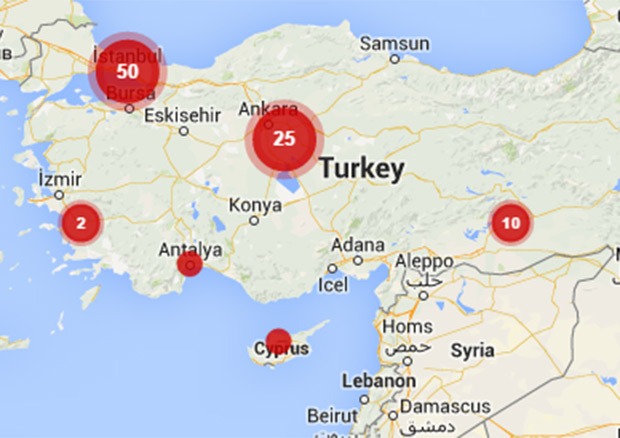
15 Jan 2015 | News and features, Turkey
Richard Howitt MEP is foreign affairs spokesperson for both the Labour Party and the Socialist and Democrat Group in the European Parliament and is a member of its joint parliamentary committee with the Turkish Parliament
As millions mourn the shooting of journalists in France, the European Parliament convening this week in Strasbourg today extended the fight for freedom of expression to legal threats, harassment and character assassination against free journalism in Turkey.
Indeed last weekend’s scenes reminded me of the hundreds of thousands who went on to the streets after the Turkish writer Hrant Dink was shot in 2007 and my deep regret that, despite the work of a foundation established by his widow, the situation in Turkey appears to have got worse not better in the intervening years.
A resolution voted for by MEPs was provoked by dawn police raids on newspapers and television stations in December that led to the arrest of 31 people, mainly journalists, on charges of terrorism – which carry some of the gravest sentences under the Turkish penal code.
Two of the leading journalists arrested openly admit sympathies for the US-based cleric Fethullah Gulen ,whose followers withdrew support from the country’s governing AKP party and whose so-called ‘movement’ does indeed deserve greater scrutiny.
Nevertheless reports suggest no evidence was presented of actual criminal intent against those arrested, with the crackdown fitting a pattern of legal harassment, smears and threats against those who provide political opposition to the government or who critically report on corruption allegations against it.
Our resolution also condemns the recent arrest of a Dutch journalist, demonstrating how foreign journalists are not exempt from attack.
Correspondents of The Economist, Der Spiegel and the New York Times in Turkey have all been threatened, with one CNN correspondent forced to flee the country after being accused of espionage.
Previous attempts to ban social media are also being revived in the country this week, in an apparent attempt to suppress reports Turkey’s intelligence organisation may have been implicated in the supply of arms to ISIS fighters in Syria.
As someone who is proud to call himself a friend of Turkey, and a keen proponent for the country’s accession to the EU, it is with a heavy heart I sign up to such criticisms.
However in negotiations I had to argue against opponents of the country seeking to use this latest incident to introduce wording that would have imposed immediate financial penalties against Turkey or put up new barriers in the membership negotiations.
I did so because politicians as well as journalists must not allow ourselves to be trapped in to self-censorship. On these arrests, it was our duty to speak out.
I am saddened explanations that the release of all but four of the journalists given to me and to my fellow MEPs by the Turkish representative in Strasbourg this week seemed wantonly to ignore the climate of fear and self-censorship which remains inflicted on the country’s press as a result.
It is the blatant denials that undermine trust and confidence with those of us who want to support reform efforts in the country, and which one very senior EU official told me had led to “desperation” in the telephone calls between Brussels and Ankara which followed the arrests.
Meanwhile, former prime minister Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, now elected as the country’s president, reacted characteristically by telling a news conference: “Nowhere in Europe or in other countries is there a media that is as free as the press in Turkey.”
The sober truth is that Turkey ranks 154 out of 180 in press freedom according to the Reporters Without Borders index last year.
The annual survey by the Committee to Protect Journalists, published only last month, showed Turkey amongst the top ten countries in the world for imprisoning journalists, ranking alongside Azerbaijan, Iran and China.
