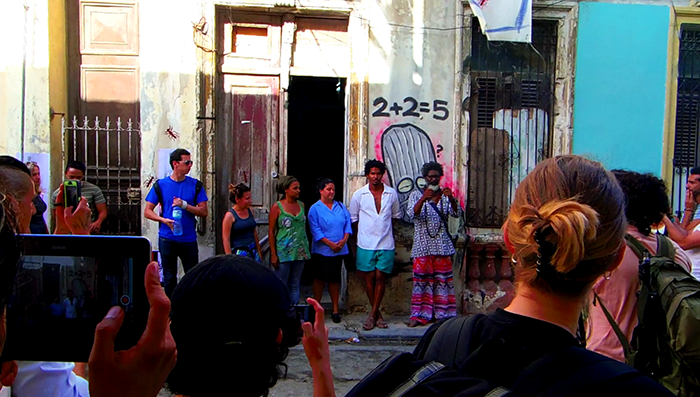8 Jun 2018 | Americas, Artistic Freedom, Awards, Cuba, Fellowship, Fellowship 2018, News and features
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
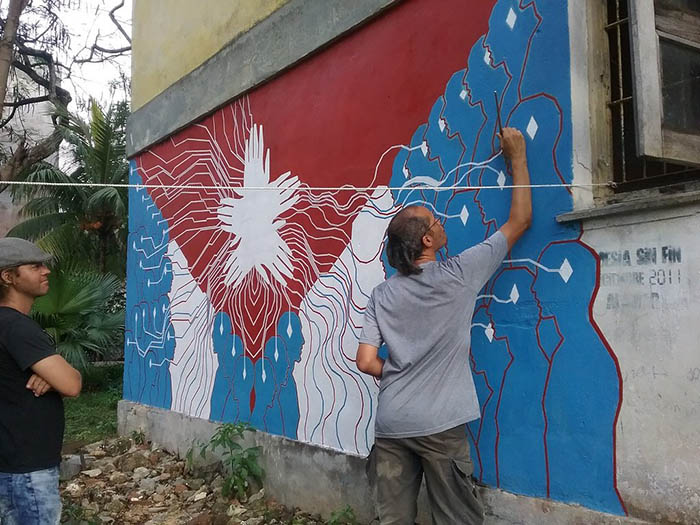

Cuban artist Yasser Castellanos
Despite official efforts to stop it in its tracks, Cuba saw the successful completion of its first independent art biennial, organised without the support of the state, on 15 May. Artist Luis Manuel Otero Alcantara and curator Yanelys Nuñez Leyva, members of the Museum of Dissidence, winner of the 2018 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Award for art, organised the ten-day #00Bienal de la Habana, which included over 170 artists, writers, musicians and theorists across nine different exhibitions in artists’ homes and studios around the country’s capital.
“Cuban culture is centralised culture and the government has absolute control,” Nuñez Leyva tells Index on Censorship. “The Ministry of Culture, together with all its branches such as the Union of Writers and Artists of Cuba and the National Council of Plastic Arts, are tentacles of the Ministry of the Interior, so all independent proposals, whether cultural, ecological or campaigns against gender violence, for example, are cursed with all the might of the government-controlled media.”
Even at schools pupils are served up propaganda intent on turning them against non-state-approved artists. Some art school students were shown a video portraying Otero Alcantara as a mercenary. “Such a campaign inevitably generates fear around independent projects which then suffer due to lack of both social and economic support,” Nuñez Leyva says.
