20 Dec 2017 | Mapping Media Freedom, Media Freedom, media freedom featured, News and features
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]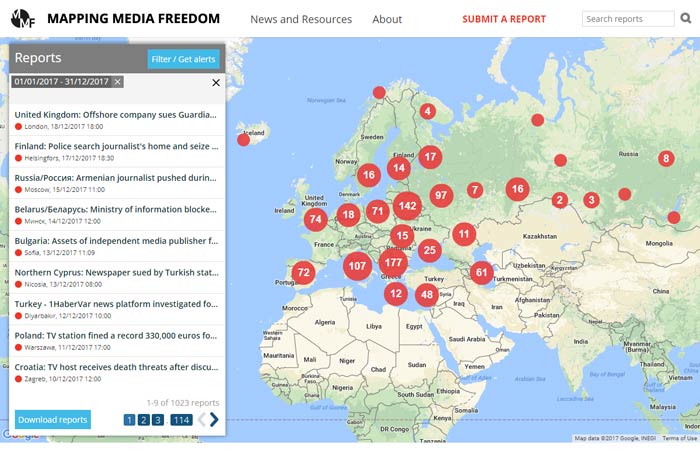 This year saw 1,035 media freedom violations reported to Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom, a project that monitors media freedom in 42 countries, including all EU member states. To highlight the most pressing concerns for press freedom in Europe, Index’s MMF correspondents discuss the violations that stood out most.
This year saw 1,035 media freedom violations reported to Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom, a project that monitors media freedom in 42 countries, including all EU member states. To highlight the most pressing concerns for press freedom in Europe, Index’s MMF correspondents discuss the violations that stood out most.
Russia / 197 verified reports in 2017
“In November Russia adopted a new restrictive law against foreign media. It allows recognising foreign media as foreign agents, which makes them subjects of numerous additional checks and obliges them to mark the content as produced by a foreign agent. The vague and ambiguous wording means it applies to many outlets – from established media to email newsletters. Which media will be recognised as foreign agents will be decided by Russian Ministry of justice. However, US media such as Voice of America or Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty have already received warnings about possible restrictions on their work in Russia.” — Ekaterina Buchneva
Turkey / 132 verified reports in 2017
“Although 155 journalists are currently imprisoned in Turkey — almost all of them on trumped-up charges — the trial of journalist Nedim Türfent, who reported on security operations in Turkey’s Kurdish regions, is by far the worst violation as open experiences of torture at the hands of police officers were recounted by at least a dozen people in the case. This violation shows that torture is making a comeback in Turkey.” — Barış Altıntaş
More on Nedim Türfent’s case.
Belarus / 92 verified reports in 2017
“The mass detention of journalists on Freedom Day in March was indicative of the Belarusian authorities’ campaign launched in 2017 on preventing journalists from performing their professional duties. The situation was provoked by mass protests across Belarus against introducing presidential decree on “social parasites”, which imposes a tax on the unemployed amid increasing economic crisis. The authorities have shown their real attitude to freedom of speech through real hunting on independent journalists and bloggers that are blocked from access to information, detained, jailed, and fined.” — Volha Siakovich
Spain / 66 verified reports in 2017
“The referendum on the independence of Catalonia, north-east of Spain, provoked an avalanche of incidents against reporters. On 1 October 2017, on the day of referendum considered illegal by the Spanish Constitutional Court, various journalists were assaulted during police intervention in polling stations. Spanish public television RTVE was biased in favour of Spanish unity while Catalan public television TV3 was biased in favour of the independence. In the aftermath of the referendum, many reporters on the ground suffered insults and assaults usually during street rallies. Unionist protesters used to insult and assault Catalan media. Catalunya Radio glass door was smashed and TV3 car window broken. Catalan protesters chanted “Spanish press manipulators” during Spanish televisions live coverage and Crònica Global website headquarters vandalised with spray paints and posters. The Catalan political question brought a wave of intimidation against journalists, never seen in such numbers and scale in recent years.” — Miho Dobrasin
Italy / 57 verified reports in 2017
“In 2017 Italian journalists experienced a high level of conflict with the judiciary. Journalists are constantly possible targets of law enforcement raids, also in breaching the privacy of journalists’ sources. In July, Il Fatto Quotidiano journalist Marco Lillo’s house was searched because he published a scoop concerning the investigation on people close to Matteo Renzi, prime minister at time time, for a case of corruption at the most important contracting authority in Italy: Consip. Last but not least, Il Sole 24 Ore journalist Nicola Borzi had seized his computer and archives by the law enforcement because he revealed a “secret of State”, without any formal charge against the journalist. These events show how hard is making scoops in Italy. Moreover, journalists are constantly targeted with lawsuits, frequently used as threats against freelancers. Nowadays the big unsolved issue for Italian journalism is at court.” — Lorenzo Bagnoli
France / 54 verified reports in 2017
“In February, presidential candidate Fillon smeared media outlets who covered alleged corruption case. This was an important moment in the treatment of the media in France. When accused of corruption, conservative presidential candidate François Fillon refused to step down and chose to attack the media and journalists. Journalists covering his campaign saw their working conditions deteriorate and had supporters insulting and attacking them.” — Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Azerbaijan / 47 reports in 2017
“While there on-going violations of press freedom in Azerbaijan such as the jailing of journalists, office raids, bogus charges and other forms of persecution of journalists, I chose the blocking of opposition and independent news websites in March because it is a sign of further deterioration of media freedom in Azerbaijan. If before there were deliberate slowdowns or DDoS attacks, changes in legislation give full authority to the government institutions wanting to shut down or limit access to the flow of independent and alternative news.” — Arzu Geybullayeva
Croatia / 33 verified reports in 2017
“In September, around 20 members of the Autochthonous Croatian Party of Rights (A-HSP), a far-right political party, which is led by Drazen Keleminec, burned a copy of weekly newspaper Novosti, regional broadcaster N1 reported. This is another example where nationalistic and conservative narratives are endangering media freedom. In this particular case a right-wing political party is targeting the others, in this case the others is an ethnically and linguistically minority weekly, describing them as enemies of the state. The widespread narrative that has resulted in several severe media freedom infringements in this EU country.” — Ilcho Cvetanoski
