24 Oct 2014 | Europe and Central Asia, News and features, Turkey
When Turkish political cartoonist Musa Kart faced nine years in prison for “insulting” President Recep Tayyip Erdogan, his colleagues from across the world fought back in the best way they know how — by drawing their own #erdogancaricature.
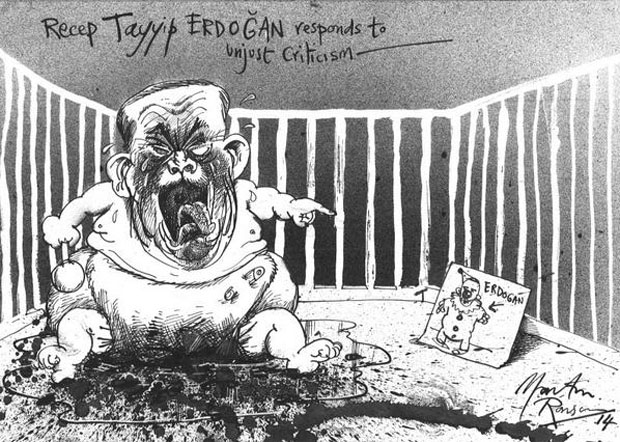

By: Martin Rowson
The online campaign was started on Thursday by Martin Rowson, cartoonist for The Guardian, The Independent and Index on Censorship among others, as Kart was scheduled to appear in court.
Erdogan himself filed the complaint against Kart over a cartoon published in the daily Cumhuriyet on 1 February 2014 showing the then prime minister as a hologram watching over a robbery. This was a reference to his alleged involvement covering up a high-profile graft scandal.
Erdogan claimed Kart was guilty of “insulting through publication and slander,” reports Today Zaman. And while the court initially ruled that there were no legal grounds for action, this decision was revoked following complaints from Erdogan’s lawyer. Kart was also fined in 2005 for drawing Erdogan as a cat.
In court on Thursday, Kart stated: “Yes, I drew it [the cartoon] but I did not mean to insult. I just wanted to show the facts. Indeed, I think that we are inside a cartoon right now. Because I am in the suspect’s seat while charges were dropped against all the suspects [involved in two major graft scandals]. I need to say that this is funny.”
He was finally acquitted, but many of his fellow cartoonists has already shared their artistic interpretations of Erdogan and the case.
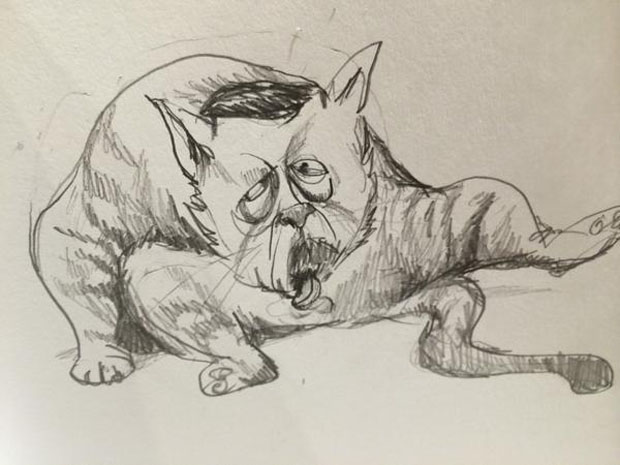

