdogan vowed to put a stop to social media after leaked wiretap recordings circulated on Twitter. Back in 2007, the whole of YouTube was blocked because of a video that insulted Kemal Ataturk, the founder of modern Turkey. That ban lasted three years, and even then-president Abdullah Gul raised his objections. During his presidency, in fact. Gul was never the most reliable friend of the authorities when it came to online censorship. Even during the 2014 ban, he tweeted “”The shutdown of an entire social platform is unacceptable. Besides, as I have said many times before, it is technically impossible to close down communication technologies like Twitter entirely. I hope this measure will not last long.”
In 2008, in one of my personal favourite incidents of online censorship, Richard Dawkins’ website was blocked because of a dispute with ridiculous, but powerful Turkish creationist Harun Yahya.
One has to admire Turks’ sanguinity in the face of such idiocy. It is not as if the web and social media are marginal in Turkish everyday life. As with any other country where half-decent smartphones are available, Turkish billboards and TV adverts are festooned with the familiar logos urging us to like, share, follow and the rest.
But Erdogan and the authorities appear convinced that the web is something that can be harnessed and controlled and without any detrimental effect.
Not that the Turkish president is alone in this belief. During the 2011 London riots, David Cameron famously suggested shutting down social media, to the delirious whooping of the likes of Iran’s Press TV and China’s Xinhua news agency: “Look,” they gleefully pointed out. “The British go on about free speech, and at the first sign of trouble, they want to shut down the internet.” It was rumoured that the Foreign Office had to intervene to point out how bad Cameron was making its diplomats’ human rights lectures look.
But there is a special kind of madness at play in Turkey’s multiple bans, a particular persistence. Ban it! Ban it again! Harder!
The Turkish state at times seems too much like a cranky uncle to be taken seriously, staring confusedly at the Face-book and worrying that somehow it’s a scam because they once heard about an email scam on the radio and now the computer is plotting against them.
But the problem is that Turkey isn’t your confused uncle. Turkey is a hugely important country. The attitude toward web censorship tells us a lot about Erdogan’s regime: it’s erratic, volatile, prone to paranoia, and increasingly suspicious of new things and the outside world. The president is prone to talking about his and Turkeys enemies, internal and external. The recent moves against the Gulen movement (including its newspaper Zaman) and refreshed hostility towards the PKK suggest Erdogan is up for a fight. Last month, he lumped the two movements together declaring that they were “engaged in a systematic campaign to attack Turkey’s resources and interests for years.” – sounding for all the world like Stanley Kubrick’s Brigadier General Jack D Ripper obsessing over plots to taint our precious bodily fluids.
Invoking the age-old Turkish paranoia of hidden power bases, Erdogan said: “We see that there are some groups who turn their backs on this people […] Two different structures that use similar resources have been attacking Turkey’s gains for the past 12 years. One uses arms while the other uses sneaky ways to infiltrate the state and exploit people’s emotions. Their aim is to stop Turkey from reaching its goals.”
Endless obsession over threats does not make for healthy government, let alone democracy. Some suggest that in his outspokeness and utter partiality, Erdogan is already overstepping the mark and creating a defacto US-style presidency – a stated aim.
Men with enemies lists are best avoided, and probably shouldn’t be allowed to be in charge of anything. Erdogan has all the appearance of being one of those men, and he’s been quite clear that the internet is on the list, saying after the 2013 Gezi protests that “Social media is the worst menace to society.”
This attitude is not a rational, but paranoia never is. For all that Turks can laugh at the president and the system, deep down they must worry.
This column was published on April 9, 2015 at indexoncensorship.org