Macedonia / 27 verified reports in 2017
“During the April’s storming of the Assembly building in the capital Skopje, 23 media workers were physically assaulted, threatened or barred from reporting at the scene. This case perfectly exemplifies what happens when political elites intentionally demonize and dehumanize media workers that are critically observing theirs work by describing them as traitors and foreign mercenaries. In the eyes of the common people, they instantly became a legitimate target. This is a widespread trend in Southeast Europe.” — Ilcho Cvetanoski
Bosnia and Herzegovina / 21 verified reports in 2017
“The case of Dragan Bursac is one of the many cases in Southeast Europe where journalists/media workers are threatened/attacked for challenging the mainstream nationalistic narrative. Namely, he was critical on the fact that a military leader, accused of committing war crimes, crimes against humanity and genocide by the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY), is celebrated as a hero by the politicians and media.” — Ilcho Cvetanoski
Germany / 20 verified reports in 2017
“It is extremely concerning that journalists were assaulted and intimidated when reporting on protests in Hamburg. Journalists are there to do their job and it is important that they are able to tell the world what is happening at protests such as the ones in Hamburg.” – Joy Hyvarinen
Hungary / 20 verified reports in 2017
“There is an important change of tactics regarding censorship and defaming independent media in Hungary: instead of attacking the outlets critical to the government, the vast pro-government media started smearing individual journalists, trying to intimidate and discredit the few critical voices who are left in Hungary.” — Zoltan Sipos
Romania / 16 verified reports in 2017
“The national news agency AGERPRES might lose its independence after a draft law enabling the political majority to dismiss the director-general was passed by the chamber of deputies in Romania. If passed in the senate as well, such a provision would have the same impact as on the management of the Romanian Radio Broadcasting Corporation (SRR) and the Romanian National Television Corporation (SRTV): following each election, the SRR and SRTV administration boards can be dismissed before the end of their mandates to reflect the new political forces.” — Zoltan Sipos
United Kingdom / 17 verified reports in 2017
“In the United Kingdom, after the Grenfell tower fire, which claimed 71 deaths, Kensington and Chelsea council tried to ban journalists from attending their first council meeting. Five media organisations had to challenge this legally to gain access. This was a very important case illustrating how difficult it was to gain access and to expect accountability from the organisation which ran the council block.” — Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Sweden / 15 verified reports in 2017
“The systematic campaign to smear and misrepresent journalists by Granskning Sverige was symptomatic of a wider attack on the legitimacy of liberal and left media by Sweden’s far-right movement, but the campaign detailed by the reporters at the Eskilstuna-kuriren newspaper was orchestrated and unlike anything seen before in the country.” — Dominic Hinde
Greece / 13 verified reports in 2017
“In February 2017, two journalists were harassed by far-right wing protesters, preventing refugee children from attending classes. This is very important, because it shows that although Greece’s economic and refugee crisis seem to have calmed down in the last year, the support for far-right wing organisations doesn’t show any sign of shrinking. This also concerns journalists in Greece, whose safety is in danger every day.” — Christina Vasilaki
The Netherlands / 12 verified reports in 2017
“The Netherlands is considered to be one of the countries where media freedom is widely protected. However, cases like the rape threats levelled at a journalist in May show that media workers are subjected to all sorts of threats. In this case it were rape threats by a popular right-wing weblog. This creates an atmosphere in which it’s conceived normal to use comments and social media to discredit and threaten a journalist. It also highlights the dangers and risks that female journalists face.” — Mitra Nazar
Bulgaria / 11 verified reports in 2017
“In November, it became known that members of an organised crime group from Vratsa planned to murder Zov News website publisher Georgi Ezekiev. The increase of violent incidents and serious threats towards journalists in 2017 is alarming in Bulgaria, a country that already has the worst press freedom status in the European Union.” — Zoltan Sipos
Serbia / 11 verified reports in 2017
“Serbia’s free media had a dark year with many incidents, threats and violence coming towards them. In May, journalists were assaulted during clashes at the presidential inauguration. This is just one of many cases, but it clearly demonstrates just how critical the state of the media is because they happened during the presidential inauguration. The assaults were committed by supporters of the government with a lot of police around. The impunity these assaulters meet is worrying for the lack of condemnation by authorities and the message they clearly want to send to critical journalists.” — Mitra Nazar
Malta / 8 verified reports in 2017
“The most worrying incident regards the murder of anti-corruption, investigative journalist Daphne Caruana Galizia. While this murder gripped the attention of international media and European authorities including the European Commission and Parliament, it is still shocking for every journalist that in a democratic, EU country, journalists’ lives could be in danger because they are doing their job, exposing high-level corruption in political, business and criminal elites.” — Christina Vasilaki
Kosovo / 6 verified reports in 2017|