By: Morten Morland
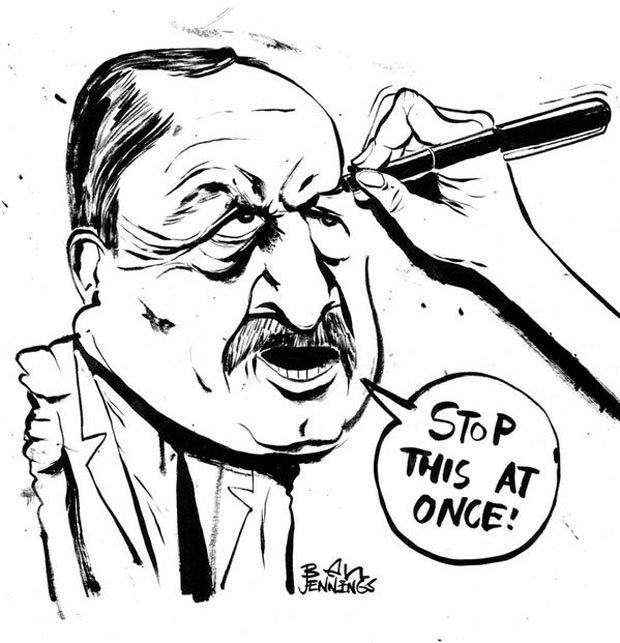

By: Ben Jennings
“I was alerted to Musa Kart’s plight by the excellent Cartoonists’ Rights Network International (CRNI) and previously, when an Iranian cartoonist was sentenced to 40 lashes, a bunch of us got together to draw the offended politician who’d had him arrested, the sentence was commuted,” Martin Rowson told Index via email.
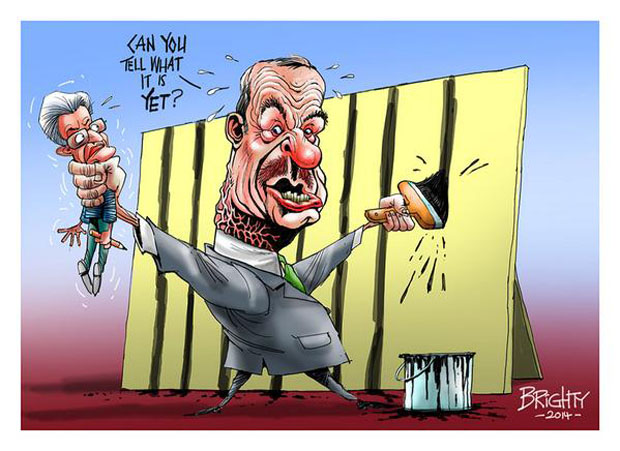

By: Steve Bright

By: Kanika Mishra
“It seems this kind of international bullying by cartoon does have an effect, as even the chippiest despot out there can usually detect a batsqueak of the shamefulness of not being able to take a joke. In Musa Kart’s case, the threat of up to nine years in prison was such an outrageous abuse of power I didn’t wait for anyone else to organise this and simply put out a call via Twitter for cartoons of Erdogan to show solidarity. No idea if it had any effect on the court (I doubt it) though it may put Erdogan off the idea of taking the case to a higher court. I hope so. And I hope it gave Musa Kart a feeling that he wasn’t on his own in there. Basically, this is cartoonists playing the Spartacus card, because if one of us, anywhere, is persecuted for laughing at power, we all are,” said Rowson.

By: Harry Burton

By: Brian Adcock
“Cartoonists are often the last bastion of free speech in repressive regimes and equally valued for telling the truth as it is, in democratic societies too; some consider their work to be of just as much value, if not more, as journalists, and many respected for the courage and ability to often say and report what others cannot, or fear to do, alongside the just as valued use of satire to reveal a truth which otherwise might not see the light of day,” Patricia Bargh from CRNI explained to Index in an email.

By: Mike Roberts

By: Tjeerd Royaards
“Thus as societies we should value and protect their right to do what they do, and if they know there is an organisation out there who will take up their case, should they be targeted, we hope that gives them the confidence to continue to on and assists them in their valuable work too,” Bargh added.
This article was originally posted on 20 October at indexoncensorship.org
24 Sep 2014 | Digital Freedom, Mapping Media Freedom, News and features, Turkey

