20 Jan 2017 | Statements
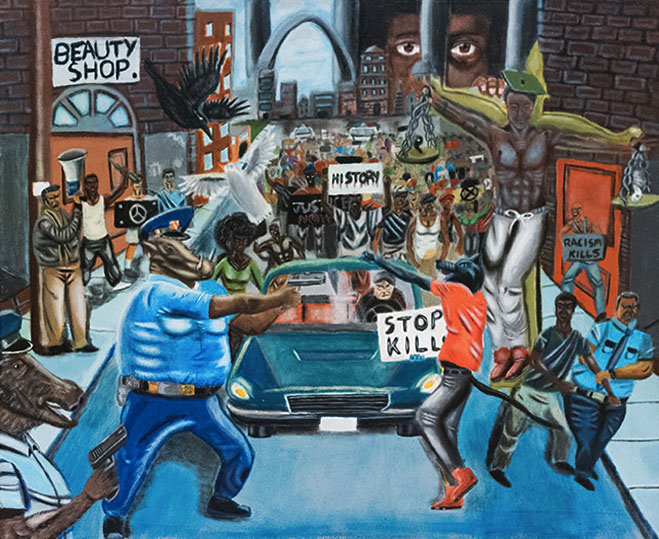
Untitled #1, by David Pulphus
As organisations devoted to promoting the arts and freedom of expression, we condemn the recent removal of a student painting from a public passageway on Capitol Hill. The removal shows a deep disregard of a young person’s constitutional right to free expression and is a flagrant violation of the principles underlying the nation’s commitment to the protection of free speech. It is a sad day when elected representatives of the people of the United States send a message to young people in this country that they should stifle passionate expression concerning important issues of public policy.
The painting, by St. Louis High School Senior David Pulphus, is among the winners of the annual Congressional Art Competition. It depicts, in an allegorical manner, a young artist’s vision of one of the facts of our recent past: a protest against police violence. Pulphus’ painting was selected through a process set by the Competition, which included a review by the office of the Architect of the Capitol. It was approved and remained on display for six months until conservative news outlets built up a controversy around it in late December.
The media-generated controversy was followed by multiple attempts on the part of several Republican Representatives to take down the work with their own hands (each time, Representative Clay (D-Mo) put it back up). On Friday, January 13th, Stephen Ayers, the Architect of the Capitol, ordered the painting’s removal on the basis that it violated competition guidelines stipulating that “subjects of contemporary political controversy or a sensationalistic or gruesome nature are not allowed.”
The retroactive use of the very guidelines by which the painting was selected in the first place to remove the work only serves to draw attention to the how vague these guidelines are. Worse, the fact that the decision to censor the work was made under strong political pressure coming from one side of the aisle proves how easy it is to use the vague guidelines to suppress political viewpoints.
What is “controversial” is entirely subjective and thus open to abuse and the enforcement of political bias: Indeed, many other artworks in the exhibition may be deemed controversial, including a depiction of white police officers harassing an African American playing checkers, a portrait of Bernie Sanders and another of President Obama. And, of course, portraits and statuary on permanent display in Congressional buildings represent many political figures that are controversial. That Pulphus’ painting of police protests was singled out among all these for a hasty removal, after partisan political pressure by representatives who claimed the work was offensive to law enforcement, only deepens our concerns about the elected representatives enforcing political bias and stifling speech.
Political artistic expression is protected speech, no matter how controversial or offensive some may find it. Criticism of government actors such as law enforcement officials is one of the foremost reasons why we have the First Amendment. Citizens’ freedom to speak out against perceived governmental abuses and injustices is necessary to the health of our democracy: were government able to silence such criticisms, meaningful political discourse would be rendered impossible.
Removing the work sends a message to young people – and everybody else – that they should not depict the world around them for fear of offending our political representatives. At a time when we have a new administration and nationwide concerns about free speech, the censoring of an artwork because of its viewpoint is a deeply disturbing and divisive act in an already polarised nation.
We urge the Architect of the Capitol to take the time to consider arguments from both sides of the aisle and make a decision that upholds one of the nation’s most cherished values, a value that should not be subject to partisan strife: the value of free speech. We hope that rather than exacerbating partisan conflict, the controversy around this young person’s painting becomes a unifying educational opportunity to reinforce free speech principles across both sides of the aisle.