“Kosovo’s media have been shaken up by two attacks on Insajderi investigative journalists. Insajderi is home to the best investigative journalists in the country, covering corruption and crime topics that nobody else dares to touch. Journalist Parim Olluri was beaten up outside his home in Pristina on 16 August. He needed medical assistance in a hospital. Nobody has been held responsible for the attack. Two months later, his colleague Vehbi Kajtazi was hit on the head in a cafe in downtown Pristina on 13 October. One person was arrested on the spot. We are talking about two violent incidents to Insajderi journalists within a period of three months. This shows that Kosovo’s journalists continue to face violence, even in very public places like cafe’s and neighbourhoods they live. For this reason there are just a few brave journalists who dare to touch sensitive topics, which is a worrying sign for the future of journalism and truth finding in the youngest country in Europe.” — Mitra Nazar
Montenegro / 6 verified reports in 2017
“Attack on journalist’s property is one of most common ways of intimidation. This is not only case for Montenegro, but also for all other countries in the region. What is striking is that intentional setting on fire of journalist’s vehicles is one of most common ways of limitation of media freedom in Montenegro. In recent years there have been several burnt vehicle in this small EU candidate country.” — Ilcho Cvetanoski
Portugal / 5 verified reports in 2017
“Similarly to what’s happening in other countries, Portugal has seen a rise of questioning towards journalism, those who work in the media industry and their work. Besides motivating a new and stimulating debate between journalists and their readers/viewers/listeners, this has also opened the gates to instances of abuse, cyberbullying and slander. The most significant example of that is that of Público’s journalist Margarida Gomes, whose work ethic was put in question by Facebook groups and public officials, who both used false information regarding her personal life to denigrate her work.” — João de Almeida Dias
Latvia / 3 verified reports in 2017
“In Latvia it was a quiet year for press freedom. However, the sudden and swift dismissal of Sigita Roķe, the head of public service Latvian Radio for alleged economic irregularities was seen as a pretext for dismissing her for efforts to disengage the radio from sponsorship agreements with the city of Ventspils, whose politically influential mayor has is on trial for money laundering and corruption. The dismissal raised questions about the political neutrality of Latvia’s media watchdog, the National Electronic Mass Media Council.” — Juris Kaza
Ireland / 3 verified reports in 2017
“Compared to the long list of countries in Europe where it is getting progressively dangerous for reporters to do their work, the situation in Ireland is relatively benign. There are renewed concerns over source protection, and the strict libel regime. However, the most serious concern is regarding media ownership. Index on Censorship published a detailed report on this in August 2017. One significant media takeover – Independent News and Media buying up Celtic Media – fell through after the Government ordered a statutory investigation following objections.” — Flor Mac Carthy
Estonia / 3 verified reports in 2017
“In March, journalists for Estonia’s largest daily in circulation Postimees, sent a letter to the owners and managers to complain about interference with editorial freedom. This event is a disturbing example of the interference attempts from media owners and advertisement department that had grown to the level that journalists of a daily, that prides itself with a long history and high-quality content, had to resort to an unprecedented united protest letter to fight it. Interference in journalistic decision making and content from outside or inside sources is in general the worrisome threat.” — Helle Tiikmaa
Belgium / 2 verified reports in 2017
“In Belgium, a journalist who had published a story on surveillance in Bruxelles’ metro was interrogated on her sources by the police, in clear breach of the principle of sources confidentiality. The case also reminds us of the risk for journalists covering surveillance.” — Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Denmark / 2 verified reports in 2017
“The killing of Kim Wall by the inventor and entrepreneur Peter Madsen was a headline news event around the world. Stabbed to death and dumped at sea whilst interviewing Madsen on board his home-built submarine, her body was recovered after an extensive marine search. Although not typical of any wider trend, her murder was so brutal it raised significant questions about the safety and ethics of female freelancers working alone without support or safeguards.” — Dominic Hinde
Finland / 2 verified reports in 2017
“In March the Finnish government introduced restrictive changes to the functioning of the public broadcasting company Yle, which entailed putting the state-owned company more firmly under politicians’ decision-making power. The proposal was driven by the True Finns, a nationalist party that have repeatedly complained about Yle’s liberal views and non-sceptical approach to ‘multicultural Finland’. In the official briefing, stated the following: “The proposal is to strengthen the role of the Administrative Council so that they can decide on Yle’s journalistic strategy and regulate the permanent expert consultation process”. The council referred is mainly composed of politicians. — Katariina Salomäki
Iceland / 1 verified report in 2017
“Iceland has been rocked by political scandals and collapsing governments twice in the space of a year. In October it came to light that the prime minister had used financial confidentiality legislation to stop the investigative newspaper Stundin from publishing details of his offshore financial dealings in the run-up to the 2008 financial crash. Iceand’s main newspaper Morgunbladid is controlled by another former Prime Minister, also a member of the powerful Icelandic independence party, and Stundin has consistently sought to expose the Icelandic financial and political elite where other titles have remained silent.” — Dominic Hinde[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Mapping Media Freedom” use_theme_fonts=”yes” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fmappingmediafreedom.org%2F%23%2F|||”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-times-circle” color=”black” background_style=”rounded” size=”xl” align=”right”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”3/4″][vc_column_text]
Since 24 May 2014, Mapping Media Freedom’s team of correspondents and partners have recorded and verified more than 3,700 violations against journalists and media outlets.