Former Turkish Prime Minister and current president Recep Tayyip Erdogan spoke to tens of thousands of supporters during a presidential campaign rally in Istanbul in early August. (Avni Kantan / Demotix)
Seven months after a previous amendment was introduced to Turkey’s contentious 5651 law governing internet activity, new restrictions were passed late on September 8. Before the February amendments were signed into law by then President Abdullah Gül, a protracted approval process over the course of a few weeks helped bring attention to the proposals. In contrast to the online and street protests against internet censorship that preceded the amendments’ approval earlier this year, last week’s changes to the 5651 law were rushed through a vote before word could spread about them.
The newest restrictions are only two articles tucked into a lengthy omnibus reform bill: in a total of seven sentences, amendments number 126 and 127—part of a list of 146—succinctly make way for invasive data logging and the speedier blocking of access to websites. Nihan Güneli, an Istanbul-based technology and media lawyer, said the hurried vote on the bill kept opposition to the internet regulations muffled. When the details of the earlier 5651 amendments were first presented in January, Güneli said, “everybody was protesting it. I believe that was one of the main reasons Abdullah Gül rejected these two main articles. But this time we didn’t have any time. We just saw the article and everybody was shocked.”
Before approving the last amendments in February, Gül urged legislators to adjust two of its articles: one measure allowing for Turkey’s Telecommunications Directorate (TİB) to block access to some websites within four hours – without a court order, was changed to require judicial review. Another measure that gave TİB the right to collect internet users’ data was changed to restrict access to user logs.
Former Prime Minister Erdogan replaced Gül as Turkey’s new president on August 28. Less than two weeks after his inauguration, these newest internet restrictions allow for websites to be blocked within four hours if their content is ruled a threat to national security or public order, or if restricting access to them can prevent a crime. Under the new amendment, TİB is also allowed to store internet users’ traffic logs and metadata. In an attempt to make the February bill amendable to critics, these two most offensive parts of the previous amendments to 5651 were dropped at Gül’s request. Now exactly those measures have been quietly put into effect under Turkey’s new president.
The targeting of websites determined to be threats to national security comes after the Turkish government struggled to suppress a series of leaked phone recordings earlier this year that spread on social media. The wiretapped phone conversations featured what appeared to be the voices of Prime Minister Erdogan and people close to him, and pointed to their implication in an ongoing corruption scandal. Other recordings ostensibly showed Erdogan’s meddling in the judiciary and with owners of major media outlets. In March, a leaked recording from a meeting at Turkey’s foreign ministry detailed the government’s considerations for military involvement in Syria. Shortly after that recording was posted on YouTube, access to the platform was blocked entirely in Turkey.
YouTube is one prominent example of access restrictions prior to the most recent legislation reform—the website was previously banned for over two years up until 2010. The possible effects of the newest amendments’ measures for blocking websites are still unclear, although the implications for access to information are startling. A number of small, alternative news websites have been aggressively covering the Turkish government’s recent corruption scandal. With no offline distribution form, their livelihood would be put at risk if their websites became inaccessible.
