2 Sep 2016 | Bahrain, Bahrain Letters, Campaigns, Campaigns -- Featured, mobile, Statements, United Kingdom, United States
HM Shaikh Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa
Office of HM the King
P.O. Box 555, Rifa’a Palace
Kingdom of Bahrain
Cc. The Rt Hon Boris Johnson MP
Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs
Foreign & Commonwealth Office
King Charles Street, London SW1A2AH
Cc. The Honorable John F. Kerry
Secretary of State
United States Department of State
2201 C Street NW, Washington, DC 20520
Cc. Federica Mogherini
High Representative of the European Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy
Cc. Zeid Ra’ad Al Hussein
United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights
2 September 2016
Urgent Appeal for the Release of Human Rights Defender Nabeel Rajab
Your Excellency,
In light of recent alarming events in Bahrain, the undersigned NGOs express our deepest concerns about the ongoing detention of prominent human rights defender Nabeel Rajab based on his peaceful exercise of the right to freedom of expression. We urge the government of Bahrain to immediately and unconditionally release Rajab.
On 13 June 2016, the authorities arrested Rajab, who serves as President of the Bahrain Center for Human Rights (BCHR), Founding Director of the regional Gulf Center for Human Rights (GCHR), Deputy Secretary-General of FIDH, and a member of the Advisory Committee of Human Rights Watch’s Middle East Division. Rajab’s arrest is one in a series of repressive actions to severely restrict the work of human rights defenders and civil society members in the Kingdom of Bahrain.
In the wake of an unprecedented crackdown, we believe the detention of Rajab to be an act of reprisal for his work to promote fundamental human rights in Bahrain, as well as a means to restrict Rajab’s freedom of expression and speech. He is charged for tweets and re-tweets about allegations of torture in Bahrain’s Jau Prison, which were investigated by many local and international NGOs, and about the widely reported and criticised human rights violations during the war in Yemen. In total, Rajab could serve up to 15 years in prison for his statements via Twitter.
Rajab faces up to 10 years in prison if convicted of spreading “false or malicious news, statements, or rumours” under article 133 of Bahrain’s penal code; a further two years imprisonment if convicted under article 215 of the penal code for “offending a foreign country [Saudi Arabia]” for tweets related to the Saudi-led war in Yemen and an additional three-year sentence if convicted of “offending a statutory body” under article 216 of the penal code for comments relating to Jau prison in Bahrain.
In addition to these charges, he may also face a trial on charges of “spreading false news” for similar statements made during televised interviews last year. That case has not yet been referred to court, but is believed to have served, among others, for his arrest on 13 June.
Due to the poor detention conditions, Rajab’s health has been severely deteriorating since the time of his arrest. He continues to be held at West Riffa police station and family visits are being monitored very closely, according to his lawyers. His cell does not meet the requirements for long-term detention and the sanitary facilities are unhygienic. He has lost eight kilos since his arrest. Rajab has chronic inflammation in his lower back requiring urgent surgery, which has been delayed by the authorities until early September. In addition, he is also suffering from an irregular heartbeat, which has decreased below the normal range during his detention, and has also suffered from chest pains recently, having required a visit to the clinic. Despite the fact that he requires urgent medical treatment, prison authorities do not appear to provide sufficient medical assistance for most of these ailments. In the meantime, Rajab is dependent on his family to provide him with painkillers and bandages for his bleeding due to his ulcer.
Following his arrest, Rajab’s case has received widespread international attention by government officials and UN dignitaries, inter alia, by the spokesperson of the US State Department, the spokesperson of UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-Moon, as well as by members of the European Parliament, who adopted an urgent resolution condemning the Bahraini authorities’ crackdown on civil society and on the political opposition.
As a signatory to international human rights conventions, the Government of Bahrain is bound to guarantee the right to freedom of expression for all in Bahrain, including Nabeel Rajab. Depriving Rajab of his liberty for peaceful social media posts goes against Bahrain’s commitment to uphold these international conventions and raises the question of its ability to respect its legal obligations within the wider international community.
To date, the government in Bahrain has repeatedly demonstrated unwillingness to comply with international legal standards, despite promises made at the United Nations during its Universal Periodic Review, and during its own national inquiry, the Bahrain Independent Commission of Inquiry (BICI).
