Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
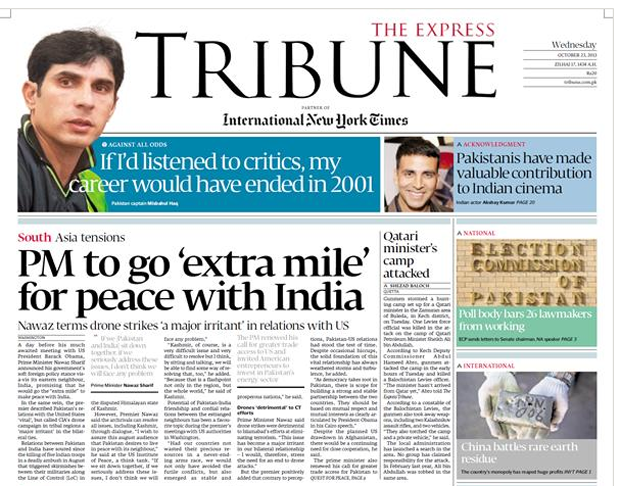
It’s been over two weeks now that Rana Tanveer, a reporter in Lahore at the English daily, Express Tribune, has not gone to work.
Early this month, he received a one-page letter, in the Urdu language, terming him an apostate and accusing him of writing in favour of Ahmadis and Christians.
“It warned me to stop writing ‘against’ Islam and seek ‘forgiveness’ from God,” he said over the phone from his home in the Punjab province.
It further warned him that if he did not desist, he would be killed — since that is the punishment of a person declared an apostate.
“I can’t work like this; no reporter can, if he cannot roam about freely,” said Tanveer.
Initially, he did not take the letter too seriously, but a week after he received the letter, he felt he was being followed on a motorbike. “It’s a scary experience,” he conceded, adding: “I made a few turns just to be sure that this was not a figment of my imagination, but the man on the motorbike persisted. I knew then that this was no joke and I had to do something.”
His seniors at work advised him to at least file a complaint with the police, which he did, but he did not name anyone “due to security reasons”.
“My editor told me to keep a low profile and not to report on minority issues for a while, and if I had to, it would go without by byline,” said the journalist.
Farahnaz Zahidi, features editor in the same paper as Tanveer’s feels very strongly about one’s byline being taken away. “As a journalist, perhaps the biggest satisfaction in this otherwise perilous and often under-paid profession is one’s by-line; it also lends credibility.”
However, she added, by shooting the messenger, society loses out. “The right to information is threatened when media persons threatened.”
Tanveer finds a plethora of minority rights abuses strewn around his city but says few journalists feel inclined to take up these issues.
“Mine seems to be a lone battle,” he said. “I am often scorned by my colleagues for reporting ‘chooras’ (derogatory term used for Christians, also among the poorest sections of society and consigned to menial janitorial jobs) and ‘Qadianis’ (also a derogatory name for those belonging to the Ahmadi faith, declared non-Muslims by state in 1974),” he said.
But it’s not indifference to these rights issue alone that keeps journalists from reporting on them. Senior journalist and communication expert, Babar Ayaz, says it is also quite dangerous to write about “the victimisation of Ahmadis, Christians or Hindus”.
Nevertheless, he added: “Journalists have to write what is right. Threats and killings are hazards of this job living in an increasingly intolerant society.”
He remembered when he wrote a piece on the attack on the massacre of Ahmadis in Lahore [in May 2010], he received a couple “abusive phone calls”. He also received some angry messages on a chapter in his book titled: What’s Wrong With Pakistan? The book, which was published in August criticises Islamic laws in Pakistan.
“But we are small fry,” said Ayaz. “When Nawaz Sharif expressed condolence on the killings of ‘our Ahmadis bhais [brothers]’ some mullahs said that by calling them ‘bhai’ he had committed a sin. The extremists have no logic but they have muscle power,” he added.
According to Aamer Mahmood, who heads the press section of the Ahmadiyya Jammat, and is in regular touch with several journalists: “The fear among them is palpable. While many empathise with us for the way our rights are trampled, they say their hands are tied. Some are scared of the wrath of the extremists; others fear they will lose their jobs.”