National Coalition Against Censorship
American Civil Liberties Union
American Civil Liberties Union of the District of Columbia
American Society of Journalists and Authors
Authors Guild
College Art Association
Comic Book Legal Defense Fund
Free Speech Coalition
Index on Censorship
PEN America
Vera List Center for Art and Politics
Washington Area Lawyers for the Arts
19 Dec 2016 | Malaysia, News and features
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
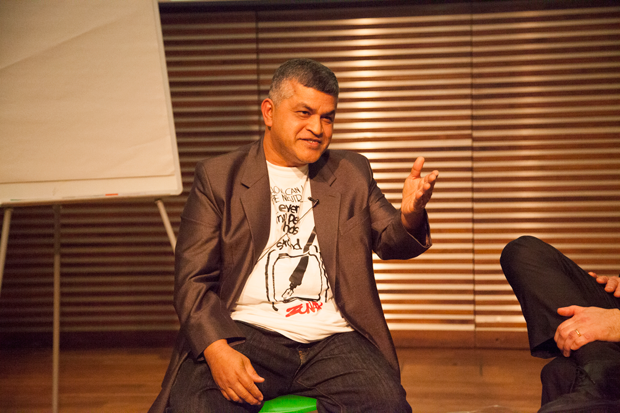

Malaysian cartoonist Zunar is facing charges under a colonial era Sedition Act. (Photo: Sean Gallagher/Index on Censorship)
Malaysian cartoonist Zulkiflee Anwar Ulhaque, aka Zunar, was arrested on Saturday 17 December during a fund-raising event to recoup losses related to the seizure of 20 of his artworks. Police also confiscated 1,000 books during the arrest.
In a statement, the award-winning cartoonist wrote that authorities took him into custody under Section 124 of the country’s penal code for “being detrimental to parliamentary democracy”. Two of Zunar’s assistants were also arrested, as were two of his fans.
“I was questioned for almost six hours and released under bail at midnight. I would have to report back to the police station on the 30 Dec 2016,” Zunar wrote.
The police also said that they would be banning all his books.
It was the cartoonist’s second arrest in three weeks. On 25th Nov 2016, he was arrested under the Sedition Act for his cartoons which are deemed insulting to the country’s prime minister Najib Razak.
The artist was questioned under the penal code under suspicion of intentionally humiliating a person. He was released the next day.
“Even though I have been released, the harassment from the Malaysian government is far from over. I have to report back to the police in Penang on 27 December 2016 for further investigation. And yesterday (26 November), two people who assisted me in organizing the exhibition were also called up by the police for questioning,” the cartoonist said in a statement.
On 25 November Zunar was forced to end his three-day exhibition after only a few hours when a group of “pro-government thugs,” believed to be a part of the United Malays National Organisation, physically assaulted the cartoonist and damaged his displayed work. “They pulled my shirt and threw a punch at me,” Zunar told Index, “but people came and rescued me.”
The Malaysian government has long attempted to silence the cartoonist, who currently is awaiting trial on nine charges of sedition, which carry a potential 43-year jail term, for his cartoons government-critical cartoons. The trial is set for 24 January 2017 and Zunar is currently on bail.
A travel ban was placed on Zunar on 24 June of this year but was Zunar only became aware of the limitation when he was held by immigration police at the Kuala Lumpur International Airport when attempting to leave Malaysia on 17 October.
Zunar has been arrested twice before, once for two days in 2010 for publishing his book Cartoon-O-Phobia, and again for three days in 2015 for violating the Sedition Act.
The Sedition Act, which was put in place to silence opposition to British colonial rule in 1948, has become a popular way for the Malaysian government to silence critical voices such as Zunar. The award-winning cartoonist has been challenging the law for years.
“I can smell that the 10th charge of the Sedition Act is on the way. I am already facing 9 charges under that draconian act and the trial is set to be on 24 January 2017,” Zunar said.
The artist was questioned under the penal code under suspicion of intentionally humiliating a person. He was released the next day.
“Even though I have been released, the harassment from the Malaysian government is far from over. I have to report back to the police in Penang on 27 December 2016 for further investigation. And yesterday (26 November), two peeple who assisted me in organizing the exhibition were also called up by the police for questioning,” the cartoonist said in a statement.
On 25 November Zunar was forced to end his three-day exhibition after only a few hours when a group of “pro-government thugs,” believed to be a part of the United Malays National Organisation, physically assaulted the cartoonist and damaged his displayed work. “They pulled my shirt and threw a punch at me,” Zunar told Index, “but people came and rescued me.”
