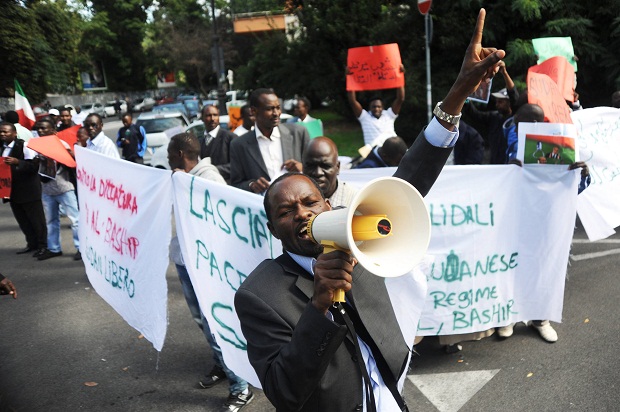12 Feb 2014 | Lebanon, Volume 42.04 Winter 2013

Publicity photograph for Will it Pass or Not?
(Image: http://bourjeily.com)
When writer Lucien Bourjeily made censorship the theme of his latest play, he knew he was in for a battle. And he was right. His play about censorship ended up being banned. Not surprisingly, he thinks this decision tells its own story about Lebanon today.
“Because the censorship law in Lebanon is so vague and elusive,” he says, artwork that might have received approval two years ago are “censored or banned today”. “In this climate of fear,” he adds, “the military obviously becomes more present in day-to-day life, tightening security (through countless check points in almost every corner of Lebanon) and tightening their grip on freedom of expression. For the near future, I fear that we will be hearing about more bans, more censorship, and more constraints on freedom of speech in Lebanon: censorship thrives when the state feels insecure or when it makes the common mistake of correlating security and freedom of expression.”
On 28 August, he was summoned to the Lebanese Censorship Bureau and told that his play, Will It Pass or Not?, could not go ahead. The play, which tackles the theme of censorship head on, poses the difficult question that any Lebanese artist who explores controversial or sensitive issues must consider. Prior to Bourjeily’s encounter with the interior ministry, the play was performed on university campuses to invited audiences instead of theatres. Members of the censorship board attended and broke up the performance, even though a loophole in the law meant that the play could legally be performed in the venue. So Bourjeily decided to test the board and submitted the play for their consideration. On 3 September 2013, the censorship board’s General Mounir Akiki appeared on television, presenting evidence from four so-called “critics” who insisted the play had no artistic merit and therefore would not be passed. Often, the board will recommend changes that will make an artistic work more palatable – a line removed, the omission of controversial material. But in this case, the play was simply rejected. Index decided to publish an extract of the play so readers could make their own minds up.
In this extract from Will It Pass or Not?–published for the first time in English–Lucien Bourjeily exposes the ridiculousness – and arbitrary nature – of the Lebanese Censorship Bureau, which commonly bans material that is deemed to be obscene, offensive to religions or politically sensitive. Use of this translated script is copyrighted, please contact the magazine editor at Index about use of this material
Scene 2
Sergeant Da’ja, 35, is at his desk, looking through some papers. Kareem, 27, a director, is sitting on a chair next to the desk
Kareem raises his hand.
Sergeant Da’ja How long have you been waiting?
Kareem About an hour.
Sergeant Da’ja What have you got?
Kareem A screenplay.
Sergeant Da’ja Go on then, show me.
Kareem Please, here you are.
Kareem passes Da’ja the screenplay.
Sergeant Da’ja You’ve been here before, haven’t you?
Kareem Yes, I submitted a request, but it just got sent back. Someone from your office contacted me.
Sergeant Da’ja Okay. But I can’t do anything with it. Revisions are done by Captain Shadid.
Kareem Can I see Captain Shadid?
Sergeant Da’ja When the Captain is willing to see you. You’ll have to wait.
Kareem I’ll wait.
Captain Shadid, 40, enters the room. Da’ja stands to attention.
Sergeant Da’ja Good day to you, sir.
Flustered, Da’ja shuffles his papers. Kareem raises his hand again but Da’ja ignores him. Da’ja enters the Captain’s office, stamps his foot on the ground and gives a military salute.
Captain Shadid What have we got today, then?
Sergeant Da’ja The Sun newspaper, as usual, sir.
Da’ja hands the newspaper to the captain.
Captain Shadid Madame Noha again, I suppose…
Sergeant Da’ja As usual, sir.
Captain Shadid Have you even read it, you little shit? No, no, no…Just the same old rubbish. Goodness me … What am I to do with her?