Index campaigns to protect journalists and media freedom. You can help us by submitting reports to Mapping Media Freedom.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator color=”black”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Don’t lose your voice. Stay informed.” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_separator color=”black”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship is a nonprofit that campaigns for and defends free expression worldwide. We publish work by censored writers and artists, promote debate, and monitor threats to free speech. We believe that everyone should be free to express themselves without fear of harm or persecution – no matter what their views.
Join our mailing list (or follow us on Twitter or Facebook) and we’ll send you our weekly newsletter about our activities defending free speech. We won’t share your personal information with anyone outside Index.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][gravityform id=”20″ title=”false” description=”false” ajax=”false”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator color=”black”][/vc_column][/vc_row]
9 Nov 2017 | Awards, Awards year slider
[vc_row full_width=”stretch_row_content_no_spaces” css_animation=”fadeIn” css=”.vc_custom_1500380806420{padding-top: 250px !important;padding-bottom: 250px !important;background-image: url(https://www.indexoncensorship.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/logo-2018-1460×490.jpg?id=94317) !important;background-position: center !important;background-repeat: no-repeat !important;background-size: cover !important;}”][vc_column][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row” css=”.vc_custom_1500449679881{margin-top: -50px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”2018 FREEDOM OF EXPRESSION AWARDS” font_container=”tag:h1|text_align:center” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_row_inner disable_element=”yes”][vc_column_inner][vc_empty_space height=”15px”][vc_custom_heading text=”ABOUT THE AWARDS” font_container=”tag:h2|text_align:center” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner equal_height=”yes” content_placement=”middle”][vc_column_inner el_class=”awards-inside-desc” width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship’s Freedom of Expression Awards exist to celebrate individuals or groups who have had a significant impact fighting censorship anywhere in the world.
- Awards are offered in four categories: Arts, Campaigning, Digital Activism and Journalism
- Anyone who has had a demonstrable impact in tackling censorship is eligible
- Winners are honoured at a gala celebration in London
- Winners join Index’s Awards Fellowship programme and receive dedicated training and support
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_video link=”https://youtu.be/a9Yl-nkwpig”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”2018 Fellowship” font_container=”tag:h3|text_align:center” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]
Selected from over 400 public nominations and a shortlist of 16, the 2018 Freedom of Expression Awards Fellows exemplify courage in the face of censorship. Learn more about the fellowship.
[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”97994″ img_size=”full”][vc_column_text]Arts | The Museum of Dissidence
The Museum of Dissidence is a public art project and website celebrating dissent in Cuba. Set up in 2016 by acclaimed artist Luis Manuel Otero Alcántara and curator Yanelys Nuñez Leyva, their aim is to reclaim the word “dissident” and give it a positive meaning in Cuba. The museum organises radical public art projects and installations, concentrated in the poorer districts of Havana. Their fearlessness in opening dialogues and inhabiting public space has led to fierce repercussions: Nuñez was sacked from her job and Otero arrested and threatened with prison for being a “counter-revolutionary.” Despite this, they persist in challenging Cuba’s restrictions on expression.
Full profile | Speech[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”97988″ img_size=”full”][vc_column_text]Campaigning | Egyptian Commission for Rights and Freedoms
The Egyptian Commission for Rights and Freedoms is one of the few human rights organisations still operating in a country which has waged an orchestrated campaign against independent civil society groups. Egypt is becoming increasingly hostile to dissent, but ECRF continues to provide advocacy, legal support and campaign coordination, drawing attention to the many ongoing human rights abuses under the autocratic rule of President Abdel Fattah-el-Sisi. Their work has seen them subject to state harassment, their headquarters have been raided and staff members arrested. ECRF are committed to carrying on with their work regardless of the challenges.
Full profile | Speech[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”97990″ img_size=”full”][vc_column_text]Digital Activism | Habari RDC
Launched in 2016, Habari RDC is a collective of more than 100 young Congolese bloggers and web activists, who use Facebook, Twitter and YouTube to give voice to the opinions of young people from all over the Democratic Republic of Congo. Their site posts stories and cartoons about politics, but it also covers football, the arts and subjects such as domestic violence, child exploitation, the female orgasm and sexual harassment at work. Habari RDC offers a distinctive collection of funny, angry and modern Congolese voices, who are demanding to be heard.