“It is indeed becoming more dangerous to write on these issues, in any language,” agreed Kamila Hyat, a rights activist and former editor of English daily The News. “I believe that while sections of the English language press remain relatively liberal, more and more are succumbing to the bias and intolerance we see everywhere,” she pointed out.
“The manner in which the ‘agenda’ for news is set, notably by the electronic media, also shoves minority issues to the sidelines, and intolerant mindsets exist everywhere — even among the educated,” she said.
With seven journalists having lost their lives since January this year, according to the 2013 Impunity Index report by the Committee to Protect Journalists (CJP), just last year, Pakistan which was ranked tenth, has moved two spots up at eighth position for the worst place for the press. Further, it has been declared more dangerous than Russia, Brazil, Nigeria and India.
According to the CJP, 28 Pakistani journalists have been murdered since 1992 in connection with their work, 27 of whom were killed with impunity. The deaths of 24 additional killed during the same period cannot be confirmed as “targeted.”
“Doing journalism in Pakistan is not easy, which is ranked the third most dangerous country for reporting after Syria and Egypt,” observes Mazhar Abbas, former secretary general of the Pakistan Federal Union of Journalists, a formidable voice fighting for the rights of journalists. While journalists continue reporting despite threats particularly those working in the Federally Administered Tribal Area (FATA), Balochistan and even in the southern port city of Karachi, Abbas said, reporters from the Punjab province seemed comparatively safer.
But not anymore, it seems.
Abbas said every threat should be taken seriously. “The letter to Tanveer could be an individual act or from a group. The government and administration need to probe this matter and find out about the person who sent this letter in the first place. Journalists reporting on sensitive issues should do so responsibly; their reports should be factually correct with minimum expression that can lead to stoking up controversy.”
This article was originally posted on 23 Oct 2013 at indexoncensorship.org
The following speech by Sarah Brown, education campaigner for A World at School, was delivered at the launch event for the autumn issue of Index on Censorship magazine.
I am delighted to be at Lilian Baylis Technology School – I went to school in North London, but my first flat was just down the road from here – I know how hard everyone at this school has worked for it become the first in Lambeth to get an outstanding in its Ofsted and now stands out as ‘outstanding in all aspects’ in the top 10% in the country. Being named for a pioneering woman who nurtured some amazing talent in the theatre, opera and ballet worlds leaving her mark across London gives the school a lot to live up to, but clearly nurturing some amazing talent here of its own these days.
Index on Censorship’s magazine that we are launching here tonight also serves to highlight some talented voices, and some very courageous ones too. Like all of the magazine editions which came before it, it is distinguished by both the quality of its writing and the bravery of its stance. But this one is particularly important to me for the priority it has placed on the voices of women. From pioneering feminists writing about women’s safety in India to the stories of female resistance and of hope from the Arab Spring, this magazine is giving a megaphone to the people whose contribution is so often marginalised, ignored, or eliminated altogether.
In the spirit of Index on Censorship’s core values, the power of our voice is the theme of my remarks tonight. And I want to start by updating a feminist slogan that lots of women who have done pioneering work on role models have been using for years now. Their view is ‘if she can see it, she can be it’. In other words, if you have a visible role model you are much more likely to keep fighting to get past all of the hurdles that are still too often put in the way of girls and women, just as they are for people who are disabled, or LGBT or BAME, or hold a forbidden political viewpoint in the harshest of regimes around the world.
‘If you can see it, you can be it’ – I very much think that’s true – the importance of strong visible women role models. Even my own sense of what is possible for me has certainly been determined by watching women – whether my own mother learning and leading throughout her life, from running an infant’s school in the 70’s in the middle of Africa, completing her PhD a few years go in her seventies and even now I am struggling to keep up her as she launches a new project leading the research on a study of quilt-makers (mostly women) and the stories they tell. Other role models from me have ranged from the icons of my teenage years from poet and rock artist Patti Smith to writer Jill Tweedie to American feminist Gloria Steinum. Today my work leads me to meet such a range of inspirational women leaders from Graca Machel to Aung San Suu KyI to President Joyce Banda of MalawI to young women like AshwinI Angadi, born blind in a poor rural community in India she fought for her education, graduated from Bangalore university with outstanding grades, gave up her job in IT to campaign for the rights of people with disabilities, and I find myself alongside at the UN last month.
