9 Feb 2016 | About Index, Awards, Events, mobile, Press Releases

An Aleppo-based journalist training women to report on the crisis in war-torn Syria, an Indonesian comic who jokes about Islamic extremism and a 19-year-old campaigner against repression in Eritrea are among those shortlisted for the 2016 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards.
Drawn from more than 400 crowdsourced nominations, the Index awards shortlist celebrates artists, writers, journalists and campaigners tackling censorship and fighting for freedom of expression. Many of the 20 shortlisted nominees are regularly targeted by authorities or by criminal and extremist groups for their work: some face regular death threats, others criminal prosecution.
Judges for this year’s awards are Nobel Prize-winning author Wole Soyinka, pianist James Rhodes, tech entrepreneur Bindi Karia, Colombian journalist Maria Teresa Ronderos, human rights lawyer Kirsty Brimelow QC and Bahraini campaigner Nabeel Rajab.
“Censorship is not something that happens ‘somewhere else’,” said Jodie Ginsberg, CEO of Index on Censorship. “It occurs on a daily basis in every country, in every part of the world. The shortlist honours those who are among the bravest and most creative in tackling such threats.”
Awards are offered in four categories: journalism; arts; campaigning; and digital activism.
Nominees include Good Chance Theatre who work in the infamous “Jungle” refugee camp in Calais, France; imprisoned Bahraini academic and blogger Dr Abduljalil Al-Singace, who has continued to protest in prison despite being subjected to torture and abuse for daring to speak out on human rights abuses in his country; GreatFire, an anonymous group that battles China’s severe web censorship; and Pravit Rojanaphruk, a veteran reporter who was arrested, interrogated and forced out of his job for criticising Thailand’s military government.
Other nominees include Zaina Erhaim, who returned to her native Syria to report on the conflict and train women to tell unreported stories; Sakdiyah Ma’ruf, a female Muslim stand-up comedian from Indonesia; and campaigner Nkosilathi Emmanuel Moyo, a Zimbabwean who fights corruption in his country, currently in hiding after sending Robert Mugabe a prison uniform for his 92nd birthday this month.
Winners, who will be announced at a gala ceremony in London on 13 April, become Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards Fellows and are given support for their work.
“How do you fight for free expression beyond a moment? How do you keep it alive? You must remember how stressful it is for people on the ground. This fellowship, following us for a year, it is a good idea,” said Rafael Marques de Morais, Freedom of Expression Award winner for Journalism in 2015.
Notes for editors:
- Index on Censorship is a UK-based non-profit organisation that publishes work by censored writers and artists and campaigns against censorship worldwide.
- More detail about each of the nominees is included below.
- The winners will be announced at a ceremony at The Unicorn Theatre, London, on 13 April.
For more information, or to arrange interviews with any of those shortlisted, please contact: David Heinemann on 0207 260 2660. More biographical information and photos of the nominees are available at awards.indexoncensorship.org
Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards nominees 2016
Arts
Belarus Free Theatre and The Ministry of Counterculture (UK/Belarus)
Ten-year-old Belarus Free Theatre has been using their creative and subversive art to protest the dictatorial rule of Aleksandr Lukashenko for a decade
Tania Bruguera (Cuba)
American-Cuban artist Tania Bruguera, who uses art to campaign for greater openness in Cuban society, was arrested after attempting to stage her play #YoTambienExijo at a festival in Havana. It is now a global movement
Good Chance Theatre (UK)
Good Chance works in the infamous Jungle refugee camp in Calais, France, to provide a space for refugees to express themselves
Sakdiyah Ma’ruf (Indonesia)
Sakdiyah Ma’ruf is a female Muslim stand-up comedian from Indonesia who challenges Islamic fundamentalism and advocates for women’s rights
Murad Subay (Yemen)
Artist Murad Subay uses his country’s streets as a canvas to protest Yemen’s war, institutionalised corruption and forced “disappearings”
Campaigning
Abduljalil Al-Singace (Bahrain)
Dr. Abduljalil Al- Singace is an imprisoned Bahraini human rights activist, academic and blogger who has not let prison stop him from calling attention to his country’s human rights practices
Vanessa Berhe (US)
University student Vanessa Berhe is fighting for the release of her uncle, Eritrean journalist Seyoum Tsehaye, and for freedom of expression in Eritrea, one of the world’s worst most censored countries
Bolo Bhi (Pakistan)
A women-lead digital rights campaigning group who have orchestrated an impressive effort to turn back the Pakistani government’s draconian attempt to censor the internet
Nkosilathi Emmanuel Moyo (Zimbabwe)
Prolific author and activist Nkosilathi Emmanuel Moyo campaigned against political corruption and worked with young people to foster human rights