However, Erdogan’s protestations must be put in to a context where he also rebuffed European criticisms of the arrests saying the EU should “mind its own business”, and last week when he was prepared to partly attribute the Charlie Hebdo terrorist attack to “Western hypocrisy”.
Today’s European Parliament vote ascribes that hypocrisy instead to the government in Ankara.
I wonder whether the Turkish press will fairly report even this?
This article was posted on 15 January 2015 at indexoncensorship.org
6 Nov 2014 | News and features, Politics and Society
![People taking part in the funeral procession of Lasantha Wickrematunge (By Indi Samarajiva [CC-BY-2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://www.indexoncensorship.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/11/Lasantha_Wickrematunge_funeral_banners_1.jpg)
People taking part in the funeral procession of murdered journalist Lasantha Wickrematunge (Photo by: Indi Samarajiva [CC-BY-2.0], via Wikimedia Commons)
This would be no defence for Lasantha. President Mahinda Rajapaksa repeatedly referred to him as a “terrorist journalist” and “Kotiyek” (a Tiger).
According to exiled journalist Uvindu Kurukulasuriya, shortly before Lasantha was killed, the president offered to buy the Sunday Leader, with the intention of muting its voice. Lasantha declined the generous offer. On 8 January 2009, he was shot dead.
Days later, an astonishing editorial, written by Lasantha before his death, appeared in the Sunday Leader, and subsequently in newspapers throughout the world. After describing his pride in the Sunday Leader’s journalism, Wickrematunge wrote chillingly: “When finally I am killed, it will be the government that kills me.”
Lasantha’s murder was shocking. As was the murder of Hrant Dink, the Armenian editor who “insulted Turkishness” by daring to speak of the genocide of his people; as was the murder of Anastasia Barburova, the young Novaya Gazeta reporter who investigated the Russian far right; as was the murder of Martin O’Hagan, who took on the criminality of Northern Ireland’s loyalist gangs. As were the murders of the dozens of Filipino journalists killed in the Maguindanao massacre in 2009, too numerous to name, caught up in a ruthless turf war.
Then there are the reporters killed in war zones. The conflict in Syria has been a killing field for journalists. Where once the media were seen as protected, even potential allies, now they are seen as targets. The killings of Steven Sotloff and James Foley by ISIS in Iraq brought back memories of the beheading of Daniel Pearl in Pakistan in 2002. As Joel Simon of Committee to Protect Journalists relates in his forthcoming book, the New Censorship, that crime marked a turning point. In the Pearl case, even Osama bin Laden, who viewed the media as a potential tool in his global war, was shocked by the tactic employed by his lieutenant Khalid Sheikh Mohammed, who claimed to have carried out the murder himself. From that point on, journalists were not just fair game, but trophies.
As money is drained from news, many organisations choose not to send correspondents to areas where reporters are needed most. Too dangerous, too expensive. As a result, freelancers, local journalists and fixers take ever greater risks. Under-resourced, undersupported and out on a limb, they are picked off.
Regional journalists covering tough domestic beats are easy prey. In Mexico, drug cartels boast of their ability to murder reporters. In Burma, the army kills a reporter who dares report its activities.
The numbers are horrifying: over 1,000 media workers have been killed because of their work since 1992.
Every single time, the message is sent: don’t get involved; don’t ask questions; don’t do your job. No journalism here. No inconvenient truths, no dissenting voices.
With rare exceptions, those responsible for these crimes act with impunity. Sometimes, as in the case of Anna Politkovskaya, outspoken on war crimes in Chechnya, the man who pulled the trigger is traced but those who gave the orders remain untouched. In over 90 per cent of cases of attacks on journalists, there are no convictions.
There is no greater infringement of human rights than to deliberately take an innocent life. The killing of a journalist also signals contempt for the concept of free expression as a right. As the United Nation’s Plan of Action on the Safety of Journalists and the Issue of Impunity, states, violent attacks on journalists and free expression do not happen in a vacuum: “[T]he existence of laws that curtail freedom of expression (e.g. overly restrictive defamation laws), must be addressed. The media industry also must deal with low wages and improving journalistic skills. To whatever extent possible, the public must be made aware of these challenges in the public and private spheres and the consequences from a failure to act.”
