30 Jun 2016 | Africa, Kenya, Magazine, mobile, Volume 45.02 Summer 2016 Extras
“Yassin Juma is an extraordinary journalist, who has taken great personal risks to get the story of what is happening in the war that is being waged in Somalia against Al-Shabaab,” writer Ismail Einashe told Index on Censorship.
But Juma is now in hiding.
Einashe interviewed the Kenyan investigative journalist for the latest issue of Index on Censorship magazine, which is themed on the risks of reporting worldwide.
Juma was arrested in January for posting information on social media about a recent attack on the Kenyan Defence Force by the Al-Shabaab militant group. Juma revealed that, according to a credible source within the KDF, 103 soldiers had been killed in an attack on the Kenyan army base in El Adde, Somalia.
The journalist was later arrested and faced charges of “misuse of a telecommunication gadget”. After being grilled by police and detained for two days, he was released without charge but has since gone into hiding, fearing that his reporting is angering the authorities.
Listen to Einashe explaining the significance of this case on the Soundcloud above. The full article, written by Einashe, is in the latest issue of Index on Censorship magazine.
Print copies of the magazine are available here, or you can take out a digital subscription via Exact Editions. Copies are also available at the BFI, the Serpentine Gallery, MagCulture, (London), News from Nowhere (Liverpool), Home (Manchester) and on Amazon. Each magazine sale helps Index on Censorship continue its fight for free expression worldwide.
25 Feb 2016 | Africa, Campaigns, Digital Freedom, Digital Freedom Statements, Statements, Uganda
Mr. Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein, Mr. David Kaye, Mr. Joseph Cannataci, Mr. Maina Kiai, Mr. Michel Forst, Ms. Faith Pansy Tlakula, and Ms. Reine Alapini-Gansou
cc: African Union
African Peer Review Mechanism (APRM) Secretariat
Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa Secretariat
Domestic & International Election Observer Missions to the Republic of Uganda
East African Community Secretariat
International Conference on the Great Lakes Region Secretariat
New Partnership for Africa’s Development (NEPAD) Secretariat
Uganda Communications Commission
Uganda Electoral Commission
Uganda Ministry of Information and Communications Technology
23 February 2016
Re: Internet shutdown in Uganda and elections
Your Excellencies,
We are writing to urgently request your immediate action to condemn the internet shutdown in Uganda, and to prevent any systematic or targeted attacks on democracy and freedom of expression in other African nations during forthcoming elections in 2016. [1]
On February 18, Ugandan internet users detected an internet outage affecting Twitter, Facebook, and other communications platforms. [2] According to the Uganda Communications Commission (UCC), blocking was carried out on orders of the Electoral Commission, for security reasons. [3] The shutdown coincided with voting for the presidential election, and remained in place until the afternoon of Sunday, February 21. During this period, two presidential candidates were detained under house arrest. [4] The telco MTN Uganda confirmed the UCC directed it to block “Social Media and Mobile Money services due to a threat to Public Order & Safety.” [5] The blocking order also affected the telcos Airtel, Smile, Vodafone, and Africel. President Museveni admitted to journalists on February 18 that he had ordered the block because “steps must be taken for security to stop so many (social media users from) getting in trouble; it is temporary because some people use those pathways for telling lies.” [6]
Research shows that internet shutdowns and state violence go hand in hand. [7] Shutdowns disrupt the free flow of information and create a cover of darkness that allows state repression to occur without scrutiny. Worryingly, Uganda has joined an alarming global trend of government-mandated shutdowns during elections, a practice that many African Union member governments have recently adopted, including: Burundi, Congo-Brazzaville, Egypt, Sudan, the Central African Republic, Niger, Democratic Republic of Congo. [8], [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14]
Internet shutdowns — with governments ordering the suspension or throttling of entire networks, often during elections or public protests — must never be allowed to become the new normal. Justified for public safety purposes, shutdowns instead cut off access to vital information, e-financing, and emergency services, plunging whole societies into fear and destabilizing the internet’s power to support small business livelihoods and drive economic development.