Pu Zhiqiang (China)
A human rights lawyer who represented Ai Weiwei, Pu Zhiqiang has been targeted by China’s authorities for his unwavering support of free speech
Digital Advocacy
Dokuz8 Haber and Gökhan Biçici (Turkey)
Journalist Gökhan Biçici launched citizen news agency Dokuz8Haber to foster uncensored information and strengthen Turkish democracy, circumventing intense press censorship
GreatFire (China)
GreatFire campaigns for transparency of Chinese censorship by providing numerous effective circumvention tools to the “Great Firewall”
Love Matters (international)
An international platform dedicated to opening up conversation about sexual health in countries where such subjects are censored or taboo
Mexicoleaks (Mexico)
An anonymous news-sharing platform seeking to bring more transparency to Mexico’s society by uncovering corruption
Hebib Muntezir (Azerbaijan)
An exiled Azerbaijani activist and blogger, who works with Meydan TV, mobilising social media to get uncensored news to a surprising number of his fellow citizens
Journalism
Zaina Erhaim (Syria)
One of the few female journalists still reporting from Syria, Zaina Erhaim of Aleppo works to train women to tell the story of the war-ravaged country
Mada Masr (Egypt)
Mada Masr is an independent news cooperative launched to offer an alternative narrative to government-controlled media
Hamid Mir (Pakistan)
Hamid Mir, a television journalist whose 30-year-career has been punctuated by threats, physical assaults, abductions and assassination attempts for taking on unchallenged powers in Pakistan
Pravit Rojanaphruk (Thailand)
Pravit Rojanaphruk is a veteran reporter who was arrested, interrogated and forced to resign for speaking out against Thailand’s lèse majesté law and military government
Ferit Tunç (Turkey)
Ferit Tunç is a Kurdish journalist who set up an independent newspaper in eastern Turkey and used inventive methods including publishing recipes with hidden messages to challenge censorship of his reporting on corruption
7 Jan 2016 | France, Mapping Media Freedom, News and features, Statements, United Kingdom

When I started working at Index on Censorship, some friends (including some journalists) asked why an organisation defending free expression was needed in the 21st century. “We’ve won the battle,” was a phrase I heard often. “We have free speech.”
There was another group who recognised that there are many places in the world where speech is curbed (North Korea was mentioned a lot), but most refused to accept that any threat existed in modern, liberal democracies.
After the killing of 12 people at the offices of French satirical magazine Charlie Hebdo, that argument died away. The threats that Index sees every day – in Bangladesh, in Iran, in Mexico, the threats to poets, playwrights, singers, journalists and artists – had come to Paris. And so, by extension, to all of us.
Those to whom I had struggled to explain the creeping forms of censorship that are increasingly restraining our freedom to express ourselves – a freedom which for me forms the bedrock of all other liberties and which is essential for a tolerant, progressive society – found their voice. Suddenly, everyone was “Charlie”, declaring their support for a value whose worth they had, in the preceding months, seemingly barely understood, and certainly saw no reason to defend.
The heartfelt response to the brutal murders at Charlie Hebdo was strong and felt like it came from a united voice. If one good thing could come out of such killings, I thought, it would be that people would start to take more seriously what it means to believe that everyone should have the right to speak freely. Perhaps more attention would fall on those whose speech is being curbed on a daily basis elsewhere in the world: the murders of atheist bloggers in Bangladesh, the detention of journalists in Azerbaijan, the crackdown on media in Turkey. Perhaps this new-found interest in free expression – and its value – would also help to reignite debate in the UK, France and other democracies about the growing curbs on free speech: the banning of speakers on university campuses, the laws being drafted that are meant to stop terrorism but which can catch anyone with whom the government disagrees, the individuals jailed for making jokes.
And, in a way, this did happen. At least, free expression was “in vogue” for much of 2015. University debating societies wanted to discuss its limits, plays were written about censorship and the arts, funds raised to keep Charlie Hebdo going in defiance against those who would use the “assassin’s veto” to stop them. It was also a tense year. Events discussing hate speech or cartooning for which six months previously we might have struggled to get an audience were now being held to full houses. But they were also marked by the presence of police, security guards and patrol cars. I attended one seminar at which a participant was accompanied at all times by two bodyguards. Newspapers and magazines across London conducted security reviews.