The Malaysian government has long attempted to silence the cartoonist, who currently is awaiting trial on nine charges of sedition, which carry a potential 43-year jail term, for his cartoons government-critical cartoons. The trial is set for 24 January 2017 and Zunar is currently on bail.
A travel ban was placed on Zunar on 24 June of this year but was Zunar only became aware of the limitation when he was held by immigration police at the Kuala Lumpur International Airport when attempting to leave Malaysia on 17 October.
Prior to 25 November, Zunar had been arrested twice before, once for two days in 2010 for publishing his book Cartoon-O-Phobia, and again for three days in 2015 for violating the Sedition Act.
The Sedition Act, which was put in place to silence opposition to British colonial rule in 1948, has become a popular way for the Malaysian government to silence critical voices such as Zunar. The award-winning cartoonist has been challenging the law for years.
“I can smell that the 10th charge of the Sedition Act is on the way. I am already facing 9 charges under that draconian act and the trial is set to be on 24 January 2017,” Zunar said.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1482137483571-c06078d4-e22e-2″ taxonomies=”4218″][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][/vc_column][/vc_row]
13 Dec 2016 | News and features, Turkey, Turkey Uncensored
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

Turkey Uncensored is an Index on Censorship project to publish a series of articles from censored Turkish writers, artists and translators.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]

Women’s Voices by Meltem Arikan
The piece of land surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…big big men are leeching children’s blood, viciously…those who know know, those who know keep quiet, those who see look away…children with dying spirits imprisoned in their own bodies endlessly bleeding within…unhappy, fearful, insecure…No one is making a sound…
The place surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…While shouting out loud “We have never been this free”, and putting writers, translators and journalists behind bars yet life goes on as if everything was normal. While lies feed each other with more lies, liars and yes-men feed off each other murderously. Denying even the smell of death leaking from prison cells, still, more deaths are being called for.
The peninsula surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…the number of people queuing up to turn each other in never ends. The more hatred is carefully fed and made bigger, the more solutions are generated with violence…the violence of hatred and the hatred born out of violence are plunging the spirit of life into a pitch-dark void.
The slippery heaven surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where bloodsucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…while religious extremists obsessed with power are accusing one another, those applauding them are constantly switching sides. Fraud intellectuals, phoney writers, scam businessmen are crossing from one side to the other like a peg-top. Whoever gets to shout louder has their lie spread across the whole world. And sadly, it is always those who do not belong to either side that end up paying the price.
The piece of heaven here on earth surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…while the words of those who can shout out louder, who can buy more, who can be purchased more are suppressing the truth, everyone is turning a blind eye to this. Being closed down, those newspapers and news agencies which once caused innocent people to be sentenced to years in prison with the false evidence they provided are now being proclaimed as the representatives of free press around the world. Without carrying the slightest regret or shame for having destroyed other lives, without engaging in any self-criticism, not even once. As each side becomes more fanatical, truth is drowning further down in a well in which those who choose not to take sides become more and more invisible….Understanding what is happening inside the well is becoming impossible to those outside it. The stories of those who provide the money are marketed as the truth to the world.
The place I once used to live, surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies
The country surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…Those who, until not so long ago, would applaud the government in power today until their palms hurt and blame those who didn’t, for being the enemies of democracy, are today still preaching shamelessly from the same TV channels, from the same papers this time saying “we have been deceived.” Those who, until not so long ago, turned a blind eye to and even from time to time supported what today’s government did to some artists and writers are now expecting support from those whom they had, back then, turned their backs against. Those, who, until not so long ago, said “not enough but yes” (liberals used this slogan during the 2010 referendum) to pretty much all the actions taken by today’s government, and even called their critics fascists are now saying “fascism is coming, can’t you see, why are you keeping quiet?” The climate today is turning into a desert of memoryless miserables in which those, who, not so long ago, hailed the government’s policies on women as freedom are now, interestingly getting frustrated with the child rape law introduced by the same government and are clearing their consciences by saying they had previously been deceived. The hour and minute hand travel in time, but always around the same faces of people who are constantly in self-denial.