Uganda’s shutdown occurred as more than 25 African Union member countries are preparing to conduct presidential, local, general or parliamentary elections. [15]
A growing body of jurisprudence declares shutdowns to violate international law. In 2015, various experts from the United Nations (UN) Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), Organization of American States (OAS), and the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights (ACHPR), issued an historic statement declaring that internet “kill switches” can never be justified under international human rights law, even in times of conflict. [16] General Comment 34 of the UN Human Rights Committee, the official interpreter of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, emphasizes that restrictions on speech online must be strictly necessary and proportionate to achieve a legitimate purpose. Shutdowns disproportionately impact all users, and unnecessarily restrict access to information and emergency services communications during crucial moments.
The internet has enabled significant advances in health, education, and creativity, and it is now essential to fully realize human rights including participation in elections and access to information.
We humbly request that you use the vital positions of your good offices to:
- call upon the Ugandan government to provide redress to victims of the internet shutdown, and pledge not to issue similar orders in the future;
- call on African states to uphold their human rights obligations, and not to take disproportionate responses like issuing shutdown orders, especially during sensitive moments like elections;
- investigate shutdowns, in their various forms, in order to produce public reports that examine this alarming trend and its impact on human rights, and make recommendations to governments and companies on how to prevent future disruptions;
- encourage telecommunications and internet services providers to respect human rights and resist unlawful orders to violate user rights, including through public disclosures and transparency reports;
- encourage the African Commission on People’s and Human Rights, the United Nations Human Rights Council, and the UN General Assembly to resolve that Internet Shutdowns violate freedom of expression per se and without legal justification.
We are happy to assist you in any of these matters.
Sincerely,
Access Now
African Centre for Democracy and Human Rights Studies (ACDHRS)
Association for Progressive Communications (APC)
Article 19 East Africa
Chapter Four Uganda
CIPESA
CIVICUS
Committee to Protect Journalists
DefendDefenders (The East and Horn of Africa Human Rights Defenders Project)
Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF)
Global Partners Digital
Hivos East Africa
ifreedom Uganda
Index on Censorship
Integrating Livelihoods thru Communication Information Technology (ILICIT Africa)
International Commission of Jurists Kenya
ISOC Uganda
KICTANet (Kenya ICT Action Network)
Media Rights Agenda
Paradigm Initiative Nigeria
The African Media Initiative (AMI)
Unwanted Witness
Web We Want Foundation
Women of Uganda Network (WOUGNET)
Zimbabwe Human Rights NGO Forum
Endnotes
[1] Uganda election: Facebook and Whatsapp blocked’ (BBC, 18 February 2016) <http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-africa-35601220> accessed 18 February 2016.
[2] Omar Mohammed, ‘Twitter and Facebook are blocked in Uganda as the country goes to the polls’ (Quartz Africa, 18 February 2016) <http://qz.com/619188/ugandan-citizens-say-twitter-and-facebook-have-been-blocked-as-the-election-gets-underway/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[3] Uganda blocks social media for ‘security reasons’, polls delayed over late voting material delivery (The Star, 18 February 2016) <http://www.the-star.co.ke/news/2016/02/18/uganda-blocks-social-media-for-security-reasons-polls-delayed-over_c1297431> accessed 18 February 2016.
[4] Brian Duggan, “Uganda shuts down social media; candidates arrested on election day” (CNN, 18 February 2016) <http://www.cnn.com/2016/02/18/world/uganda-election-social-media-shutdown/> accessed 22 February 2016.
[5] MTN Uganda <https://twitter.com/mtnug/status/700286134262353920> accessed 22 February 2016.
[6] Tabu Batugira, “Yoweri Museveni explains social media, mobile money shutdown” (Daily Nation, February 18, 2016) <http://www.nation.co.ke/news/Yoweri-Museveni-explains-social-media-mobile-money-shutdown/-/1056/3083032/-/8h5ykhz/-/index.html> accessed 22 February 2016.