But after the dust settled, after the initial rush of apparent solidarity, it became clear that very few people were actually for free speech in the way we understand it at Index. The “buts” crept quickly in – no one would condone violence to deal with troublesome speech, but many were ready to defend a raft of curbs on speech deemed to be offensive, or found they could only defend certain kinds of speech. The PEN American Center, which defends the freedom to write and read, discovered this in May when it awarded Charlie Hebdo a courage award and a number of novelists withdrew from the gala ceremony. Many said they felt uncomfortable giving an award to a publication that drew crude caricatures and mocked religion.

Index’s project Mapping Media Freedom recorded 745 violations against media freedom across Europe in 2015.
The problem with the reaction of the PEN novelists is that it sends the same message as that used by the violent fundamentalists: that only some kinds of speech are worth defending. But if free speech is to mean anything at all, then we must extend the same privileges to speech we dislike as to that of which we approve. We cannot qualify this freedom with caveats about the quality of the art, or the acceptability of the views. Because once you start down that route, all speech is fair game for censorship – including your own.
As Neil Gaiman, the writer who stepped in to host one of the tables at the ceremony after others pulled out, once said: “…if you don’t stand up for the stuff you don’t like, when they come for the stuff you do like, you’ve already lost.”
Index believes that speech and expression should be curbed only when it incites violence. Defending this position is not easy. It means you find yourself having to defend the speech rights of religious bigots, racists, misogynists and a whole panoply of people with unpalatable views. But if we don’t do that, why should the rights of those who speak out against such people be defended?
In 2016, if we are to defend free expression we need to do a few things. Firstly, we need to stop banning stuff. Sometimes when I look around at the barrage of calls for various people to be silenced (Donald Trump, Germaine Greer, Maryam Namazie) I feel like I’m in that scene from the film Lock, Stock and Two Smoking Barrels where a bunch of gangsters keep firing at each other by accident and one finally shouts: “Could everyone stop getting shot?” Instead of demanding that people be prevented from speaking on campus, debate them, argue back, expose the holes in their rhetoric and the flaws in their logic.
Secondly, we need to give people the tools for that fight. If you believe as I do that the free flow of ideas and opinions – as opposed to banning things – is ultimately what builds a more tolerant society, then everyone needs to be able to express themselves. One of the arguments used often in the wake of Charlie Hebdo to potentially excuse, or at least explain, what the gunmen did is that the Muslim community in France lacks a voice in mainstream media. Into this vacuum, poisonous and misrepresentative ideas that perpetuate stereotypes and exacerbate hatreds can flourish. The person with the microphone, the pen or the printing press has power over those without.
It is important not to dismiss these arguments but it is vital that the response is not to censor the speaker, the writer or the publisher. Ideas are not challenged by hiding them away and minds not changed by silence. Efforts that encourage diversity in media coverage, representation and decision-making are a good place to start.
Finally, as the reaction to the killings in Paris in November showed, solidarity makes a difference: we need to stand up to the bullies together. When Index called for republication of Charlie Hebdo’s cartoons shortly after the attacks, we wanted to show that publishers and free expression groups were united not by a political philosophy, but by an unwillingness to be cowed by bullies. Fear isolates the brave – and it makes the courageous targets for attack. We saw this clearly in the days after Charlie Hebdo when British newspapers and broadcasters shied away from publishing any of the cartoons featuring the Prophet Mohammed. We need to act together in speaking out against those who would use violence to silence us.
As we see this week, threats against freedom of expression in Europe come in all shapes and sizes. The Polish government’s plans to appoint the heads of public broadcasters has drawn complaints to the Council of Europe from journalism bodies, including Index, who argue that the changes would be “wholly unacceptable in a genuine democracy”.
In the UK, plans are afoot to curb speech in the name of protecting us from terror but which are likely to have far-reaching repercussions for all. Index, along with colleagues at English PEN, the National Secular Society and the Christian Institute will be working to ensure that doesn’t happen. This year, as every year, defending free speech will begin at home.
16 Dec 2015 | Awards, Events, mobile, Press Releases
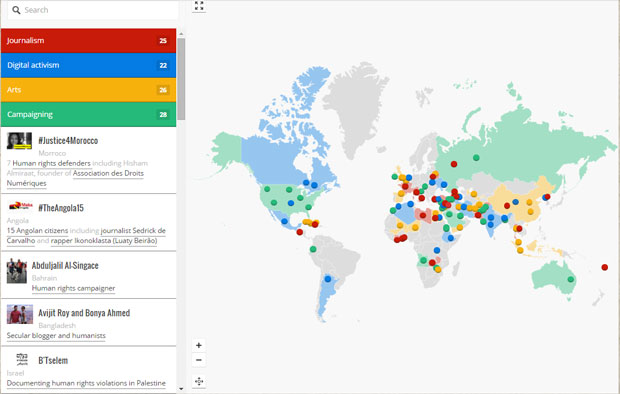
A graffiti artist who paints murals in war-torn Yemen, a jailed Bahraini academic and the Ethiopia’s Zone 9 bloggers are among those honoured in this year’s #Index100 list of global free expression heroes.