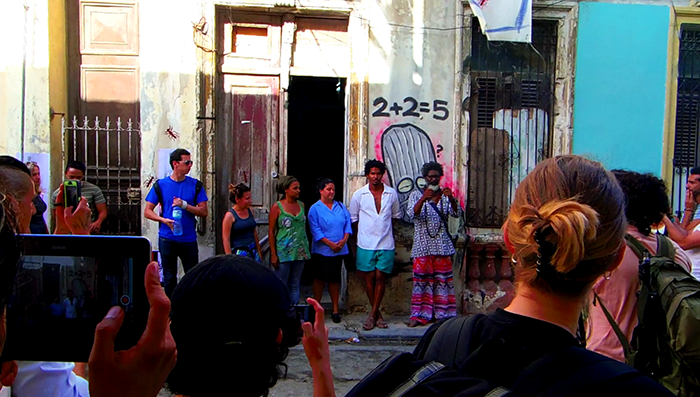
Economic support was one of the biggest obstacles for #00Bienal. “At the beginning, we thought that we would produce it with what we had at hand, but along the way we realised that we needed more,” Nuñez Leyva says. So a Gofundme campaign was set up, which raised $6,574. “But this wasn’t easy: the impact of the US blockade, our isolation from the world of networks and the impossibility of having credit cards made the process anguishing.”
Otero Alcantara was also imprisoned without cause on several occasions as part of the Cuban government’s campaign of harassment. Others who took part in #00Bienal, whether Cuban or foreign, received similar harassment. Many were even denied entry to the country, including the Cuban-American artist Coco Fusco.
When #00Biennial was announced in September 2017, the Cuban government immediately began to show its discontent through its cultural institutions. In an official declaration they branded the organisers as “unscrupulous people”. In response, #00Bienal’s first slogan was: “From the official to the unscrupulous.”
As culture is so tightly controlled in Cuba, only artists seen to be working in the interests of the regime can operate without restriction. Approved artists usually receive perks, something that gives them a higher status in society. Some artists risked all of this by taking part in #00Bienal. “The system used the worst blackmail against them because they gave the event a legitimacy that the government did not want,” Otero Alcantara says. “These artists were threatened by having their government accreditation taken away. Without this, they would find themselves without ‘official work’.”

Government agents stalked the exhibitions while the organisers were accused of being in league with Cuba’s enemies. How does one respond to such accusations? “We responded by making an event that is as honest as possible, with a wide range of manifestations and artistic expressions that reflected the reality of Cuban art,” Nuñez Leyva says. “We responded with a list of more than 170 participants, not only Cubans, but from Mexico, Spain, Germany, the United States, Romania, Angola, Colombia, Denmark, Ukraine, Brazil, Venezuela, among them high-profile artists that Cuban institutions admire and collaborated with.”
The authorities even tried to prohibit the public from attending, sometimes successfully. Flyers and stickers were also confiscated. “But none of these actions were ever going to stop the energy of the event,” Otero Alcantara says.
“Despite all this pressure, the event went ahead, demonstrating that there is a group of people who are very courageous and have a real commitment culture,” Nuñez Leyva says. #00Bienal helped revive “a spirit of alternative rebellion” through the involvement of “countless numbers of totally unknown artists” that the state would never endorse.
For Otero Alcantara, the event’s success lies in the cohesion it created between artists, scholars and art enthusiasts, something that is unprecedented in the world of Cuban art. “We built an inclusive space of free creation and true collaboration between the people involved, exhibited the work of artists who were never going to have space in an official Havana Biennial and set a precedent for future projects,” he says. “This is one more step towards eliminating a fear that exists throughout Cuba.”

According to the organisers, the terms “revolution” or “revolutionary” have been hijacked and distorted by the Cuban regime. Such deformation has taken root so deep in the imagination of the Cuban people that just by mentioning the word “dissidence” is enough to be shunned, they explain.
“The #00Bienal was a humanistic project that brought to the fore essential values for any society such as unity, solidarity and collaboration,” Nuñez Leyva says. “The event also favoured the less privileged and created beauty and dialogue in favour of a new Cuba.”