We therefore urge you to abide by the principles of democracy and human rights and to safeguard freedom of expression in Bahrain, as enshrined in international human rights legislation, by dropping all charges against the human rights defender, Nabeel Rajab and ensure his immediate and unconditional release.
Sincerely,
Americans for Democracy and Human Rights in Bahrain (ADHRB)
Bahrain Center for Human Rights (BCHR)
Bahrain Institute for Rights and Democracy (BIRD)
Bahrain Press Association (BPA)
Brian Dooley, Human Rights First
Canadian Journalists for Free Expression
CIVICUS
Committee for the Respect of Liberties in Tunisia
English PEN
European-Bahraini Organisation for human rights (EBOHR)
European Center for Democracy and Human Rights (ECDHR)
FIDH, within the framework of the Observatory for the Protection of Human Rights Defenders
Gulf Centre for Human Rights (GCHR)
Human Rights Sentinel
IFEX
Index on Censorship
International Press Institute (IPI)
Jesper Højberg, Executive Director, International Media Support
Khiam Rehabilitation Center for Victims of Torture
Lawyers Rights Watch Canada
Libya Al-Mostakbal Centre for Media & Culture
MADA Palestinian Center for Development & Media Freedoms
Maharat Foundation
Moroccan Association for Human Rights (AMDH)
No Peace Without Justice
Pakistan Press Foundation
Project on Middle East Democracy (POMED)
Reporters Without Borders (RSF)
Salam for Democracy and Human Rights
Tunis Centre for Press Freedom
Tunisian League for Human Rights (LTDH)
Tunisian Forum for Economic and Social Rights
Vigilance for Democracy and the Civic State
World Organisation Against Torture (OMCT), within the framework of the Observatory for the Protection of Human Rights Defenders
31 Aug 2016 | Bahrain, Bahrain Letters, Campaigns, Campaigns -- Featured, Press Releases, Statements
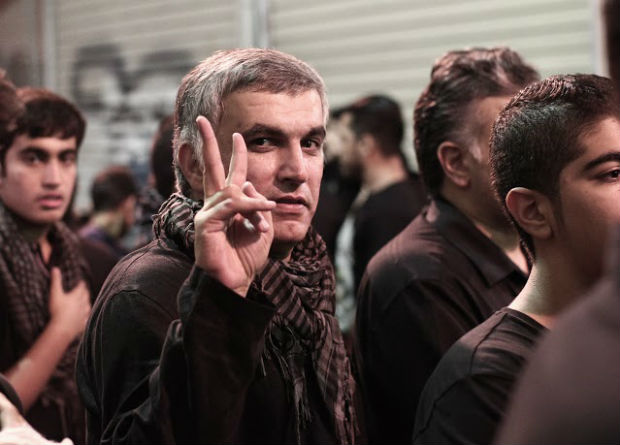

Bahraini human rights defender Nabeel Rajab (Photo: The Bahrain Institute for Rights and Democracy)
Playwright David Hare, author Monica Ali, comedian Shazia Mirza, MP Keir Starmer and Nobel laureate Wole Soyinka are among those who have written to Prime Minister Theresa May asking the UK government to call on Bahrain to release a campaigner imprisoned for just tweeting his opinions.
Nabeel Rajab has been in pre-trial detention in Bahrain since July. He has been held largely in solitary confinement, and for the first two weeks after his arrest was held in a filthy police cell that aggravated heart and other health issues.
Rajab was arrested for expressing opinions. He did not advocate or condone violence, nor is he accused of any violent act. Some of the “criminal” communications he is charged with include retweets of his support for organisations like Index on Censorship, which organised the letter. Rajab is also accused of “insulting“ Bahrain’s ally Saudi Arabia. He faces up to 15 years in prison for his “crimes”.
Rajab is a former winner and judge of the Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards and those who signed the letter included former fellow winners and judges.
“Free expression is under severe threat in Bahrain and the region,” said Index on Censorship CEO Jodie Ginsberg. “It is vital that Bahrain’s democratic allies make clear to Bahraini authorities that their behaviour is unacceptable. The US State Department has already publicly called for Nabeel’s release. The British government should do the same.”