The news website Diken was founded in January 2014 and has since gained a following for its alternative reporting. In June, Diken was named “internet newspaper of the year” by an environmental organisation. Editor in chief Erdal Güven says Diken published almost every one of the leaked government phone recordings earlier this year. So far, Diken has not been shut down or admonished by authorities, which Güven suggests may be because the website is still less than one year old and may not be considered a sufficient threat. Diken risks being targeted by TİB at any point, though, says Güven. “It depends on an advisor to a minister, an MP, the president. Just to read a story of ours and then complain to the legal authorities,” Güven said. Referring to the fines media companies can face for publishing information deemed illegal, Güven added, “They can ask us to pay a huge amount of money. We don’t know what they will do. We don’t have a huge amount of money, we have a tight budget. Of course this would affect us.”
Because of their editorial choices and coverage of government scandals, alternative news sources and social media are the main targets of the new restrictions on website access. Elif Örnek, a reporter for the leftist newspaper soL, says that journalists are often pressured or face censorship, and in reporting on issues that the government is trying to suppress, like the leaked phone recordings, the stakes can be especially high for the media. “The main thing is that when you’re thinking about the public interest, there are some dangers you have to risk,” Örnek said.
For internet users, TİB’s broad collection of metadata is a newly legal tool for monitoring online activity. Nihan Güneli says it’s impossible to predict how TİB will purpose users’ traffic logs. “Within six months, maybe we’ll hear about a case, maybe somebody will be arrested or someone committed a crime and we’ll see this traffic information in court. Then we’ll know what they’re doing with it,” Güneli said. Censorship of websites within Turkey is not new, making it hard to predict whether the new bill’s other article, which gives TİB the authority to block sites within four hours, will have palpable effects on access to information. “TİB has power right now and nobody knows what they’re going to do with it. I don’t think they know either,” Güneli said.
Media violation reports from Turkey via mediafreedom.ushahidi.com
Twitter account of Today’s Zaman editor faces closure
Habertürk fires reporter
Journalist kidnapped and released by PKK
Report shows media use of hate speech increased in early 2014
Several media organisations denied accreditation to AK Party congress
This article was posted on 24 Sept 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
15 Aug 2014 | Europe and Central Asia, News and features, Turkey
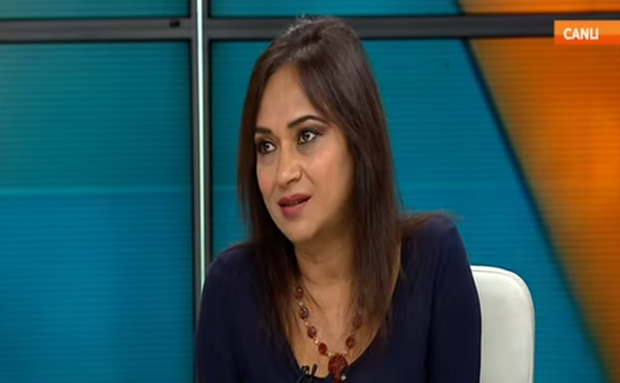
Amberin Zaman during a TV appearance (Image: serm canker/YouTube)
“A militant in the guise of a journalist, a shameless woman.” “Know your place.” “[Y]ou insult at a society of 99 percent Muslims.”
The comments from Recep Tayyip Erdogan — Turkey’s newly elected president and outgoing prime minister — were heard across the world. While he did not mention a name, it was the clear the woman in question was Amberin Zaman, a journalist for The Economist and Taraf. Erdogan’s tirade came during a campaign rally last Thursday in the city of Malatya, ahead of Sunday’s presidential vote. Zaman had expressed opinions critical of Erdogan during a TV discussion the night before.
Erdogan continued during a rally in Ankara on Saturday, calling her a “despicable woman” and saying she had insulted Islam. She has also been targeted online by Erdogan supporters, in what the Organisation for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) has labelled a “widespread smear campaign“.
“The pro-Erdogan camp emboldened by his very public insults against me continue to mob lynch me via the social media,” Zaman told Index on Censorship. “My Twitter feed is flooded with threats and profanities. Being called an enemy of Islam in a Muslim country, when radical groups like IS have Turkish members who are active Twitter users, puts me at physical risk and hobbles my work.”