[7] Sarah Myers West, ‘Research Shows Internet Shutdowns and State Violence Go Hand in Hand in Syria’ (Electronic Frontier Foundation, 1 July 2015)
<https://www.eff.org/deeplinks/2015/06/research-shows-internet-shutdowns-and-state-violence-go-hand-hand-syria> accessed 18 February 2016.
[8] ‘Access urges UN and African Union experts to take action on Burundi internet shutdown’ (Access Now 29 April 2015) <https://www.accessnow.org/access-urges-un-and-african-union-experts-to-take-action-on-burundi-interne/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[9] Deji Olukotun, ‘Government may have ordered internet shutdown in Congo-Brazzaville’ (Access Now 20 October 2015) <https://www.accessnow.org/government-may-have-ordered-internet-shutdown-in-congo-brazzaville/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[10] Deji Olukotun and Peter Micek, ‘Five years later: the internet shutdown that rocked Egypt’ (Access Now 21 January 2016) <https://www.accessnow.org/five-years-later-the-internet-shutdown-that-rocked-egypt/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[11] Peter Micek, ‘Update: Mass internet shutdown in Sudan follows days of protest’ (Access Now, 15 October 2013) <https://www.accessnow.org/mass-internet-shutdown-in-sudan-follows-days-of-protest/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[12] Peter Micek, ‘Access submits evidence to International Criminal Court on net shutdown in Central African Republic’(Access Now 17 February 2015) <https://www.accessnow.org/evidence-international-criminal-court-net-shutdown-in-central-african-repub/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[13] ‘Niger resorts to blocking in wake of violent protests against Charlie Hebdo cartoons.’ (Access Now Facebook page 26 January 2015) <https://www.facebook.com/accessnow/posts/10153030213288480> accessed 18 February 2016.
[14] Peter Micek, (Access Now 23 January 2015) ‘Violating International Law, DRC Orders Telcos to Cease Communications Services’ <https://www.accessnow.org/violating-international-law-drc-orders-telcos-vodafone-millicon-airtel/> accessed 18 February 2016.
[15] Confirmed elections in Africa in 2016 include: Central African Republic (14th February), Uganda (18th February), Comoros and Niger (21st February), Rwanda (22nd -27th February), Cape Verde (TBC February), Benin (6th-13th March), Niger, Tanzania and Congo (20th March), Rwanda (22nd March), Chad (10th April), Sudan (11th April), Djibouti (TBC April), Niger (9th May), Burkina Faso (22nd May), Senegal (TBC May), Sao Tome and Principe (TBC July), Zambia (11th July), Cape Verde (TBC August), Tunisia (30th October), Ghana (7th November), Democratic Republic of Congo (27th November), Equatorial Guinea (TBC November), Gambia (1st December), Sudan, and Cote d’Ivoire (TBC December). Other elections without confirmed dates are scheduled to occur in Sierra Leone, Mauritania, Libya, Mali, Guinea, Rwanda, Somalia, and Gabon.
[16] Peter Micek, (Access Now 4 May 2015) ‘Internet kill switches are a violation of human rights law, declare major UN and rights experts’ <https://www.accessnow.org/blog/2015/05/04/internet-kill-switches-are-a-violation-of-human-rights-law-declare-major-un> accessed 18 February 2016.
16 Dec 2015 | Awards, Events, mobile, Press Releases
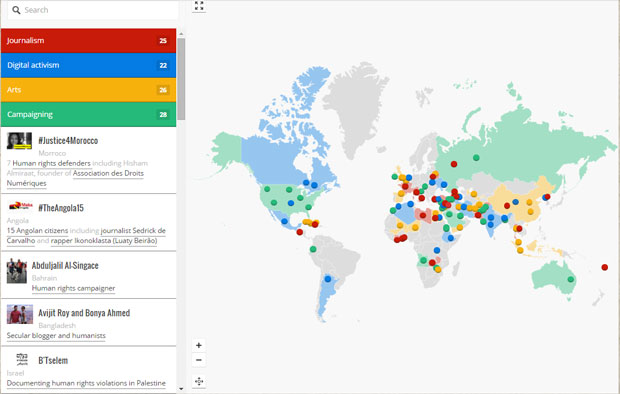
A graffiti artist who paints murals in war-torn Yemen, a jailed Bahraini academic and the Ethiopia’s Zone 9 bloggers are among those honoured in this year’s #Index100 list of global free expression heroes.