Selected from public nominations from around the world, the #Index100 highlights champions against censorship and those who fight for free expression against the odds in the fields of arts, journalism, activism and technology and whose work had a marked impact in 2015.
Those on the long list include Chinese human rights lawyer Pu Zhiqiang, Angolan journalist Sedrick de Carvalho, website Raqqa is Being Slaughtered Silently and refugee arts venue Good Chance Calais. The #Index100 includes nominees from 53 countries ranging from Azerbaijan to China to El Salvador and Zambia, and who were selected from around 500 public nominations.
“The individuals and organisations listed in the #Index100 demonstrate courage, creativity and determination in tackling threats to censorship in every corner of globe. They are a testament to the universal value of free expression. Without their efforts in the face of huge obstacles, often under violent harassment, the world would be a darker place,” Index on Censorship CEO Jodie Ginsberg said.
Those in the #Index100 form the long list for the Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards to be presented in April. Now in their 16th year, the awards recognise artists, journalists and campaigners who have had a marked impact in tackling censorship, or in defending free expression, in the past year. Previous winners include Nobel Peace Prize winner Malala Yousafzai, Argentina-born conductor Daniel Barenboim and Syrian cartoonist Ali Ferzat.
A shortlist will be announced in January 2016 and winners then selected by an international panel of judges. This year’s judges include Nobel Prize winning author Wole Soyinka, classical pianist James Rhodes and award-winning journalist María Teresa Ronderos. Other judges include Bahraini human rights activist Nabeel Rajab, tech “queen of startups” Bindi Karia and human rights lawyer Kirsty Brimelow QC.
The winners will be announced on 13 April at a gala ceremony at London’s Unicorn Theatre.
The awards are distinctive in attempting to identify individuals whose work might be little acknowledged outside their own communities. Judges place particular emphasis on the impact that the awards and the Index fellowship can have on winners in enhancing their security, magnifying the impact of their work or increasing their sustainability. Winners become Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards Fellows and are given support for the year after their fellowship on one aspect of their work.
“The award ceremony was aired by all community radios in northern Kenya and reached many people. I am happy because it will give women courage to stand up for their rights,” said 2015’s winner of the Index campaigning award, Amran Abdundi, a women’s rights activist working on the treacherous border between Somalia and Kenya.
Each member of the long list is shown on an interactive map on the Index website where people can find out more about their work. This is the first time Index has published the long list for the awards.
For more information on the #Index100, please contact [email protected] or call 0207 260 2665.
21 Oct 2015 | About Index, Academic Freedom, Counter Terrorism, Digital Freedom, Digital Freedom Statements, News and features, Statements
Good morning.
First I would like to thank the Internet Librarian International conference for inviting me to speak to you this morning. It is an honour to speak to a group of people who have been so important in forming me as a person. As a child I was the kind of person who got six books out of the library on a Saturday afternoon and had read all of them by Monday morning. I was addicted to reading, hooked on the spellbinding power and beauty of words.
Today I am very proud to work for an organisation that defends expression in all its forms; one that recognises not only the power of words, but also of images, of music, of performance – to convey ideas, thoughts, opinions and feelings.
In this morning’s talk I want to talk about how we balance what often seems like competing rights: the rights to privacy, security – the right to life – and freedom of expression in an information age. I want to argue that these should not be seen as mutually exclusive rights but importantly symbiotic rights, which must co-exist equally for the other to survive. I will illustrate this from examples from our work at Index on Censorship, and consider some of the challenges and causes for optimism for the next few years.
First, a little about Index on Censorship. Index on Censorship is a 43 year old organisation founded by the poet Stephen Spender in response to what seemed like a simple request: what could the artists and intellectuals of the West do to support their counterparts behind the Iron Curtain and those under the thumb of oppressive regimes elsewhere? Organisations like Amnesty and PEN already existed, doing then – as now – a formidable job of petitioning and campaigning, particularly on the cases of the imprisoned. What more could be done? The answer – those who established Index decided – was to publish the works of these censored writers and artists and stories about them. Index on Censorship magazine was born and we have continued to produce the magazine – this magazine – on at least a quarterly basis ever since. The motivation, as Stephen Spender wrote in the first edition of the magazine, was to act always with concern for those not free, responding to the appeals from Soviet writers to their Western counterparts. “The Russian writers,” Spender wrote, “seem to take it for granted that in spite of the ideological conditioning of the society in which they live, there is nevertheless an international community of scientists, writers and scholars thinking about the same problems and applying to them the same human values. These intellectuals regard certain guarantees of freedom as essential if they are to develop their ideas fruitfully… Freedom, for them, consists primarily of conditions which make exchange of ideas and truthfully recorded experiences possible.”