The organisers of #00Bienal are under no illusions that life for Cuba’a dissident artists will magically become any easier under Cuba’s new president, Miguel Díaz‑Canel, who took over from Raúl Castro in April 2018. “The Cuban regime is more than any Castro,” Nuñez Leyva says. “It is a system based on a group of families that live both inside and outside the island, who have control over everything, which ultimately contributes to their own wealth.” This corrupt system relies on the deception of a people who have been left without even the strength even to protect themselves against poverty, she adds. “This situation leaves us with little hope, but we have to keep working.”
Otero Alcantara and Nuñez Leyva’s now want to show that #00Bienal wasn’t just a one-off, but is a serious project with longevity. “We will see if it is possible in two years to achieve something similar,” Otero Alcantara says.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_media_grid grid_id=”vc_gid:1528443291288-dfd45bff-0a16-7″ include=”100716,100712,100711,100710,100713,100709,100708,100707,100706,100704,100715,100705″][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Artists, writers, musicians and theorists who took part in #00Bienal
Amaury Pacheco (Cuba), Iris Ruiz (Cuba), Coco Fusco (Cuba-USA), Tania Bruguera (Cuba), Reynier Leyva Novo (Cuba), Ernesto Oroza (Cuba), Gerardo Mosquera (Cuba), Katherine Bisquet (Cuba), Jose Ernesto Alonso, Yuri Obregón (Cuba), Alein Somonte (Cuba), Alejandro Barreras (Cuba), Anaeli Ibarra (Cuba), Alejandro Taquechel (Cuba), Ariel Maceo Tellez (Cuba), Aryam (Cuba), Aldeide Delgado (Cuba), Armando Cuspinera (Mexico), Antonio Mas (Spain), Alicia Torres (Spain), Ana Olema (Cuba), Alexis Ruiseco (Cuba-USA), Alexandru Raevschi (Germany), Andrés X (Cuba), Alain Aspiolea (Cuba), Alexandre Arrechea (Cuba), Antoni Muntadas (Spain), Biennial Project (USA), Boris González Arenas (Cuba), Colectivo Corason i uevo (Antonio A. Orta, Maykel Almenteros y Pedro Pablo Bacallao) (Cuba), Colectivo Guerrillas Girls, Celia y Yunior (Cuba), Colectivo 2.50 (Ana Gómez, Argelia Leodegarío, Marco Antonio Rodríguez, Itandehuitl Orta, Yuvia Pérez, Esmeralda Pérez) (Mexico), Carlos Manuel Álvarez (Cuba), Clara Astiasarán, Chu (Cuba), David de Omni, David León (Cuba), Danilo Maldonado (El Sexto), Diego Gil (Spain), Eliecer Jiménez Almeida (Cuba), Erish (Mexico), El Oficio (Cuba), Ernesto Hernandez Busto, Enfori García, Filipa César (Portugal), Fabián (2+2 =5) (Cuba), Francis Sánchez (Cuba), Francisco Méndez (Mexico), Francisco Masó (Cuba), Fabian Martínez, Filio Gálvez, Fredric Snitzer, Gabriel Coto (Cuba), Gerardo Stübing (España), Gean Moreno, Henri Eric Hernández (Cuba), Hamlet Lavastida (Cuba), Héctor Trujillo (Cuba), Hugo Patao, Italo Expósito (Cuba), Iván de la Nuez (Cuba), Jesús Hdez-Güero (Cuba), Jesús Benítez (Mexico), José Luis Marrero (Cuba), Josvan Gonzalez Agramonte (Cuba), Julián Yunda Yepes (Mexico), Jenifer Acuña (Cuba), Juan Melo (Colombia), Juan Carlos Alvarez Miranda (Cuba), Jean-Lorin Sterian (Romania), José Bedia (Cuba), Julio César Llopiz (Cuba), Javier Marimón, José Manuel Mesías (Cuba), Keyezua (Angola), Kevin Arrow, Lía Villares (Cuba), Luis Trápaga (Cuba), Luiso, Leandro Villanueva (Sam 33) (Cuba), Lester Dubé (Cuba), Lala Misosniky (Romania), La Alianza (Cuba), Liliam Dooley, Leandro Feal (Cuba), Lourdes Porrata, Miquel García (Spain), Marisol Maza (Mexico), Marcel Marquez (Cuba), Marianna Liosi (Germany), MO colectivo (Mariam Abrajim y Octavio Salazar) (Colombia), Magdiel Aspillaga, Mysora García, Nonardo Perea (Cuba), Natalia López (Colombia), Osmel Almaguer Delgado (Cuba), Osmany Carratalá (Cuba), Oscar Salamanca (Colombia), Orlando Hernández (Cuba), Pablo Pinto (Colombia), Polyanna Morgana (Brazil), Political Architecture: Critical Sustainability (PA:CS) (Denmark), Peter Menéndez, Rafael Carabano (Venezuela), Raúl Meriño (Cuba), Ras Yoe, Ricardo Figueredo, Rodolfo Peraza (Cuba), Rafael Domenech, Rirkrit Tiravanija, Svitlana Biedarieva (Ukraine), Soandry del Río (Cuba), Sandra Ceballos (Cuba), Santiago Alvarez Méndez (Colombia), Sandor (Cuba), Thiago Morandi (Brazil), Tomás Sánchez (Cuba), Tomas Vu, Tonel (Cuba), unx Pardo Ibarra (Colombia), Ulises Valdés (Mexico), Walfrido Valera (Cuba), Yaima Pardo (Cuba), Yasser Castellanos (Cuba), Yesica Suárez (Colombia), Yulier P. (Cuba), Yoenis Eloy Mayeta (Cuba), Yimi Konclase (Cuba), Yvelin Buenrostro (Mexico), Yucef Merhi (Venezuela), Yornel Martínez (Cuba), Yali Romagoza (Cuba), Yanier H. Palao (Cuba).[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1528443291296-0ad2c295-a239-7″ taxonomies=”104″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
8 Jan 2018 | Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Honduras, Mexico, News and features, Venezuela
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
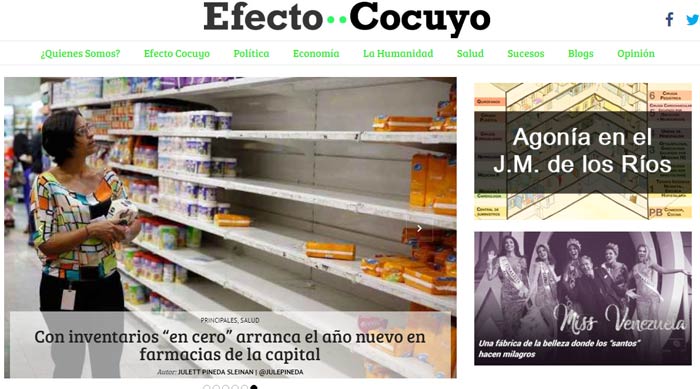
Latin America is home to a growing number of independent publications, like Venezuela’s Efecto Cocuyo, that do not depend on government advertising
With general elections scheduled in six Latin American countries this year, and another six to follow in 2019, the relationship between the media and democracy could have a major impact on the future of the region. However, mounting financial pressures are robbing many media outlets of their objectivity and forcing them to toe pro-government lines.
With traditional advertising revenue in decline, Latin American governments are using vast publicity budgets to keep cash-strapped publications afloat. In return, the media are expected to portray their benefactors in a favourable light.
According to the NGO Freedom House, much of the media in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Honduras and Mexico is heavily dependent on government advertising, resulting in widespread self-censorship and collusion between public officials, media owners and journalists.
“The history of journalism in Latin America is a history of collusion between the press and powerful people,” said Rosental Alves, a Brazilian journalist and founder of the Knight Center for Journalism in the Americas, in an interview with Index. Sections of the media have become subservient, he explained, as any critical coverage could be punished with audits or a loss of advertising revenue.