She says she was unable conduct interviews on the streets on election day, “for fear of being recognised and attacked”.
This is not the first time Zaman has been targeted for speaking out against Turkish authorities. She was fired last year from Haberturk over articles critical of the government, and she was also one of the journalists reportedly wiretapped with the approval of Erdogan. As she said at a recent Index event on digital freedom, she is attacked online daily by pro-government trolls.
But Zaman is not the only member of the Turkish media under threat. According to recent figures there are 40 journalists behind bars in the country, making it one of the world’s worst jailers of press. Since 1992, 14 journalists have been murdered with impunity. Turkey stands at 154th out of 180 countries in the latest Reporters Without Borders Press Freedom Index, and its ranking has deteriorating over the past years.
In addition to Zaman’s case, there have been a number of other attacks on press freedom just over the past few days, as reported by the Index media mapping tool among others. Enis Berberoglu, editor-in-chief of Hurriyet, resigned on 8 August. The paper has denied that it was as a result of political pressure. However, in his attacks on Zaman during the Malatya rally, Erdogan specifically mentioned the owners of the TV channel she was on, Dogan Holding. Hurriyet is also owned by Dogan.
“The consensus is that he was pushed out but his departure coincided with the elections so it didn’t get the attention it deserved. But it is a further sign that media bosses will continue to cave in to power. It’s a tragic comment on the state of the Turkish media,” says Zaman.
The same day as Berberoglu’s resignation, investigative journalist Mehmet Baransu was beaten by police. The day after he was detained for tweeting about the incident, and about the Istanbul public prosecutor. There have also been reports that the Cihan news agency was restricted from covering the presidential election, with police ordered to keep journalists out of polling sites across the country.
The election also put the spotlight on issues surrounding biased media coverage in favour of Erdogan; something that was highlighted by observers after the vote. Zaman says it is difficult to measure the impact of the poor state of media freedom on the election and its outcome — Erdogan won comfortably after one round. But it was not, she says, “a level playing field”.
“Erdogan has indirect control over a broad swathe of media outlets, most crucially of television. So the opposition candidates received scant coverage, and the little they got in pro-government was more of a smear campaign to which they were unable to effectively respond. Intimidation of the media and of media bosses has created an environment of self-censorship where journalists fear losing their jobs,” she explains.
“Even the mildest criticism is no longer tolerated. It’s stifling.”
Despite the attacks from Erdogan and his supporters, Zaman says she is “very heartened by the thousands of messages of support I have received, including from pious Muslims”.
The Women’s Equality Monitoring Group, whose membership includes female journalists, academics and writers has called on Erdogan to apologise.
“Making a female journalist a target by calling her shameless for simply performing her job was the last link in a chain of sexist stances,” they said. “This attack was also an attempt to silence the few remaining critical voices in the media, which has been silenced with bribery, censorship and self-censorship.” The Economist have stated that they “stand firmly” by Zaman.
“I am not alone,” she said.
But as Erdogan has indicated intention to expand the powers of the presidency, Zaman is not optimistic about the future.
“Should he continue to run the government as he announced he would it is horrible news for journalists. Things can only get worse not better.”
This article was posted on August 15, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
19 Mar 2014 | Digital Freedom, News and features, Turkey
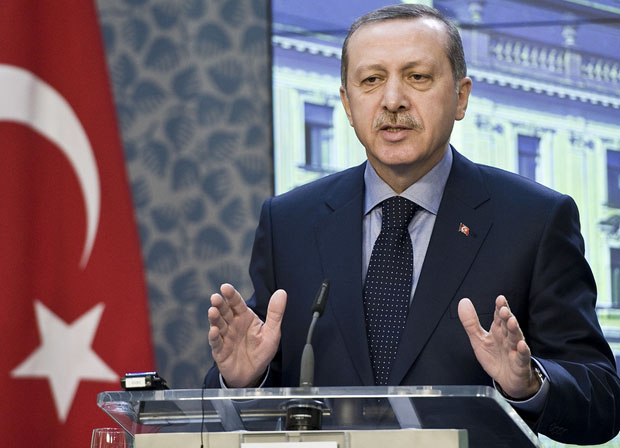