I will come back later to that notion of ‘conditions which make exchange of ideas possible’ as a central tenet of my argument regarding the essential interplay between privacy and free expression.
I hope you will allow me a brief pause before that, however, to describe to you the evolution of Index. Over time, Index has developed a campaigning and advocacy arm in addition to its publishing work, but we remain focused on the notion that it is that by providing a voice to the voiceless – by providing the information that others seek to keep from us – that we take the first important steps to overcoming censorship.
Why is it important to tackle censorship? Sometimes we forget to ask ourselves this question because we take it for granted that freedom is a good thing. Consider all those who were quick to shout ‘Je Suis Charlie’ following the attacks on French satirical magazine Charlie Hebdo – the knee jerk reaction in Western liberal democracies is often to say you are for free speech, without ever really stopping to consider why you might be for it. Or why free speech is and of itself a good thing.
I would argue this failure to understand the value of free speech lies at the heart of one of the dilemmas we face in modern democracies where free speech is being gradually eroded – where ‘Je Suis Charlie’ quickly became ‘Je Suis Charlie, but…’.
It is vital to understand the value inherent in free expression to understand why some of the current tensions between privacy and security on the one hand and free speech on the other exist. It is also crucial for understanding ways to tackle the dangerous trade offs that are increasingly being made in which free expression is seen as a right that can legitimately be traded off against privacy and security.
So forgive me for what might seem like making a small diversion to rehearse some of the arguments on the value of free expression. Locke, Milton, Voltaire have all written eloquently on the benefits of free expression, but I think Mill expresses it best when he talks of free expression being fundamental to the “permanent interests of man as a progressive being.” “The particular evil of silencing the expression of an opinion,” he argues in On Liberty, “is that it is robbing the human race… If the opinion is right, they are deprived of the opportunity of exchanging error for truth; if wrong, they lose, what is almost as great a benefit, the clearer perception and livelier impression of truth produced by its collision with error.”
This latter argument is particularly powerful when we consider, for example, the introduction of Holocaust denial laws. Such laws suggest that there are some truths so precious that they have to be protected by laws, rather than having their truth reinforced by repeated “collision with error.” You can imagine authoritarian regimes everywhere looking at such laws and rubbing their hands with glees at the prospect of being able to impose a single view of history on the populace, without any kind of challenge.
The free exchange of ideas, opinions, and information is in Mill’s – and others’ – doctrine a kind of positive cacophony from which clear sounds emerge. In this doctrine, it is not just the having of ideas, but the expressing of them that becomes vital. And it is here that those who would pit freedom of expression against privacy find grounds for the undermining of the latter. If the goal of free expression is the exchange of ideas for the better progression of mankind through the discovery of truths, then keeping ideas secret undermines that goal.
This is the particularly pervasive argument used in Western liberal democracies to justify surveillance. If you have nothing to hide, you have nothing to fear, the mantra goes: in liberal democracies, we’re not interested in your ideas, we’re just out to get the bad guys committing crimes. It shouldn’t stop you expressing yourself.
Except that it does. Anyone who has read Dave Eggers book The Circle will be familiar with a world in which privacy is demolished, in which every action and movement is recorded – in an inversion of Mill’s vision – for the betterment of society. The result is a world in which actions and habits are changed because there is no longer a private sphere in which thought and behaviour can developed. And it is a world that is not just a dystopian alternative reality. A study by the PEN American center earlier this year demonstrated that knowledge of mass surveillance by governments is already changing the way in which writers work. The report, Global Chilling, showed an astonishing one third of writers – 34 percent – living in countries deemed “free” – based on the level of political rights and civil liberties – have avoided writing or speaking on a particular topic, or have seriously considered it, due to fear of government surveillance. Some 42 percent of writers in “free countries” have curtailed or avoided activities on social media, or seriously considered it, due to fear of government surveillance, the survey found.
In countries that are not free, the consequence of a lack of privacy is acute. Colleagues in Azerbaijan, for example, note that authorities are quick to demonstrate the country’s openness by arguing a lack of curbs on social media.
As one commentator points out, such curbs are unnecessary, because as soon as an individual expresses an opinion unpalatable to government on an outlet such as Twitter, they are soon targeted, arrested, and jailed – often on spurious charges unrelated to free speech but which effectively at curbing it.