Financial pressures on the media are particularly pronounced in Venezuela. Alves observed that the Nicolás Maduro regime has applied “waves of censorship” to the media by first decrying it as “the enemy of the people” and then buying up media companies to “make them friendly.”
Freedom House notes that “although privately owned newspapers and broadcasters operate alongside state outlets, the overall balance has shifted considerably toward government-aligned voices in recent years. The government officially controls 13 television networks, dozens of radio outlets, a news agency, eight newspapers, and a magazine.”
This is compounded by Venezuela’s severe economic problems and the virtual government monopoly on newsprint supplies that have led to newspaper closures, staff cutbacks and reduced circulation of critical media.
Mexico’s government has taken the more subtle approach of co-opting swathes of the media through unprecedented expenditure on advertising. According to the transparency group Fundar, President Enrique Peña Nieto has spent almost £1.5 billion on advertising in the past five years, more than any president in Mexican history. On top of that, state and municipal administrations have also spent millions on publicity in local media.
Darwin Franco, a freelance journalist in Guadalajara, told Index that government spending has led to some publications telling reporters “who they can and cannot criticise in their work.”
Then there is the infamous chayote, a local term for bribes paid to journalists in return for favourable coverage. Franco said Mexican reporters are particularly vulnerable to economic pressures or under-the-table incentives because it’s so hard for them to make a living.
“Freelance journalists in Mexico don’t receive the benefits that employees are legally entitled to,” he said. “National media outlets — and even some international ones — pay us minimal fees for stories, which in some cases don’t even cover the costs of reporting.”
Franco, who also teaches journalism at a local university, added that many reporters take on second jobs to supplement their income. With Mexican journalists making less than £450 per month on average, he acknowledged that “there may be people who are tempted” to take money from the government.
Despite these financial pressures, Alves is encouraged by the technology-driven democratisation of the media across Latin America, with increased internet penetration and the affordability of smartphones allowing people who could not afford computers to access nontraditional media for the first time.
These include rudimentary blogs, social media accounts and more sophisticated media startups, Alves said, with countries like Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Mexico and even Venezuela home to a growing number of independent publications that do not depend on government advertising.
“We are living a time of the decline of advertisements as the main source of revenue for news organisations. On the one hand you have this huge decline in traditional advertising because of Google and Facebook getting all this money, and on the other hand you see the virtual disappearance of the entry barriers for becoming a media outlet,” Alves noted.
“We’re moving from the mass media to a mass of media because there’s this proliferation of media outlets that don’t depend on a lot of money,” he added. “If you can gather some philanthropic support or membership, or you’re just doing it by yourself, like many courageous bloggers are doing in many parts of the region, you don’t make any money but you don’t spend any money either.”[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Survey: How free is our press?” use_theme_fonts=”yes” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2F2017%2F12%2Fsurvey-free-press%2F|title:Take%20our%20survey||”][vc_separator color=”black”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/4″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-pencil-square-o” color=”black” background_style=”rounded” size=”xl” align=”right”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”3/4″][vc_column_text]
This survey aims to take a snapshot of how financial pressures are affecting news reporting. The openMedia project will use this information to analyse how money shapes what gets reported – and what doesn’t – and to advocate for better protections and freedoms for journalists who have important stories to tell.
More information[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator color=”black”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”97191″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2018/01/tracey-bagshaw-compromise-compromising-news/”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Commercial interference pressures on the UK’s regional papers are growing. Some worry that jeopardises their independence.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator color=”black”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”81193″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2017/12/jean-paul-marthoz-commercial-interference-european-media/”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Commercial pressures on the media? Anti-establishment critics have a ready-made answer: of course, journalists are hostage to the whims of corporate owners, advertisers and sponsors. Of course, they cannot independently cover issues which these powers consider “inconvenient”.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator color=”black”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”96949″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.opendemocracy.net/openmedia/mary-fitzgerald/welcome-to-openmedia”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Forget fake news. Money can distort media far more disturbingly – through advertorials, and through buying silence. Here’s what we’re going to do about it.