Full profile | Speech[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”98000″ img_size=”full”][vc_column_text]Journalism | Wendy Funes
Wendy Funes is an investigative journalist from Honduras who regularly risks her life for her right to report on what is happening in the country, an extremely harsh environment for reporters. Two journalists were murdered in 2017 and her father and friends are among those who have met violent deaths in the country – killings for which no one has ever been brought to justice. Funes meets these challenges with creativity and determination. For one article she had her own death certificate issued to highlight corruption. Funes also writes about violence against women, a huge problem in Honduras where one woman is killed every 16 hours.
Full profile | Speech[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][awards_gallery_slider name=”2018 AWARDS GALA” images_url=”99875,99880,99879,99881,99882,99884,99885,99886,99887,99888,99889,99890,99891,99892,99893,99902,99906,99907,99908,99909,99910,99911,99912,99913,99914,99915,99916,99917,99918,99919,99920,99921,99922,99923,99924,99926,99925″][vc_column_text]
The Awards were held at London’s May Fair Hotel on Thursday 19 April 2018.
High-resolution images are available for download via Flickr.
[/vc_column_text][vc_custom_heading text=”THE 2018 FELLOWSHIP SHORTLIST” font_container=”tag:h2|text_align:center” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_tta_tabs][vc_tta_section title=”Arts” tab_id=”Arts”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
ARTS
for artists and arts producers whose work challenges repression and injustice and celebrates artistic free expression
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_video link=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VfntVe_SrPY”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97991″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/03/indexawards-2018-jamal-alis-music-fights-oppression-in-azerbaijan/”][vc_column_text]Jamal Ali, Azerbaijan[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97998″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/03/index-awards-silvanos-mudzvova/”][vc_column_text]Silvanos Mudzvova, Zimbabwe[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”99853″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/03/indexawards2017-museum-of-dissidence-cuba-activism/”][vc_column_text]The Museum of Dissidence, Cuba[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97985″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/03/index-awards-abbad-yahya/”][vc_column_text]Abbad Yahya, Palestine[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_tta_section][vc_tta_section title=”Campaigning” tab_id=”1524476396272-7b8a9fcb-bce7″][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
CAMPAIGNING
for activists and campaigners who have had a marked impact in fighting censorship and promoting freedom of expression
Supported by Doughty Street Chambers
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_video link=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iV2qFGmPhUU”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”99421″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/03/indexawards2018-ecrf-advocates-for-democratic-egypt/”][vc_column_text]Egyptian Commission for Rights and Freedoms, Egypt[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97995″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/03/index-awards-nglhrc/”][vc_column_text]National Gay and Lesbian Human Rights Commission, Kenya[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97997″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/03/index-awards-open-stadiums/”][vc_column_text]Open Stadiums, Iran[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97999″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/03/index-awards-team-29/”][vc_column_text]Team 29, Russia[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_tta_section][vc_tta_section title=”Digital activism” tab_id=”1524476516614-1a2ebb46-7ed2″][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
DIGITAL ACTIVISM
for innovative uses of technology to circumvent censorship and enable free and independent exchange of information
Supported by Private Internet Access
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_video link=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dz0rqQOlutw”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97987″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/04/index-awards-digital-rights-foundation/”][vc_column_text]Digital Rights Foundation, Pakistan[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97989″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/04/index-awards-fereshteh-forough/”][vc_column_text]Fereshteh Forough, Afghanistan[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”99851″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/04/index-awards-habari-rdc-digital-activism/”][vc_column_text]Habari RDC, Congo[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97992″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/04/index-awards-media-cat-free-speech/”][vc_column_text]Mèdia.cat, Spain[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_tta_section][vc_tta_section title=”Journalism” tab_id=”1524476563543-4fdf3da9-962c”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
JOURNALISM
for courageous, high-impact and determined journalism that exposes censorship and threats to free expression
Sponsored by Vice News
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_video link=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i8KfzAtARGQ”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97986″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/04/index-awards-avispa-midia/”][vc_column_text]Avispa Midia, Mexico[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”99850″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/04/index-awards-wendy-funes/”][vc_column_text]Wendy Funes, Honduras[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97993″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/04/index-awards-muck-rock/”][vc_column_text]MuckRock, United States[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_single_image image=”97996″ onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/04/novosti-combats-croatian-natinalism/”][vc_column_text]Novosti, Croatia[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_tta_section][/vc_tta_tabs][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row” css=”.vc_custom_1484569093244{background-color: #f2f2f2 !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”JUDGING” font_container=”tag:h1|text_align:center” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_row_inner el_class=”mw700″][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
Each year Index recruits an independent panel of judges – leading voices with diverse expertise across campaigning, journalism, the arts and human rights. Judges look for courage, creativity and resilience. We shortlist on the basis of those who are deemed to be making the greatest impact in tackling censorship in their chosen area, with a particular focus on topics that are little covered or tackled by others. Where a judge comes from a nominee’s country, or where there is any other potential conflict of interest, the judge will abstain from voting in that category.