In that famous final editorial, Lasantha Wickrematunge wrote: “In the course of the last few years, the independent media have increasingly come under attack. Electronic and print institutions have been burned, bombed, sealed and coerced. Countless journalists have been harassed, threatened and killed. It has been my honour to belong to all those categories.”
Like many journalists, Lasantha prided himself on bravery: there is no higher compliment in the profession than to call a colleague “courageous”.
But there is a danger in this that we create martyrs: that we become enamoured of the idea that a good journalist should die for the cause. That persecution and suffering are marks of valour.
They are not. Journalism should be intrepid, of course, but we shouldn’t accept the idea that intrepid journalism comes with a price. Journalism, the exercise of free expression, is a basic right both for practitioners and for the readers, viewers and listeners who benifit from it. They should be able to practice this right without fear of persecution from states, criminals or terrorists. If they are to suffer, their oppressors must face justice.
Correction 10:02, 10 November: An earlier version of this article stated that a government minister offered to buy the Sunday Leader.
Index on Censorship is mapping harassment and violence against journalists across the European Union and candidate countries at mediafreedom.ushahidi.com.
This article was posted on 6 November 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
2 Nov 2014 | Campaigns, Russia, Statements
Aleksandr Bastrykin
Head of the Investigative Committee of Russian Federation
The Investigative Committee of Russian Federation
105005, Russia, Moscow, Technicheskii Lane, 2
Sunday 2 November 2014
Dear Mr Bastrykin,
RE: Request for investigation into the murder of Akhmednabi Akhmednabiyev to be transferred to the Central Investigative Department of the Russian Federation’s Investigative Committee.
On the International Day to End Impunity for Crimes against Journalists (2 November) we, the undersigned organisations, are calling upon you, in your position as Head of the Investigative Committee of the Russian Federation, to help end the cycle of impunity for attacks on those who exercise their right to free expression in Russia.
We are deeply concerned regarding the failure of the Russian authorities to protect journalists in violation of international human rights standards and Russian law. We are highlighting the case of Ahkmednabi Akhmednabiyev, a Russian independent journalist who was shot dead in July 2013 as he left for work in Makhachkala, Dagestan. In his work as deputy editor of independent newspaper Novoye Delo, and a reporter for online news portal Caucasian Knot, Akhmednabiyev, 51, had actively reported on human rights violations against Muslims by the police and Russian army.
His death came six months after a previous assassination attempt carried out in a similar manner in January 2013. That attempt was wrongly logged by the police as property damage, and was only reclassified after the journalist’s death. This shows a shameful failure to investigate the motive behind the attack and prevent further attacks, despite a request from Akhmednabiyev for protection. The journalist had faced previous threats, including in 2009, when his name was on a hit-list circulating in Makhachkala, which also featured Khadjimurad Kamalov, who was gunned down in December 2011. The government’s failure to address these threats is a breach of the State’s “positive obligation” to protect an individual’s freedom of expression against attacks, as defined by European Court of Human Rights case law (Dink v. Turkey).
A year after Akhmednabiyev’s killing, with neither the perpetrators nor instigators identified, the investigation was suspended in July 2014. As well as ensuring impunity for his murder, such action sets a terrible precedent for future investigations into attacks on journalists in Russia. ARTICLE 19 joined the campaign to have his case reopened, and made a call for the Russian authorities to act during the United Nations Human Rights Council (HRC) session in September 2014. During the session, HRC members, including Russia, adopted a resolution on safety of journalists and ending impunity. States are now required to take a number of measures aimed at ending impunity for violence against journalists, including “ensuring impartial, speedy, thorough, independent and effective investigations, which seek to bring to justice the masterminds behind attacks”.
While the Dagestani branch of the Investigative Committee has now reopened the case, as of September 2014, more needs to be done in order to ensure impartial, independent and effective investigation. We are therefore calling on you to raise Akhmednabiyev’s case to the Office for the investigation of particularly important cases involving crimes against persons and public safety, under the Central Investigative Department of the Russian Federation’s Investigative Committee.