This article is also available in Dutch | French | German | Hungarian | Italian |
Serbian | Spanish| Russian[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator color=”black”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Don’t lose your voice. Stay informed.” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][vc_separator color=”black”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship is a nonprofit that campaigns for and defends free expression worldwide. We publish work by censored writers and artists, promote debate, and monitor threats to free speech. We believe that everyone should be free to express themselves without fear of harm or persecution – no matter what their views.
Join our mailing list (or follow us on Twitter or Facebook) and we’ll send you our weekly newsletter about our activities defending free speech. We won’t share your personal information with anyone outside Index.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][gravityform id=”20″ title=”false” description=”false” ajax=”false”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator color=”black”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1515148254502-253f3767-99a5-8″ taxonomies=”8996″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
11 Dec 2017 | News and features, Volume 46.04 Winter 2017
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Fifty years after 1968, the year of protests, increasing attacks on the right to assembly must be addressed says Rachael Jolley”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Close to where I live is a school named after an important protester of his age, John Ball. Ball was the co-leader of the 14th century Peasants’ Revolt, which looked for better conditions for the English poor and took to the streets to make that point. Masses walked from Kent to the edges of London, where Ball preached to the crowds. He argued against the poor being told where they could and couldn’t live, against being told what jobs they were allowed to pursue, and what they were allowed to wear. His basic demands were more equality, and more opportunity, a fairly modern message.
For challenging the status quo, Ball was put on trial and then put to death.
These protesters saw the right to assembly as a method for those who were not in power to speak out against the conditions in which they were expected to live and taxes they were expected to pay. In most countries today protest is still just that; a method of calling for change that people hope and believe will make life better.
However, in the 21st century the UK authorities, thankfully, do not believe protesters should be put to death for asserting their right to debate something in public, to call for laws to be modified or overturned, or for ridiculing a government decision.
Sadly though this basic right, the right to protest, is under threat in democracies, as well as, less surprisingly, in authoritarian states.
Fifty years after 1968, a year of significant protests around the world, is a good moment to take stock of the ways the right to assembly is being eroded and why it is worth fighting for.
In those 50 years have we become lazier about speaking out about our rights or dissatisfactions? Do we just expect the state to protect our individual liberties? Or do we just feel this basic democratic right is not important?
Most of the big leaps forward in societies have not happened without a struggle. The fall of dictatorships in Latin America, the end of apartheid, the right of women to vote, and more recently gay marriage, have partly come about because the public placed pressure on their governments by publicly showing dissatisfaction about the status quo. In other words, public protests were part of the story of major social change, and in doing so challenged those in power to listen.
Rigid and deferential societies, such as China, do not take kindly to people gathering in the street and telling the grand leaders that they are wrong. And with China racheting up its censorship and control, it’s no wonder that protesters risk punishment for public protest.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/4″][vc_icon icon_fontawesome=”fa fa-quote-left” color=”custom” align=”right” custom_color=”#dd3333″][/vc_column][vc_column width=”3/4″][vc_custom_heading text=”Protecting protest is vital, even if it doesn’t feel important today. ” google_fonts=”font_family:Libre%20Baskerville%3Aregular%2Citalic%2C700|font_style:400%20italic%3A400%3Aitalic”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
But it is not just China where the right to protest is not being protected. Our special report on the UK discovers that public squares in Bristol and other major cities are being handed over to private companies to manage for hundreds of years, giving away basic democratic rights like freedom of speech and assembly without so much as a backwards glance.
Leading legal academics revealed to Index that it was impossible to track this shift of public spaces into private hands in detail, as it was not being mapped as it would in other Western countries. As councils shrug off their responsibilities for historic city squares that have been at the centre of shaping those cities, they are also lightly handing over their responsibilities for public democracy, for the right to assembly and for local powers to be challenged.