Selected from public nominations from around the world, the #Index100 highlights champions against censorship and those who fight for free expression against the odds in the fields of arts, journalism, activism and technology and whose work had a marked impact in 2015.
Those on the long list include Chinese human rights lawyer Pu Zhiqiang, Angolan journalist Sedrick de Carvalho, website Raqqa is Being Slaughtered Silently and refugee arts venue Good Chance Calais. The #Index100 includes nominees from 53 countries ranging from Azerbaijan to China to El Salvador and Zambia, and who were selected from around 500 public nominations.
“The individuals and organisations listed in the #Index100 demonstrate courage, creativity and determination in tackling threats to censorship in every corner of globe. They are a testament to the universal value of free expression. Without their efforts in the face of huge obstacles, often under violent harassment, the world would be a darker place,” Index on Censorship CEO Jodie Ginsberg said.
Those in the #Index100 form the long list for the Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards to be presented in April. Now in their 16th year, the awards recognise artists, journalists and campaigners who have had a marked impact in tackling censorship, or in defending free expression, in the past year. Previous winners include Nobel Peace Prize winner Malala Yousafzai, Argentina-born conductor Daniel Barenboim and Syrian cartoonist Ali Ferzat.
A shortlist will be announced in January 2016 and winners then selected by an international panel of judges. This year’s judges include Nobel Prize winning author Wole Soyinka, classical pianist James Rhodes and award-winning journalist María Teresa Ronderos. Other judges include Bahraini human rights activist Nabeel Rajab, tech “queen of startups” Bindi Karia and human rights lawyer Kirsty Brimelow QC.
The winners will be announced on 13 April at a gala ceremony at London’s Unicorn Theatre.
The awards are distinctive in attempting to identify individuals whose work might be little acknowledged outside their own communities. Judges place particular emphasis on the impact that the awards and the Index fellowship can have on winners in enhancing their security, magnifying the impact of their work or increasing their sustainability. Winners become Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards Fellows and are given support for the year after their fellowship on one aspect of their work.
“The award ceremony was aired by all community radios in northern Kenya and reached many people. I am happy because it will give women courage to stand up for their rights,” said 2015’s winner of the Index campaigning award, Amran Abdundi, a women’s rights activist working on the treacherous border between Somalia and Kenya.
Each member of the long list is shown on an interactive map on the Index website where people can find out more about their work. This is the first time Index has published the long list for the awards.
For more information on the #Index100, please contact [email protected] or call 0207 260 2665.
25 Mar 2015 | Magazine, mobile, Volume 44.01 Spring 2015
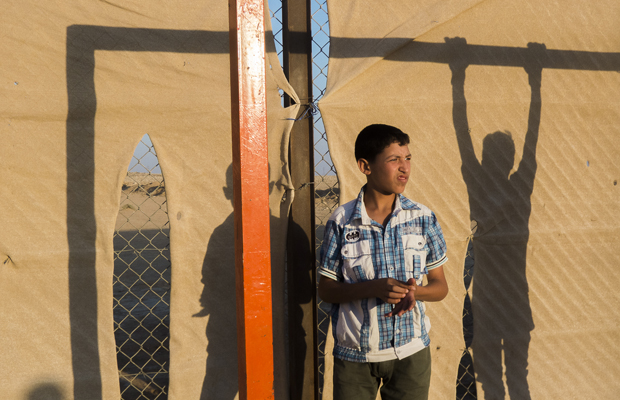

A picture from the Do You See What I See project which teaches photography skills to young refugees, Zaatari camp, Jordan (Credit: Mohamed Soleman/Do You See What I See)
In an article from the refugee voices special issue of Index on Censorship Magazine, Jason DaPonte looks at how migrants are using technology to keep in touch with distant relatives, and the security risks this can bring
“My wife changes her sim card every week,” said Omid, an Iranian refugee who hasn’t seen his wife in the seven years he has been awaiting a decision in his UK asylum case. The couple use Viber, a mobile app that allows free voice calls over the internet, but his wife remains in constant fear of surveillance. Omid is wanted by the Iranian state for political offences. He’s also a convert to Christianity and his wife fears discussing his new religion, as even members of his own family have branded him an infidel.