Sadly, Akhmednabiyev’s case is only one of many where impunity for murder remains. The investigations into the murders of journalists Khadjimurad Kamalov (2011), Natalia Estemirova (2009) and Mikhail Beketov (who died in 2013, from injuries sustained in a violent attack in 2008), amongst others have stalled. The failure to bring both the perpetrators and instigators of these attacks to justice is contributing to a climate of impunity in the country, and poses a serious threat to freedom of expression.
Cases of violence against journalists must be investigated in an independent, speedy and effective manner and those at risk provided with immediate protection.
Yours Sincerely,
ARTICLE 19
Amnesty International
Albanian Media Institute
Association of Independent Electronic Media (Serbia)
Azerbaijan Human Rights Centre
Center for Civil Liberties (Ukraine)
Center for National and International Studies (Azerbaijan)
Civic Assistance Committee (Russia)
Civil Society and Freedom of Speech Initiative Center for the Caucasus
Committee to Protect Journalists
Glasnost Defence Foundation (Russia)
Helsinki Citizens’ Assembly – Vanadzor (Armenia)
Helsinki Committee of Armenia
Human Rights House Foundation
Human Rights Monitoring Institute (Lithuania)
Human Rights Movement “Bir Duino-Kyrgyzstan”
Memorial (Russia)
Moscow Helsinki Group
Norwegian Helsinki Committee
Index on Censorship
International Partnership for Human Rights
International Press Institute
International Youth Human Rights Movement
IREX Europe
Kazakhstan International Bureau for Human Rights and Rule of Law
Kharkiv Regional Foundation – Public Alternative (Ukraine)
PEN International
Public Verdict Foundation (Russia)
Reporters without Borders
The Kosova Rehabilitation Center for Torture Victims
World Press Freedom Committee
cc.
President of the Russian Federation
Vladimir Putin
23, Ilyinka Street, Moscow, 103132, Russia
Prosecutor General of the Russian Federation
Yury Chaika
125993, GSP-3, Moscow, Russia
st. B.Dmitrovka 15a
Minister of Justice of the Russian Federation
Alexander Konovalov
Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation
119991, GSP-1, Moscow, street Zhitnyaya, 14
Chairman of the Presidential Council for Civil Society and Human Rights
Mikhail Fedotov
103132, Russia, Moscow
Staraya Square, Building 4
Head of the Investigative Committee of the Russian Federation for the Republic of Dagestan
Edward Kaburneev
The Investigative Committee of the Russian Federation for the Republic of Dagestan
367015, Republic of Dagestan, Makhachkala,
Prospekt Imam Shamil, 70 A
Ambassador of the Permanent Delegation of the Russian Federation to UNESCO
H. E. Mrs Eleonora Mitrofanova
UNESCO House
Office MS1.23
1, rue Miollis 75732 Paris Cedex 15
15 Oct 2014 | Press Releases, Uncategorized

- Awards honour journalists, campaigners and artists fighting censorship globally
- Judges include journalist Mariane Pearl and human rights lawyer Sir Keir Starmer
- Nominate at www.indexoncensorship.org/nominations
Beginning today, nominations for the annual Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards 2015 are open. Now in their 15th year, the awards have honoured some of the world’s most remarkable free expression heroes – from Israeli conductor Daniel Barenboim to Syrian cartoonist Ali Farzat to education activist Malala Yousafzai.
The awards shine a spotlight on individuals fighting to speak out in the most dangerous and difficult of conditions. As Idrak Abbasov, 2012 award winner, said: “In Azerbaijan, telling the truth can cost a journalist their life… For the sake of this right we accept that our lives are in danger, as are the lives of our families. But the goal is worth it, since the right to truth is worth more than a life without truth.” Pakistani internet rights campaigner Shahzad Ahmad, a 2014 award winner, said the awards “illustrate to our government and our fellow citizens that the world is watching”.