The Bristol Alliance, which already controls one central shopping district with a 250-year lease, is now seeking to take over two central thoroughfares as part of a 100,000-square-metre deal (see page 15). And the people who are deciding to hand them over are elected representatives.
In the USA, where a similar shift has happened with private companies taking over the management of town squares, the right to protest and to free speech has, in many cases, been protected as part of the deal. But in the UK those hard-fought-for rights are being thrown away.
Another significant anniversary in 2018 is the centenary of the right to vote for British women over 30. That right came after decades of protests. Those suffragettes, if they were alive today, would not look kindly on English city councils who are giving away the rights of their ancestors to assemble and argue in public arenas.
For a swift lesson in why defending the right to assembly is vital, look to Duncan Tucker’s report on how protesters in Mexico, Argentina, Venezuela and Brazil are facing increasing threats, tear gas and prison, just for publicly criticising those governments.
In Venezuela, where there are increasing food and medicine shortages, as well as escalating inflation, legislation is being introduced to criminalise protest.
As Tucker details on page 27 and 28, Mexican authorities have passed or submitted at least 17 local and federal initiatives to regulate demonstrations in the past three years.
Those in power across these countries are using these new laws to target minorities and those with the least power, as is typically the case throughout history. When the mainstream middle class take part in protest, the police often respond less dramatically. The lesson here is that throughout the centuries freedom of expression and freedom of assembly have been used to challenge deference and the elite, and are vital tools in our defences against corruption and authoritarianism. Protecting protest is vital, even if it doesn’t feel important today. Tomorrow when it is gone, it could well be too late.
But it is not all bad news. We are also seeing the rise of extreme creativity in bringing protests to a whole new audience in 2017. From photos of cow masks in India to satirical election posters from the Two-Tailed Dog Party in Hungary, new techniques have the power to use dangerous levels of humour and political satire to hit the pressure points of politicians. These clever and powerful techniques have shown protest is not a dying art, but it can come back and bite the powers that be on the bum in an expected fashion. And that’s to be celebrated in 2018, a year which remembers all things protest.
Finally, don’t miss our amazing exclusive this issue, a brand new short story by the award-winning writer Ariel Dorfman, who imagines a meeting between Shakespeare and Cervantes, two of his heroes.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Rachael Jolley is the editor of Index on Censorship magazine.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”From the Archives”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”91582″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03064228808534472″][vc_custom_heading text=”Uruguay 1968-88″ font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1080%2F03064228808534472|||”][vc_column_text]June 1988
In 1968 she was a student and a political activist; in 1972 she was arrested, tortured and held for four years; then began the years of exile.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”94296″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/03064228108533158″][vc_custom_heading text=”The girl athlete” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1080%2F03064228108533158|||”][vc_column_text]February 1981
Unable to publish his work in Prague since the cultural freeze following the Soviet invasion in 1968, Ivan Klíma, has his short story published by Index. [/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”91220″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422017716062″][vc_custom_heading text=”Cement protesters” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422017716062|||”][vc_column_text]June 2017
Protesters casting their feet in concrete are grabbing attention in Indonesia and inspiring other communities to challenge the government using new tactics.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row content_placement=”top”][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”What price protest?” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2F2017%2F12%2Fwhat-price-protest%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In homage to the 50th anniversary of 1968, the year the world took to the streets, the winter 2017 issue of Index on Censorship magazine looks at all aspects related to protest.
With: Micah White, Ariel Dorfman, Robert McCrum[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”96747″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2017/12/what-price-protest/”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″ css=”.vc_custom_1481888488328{padding-bottom: 50px !important;}”][vc_custom_heading text=”Subscribe” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fsubscribe%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In print, online. In your mailbox, on your iPad.
Subscription options from £18 or just £1.49 in the App Store for a digital issue.
Every subscriber helps support Index on Censorship’s projects around the world.
 SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]

![]() SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]