The 2018 judging panel:
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][staff name=”Razia Iqbal” title=”Journalist” profile_image=”97201″]Razia Iqbal is a presenter for BBC News, where she is one of the main presenters of Newshour, the flagship news and current affairs programme on BBC World Service radio. [/staff][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][staff name=”Tim Moloney QC” title=”Barrister” profile_image=”97202″]Tim Moloney QC is the deputy head of Doughty Street Chambers. His practice encompasses crime, extradition, international criminal law, international death penalty litigation, public law and media law. [/staff][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][staff name=”Yana Peel” title=”Chief Executive” profile_image=”97203″]Yana Peel is CEO of the Serpentine Galleries, London, one of the most recognised organisations in the global contemporary art, design and architecture worlds. [/staff][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][staff name=”Eben Upton CBE” title=”Tech entrepreneur” profile_image=”97204″]Eben Upton CBE is a founder of the Raspberry Pi Foundation and serves as the CEO of Raspberry Pi (Trading), its commercial and engineering subsidiary.[/staff][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row” css=”.vc_custom_1510244917017{margin-top: 30px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”THE FREEDOM OF EXPRESSION AWARDS FELLOWSHIP” font_container=”tag:h2|text_align:center” use_theme_fonts=”yes” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2F2017%2F07%2F2018-freedom-of-expression-awards-fellowship%2F|||”][vc_column_text]
The Freedom of Expression Awards Fellowship is open to any individual or organisation involved in tackling free expression threats – either through journalism, campaigning, the arts or using digital techniques – is eligible for nomination. Any individual, group or NGO can nominate or self-nominate. There is no cost to apply. Nominees must have had a recognisable impact in the past 12 months.
We offer Fellowships in four categories:[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner equal_height=”yes” disable_element=”yes” el_class=”awards-4grid” css=”.vc_custom_1524481168193{margin-top: 20px !important;margin-bottom: 20px !important;}”][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″ css=”.vc_custom_1500449830213{background-color: #cb3000 !important;}”][vc_custom_heading text=”Arts” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]for artists and arts producers whose work challenges repression and injustice and celebrates artistic free expression[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″ css=”.vc_custom_1500449924825{background-color: #d98c00 !important;}”][vc_custom_heading text=”Campaigning” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]for activists and campaigners who have had a marked impact in fighting censorship and promoting freedom of expression[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″ css=”.vc_custom_1500449960164{background-color: #cb3000 !important;}”][vc_custom_heading text=”Digital Activism” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]for innovative uses of technology to circumvent censorship and enable free and independent exchange of information[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″ css=”.vc_custom_1500449938665{background-color: #d98c00 !important;}”][vc_custom_heading text=”Journalism” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_column_text]for courageous, high-impact and determined journalism that exposes censorship and threats to free expression[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row equal_height=”yes” el_class=”text_white” css=”.vc_custom_1500380887889{margin-top: 20px !important;margin-bottom: 20px !important;background-color: #cb3000 !important;}”][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_custom_heading text=”Support the Index Awards.” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:28|text_align:center” use_theme_fonts=”yes” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fsupport-the-freedom-of-expression-awards%2F|||”][vc_column_text]
By donating to the Freedom of Expression Awards you help us support individuals and groups at the forefront of tackling censorship.
Find out more
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″ css=”.vc_custom_1524481080226{background-image: url(https://www.indexoncensorship.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/2018-Fellows-4-web.jpg?id=99811) !important;background-position: center !important;background-repeat: no-repeat !important;background-size: contain !important;}”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row disable_element=”yes”][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”GALA” font_container=”tag:h1|text_align:center” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][awards_gallery_slider name=”2017 Freedom of Expression Awards” images_url=”89583,89582,89581,89580,89579,89577,89578,89576,89575,89574,89565,89560,89559,89553,89552,89551,89550,89549,89548,89547,89546,89545,89544,89543,89542,89541,89540,89539,89538,89537,89536,89535,89534,89533,89532,89531,89530,89529,89528,89527,89526,89525,89524,89523,89522,89520,89521,89519,89518,89517,89516,89515,89514,89513,89512,89511,89510,89509″][vc_column_text]
The Awards were held at London’s Unicorn Theatre on Wednesday 19 April 2017.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row_content_no_spaces” disable_element=”yes” css=”.vc_custom_1500384168164{margin-top: 20px !important;margin-bottom: 20px !important;padding-top: 20px !important;padding-right: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 20px !important;padding-left: 15px !important;background-color: #f2f2f2 !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner content_placement=”middle” el_class=”container container980″][vc_column_inner][awards_news_slider name=”NEWS” years=”2017″][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row_content_no_spaces” css=”.vc_custom_1500453384143{margin-top: 20px !important;padding-top: 20px !important;padding-bottom: 20px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_custom_heading text=”SPONSORS” font_container=”tag:h1|text_align:center” use_theme_fonts=”yes” css=”.vc_custom_1484567001197{margin-bottom: 30px !important;}”][vc_column_text]
The Freedom of Expression Awards and Fellowship have massive impact. You can help by sponsoring or supporting a fellowship.