The place I once used to live, surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…with every passing day, we are becoming strangers to the places we used to belong, to our past, to our memories and even to ourselves…with every passing day, we are feeling more and more trapped in darkness…most particularly women…if you are a woman…if you have not yet given up on being a woman…
The cage surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies..the sound of seagulls have long since been replaced by religious preachers yelling through speakers. Trees have long since surrendered to concrete walls. The sun is no longer shining in the eyes of the crying children…and lies are growing fast by being fed with more lies…and fears are being ignited by hatred…and people are giving up on themselves more and more with each passing day…and the power of bloodsucking spirits puffs up.
The temple surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…your needs count for nothing and neither do your thoughts. From now on, you are nothing more than a subject that needs to obey…you need to fully understand that you are a subject and you must surrender entirely…you no longer exist as an individual, now there are only those things you have to do and those you have to believe, as determined by the authorities. You will have to bear the brunt of giving up …the more you surrender, the more you will give up on who you are. The more you give up, the more you will be expected to do it…and the more you will give in to hatred.
The stage surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…the more applauded ignorance becomes, the more crowned the lack of knowledge becomes…As opinions get judged , giving in is embraced further. Asking questions has become dangerous now, you must accept the discourse unquestionably. And so you’ll learn to see through the eyes of bloodsuckers, but not your own.
That Sodom surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…rape and abuse have become ordinary acts…a normality. Children are being sent as appetisers for men to lay them on their beds… any sort of perversion can be legitimised as long as one says “I am a believer”. Perverts protect other perverts, perverts determine the laws…As perversion becomes normalised, everywhere is turning to hell for women and children.
That hell surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…people are queuing up to be bloodsucked and the bloodsucked turns into a bloodsucker. And gradually, ruthless vampire stories are coming to life.
That hunting ground surrounded by water on three sides is turning into a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…none of these bloodsuckers cares about freedom or humanity, but they are yearning to figure out who will suck the most blood and who will rule more…
a country where blood-sucking spirits conquer people’s bodies…
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Meltem Arikan is a poet, playwright and author. Her latest play Enough is Enough, about violence against women, will start touring in Wales between Jan-Feb 2017. And her multi award-winning short film Exhibit will continue to be screened various places in Europe. [/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1485774621131-5d65e5b1-5cf0-4″ taxonomies=”8607″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
4 Dec 2016 | News and features
 Index on Censorship is a nonprofit defends people’s freedom to express themselves without fear of harm or persecution. We fight censorship around the world.
Index on Censorship is a nonprofit defends people’s freedom to express themselves without fear of harm or persecution. We fight censorship around the world.
To find out more about Index on Censorship and our work protecting free expression, join our mailing list to receive our weekly newsletter, monthly events email and periodic updates about our projects and campaigns.
Index on Censorship will not share, sell or transfer your personal information with third parties. You may may unsubscribe at any time. To learn more about how we process your personal information, read our privacy policy.
You will receive an email asking you to confirm your subscription to the weekly newsletter, monthly events roundup and periodic updates about our projects and campaigns.
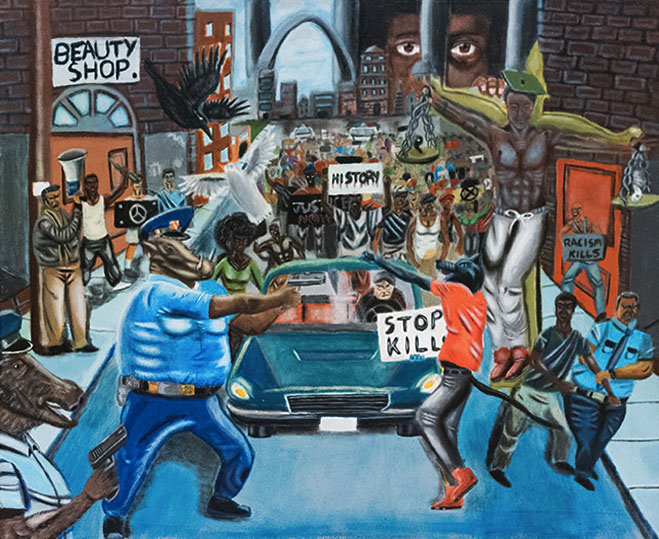




 Index on Censorship is a nonprofit defends people’s freedom to express themselves without fear of harm or persecution. We fight censorship around the world.
Index on Censorship is a nonprofit defends people’s freedom to express themselves without fear of harm or persecution. We fight censorship around the world.