Turkish Prime Minister Recep Tayyip Erdogan (Photo: Philip Janek / Demotix)
In February, Turkish president Abdullah Gül prompted intense criticism when he approved restrictive new amendments to the law that regulates internet activity in Turkey, known as 5651. Since then, the Turkish government has continued to threaten internet freedom, placing added pressure on social media platforms. Earlier this month, prime minister Recep Tayyip Erdoğan suggested that his government could block access to Facebook and Youtube after municipal elections on 30 March.
With over 34 million Facebook active users, Turkey is among the top 15 countries on the platform, and both the prime minister and Gül each have over four million Twitter followers. One day after Erdoğan’s statement during a live television interview, Gül countered that blocking access to social media was out of the question. Last week, Erdoğan followed by backtracking on his own comments.
Considering the already strained relationship that Erdoğan’s government has to social media, the turnaround on his comments is still no promise that there may be less restrictions on internet freedom to come in Turkey. In recent months, a number of wiretapped telephone recordings, allegedly of Erdoğan’s conversations, have been leaked onto social media platforms, including YouTube, SoundCloud and Vimeo, suggesting the prime minister’s meddling in corruption and intimidation of mainstream media. On the day that Erdoğan’s television interview aired, a new phone conversation was leaked onto YouTube, purportedly featuring the prime minister berating the media magnate Erdoğan Demirören for coverage in his daily Milliyet of a 2013 peace talk with Abdullah Öcalan of the separatist Kurdish Workers’ Party (PKK).
Erkan Saka, an assistant professor at Istanbul Bilgi University and a researcher on new media, says
Erdoğan’s comments about Facebook and YouTube reflect his interest in controlling Turkish media. “Most of the mainstream media is already under their control, so this seems to be the only way now for people to express their opposition,” Saka said. With leaks appearing on video or audio sharing websites and spreading through Twitter and Facebook, social media platforms have become instrumental for circulating information related to the ongoing government corruption scandal.
Shutting down entire websites as Erdoğan suggested would mean going beyond the very recent amendments to law 5651 that make possible URL-based blocking of individual web pages ruled offensive, without restricting access to entire websites. YouTube was previously censored in Turkey for over two years after a video was posted on the site that was deemed insulting to Mustafa Kemal Atatürk, the founder of the Turkish Republic. Earlier this year, Vimeo and SoundCloud were both temporarily shut down within Turkey following leaks that were published on those websites. Lawmakers from Erdoğan’s party, the AKP, have defended the controversial new version of 5651 because it allows for an alternative to restricting access to entire websites. Supporters of the law claim that with URL-based page blocking, defamatory content can instead be removed selectively.
In the run up to the elections at the end of this month, the recurring leaks and violent protests around Turkey threaten to tarnish Erdoğan’s popularity with voters. Responding aggressively in the televised interview, Erdoğan’s derision of social media platforms is personal, tactical, and aimed to discredit the websites as a threat to internet users’ safety. “We will not leave this nation at the mercy of YouTube and Facebook,” the prime minister said in his interview with journalists on broadcaster ATV. Calling the websites immoral, Erdoğan added, “they don’t have limits.” By casting social media websites as damaging to all internet users in Turkey, Erdoğan set the stage for potentially restricting access to those sites on moral grounds. Even after correcting his statement, Erdoğan’s suggestion that social media platforms are a source of danger is in line with his government’s use of internet filtering programs and ad campaigns that portray the internet as debauched to justify restricted access to content it considers harmful.
Aside from facing access restrictions, websites operating from Turkey are forced to comply with other laws that compromise their users’ privacy. Sedat Kapanoğlu, founder of the popular satirical, user-generated online dictionary Ekşi Sözlük, says internet companies in Turkey are put under pressure by laws requiring them to share user data. “A successful platform must create a free environment which protects its users’ rights. We are not able to do that. We are forced to provide IP addresses to prosecution even for completely legal content,” Kapanoğlu said.
One of the social media websites that Erdoğan singled out in his interview, Youtube, which is owned by Google, has an office in Turkey, while other large platforms like Facebook, SoundCloud, Vimeo, and Twitter do not.
Although he later rescinded his original statement, Erdoğan’s recent threat is alarming because it shows that in Turkey’s precarious climate for media independence, it might be plausible for his government to increase control of social media. With elections approaching this month, Erdoğan is himself coming under more pressure to win votes while facing a corruption scandal playing out on social media. The amendments to 5651 already make it easier for the Turkish Directorate of Telecommunication (TİB) to remove web pages from the internet. As more leaks continue to emerge, there is a lingering risk of new restrictions targeting social media platforms that have been at the centre of freedom of speech debates in Turkey.
This article was posted on 19 March 2014 at indexoncensorship.org