So I agree that visibility counts, but if I think of my role models they are all women who never give up raising their voices – who make a career literally of speaking up. And I want to update that old slogan with a rather more disturbing thought and suggest tonight that if you can hear her, you will fear her.
Let me explain what I mean.
From Nigeria to Egypt to Yemen and Afghanistan to the richest countries of the West, we are seeing the rise of targeted attacks focused on women who use their voice to speak out for other women. Sometimes these attacks are physical, and I will talk about them more in a moment. But here in the UK there has been a spate of attacks which are verbal and online, and which are perpetrated by men who fear women’s power.
From the disgusting rape threats directed at Caroline Criado-Perez for daring to suggest a woman should remain on British bank notes to the horrendous and sexualised verbal violence meted out to Mary Beard after she appeared on question time to model Katie Piper finding her online voice speaking up for the stigma of disfiguration in a defiant response to the acid attack on her, and the creation of her defiant new beauty at the hands of her NHS surgeon. And of course, the all too prevalent victims of domestic violence who get a collective voice through women’s aid and the main refuges around the UK – who speak up more when they see it can even happen to a goddess like Nigella.
It is clear that the public square – and too often the private home – simply doesn’t provide a safe environment for Britain’s women.
If anybody doubts how bad things have got, I’d encourage you to go and take a look at Laura Bates’ work with the Everyday Sexism Project, an online directory of harassment, discrimination and abuse submitted by over 50,000 women who are shouting back. It paints a picture of a Britain in which violence and the threat of violence against women is so routine, women had almost ceased to notice it as a crime and an outrage, until a platform came along that gave their problem visibility and, with it, importance.
So I want to suggest that a public square which is so hostile to women that they do not feel they can participate in it without inviting overwhelming abuse is, itself, a form of censorship. It might not be the same process as smashing up a newspaper office or burning a book or even shooting teenage girls on a school bus, but the effect is the same: that of silencing a voice which has a right to be heard.
And if you want further evidence of how hearing how women’s voices can terrify those who risk losing their power, just consider how the worst misogynists in the world were afraid of just three words.
The words I’m talking about weren’t said by somebody famous. They weren’t said by somebody powerful. They hadn’t even been planned before they were uttered. But they awoke the world.
Malala YousafzaI as a schoolgirl from rural Pakistan published her youthful diary detailing how life had changed for girls after the Taliban took over her mountain town. She and her friends Shazia and Kainat spent the next few years campaigning for girls to be allowed to return to school, although they knew how dangerous speaking out against the Taliban could be. Malala even talked in interviews about how they might try to kill her for it.
Just over a year ago, this worst imagining happened and Malala was targeted by a Taliban assassin. He boarded the school bus, identified Malala and shot her in the head, and injured Shazia and Kainat sitting either side of her. As the footage of Malala’s airlift to safety was broadcast young women used just three words to claim their solidarity and support with her “I am Malala’. She and her two friends are all now safely in the UK continuing their education, and as the worlds’ gaze has given them some safety the campaign continues with a growing movement of young people all of whom are role models for every child around the world, whether in school or waiting for the dream to come true and the opportunity to learn coming to them too.
It was such a powerful reminder of a question I first asked myself some time ago:
Why is the most terrifying thing for the Taliban a girl with a book? Or for that matter the terrifying group in Nigeria – Boko Haram – who are firebombing schools and dormitories while students sleep. Boko Haram – the name literally means – western education is evil.
These terrorists know, better than we do, that a girl with an education is the most formidable force for freedom in the world. A girl who can read and write and argue can be brutalised and oppressed, she can be bought and sold, discriminated against and denied her rights. But she cannot, in the end, be stopped.