We are now also seeing, increasingly, the tactics pursued by illiberal regimes being adopted by supposedly liberal ones. Consider the use for example of UK anti-terror laws to snoop on the phone calls of the political editor of The Sun newspaper. British police used the Regulation of Investigatory Powers Act – legislation introduced explicitly to tackle terrorism – to obtain the phone records of Tom Newton Dunn for an investigation into whether one of its officers had leaked information about a political scandal, thereby seriously comprising the basic tenet of a free and independent media: the confidentiality of sources.
And such methods, indeed even the hardware, are being used elsewhere to quash free expression. As the journalist Iona Craig wrote for Index on Censorship magazine last year: “Governments going after journalists is nothing new. But what is increasingly apparent is that those listening and watching when we work in countries infamous for their consistent stifling of freedom of speech and obstruction of a free press, are often doing so with the infrastructure, equipment or direct support of supposedly “liberal” Western nations.
Craig, a regular reporter from Yemen, describes the phone tapping and other surveillance methods that put her and her sources at risk and how she and her colleagues are resorting to traditional methods of reporting – meeting contacts in person, using pen and paper, to evade surveillance.
Privacy, then, is vital for communication, for the free exchange of ideas and information. Index knows this from a long history that has ridden both the analogue and the digital wave. In our latest edition of the magazine, for example, retired primary school teacher Nancy Martinez Villareal recalls smuggling pieces of information to the Revolutionary Left Movement in Chile in documents hidden in lipstick tubes. Copies of our own magazine were smuggled into eastern Europe during the 1980s, by intrepid reporters hiding the copies under bunches of then much-coveted bananas. We ourselves now communicate with persecuted individuals in some of the world’s most repressive environments for free speech using encrypted communications such as PGP. Again in the latest edition of the magazine, Jamie Bartlett, director of the Centre for the Analysis of Social Media at the Demos think tank, writes about new auto-encryption email services such as Mailpile and Dark Mail that will allow private communication to evade the censors. In addition to these services, projects like Ethereum and Maidsafe are building an entirely new web out of the spare power and hard drive space of millions of computers put on the network by their owners. Because the network is distributed across all these individual computers, it is more or less impossible to censor.
Surveillance is just one example in which we see the argument of security being used to justify incursions into an array of civil liberties from privacy to free expression.
In fact, privacy campaigners have been at the forefront of campaigning against mass surveillance and other techniques.
And while I hope I have shown that privacy and free expression are both necessary so that the other can flourish, it would be remiss of me not to caution against any temptation to let privacy rights – which often appear all the more important in both an age of mass surveillance and a bare-all social media culture – trump freedom of expression in such a way that they prevent us, as per the Mill’s doctrine, coming closer to the truth.
It is for this reason that Index on Censorship opposed the so-called ‘Right to be Forgotten’ ruling made in Europe last year. Europe’s highest court ruled in May 2014 that ‘private’ individuals would now be able to ask search engines to remove links to information they considered irrelevant or outmoded. In theory, this sounds appealing. Which one of us would not want to massage the way in which we are represented to the outside world? Certainly, anyone who has had malicious smears spread about them in false articles, or embarrassing pictures posted of their teenage exploits, or even criminals whose convictions are spent and have the legal right to rehabilitation. In practice, though, the ruling is far too blunt, far too broad brush, and gives far too much power to the search engines.
The ruling came about after a Spanish man, Mario Costeja González requested the removal of a link to a digitised 1998 article in La Vanguardia newspaper about an auction for his foreclosed home, for a debt that he had subsequently paid. Though the article was true and accurate, Costeja Gonzalez argued that the fact this article was commonly returned in name searches gave an inaccurate picture of him. After hearing the case, the European Court of Justice ruled that search engines must remove links to any content that is “inadequate, irrelevant or no longer relevant”. The content itself is not deleted, but Google will not list it in search results.
Index warned at the time that the woolly wording of the ruling – its failure to include clear checks and balances, or any form of proper oversight – presented a major risk. Private companies like Google should not be the final arbiters of what should and should not be available for people to find on the internet. It’s like the government devolving power to librarians to decide what books people can read (based on requests from the public) and then locking those books away. There’s no appeal mechanism, very little transparency about how search engines arrive at decisions about what to remove or not, and very little clarity on what classifies as ‘relevant’. Privacy campaigners argue that the ruling offers a public interest protection element (politicians and celebrities should not be able to request the right to be forgotten, for example), but it is over simplistic to argue that simply by excluding serving politicians and current stars from the request process that the public’s interest will be protected.
We were not the only ones to express concern. In July last year the UK House of Lords’s EU Committee published a report claiming that the EU’s Right to be Forgotten is “unworkable and wrong”, and that it is based on out-dated principles.