Index is grateful to those who are supporting the 2018 Awards:
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner equal_height=”yes” el_class=”container container980″][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″ offset=”vc_col-xs-6″][vc_single_image image=”80918″ img_size=”234×234″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” img_link_target=”_blank” link=”https://uk.sagepub.com/”][vc_single_image image=”85983″ img_size=”234×234″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.privateinternetaccess.com/”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″ offset=”vc_col-xs-6″][vc_single_image image=”80921″ img_size=”234×234″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” img_link_target=”_blank” link=”https://www.google.co.uk/about/”][vc_single_image image=”85977″ img_size=”150×150″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://www.edwardian.com/”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner equal_height=”yes” el_class=”container container980″][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_col-xs-6″][vc_single_image image=”82003″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” img_link_target=”_blank” link=”http://www.vodafone.com/content/index.html#”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_col-xs-6″][vc_single_image image=”82323″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://news.vice.com/”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_col-xs-6″][vc_single_image image=”80923″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” img_link_target=”_blank” link=”http://www.doughtystreet.co.uk/”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner equal_height=”yes” el_class=”container container980″][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_col-xs-6″][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_col-xs-6″][vc_single_image image=”80924″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” img_link_target=”_blank” link=”https://psiphon.ca/”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″ offset=”vc_col-xs-6″][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
If you are interested in sponsorship you can contact [email protected]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
16 Oct 2017 | Campaigns -- Featured, Digital Freedom, Digital Freedom Statements, Statements
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Dear President Juncker,
Dear President Tajani,
Dear President Tusk,
Dear Prime Minister Ratas,
Dear Prime Minister Borissov,
Dear Ministers,
Dear MEP Voss, MEP Boni
The undersigned stakeholders represent fundamental rights organisations.
Fundamental rights, justice and the rule of law are intrinsically linked and constitute core values on which the EU is founded. Any attempt to disregard these values undermines the mutual trust between member states required for the EU to function. Any such attempt would also undermine the commitments made by the European Union and national governments to their citizens.
Article 13 of the proposal on Copyright in the Digital Single Market include obligations on internet companies that would be impossible to respect without the imposition of excessive restrictions on citizens’ fundamental rights.
Article 13 introduces new obligations on internet service providers that share and store user-generated content, such as video or photo-sharing platforms or even creative writing websites, including obligations to filter uploads to their services. Article 13 appears to provoke such legal uncertainty that online services will have no other option than to monitor, filter and block EU citizens’ communications if they are to have any chance of staying in business.
Article 13 contradicts existing rules and the case law of the Court of Justice. The Directive of Electronic Commerce (2000/31/EC) regulates the liability for those internet companies that host content on behalf of their users. According to the existing rules, there is an obligation to remove any content that breaches copyright rules, once this has been notified to the provider.
Article 13 would force these companies to actively monitor their users‘ content, which contradicts the ‘no general obligation to monitor’ rules in the Electronic Commerce Directive. The requirement to install a system for filtering electronic communications has twice been rejected by the Court of Justice, in the cases Scarlet Extended (C 70/10) and Netlog/Sabam (C 360/10). Therefore, a legislative provision that requires internet companies to install a filtering system would almost certainly be rejected by the Court of Justice because it would contravene the requirement that a fair balance be struck between the right to intellectual property on the one hand, and the freedom to conduct business and the right to freedom of expression, such as to receive or impart information, on the other.
In particular, the requirement to filter content in this way would violate the freedom of expression set out in Article 11 of the Charter of Fundamental Rights. If internet companies are required to apply filtering mechanisms in order to avoid possible liability, they will. This will lead to excessive filtering and deletion of content and limit the freedom to impart information on the one hand, and the freedom to receive information on the other.
If EU legislation conflicts with the Charter of Fundamental Rights, national constitutional courts are likely to be tempted to disapply it and we can expect such a rule to be annulled by the Court of Justice. This is what happened with the Data Retention Directive (2006/24/EC), when EU legislators ignored compatibility problems with the Charter of Fundamental Rights. In 2014, the Court of Justice declared the Data Retention Directive invalid because it violated the Charter.
Taking into consideration these arguments, we ask the relevant policy-makers to delete Article 13.