Girls like Malala, Kainat, Shazia and others in the end, will prevail.
And that is why they hate them so.
And so it seems to me if a girl like Malala, on her own, can inspire so much fear, then imagine what she could do if backed by a movement of hundreds of millions. That is why I believe that the efforts to achieve global education are at the heart of how we unlock the potential of every young citizen. As children learn, they achieve understanding, tolerance, opportunity and the chance to contribute to a better world. Reaching girls is at the heart of this – we need to do so much better for girls.
Right now, there are 57 million children missing from school. That’s 57 million of our younger selves missing out on the education which could transform not just their lives, but the world. 31 million are girls, and of those at school, many many millions are not learning, and girls are just not getting the same number of school years as their own brothers – to the detriment of everyone.
New research has shown that providing universal education in developing countries could lift their economic growth rates by up to 2% a year and the results are starkest of all when it comes to educating girls.
All the evidence shows that for every extra year of education you give a girl, you raise her children’s chances of living past five years old, because educated mums are more likely to immunise their kids and get them the health care they need. Educated girls are more likely to stay AIDS-free and are less vulnerable to sexual exploitation by adults. They marry later, have fewer children and are more likely to educate their children in turn. Perhaps most importantly of all, education increases a girl’s chance of well-paid employment in later life and the evidence suggests that female earners are more likely to spend their wages to the benefit of their children and community than traditional male heads of the household.
And the benefits, of course, don’t always stay just on a local community level, but can sometimes have national and even global implications too. Because if you look at women who have been in leading positions in every continent around the world – from Sonia GandhI to Graca Machel to Dilma Rousseff to Joyce Banda, they all have one thing in common. They all have an above average level of education. And that’s why one of my new mantras is women who lead, read.
If we want better politics, a politics of pluralism and freedom of expression around the world, then it begins with empowering women – and that begins with educating them.
So there are plenty of good reasons to invest in education and learning for every child – but the best bit is that we’ve already promised to. We are not advocating for a new pledge, simply for the fulfilment of one already made. In the year 2000 world leaders committed to getting every child in school by 2015 as part of a series of ambitious targets called the millennium development goals. World leaders have already signed the contract, now they just need to deliver the goods.
So for me the argument about whether we should invest in education to get the 57 children missing from school into the classroom is a bit of a no brainer – and for me there is no question that closing the gender gap in education should be the priority. As soon as people hear the facts, they tend to stop asking whether we should do it and start to focus on whether we can.
That’s a fair question and people will always want to probe whether we can make a difference to decisions taken hundreds of thousands of miles away. It’s a question I ask myself a lot too. But I take heart from two things. Firstly, we know that progress is possible even on seemingly very big problems because we have made it before. You can look at the big changes in the last century or so – from the end of slavery, achieving the vote for women, the end of apartheid – all started as impossible calls for change, but change came. Enough voices gathered together calling for the same thing – even a politician can’t fail to hear the call then, or if minded to change anyway can do so with a strong mandate behind him or her. Even campaigns I have contributed- that we may all have contribute to – from drop the debt to make poverty history to the maternal mortality campaign brought big changes – but I have heard first-hand what happens at the start – “it is too big an ask, it can’t be done in the time, it is too costly” – well enough free voices calling for action and – give it a little bit of time and a whole lot of noise – change comes. Less than ten years ago over 500,000 women were dying in pregnancy and childbirth unwitnessed, unacknowledged unnoticed by political leaders who held the power to save these lives. Today thanks to the collective voices of those who cared enough – through the white ribbon alliance and others, that number is a whopping 47% lower, and the work to reduce it further continues at the highest levels, and out in the more remote rural areas where the message needs to be carried far and wide to reach every woman at risk.
A 47% drop in the number of mothers dying. That’s not just a number – that means there are thousands of dads living with the love of their lives when they would otherwise have a broken heart nobody else could possibly mend. Thousands of big brothers and sisters who didn’t need to fear that in gaining a new member of the family they risked losing an old one. And thousands of babies being nursed to sleep tonight by the person who loves them most in the world and who has survived to love them as they grow. So this stuff works: campaigning is the key for all of us lucky enough to use our voices.