“We do not believe that individuals should have a right to have links to accurate and lawfully available information about them removed, simply because they do not like what is said,” it said.
Here are some examples of stories from the UK’s Telegraph newspaper to which links have been removed since the ruling:
• A story about a British former convent girl who was jailed in France for running a ring of 600 call girls throughout Europe in 2003. Police were tipped-off about her operation by a former colleague following an argument.
• An article from 2008 about a former pupil from a leading boarding school who returned to his halls of residence after a night out drinking and drove his car around the grounds at speeds of 30mph before crashing. The Telegraph goes on to add: “He eventually collided with a set of steps in a scene reminiscent of the 1969 cult classic movie starring Michael Caine. His parents had given him the silver Mini just the day before.”
• A story which includes a section taken from the rambling “war plan” of Norwegian man Anders Behring Breivik to massacre 100 people.
• A story from 2009 on The Telegraph’s property page documenting how a couple and their two sons gave up pressured London life and moved into a rolling Devon valley.
Search engines removed such articles at the request of indviduals. Publishers have no real form of appeal against the decision, nor are the organisations told why the decision was made or who requested the removals. Though the majority of cases might be what privacy campaigners deem legitimate – such as smear campaigns – the ruling remains deeply problematic. We believe the ruling needs to be tightened up with proper checks and balances – clear guidelines on what can and should be removed (not leaving it to Google and others to define their own standards of ‘relevance’), demands for transparency from search engines on who and how they make decisions, and an appeals process. Without this, we could find that links to content that is true, factual, legitimately obtained – and indeed vitally relevant for the searcher, even if not deemed to be so by the individual – could be whitewashed from history.
In this way we see that protection of the individual, using notions of harm defined by the individual themselves – is used as an argument for censorship. I want to use the remainder of my talk to discuss ways in which this drive to shield from potential and perceived harm, is having an impact.
Let us start with libraries and the example of the United States’ Children’s Internet Protection Act (CIPA), which brought new levels of Internet censorship to libraries across the country. CIPA was signed into law in 2000 and found constitutional by the Supreme Court in 2003: two previous attempts at legislating in this area – the Communications Decency Act and the Child Online Protection Act, were held to be unconstitutional by the US Supreme Court on First Amendment grounds.
As the Electronic Frontier Foundation has written eloquently on this, the law is supposed to encourage public libraries and schools to filter child pornography and obscene or “harmful to minors” images from the library’s Internet connection. However, as with all such laws, the devil is in the implementation not the original intention.
Schools and libraries subject to CIPA must certify that the institution has adopted an internet safety policy that includes use of a “technology protection measure”— in other words filtering or blocking software — to keep adults from accessing images online that are obscene or child pornography. The filtering software must also block minors’ access to images that are “harmful to minors,” in other words, sexually explicit images that adults have a legal right to access but would be inappropriate for young people.
Only images, not text or entire websites, are legally required to be blocked. Libraries are not required to filter content simply because it is sexual in nature. Libraries aren’t required to block social networking sites, political sites, sites advocating for LGBT issues, or sites that explore controversial issues like euthanasia.
However, this is what happens – either through technological illiteracy or overzealous implementation.
As all of you will be aware, filters don’t work effectively. Not only can filters block perfectly legitimate content, they can also fail to block certain content that is obscene.
We saw this in the case of Homesafe, a network-level filter that was being offered by one of Britain’s largest internet providers. The filter was designed to block adult content on the network level, but in late 2011 IT expert Cherith Hateley demonstrated that the filter failed to block Pornhub, which offers thousands of free explicit videos and is ranked as the third largest pornography provider on the web. Hateley found that on the Pornhub website the HomeSafe blocking page had been relegated to a small box normally reserved for advertising, leaving its adult content fully accessible.
In addition to the challenge of poor filtering, there is the problem of transparency. We don’t know exactly what’s being blocked. There’s no documentation of which libraries are filtering what specific websites and most filtering technology companies keep their algorithms for blocking sites a closely guarded secret. Without clarity on precisely what is being blocked, by whom, and how often, it’s impossible to know what content is being filtered and therefore whether libraries are being over censorious.
Where does this leave ethics? Librarians play an important role in ensuring free speech online. The American Library Association’s code of ethics states: “We uphold the principles of intellectual freedom and resist all efforts to censor library resources.”
This impulse to protect from harm is also seeping away from internet controls and filters into the broader public discourse and nowhere is this more alarming than in universities. I want to argue that the impulse I described earlier – of a private realm that is so crucial for the development of ideas and in some cases their incubation and dissemination – is being warped by an extension of the idea of personal physical safety into a demand for a kind of safety from ideas that is shutting down debate more widely.