Index invites the public, NGOs, and media organisations to nominate anyone they believe deserves to be part of this impressive peer group: a hall of fame of those who are at the forefront of tackling censorship. There are four categories of award: Campaigner (sponsored by Doughty Street Chambers); Digital Activism (sponsored by Google); Journalism (sponsored by The Guardian), and the Arts. Nominations can be made online via http://www.indexoncensorship.org/nominations
Winners will be flown to London for the ceremony, which takes place at The Barbican on March 18 2015. In addition, to mark the 15th anniversary of the Freedom of Expression awards, Index is inaugurating an Awards Fellowship to extend the benefits of the award. The fellowship will be open to all winners and will offer training and support to amplify their work for free expression. Fellows will become part of a world-class network of campaigners, activists and artists sharing best practice on tackling censorship threats internationally.
Jodie Ginsberg, CEO of Index, said: “The Index Freedom of Expression Awards is a chance for those whom others try to silence to have their voices heard. I encourage everyone, no matter where they are in the world, to nominate a free expression hero.”
The 2015 awards shortlist will be announced on January 27th 2015. Judges include journalist Mariane Pearl and human rights lawyer Sir Keir Starmer. The public will be asked to participate in selecting the winner of the Google Digital Activism award through a public vote beginning January 27th 2015. Sir Keir said: “Freedom of expression is part of the bedrock of civilised, democratic society. The Index on Censorship Awards have a material influence on promoting such freedom and both celebrating and protecting those who fight against censorship worldwide. That’s why Doughty Street Chambers chooses Index as its principal charity.”
For more information please contact David Heinemann: [email protected]
_______________________________________________________________________
NOTES FOR EDITORS
About Index on Censorship:
Index on Censorship is an international organisation that promotes and defends the right to freedom of expression. The inspiration of poet Stephen Spender, Index was founded in 1972 to publish the untold stories of dissidents behind the Iron Curtain and beyond. Today, we fight for free speech around the world, challenging censorship whenever and wherever it occurs. Index believes that free expression is the foundation of a free society and endorses Article 19 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which states: “Everyone has the right to freedom of opinion and expression.”
About The Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards:
The Index Freedom of Expression Awards recognise those deemed to be making the greatest impact in tackling censorship in their chosen area.
Awards categories:
Journalism – for impactful, original, unwavering journalism across all media (sponsored by The Guardian).
Campaigner – for campaigners and activists who have fought censorship and who challenge political repression (sponsored by Doughty St Chambers).
Digital Activism – for innovative uses of new technology to circumvent censorship and foster debate (sponsored by Google).
Arts – for artists and producers whose work asserts artistic freedom and battles repression and injustice.
Previous award winners include:
Journalism: Azadliq (Azerbaijan), Kostas Vaxevanis (Greece), Idrak Abbasov (Azerbaijan), Ibrahim Eissa (Egypt), Radio La Voz (Peru), Sunday Leader (Sri Lanka), Arat Dink (Turkey), Kareen Amer (Egypt), Sihem Bensedrine (Tunisia), Sumi Khan (Bangladesh), Fergal Keane (Ireland), Anna Politkovskaya (Russia), Mashallah Shamsolvaezin (Iran)
Digital/New Media: Bassel Khartabil (Palestine/Syria), Freedom Fone (Zimbabwe), Nawaat (Tunisia), Twitter (USA), Psiphon (Canada), Centre4ConstitutionalRights (US), Wikileaks
Advocacy: Malala Yousafzai (Pakistan), Nabeel Rajab (Bahrain), Gao Zhisheng (China), Heather Brooke (UK), Malik Imtiaz Sarwar (Malaysia), U.Gambira (Burma), Siphiwe Hlope (Swaziland), Beatrice Mtetwa (Zimbabwe), Hashem Aghajari (Iran)
Arts: Zanele Muholi (South Africa), Ali Farzat (Syria), MF Husain (India), Yael Lerer/Andalus Publishing House (Israel), Sanar Yurdatapan (Turkey)
You have received this email because email address ‘[email protected]’ is subscribed to ‘AWARDS 2015 Call For Nominations’.

![People taking part in the funeral procession of Lasantha Wickrematunge (By Indi Samarajiva [CC-BY-2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://www.indexoncensorship.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/11/Lasantha_Wickrematunge_funeral_banners_1.jpg)