And on education, I am hopeful we can get even further than we have with the maternal mortality campaign, and achieve all of our goals by 2015. I know that sounds incredibly ambitious – because it means getting 57 million children into school in less than two years. Gordon and I have decided to devote the next years of our lives to this and we intend to be judged by our results. Increasing awareness is great – but if the numbers of children getting a high quality education does not increase in leaps and bounds in the years to come then we collectively will have failed.
Thankfully, we have a lot of help. When Gordon was appointed the United Nations’ Secretary General’s Special Envoy on education, the weight of the UN system was added to our cause. Business leaders have come on board to the Global Business Coalition for Education that I am fortunate to chair, and I am pleased that religious leaders have agreed to form a faith coalition to mobilise the faith communities as has happened so powerfully for debt relief and make poverty history in the past. Most significantly, younger people are lining up at as ambassadors, spokespersons, online champions and community mobilisers – the 600 strong youth leaders from the digital platform A World at School who assembled at the un on Malala Day in July, are all now engaging with their networks, supported by NGOs from around the world. The digital platform is growing rapidly, and the consistent messages, the constant call for action and the rising volume are starting to make a difference. From Syrian refugee children needing a place at school this autumn to young girls wanting to study before they marry in Yemen, Nigeria, Bangladesh to child workers who have never been inside a classroom, the momentum for them is growing.
This grand confluence of forces is powered by the single most important driver of change – every individual who cares enough to take up an action – whether just a tweet or post, or more. It includes you.
Because if we can’t mobilise millions of so-called ordinary people to do hundreds of extraordinary things, the governments of the world will conclude that the pledge they made to get every child into school can be allowed to quietly slip away, the pledge for gender equality ignored, the pledge that every child can be safe from violence, from trafficking and from finding their own voice just disappears. That would be a tragedy not just for the millions of children whose lives continue to be destroyed, but for the notion of progress itself.
If we can’t even rely on our leaders to do that which they have promised to do, can we rely on them to do all that we need them to do? I don’t want my children to grow up in a generation of cynics, a whole group of people who think that promises don’t get kept and politics doesn’t really work. I want them to see and to know that if we make a promise – particularly a promise to a child – we keep it. That when we see an injustice, we right it. That when we are presented with an opportunity we seize it. And that when we have the chance to change the world there is nothing we won’t do to see that potential fulfilled.
That, for me, is the ambitious spirit of activism which Index on Censorship embodies, and the one which we must now bring to bear in ensuring that the girls and women of the world learn first how to read, and then how to lead. This is the chance of our generation and I hope you, like me, think it is one we must grasp with both hands.
This speech transcript was originally posted on 18 Oct, 2013 at indexoncensorship.org

The government of Sudan cut the country off from the internet as protests against the end of fuel subsidies spread.
The release of the annual Freedom on the Net report for the first time includes a chapter on Sudan, authored by Index Award nominees GIRIFNA. This is more than timely, as the country is witnessing a new wave of widespread protests triggered by the Sudanese government’s announcement in late September 2013 that it will lift economic subsidies from fuel and other essential food items.
Based on a survey of 60 countries in Freedom House’s Freedom on the Net 2013, Sudan is categorised as “Not Free” with a score of 63, placing it among the bottom 14 countries in the category. As one of ten sub-Saharan African countries surveyed, Sudan joined Ethiopia as the two “Not Free” countries in the region. Kenya and South Africa were categorised as “Free” and the remaining six – Angola, Malawi, Nigeria, Rwanda, Uganda and Zimbabwe – as “Partly Free”.
Sudan has invested heavily in its telecommunications infrastructure in the last decade, resulting in a steadily increasing internet penetration rate of 21 percent and a mobile penetration rate of 60 percent by the end of 2012, according to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). It also boasts the cheapest post-paid costs in the Middle East and North Africa in 2012, and healthy market competition amongst four telecommunications providers.