Civil Liberties Union for Europe (Liberties)
European Digital Rights (EDRi)
Access Info
ActiveWatch
Article 19
Associação D3 – Defesa dos Direitos Digitais
Associação Nacional para o Software Livre (ANSOL)
Association for Progressive Communications (APC)
Association for Technology and Internet (ApTI)
Association of the Defence of Human Rights in Romania (APADOR)
Associazione Antigone
Bangladesh NGOs Network for Radio and Communication (BNNRC)
Bits of Freedom (BoF)
BlueLink Foundation
Bulgarian Helsinki Committee
Center for Democracy & Technology (CDT)
Centre for Peace Studies
Centrum Cyfrowe
Coalizione Italiana Libertà e Diritti Civili (CILD)
Code for Croatia
COMMUNIA
Culture Action Europe
Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF)
epicenter.works
Estonian Human Rights Centre
Freedom of the Press Foundation
Frënn vun der Ënn
Helsinki Foundation for Human Rights
Hermes Center for Transparency and Digital Human Rights
Human Rights Monitoring Institute
Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Without Frontiers
Hungarian Civil Liberties Union
Index on Censorship
International Partnership for Human Rights (IPHR)
International Service for Human Rights (ISHR)
Internautas
JUMEN
Justice & Peace
La Quadrature du Net
Media Development Centre
Miklos Haraszti (Former OSCE Media Representative)
Modern Poland Foundation
Netherlands Helsinki Committee
One World Platform
Open Observatory of Network Interference (OONI)
Open Rights Group (ORG)
OpenMedia
Panoptykon
Plataforma en Defensa de la Libertad de Información (PDLI)
Reporters without Borders (RSF)
Rights International Spain
South East Europe Media Organisation (SEEMO)
South East European Network for Professionalization of Media (SEENPM)
Statewatch
The Right to Know Coalition of Nova Scotia (RTKNS)
Xnet
CC: Permanent and Deputy Permanent Representatives of the Members States to the EU
CC: Chairs of the JURI and LIBE Committees in the European Parliament
CC: Shadow Rapporteurs and MEPs in the JURI and LIBE Committees in the European Parliament
CC: Secretariats of the JURI and LIBE Committees in the European Parliament
CC: Secretariat of the Council Working Party on Intellectual Property (Copyright)
CC: Secretariat of the Council Working on Competition
CC: Secretariat of the Council Research Working Party[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1508140671158-363c6122-72fc-4″ taxonomies=”16927″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
25 Aug 2017 | Digital Freedom, News and features
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

I spend a lot of my time writing about encryption. Until recently I did this from a UK perspective. That is to say, in a country where there are pretty good citizen protections. Despite the occasional hysterical article, the police don’t snoop on you without having some probable cause and a legal warrant. UK citizens aren’t constantly under surveillance and don’t get rounded up for speaking their mind.
From this vantage point, the public debate on encryption starts with its problems. Terrorists are using encrypted messaging apps. Drug dealers are using the Tor browser. End-to-end encryption used by the big tech firms is a headache for local police forces. All this is true. But any benefits are merely addendum, secondary points, “ands” or “buts”. Don’t forget, however, that encryption is also for activists and journalists, including those in less friendly parts of the world. Oh, and don’t forget ordinary citizens. Such benefits are mostly discussed abstractly, almost as an afterthought.
My view on encryption changed in 2016 when I was researching my book Radicals. This being a book about fringe political movements – often viewed with hostility by governments – I expected to use some degree of caution. But it was more than this. Over in Croatia, I was following Vit Jedlicka, the president of Liberland, a libertarian pseudo-nation on the Serb-Croat border. Jedlicka is trying to create a new nation on some unclaimed land that will run according to the principles of radical libertarianism, including voluntary taxation. The Croat authorities do not like him at all, even though he is non-violent and law abiding.
I arrived in Croatia, after an early Easy Jet flight, and was taken aside for questioning by the border police, who appeared to know I was coming. They told me not to attempt to visit Liberland. A little later, while I was away from my hotel, the police turned up and demanded a copy of my passport from the hotel manager. Jedlicka, meanwhile, was barred from entering Croatia, having been deemed a threat to national security.
I did not know a great deal about the Croatian police, but what little I did know made me doubt they cared too much about my right to privacy. I suddenly felt exposed. So Jedlicka and I communicated using an encrypted messaging app, Signal. I had considered Signal mostly a frustrating tool that helps violent Islamists avoid intelligence agencies. But suddenly this nuisance app was transformed. Thank God for Signal, I thought. Whoever invented Signal deserved a prize, I thought. Without Signal, Jedlicka couldn’t engage in activism. Without Signal, I couldn’t write about it.
This was in Croatia. Imagine what that might feel like as a democratic activist in Iran, Russia, Turkey or China.
You see the debate about encryption differently once you’ve had cause to rely on it personally for morally sound purposes. An abstract benefit to journalists or activists becomes a very tangible, almost emotional dependence. The simple existence of powerful, reliable encryption does more than just protect you from an overbearing state: it changes your mindset too. When it’s possible to communicate without your every move being traced, the citizen is emboldened. He or she is more likely to agitate, to protest and to question, rather than sullenly submit. If you believe the state is tracking you constantly, the only result is timid, self-censoring, frightened people. I felt it coming on in Croatia. Governments should be afraid of the people, not the other way around.
The debate on encryption, therefore, should change. The people who build this stuff – whether Tor, PGP or whatever else – are generally motivated by the desire to help people like Jedlicka, people like me. They don’t do it for the terrorists. Seen and understood in that light, the starting point for discussion is about the great benefits of encryption, followed by the frustrating and inevitable fact that bad guys will use the same networks, browsers and messaging apps.
Which is why any efforts to undermine encryption – through laws, endless criticism, weakening standards, bans, threats to ban, backdoors and international agreements – would hit someone like Jedlicka, or me, just as it would Isis. The questions then become: are we willing to prevent good guys having protection just because bad guys are using it? Once you’ve had cause to use it yourself, the answer is extremely clear.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1503654311600-41f8449d-cfd3-2″ taxonomies=”6914″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
 This year saw 1,035 media freedom violations reported to Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom, a project that monitors media freedom in 42 countries, including all EU member states. To highlight the most pressing concerns for press freedom in Europe, Index’s MMF correspondents discuss the violations that stood out most.
This year saw 1,035 media freedom violations reported to Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom, a project that monitors media freedom in 42 countries, including all EU member states. To highlight the most pressing concerns for press freedom in Europe, Index’s MMF correspondents discuss the violations that stood out most. 