Refugees may be some of the most excluded people in society, but social media and new technology nevertheless play a crucial role in many of their lives. Across the globe, refugees are finding ways of using them to stay connected to families, homelands and political causes, in ways they couldn’t have a decade ago – even though it can have security implications. A number of refugees, particularly from Syria, suggested they use the free messaging mobile app, WhatsApp, because they believe the messages are secure. Whether WhatsApp messages can be hacked or intercepted is not clear, however.
Ismail Einashe, a British journalist and Africa expert, originally from Somaliland, explained another way social media is changing the refugee experience. He said how his teenage cousin, who fled Somaliland for Austria, uses Facebook for photo-sharing, to craft an image of success and happiness. But this can potentially hide the true difficulties of refugee life.
“My cousin is inspired by American hiphop. He wears baseball caps and baggy jeans – so his friends at home see the glamorous ‘other’ and they don’t see the high unemployment or poverty among refugees. It’s partly encouraging the young generation. Before, people didn’t see what life on the other side could be and now they can see it,” he told Index.
Nearly every refugee interviewed for this article said that free calls on Skype and the ability to connect with relatives for free using standard social platforms (like Facebook) is invaluable to them. But for some, sharing stories from exile goes beyond simple messaging and status updates. Some refugees use blogs and social media channels to publish content banned at home to try to fight the repression they escaped.
Moses Walusimbi fled Uganda’s anti-gay laws for The Netherlands and now runs Uganda Gay On Move – a blog, Facebook and Twitter movement that helps gay Ugandans and Africans who have fled persecution, as well as providing information for those who are left behind and remain under threat.
“When I came to Holland, I realised the more you keep quiet the more you suffer,” Walusimbi told Index. “I was very eager to know if there were any other Ugandans who are in Holland who are like me, in the same situation. And when I started these social media things, many Ugandans responded.”
His movement now has almost 9,000 followers on Facebook, which he says is the most popular platform for his content. He also has followers on Twitter and his blog. Uganda Gay On Move is providing a support network that goes beyond publishing, with many photos of meetings between its members for social and political reasons.
“Uganda Gay On Move is like a family to us now. It’s like a family because we come together, we discuss, we find solutions,” said Walusimbi. These solutions have included the group petitioning and lobbying the Dutch parliament to raise awareness about the denial of the human rights of gay Ugandans and other Africans. It also publishes information that helps asylum-seekers manage their cases and gather evidence. But Walusimbi still worries about those in Uganda who could face jail sentences simply for reading it.
“Ugandan LGBTI people – unless well-known human rights defenders – tend to use false names on Facebook. There is also a danger when people attend internet cafes and do not securely log off. There is also a danger – and I have had several direct reports of family or friends seeing the Facebook pages left open on computers in homes. Some people have been exposed this way,” Melanie Nathan, an LGBTI activist and publisher who has worked closely with African LGBTI movements, told Index. “Using Facebook could result in meetings or revealing real names through trust and then in entrapment.” Walusimbi corroborated that there are real cases where this has happened.