September 1, 2016
Dear Prime Minister,
We are writing to ask you to call publicly for the release of Nabeel Rajab. One of the Gulf region’s best-known human rights defenders, Mr Rajab has been in pre-trial detention since July. He has been held largely in solitary confinement, and for the first 15 days after his arrest on 13 June was held in a filthy police cell that aggravated heart and other health issues.
Mr Rajab was arrested simply for expressing opinions. He did not advocate or condone violence, nor is he accused of any violent act. Indeed, some of the “criminal” communications he is charged with include retweets in his support from international civil rights organisations like Index on Censorship. He is also accused of “insulting” Bahrain’s ally Saudi Arabia. He faces up to 15 years in prison for his “crimes”.
Free expression is under severe threat in Bahrain and the region. It is vital that Bahrain’s democratic allies make clear to Bahraini authorities that their behaviour is unacceptable. The US State Department has already publicly called for Nabeel’s release. We ask Britain to do the same.
Yours sincerely,
Index on Censorship former winners and judges
Jodie Ginsberg, CEO, Index on Censorship
Keir Starmer MP
David Hare, playwright
Monica Ali, author
Howard Brenton, playwright
Maureen Freely, author
Shazia Mirza, comedian
Charlie Smith, GreatFire.org, China
Rafael Marques de Morais, journalist, Angola
Serge Bambara, musician, Burkina Faso
Shazad Ahmed, campaigner, Pakistan
Yoav Shamir, director, Israel
Tamas Bodoky, campaigner, Hungary
Sanar Yurdatapan, composer, Turkey
Rakesh Sharma, filmmaker, India
Maria Teresa Ronderos, journalist
Farieha Aziz, campaigner, Pakistan
Safa Al-Ahmed, journalist, Saudi Arabia
Jean Hatzfeld, journalist and author, France
Mahsa Vahdat, artist, Iran
Murad Subay, artist, Yemen
Jimmy Wales, Wikipedia founder
Baroness Helena Kennedy QC, House of Lords
Wole Soyinka, playwright and poet
Zaina Erhaim, journalist, Syria
Mouad Belrhouate, musician, Morocco