However, these infrastructural and economical advantages are highly reduced against the backdrop of a State that has little respect for freedom of expression, freedom of association, participation and peaceful assembly. The Sudanese regime is amongst the worst globally in terms its obstruction of the access to independent and diverse information both offline and online. A global study on press freedom conducted by Reporters without Borders earlier this year ranks Sudan at 170 out of 179 countries surveyed. This clearly reflects that the violations of freedom of expression impacting the traditional print media are also starting to reflect online.
The Sudan Revolts, the wave of protests triggered by economic austerity plans that hit the country between June and July 2012, was the first time the authorities implemented a large-scale crackdown and detentions of citizens using digital platforms to communicate, connect, coordinate and mobilise. Additionally, the government increased its deployment of a Cyber Jihadist Unit to monitor and hack into Facebook and email accounts of activists. The National Telecommunications Corporation (a government agency) also engages in the censoring and blocking of opposition online news forums and outlets. YouTube, for example, was blocked for two months in late 2012 in response to the “Innocence of Muslims” video.
The attacks on cyber dissidents during Sudan Revolts included the detention of digital activists, such as Usamah Mohammed, for up to two months, the forced exile of Sudan’s most prominent video blogger Nagla’a Sid Ahmad, and the kidnapping and torture of the Darfurian online journalist Somia Hundosa. Moreover, one of the most high profile political detainees from the Nuba Mountains, Jalila Khamis, spent nine months in detention without charges. When she was finally brought to trial in December 2012, the main evidence against her was a YouTube video taken by Sid Ahmad, in which Khamis testified about the shelling of civilians in the Nuba Mountains by the government.
Since September 23 this year, authorities have responded to the new wave of protests with unprecedented violence toward peacefully protesting urban dwellers. More than 200 have been killed in Khartoum and Wad Madani by live bullets fired by riot police, national security agents, and/or state sponsored militias. According to a government statement, 600 citizens have been detained, though activists say that number is much higher. On Wednesday, September 25, the government shut down internet access for 24 hours. When the internet returned, it was much slower, with Facebook inaccessible on mobile phones and YouTube blocked or non-functional due to a very slow broadband connection.
The US sanctions imposed on Omer El Bashir’s regime since 1997 also continue to hinder the free access to the internet and the free flow of information as it limits access to a number of new media tools. This includes limited access to anti virus suites, e-document readers, and rich content multimedia applications that most Sudanese citizens cannot download. The inability to download software security updates makes many users in Sudan vulnerable to malware. Smart phone applications cannot be downloaded or purchased from the iTunes and/or Android stores.
Additionally, Sudan has a combination of restrictive laws that work together to impede freedom of expression both off and online, including the 2009 Printed Press Materials Law, and a new Media law that has recently appeared in Parliament, which officials have hinted would for the first include language restricting online content. Additionally, the National Security Act (2010) gives National Intelligence and Security Services the permission to arrest journalists and censor newspapers under the pretext of “national security,”. An IT Crime Law, in effect since 2007 criminalises websites that criticise the government or publishes defamatory materials. All these laws contradict Sudan’s National Interim Constitution, which guarantees the right to freedom of expression, association and assembly.