Blogs by and for refugees from various conflict zones are building audiences. The Medeshi Somaliland blog is one example. It was founded with a desire to keep in touch with a dispersed family and diaspora in 2007 by Mo Ali, who left Somaliland to seek asylum in the UK in 2004. His work of aggregating and creating new content quickly became more political.
“There are many websites about Somaliland and those who are publishing there have been harassed by the police. They’ve been ordered to shut down because of being critical of the government on freedom of speech and press,” Ali told Index, saying he knows of at least three websites that have been shut down and explaining why he has to publish from abroad.
Even publishing from the UK, he doesn’t feel totally safe, “I’ve received death threats via email but I published the threat online and nothing happened. I’m still alive. It was just intimidation.”
Like Uganda Gay On Move, Ali has used the blog’s following to campaign, and in 2010 and 2012 rallied more than 1,000 of his followers to lobby outside London’s Parliament for official recognition of Somaliland.
Refugees are working on their own and with professional content and software creators to find bespoke ways to tell their stories. Dadaab Stories and the related Refugee News are two of the most elegant projects that have used the power of free social media tools (particularly Tumblr and YouTube) to help refugees publish stories. In these cases, professional filmmakers and refugees worked together to create ongoing social media coverage of the refugee camp for Somalians in Kenya.
Globally available and free technology platforms are helpful, but tools, platforms and projects are now emerging that are specifically aimed at refugees to allow them to self-organise and connect digitally.
Refunite is a social network designed to connect dispersed families that have low access to technology following displacement. It allows refugees to remain anonymous to everyone other than their family members, which aids those who may not be able to register with formal institutions because they are awaiting asylum decisions or are stateless. The platform currently reaches more than 500,000 refugees and is aiming to connect 1 million during 2015. It is geared towards low-end mobile technology to ensure that nearly anyone can use it. It can even be accessed using an interactive voice response system or text-messaging for those who are illiterate or don’t have internet access.
Low-cost and low-barrier-to-entry technologies such as these are proving to be a key part of connecting refugees in crisis. The UNHCR is telling the world the story of Jordan’s Zaatari camp via Twitter (which has claimed to be the first refugee camp with an official Twitter account). Nasreddine Touaibia, a UNHCR communications associate at the camp described how WhatsApp, a free or low-cost mobile messaging system, is being used by Syrian refugees to self-organise. “Urgent messages are sent to these groups and they are reflected in the Facebook group later. It’s their own emergency broadcast network,” he told Index, describing how WhatsApp had been used to give warnings when flooding occurred at the camp.
South African technology startup Vumi is now trying to build on this trend of using low-cost messaging services to create technical products that can empower refugees to self-organise at scale. Its platform uses mass mobile messaging and low-fi browsing to enable access to civic information.
Building on its success in Libya of technically enabling Wikipedia Zero (a Wikipedia Foundation project which gives access to Wikipedia without data charges in 35 countries) and distributing voter information, the company is now in the planning stages for a project focussed on empowering refugees, in partnership with South Africa’s Lawyers for Human Rights, an NGO that deals largely with refugees in South Africa.
Various NGOs and other services are also using social media to provide platforms that help refugees re-settle. These are largely regionally based and aim to help refugees understand the legal and social contexts they are in. In the UK, the Refugee Council and Bail for Immigration Detainees provide online resources and tools that help refugees build and understand their legal cases. Migrant Voice, another UK-based organisation, provides training and tools to allow migrants (including refugees) to publish and communicate their stories.
Refugees and migrants certainly benefit from the uses of social media that everyone with internet access does; but the emerging platforms in the space are where the traditional model of solitary, isolated migrants can be disrupted. Tools specifically tailored to the needs of the excluded have the potential to create the most significant change in a networked world.
To read other articles from the issue, subscribe to the magazine in print, iPad, or phone find out more here or on iTunes, search for “Index on Censorship”.
This article and photograph is part of Across the wires, the spring 2015 issue of Index on Censorship magazine, and should not be reproduced without permission of the magazine editor. Follow the magazine on @Index_magazine
© Jason DaPonte