It is clear that something is going wrong at universities. Institutions that should be crucibles for new thinking, at the forefront of challenges to established thought and practice, are instead actively shutting down debate, and shying away from intellectual confrontation.
Driven by the notion that students should not be exposed to ideas they find – or might find – offensive or troubling, student groups and authorities are increasingly squeezing out free speech – by banning controversial speakers, denying individuals or groups platforms to speak, and eliminating the possibility of “accidental” exposure to new ideas through devices such as trigger warnings.
The trend was particularly noticeable last year when a number of invited speakers withdrew from university engagements – or had their invitations rescinded – following protests from students and faculty members. Former US Secretary of State Condoleezza Rice withdrew from a planned address at Rutgers University in New Jersey after opposition from those who cited her involvement in the Iraq war and the Bush administration’s torture of terrorism suspects; Brandeis University in Massachusetts cancelled plans to award an honorary degree to Islam critic Ayaan Hirsi Ali; and Christine Lagarde backed out of a speech at Smith College following objections by students over the acts of the International Monetary Fund, which Lagarde runs. In the UK, the University of East London banned an Islamic preacher for his views on homosexuality. And a new law – a counter-terrorism bill – was proposed in Britain that could be used to force universities to ban speakers considered “extremist”.
Registering your objection to something or someone is one thing. Indeed, the ability to do that is fundamental to free expression. Actively seeking to prevent that person from speaking or being heard is quite another. It is a trend increasingly visible in social media – and its appearance within universities is deeply troubling.
It is seen not just in the way invited speakers are treated, but it stretches to the academic fraternity itself. Last year, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign withdrew a job offer to academic Steven Salaita following critical posts he made on Twitter about Israel.
In an open letter, Phyllis Wise, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign chancellor, wrote: “A pre-eminent university must always be a home for difficult discussions and for the teaching of diverse ideas… What we cannot and will not tolerate at the University of Illinois are personal and disrespectful words or actions that demean and abuse either viewpoints themselves or those who express them. We have a particular duty to our students to ensure that they live in a community of scholarship that challenges their assumptions about the world but that also respects their rights as individuals.”
These incidents matter because, as education lecturer Joanna Williams wrote in The Telegraph newspaper: “If academic freedom is to be in anyway meaningful it must be about far more than the liberty to be surrounded by an inoffensive and bland consensus. Suppressing rather than confronting controversial arguments prevents criticality and the advance of knowledge, surely the antithesis of what a university should be about?”
Yet, increasingly, universities seem to want to shut down controversy, sheltering behind the dangerous notion that protecting people from anything but the blandest and least contentious ideas is the means to keep them “safe”, rather than encouraging students to have a wide base of knowledge. In the US, some universities are considering advising students that they don’t have to read material they may find upsetting, and if they don’t their course mark would not suffer. The introduction of “trigger warnings” at a number of universities is a serious cause for concern.
In the UK, increasing intolerance for free expression is manifest in the “no platform” movement – which no longer targets speakers or groups that incite violence against others, but a whole host of individuals and organisations that other groups simply find distasteful, or in some way disqualified from speaking on other grounds.
The decision to cancel an abortion debate at Oxford in late 2014, which would have been held between two men – and noted free speech advocates – came after a slew of objections, including a statement from the students’ union that decried the organisers for having the temerity to invite people without uteruses to discuss the issue. More recently, a human rights campaigner was barred from speaking at Warwick University – a decision that was subsequently overturned – after organisers were told she was “highly inflammatory and could incite hatred” and a feminist was banned from speaking at the University of Manchester because her presence was deemed to violate the student union’s “safe space” policy.
Encountering views that make us feel uncomfortable, that challenge our worldview are fundamental to a free society. Universities are places where that encounter should be encouraged and celebrated. They should not be places where ideas are wrapped in cotton wool, where academic freedom comes to mean having a single kind of approved thinking, or where only certain “approved” individuals are allowed to speak on a given topic.
Index on Censorship knows well the importance of the scholar in freedom of expression. Though we have come to be known as Index, the charity itself is officially called Writers and Scholars Educational Trust, an effort to capture as simply as possible the individuals whom we intended to support from the outset. The title was never intended to be exclusive, but the inclusion of “scholar” signals the importance our founders attached to the role of the academic as a defender and promoter of free speech. In 2015, as we watch the spaces for free expression narrow, I hope that together we can work doubly hard to ensure that traditional bastions for free speech – such as universities and indeed libraries – remain arena for the clash of ideas, not the closure of minds.