For more information, please contact Sean Gallagher at [email protected] or +44 (0)207 963 7262
31 Aug 2016 | Bahrain, Events, Middle East and North Africa
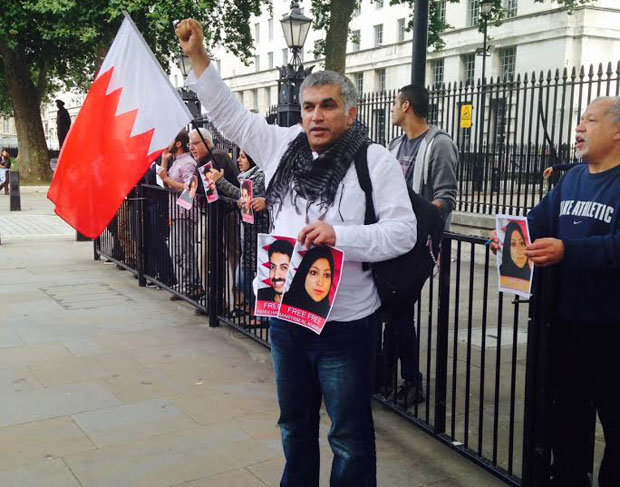

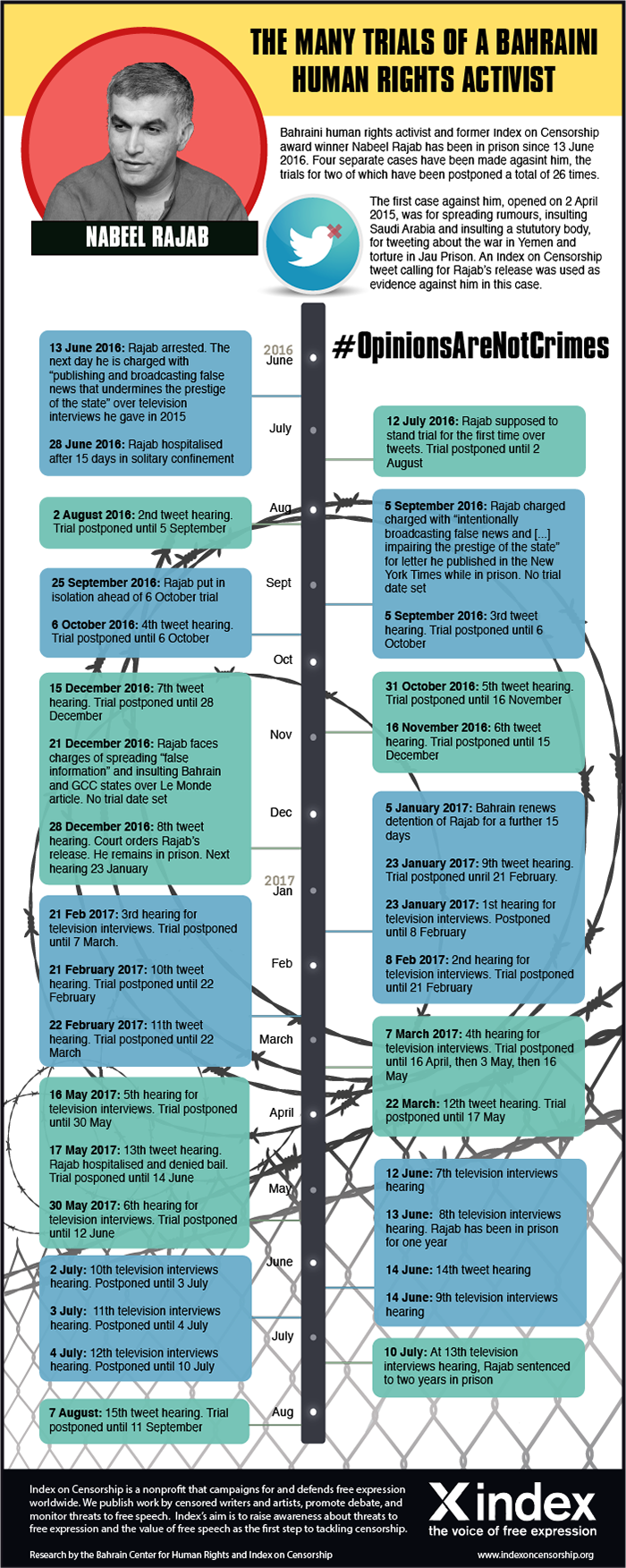
Nabeel Rajab, the Bahraini human rights activist and Index on Censorship award winner, will spend his 52nd birthday in detention.
Rajab is due in court on 5 September accused of spreading “false or malicious news” about the government (evidence for which includes a retweet of an Index tweet), “offending a foreign country” by criticising Saudi Arabia’s incursions in Yemen and “offending a statutory body” by condemning conditions in the country’s notorious Jau prison. He faces 15 years behind bars.
This is just the latest in a long line of actions taken by the Bahraini government against Rajab, one of the Middle East’s most prominent human rights defenders. He has been subjected to ongoing judicial harassment, travel bans, physical intimidation and imprisonment – including time spent in solitary confinement – for his non-violent advocacy of democracy and an end to endemic corruption.
Join Index on Censorship, English Pen, The Bahrain Institute for Rights and Democracy and others at the Bahrain Embassy in London on 1 September to mark Rajab’s birthday and call for his immediate release.
When: Wednesday 1 September 2016, 2pm
Where: Bahrain Embassy, London (Map)
26 Aug 2016 | Bahrain, mobile, News and features
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_video link=”https://youtu.be/GBQX0TvFMbs”][vc_column_text]This article was updated on 31 August 2017
Have you expressed disapproval of your government? Called for more democratic decision-making in your country? Criticised prison conditions or criticised a country allied with your government? Retweeted a comment that included #opinionsarenotcrimes?
You are a criminal. You could be facing up to 15 years in prison for simply expressing your point of view if you lived in Bahrain.