GLOBAL
Stockholm Internet Forum: Balancing rights and security
Does surveillance and monitoring chill free expression? Is population-wide mass surveillance always a bad idea? Amongst many questions and debates at today’s Stockholm Internet Forum, the answers to these two questions are surely obvious – yes to both, writes Index on Censorship CEO Kirsty Hughes from Sweden. (Index on Censorship)
Religion, freedom and social peace
I RECENTLY watched an impassioned 18-minute film on the subject of religion and freedom, made as a kind of personal statement by Jacob Mchangama, a Danish human-rights lawyer. (The Economist)
How to Fix the EU’s ‘Right to Be Forgotten’
It has been more than a year since the European Union Data Protection Regulation (DPR) was unveiled, including a controversial proposal known as the “Right to Be Forgotten” (RTBF). While the proposal is intended to give Internet users more control over their data, many critics, including CDT, have charged that the new right would pose significant unintended risks for free expression online. As the European Parliament considers amendments to the Data Protection Regulation, ensuring that good intentions do not undermine the free expression rights of EU Internet users must be a top priority. (Huffington Post)
BURMA
Myanmar’s media faces fresh challenges
It is a new dawn for media in Myanmar—censorship has been lifted; 10 daily newspapers are now being printed, with another 14 on the way; and, reporters are free to write what they please. But the rush to this liberalized market has brought with it a fresh batch of problems for journalists, editors and media company owners. (Burma News International)
ISRAEL
Al Jazeera reposts ‘anti-Jewish’ article after censorship backlash
Al Jazeera has republished a controversial article on its website after inexplicably removing it amid claims the story was “anti-Jewish”. (Al Arabyia)
JAPAN
Japanese Chat App LINE Kowtows To Chinese Censorship
Japan’s chat app LINE which is reportedly challenging Facebook in terms of the number of users, is now set to bow down to the Chinese government by building a mechanism to censor contends of its users in China. (International Digital Times)
MALAYSIA
Adam to face sedition charge tomorrow
The student activist was arrested on May 18 for remarks he allegedly made during a post-GE13 forum on May 13. (Free Malaysia Today)
NIGERIA
Court awards N750m against The Nation, Ogele over libel
AN Ado-Ekiti High Court has awarded the sum of N750 million damages against The Nation Newspapers and a human rights activist, Mr. Morakinyo Ogele, for libel and defamation of character of the Mr. Segun Ilori, former Chief of Staff to Ekiti State Governor, Segun Oni. (The Guardian Nigeria)
SOUTH AFRICA
South Africa’s secrecy bill signals growing political intolerance
The so-called secrecy bill’s passage through the South African parliament mirrors an increasing political intolerance towards diverse views that in some cases has spilled over in violence, Christi van der Westhuizen reports. (Index on Censorship)
Controversial Youth Website Dodges Censorship
“Outoilet” is an Afrikaans word meaning “old toilet”, but it also refers to a cellphone chat site, aimed mainly at Cape Flats youth. Its URLs are blocked by several service providers, but the site frequently re-emerges with different URLs. (AllAfrica.com)
SYRIA
Today is Bassel’s second birthday in prison
Software engineer and open-source advocate Bassel Khartabil will spend his second birthday in prison today. Palestinian-born Bassel was arrested on 15 March last year by Syrian security forces, and has been in prison ever since. On his birthday and the 799th day of Syria’s conflict, Index calls on the Syrian government to release Khartabil. (Index on Censorship)
UNITED STATES
Obama’s War on Free Expression
It’s the most fundamental right. Without it all others are endangered. Obama’s waging war to destroy it. He’s done so throughout his tenure. (The People’s Voice.org)
Convicted drug trafficker sues local newspaper for libel
A newspaper, which published a story about a man who pled guilty to a federal drug case, is being sued in federal court. (KGBT)
Notice of appeal filed in Campfield libel lawsuit
A former Democratic candidate for the state House has filed notice that he will appeal the dismissal of his libel lawsuit against state Sen. Stacey Campfield. (SeattlePI)
Why Facebook ‘likes’ won’t be a ‘vital’ part of free speech any time soon
Facebook recently argued in court that the “Like” feature is an integral part of free speech. A lawyer for the company argued that “Likes” are “vital” to the 500m people who use Facebook every day and that they should be protected by the US Constitution. (memeburn)
Ordinance Targeting Free Speech in Residential Zones Results in Arrests of Peaceful Christians
A Florida ordinance that was passed with the intention of hindering pro-life Christians from picketing the homes of abortionists has resulted in the arrests of three Christians. (Christian News)
ZIMBABWE
Playwright Seeks Legal Intervention Over Banning of Peace Play
An award winning playwright in Zimbabwe is seeking legal intervention after his play, whose central theme is peace, was banned last year. (AllAfrica.com)