Nabeel Rajab, just like you, thinks his country could be better. And he has made those views public. He speaks out against poor prison conditions and argues for more freedom of speech in Bahrain.
Friday 1 September 2017, marks his second birthday in prison, where he has been since 13 June 2016. He has been subjected to harsh treatment in often appalling conditions that have exacerbated his health issues.
Rajab — due in court on 11 September in one of the cases against him — is facing trial for tweets and retweets about the war in Yemen in 2015, for which he is charged with “disseminating false rumours in time of war” (Article 133 of the Bahraini Criminal Code) and “insulting a neighboring country” (Article 215 of the Bahraini Criminal Code), and for tweeting about torture in Jau prison, which resulted in a charge of “insulting a statutory body” (Article 216 of the Bahraini Criminal Code).
What’s worse, it’s just the latest in a long line of actions taken by the Bahraini government against Rajab, one of the Middle East’s most prominent human rights defenders.
Rajab has been subjected to ongoing judicial harassment, physical intimidation and imprisonment for his non-violent advocacy of democracy and for his calls for an end to endemic corruption. Police officers have beat him up, the country’s press have published the government’s accusations against without his side of the story. He has been imprisoned, pardoned, banned from travelling, rearrested and held in solitary confinement.
Despite the huge personal cost to himself and his family, Rajab continues to speak out.
His activism began during protests in the 1990s and grew with his involvement with the Bahrain Human Rights Society, which he helped found in 2000.
In 2002 he partnered with Abdulhadi al-Khawaja, who is now serving a life sentence for his human rights work, and others to launch the Bahrain Center for Human Rights, which was awarded an Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Award in 2012. BCHR has consistently spoken out for non-violent resistance and the peaceful struggle for social justice, democracy and human rights.
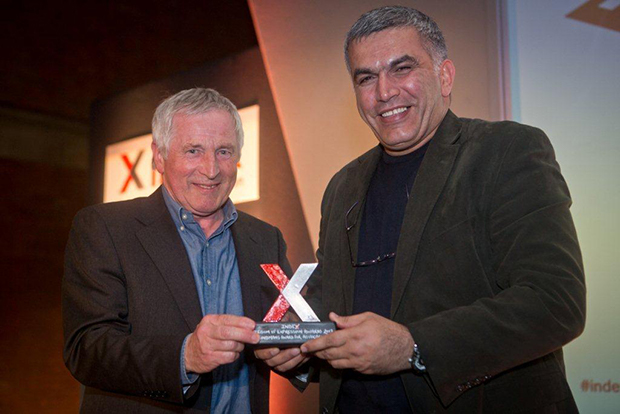

Nabeel Rajab, BCHR – winner of Bindmans Award for Advocacy at the Index Freedom of Expression Awards 2012 with then-Chair of the Index on Censorship board of trustees Jonathan Dimbleby
Rajab has also been outspoken in working for the protection of the Gulf’s migrant workers, founding, in 2003, one of the first committees in the region to advocate improved conditions for them.
When the Arab Spring swept across the Middle East in 2011, Rajab participated in the pro-democracy protests that were focused on the Pearl Roundabout in the country’s capital Manana. His vocal criticism of human rights violations and outspokenness — even after the government issued a state of emergency and invited foreign intervention to help maintain control — brought him into frequent conflict with security forces.
Born 1 September 1964 to a middle-class family, he went to university in India to study politics, before returning to work in Bahrain. Rajab is married and has two children. He is a nephew of Mohamed Hasan Jawad, one of the “Bahrain 13” — political figures imprisoned for participating in the Arab Spring protests, and a cousin of Hussain Jawad, a prominent human rights activist arrested in February 2015.
What can you do to help?
Silenced temporarily by the Bahraini government, Rajab needs you to use your voice. Speak out in support of free speech and human rights.
 [/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1504263730538-3d233804-f31e-8″ taxonomies=”3368″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1504263730538-3d233804-f31e-8″ taxonomies=”3368″][/vc_column][/vc_row]




 [/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1504263730538-3d233804-f31e-8″ taxonomies=”3368″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1504263730538-3d233804-f31e-8″ taxonomies=”3368″][/vc_column][/vc_row]