Sergeant Da’ja You know best, sir.
Captain Shadid Okay, what else have we got today? Are there many waiting out there?
Sergeant Da’ja There’s someone outside who’d like to speak to you … about his film script. It’s the tedious one about sectarianism in Lebanon and the guys who go to India and set up a secular state … and all that nonsense.
Captain Shadid Yes, yes, I remember. Show him in …
Sergeant Da’ja Yes, sir.
Da’ja stamps his feet and salutes, then leaves the room. Captain Shadid makes a phone call.
Captain Shadid Hi, Noha. Where are you? Come in to my office, please. I’d like a word.
Da’ja goes back to writing on his papers. Kareem raises his hand again.
Sergeant Da’ja Again? You’re an inquisitive type, aren’t you? Always asking questions… Okay, you can go in now.
Kareem enters Captain Shadid’s office. Captain Shadid is on the phone. He gestures to Kareem to give him the screenplay and then sit down.
Sergeant Da’ja Hello, sir. Er, one thing, sir. About your son?
Captain Shadid Yes, what about him?
Sergeant Da’ja There’s a match at 4pm today. Barcelona–Madrid. Who’s going to take him?
Captain Shadid Isn’t there anyone here? Isn’t Sobhi here?
Sergeant Da’ja Yes, Sobhi’s here.
Captain Shadid Well, send Sobhi then.
Sergeant Da’ja Yes, sir. Right you are, sir.
Captain Shadid Mr Kareem.
Kareem Yes, captain?
Captain Shadid Is this your first film?
Kareem It’s the first one I’ve decided to film, yes. It’s taken me three years to write the script.
Captain Shadid Three years and this is what you’ve got to show for yourself?
Kareem It means a lot to me. What do you mean by “this”?
Captain Shadid Listen, there’s something I want to tell you. I’m saying this to you like a brother to a brother. So, this film of yours … I’m afraid it just isn’t up to scratch. The script was 120 pages. But we’ve had to do quite a lot of work on it and it’s got a bit shorter … But it’s turned out great. Let’s take the title, to start with … I mean, how dare you use a name like that? Fucked Up until Judgment Day? Did you really think that was acceptable? Really? Where did you get that idea?
And then there’s the swearing … We counted it all up: you’ve got “fuck you” four times and “you son of a bitch” 14 times. I mean, do you really think that’s reasonable?
Kareem It’s meant to show this guy’s personality: he talks a lot of crap. It’s “dramatic tension”… it’s meant to reflect real life. People do speak like that in real life, captain.
Captain Shadid Lots of people do all kinds of things but it doesn’t mean it gets our approval, my dear man. We really couldn’t condone this character … so we’ve cut him out altogether. Dramatic tension or not: there were quite a few other things we’ve had to cut out too … Like the first scene, for example. So these guys storm out of their sectarian community and stand up to the cleric. You show the priest getting up to mischief and the sheikh taking bribes.
And these guys who just run away, off to India … We can’t have it like this. We’ve got to think of our country’s image, too. So we’ve cut out that whole scene. But don’t worry – we’ll replace it with another scene with the same ending … The guys can leave the country, that’s fine … and go to India … but for tourism instead. So we’re just changing the mood a bit. The film’s much nicer this way. Better to have a film showing a nice, pleasant world rather than this ugly nightmare you had originally. Tourists are great, so the whole idea is much nicer than the stuff with the clerics and the corruption and the bribes … And at the same time, this will encourage tourism: after all, Lebanon is a superb touristic destination.
Kareem But now the film has lost its entire meaning!
Captain Shadid What do you mean it’s lost its meaning? It’s got even more meaning now! Listen, we’re a country of diversity, of coexistence … Your film was very inflammatory. It made the country look like a well of sectarian conflict, where clerics are stirring up trouble and exploiting the country’s problems for their own political motives … No, no, no – we can’t have that.
Kareem But, sir, how can we solve our country’s problems if we don’t talk about them?
Captain Shadid Ha, ha, ha, ha, ha, ha … Ah, so you want to solve the country’s problems now, do you? With your film? Ah, that’s wonderful … Ha, ha, ha … Listen, I’ve got to uphold the law. There are certain parameters I have to work within. And the second scene, where they arrive in India and meet the Indian cleric … well, if he’s portrayed in a negative light, then – even if he’s Indian – it reflects negatively on Lebanese clerics, too. No, no, no – we can’t allow that. Why don’t we have him meeting someone else, instead – a salesman, perhaps? Something useful like that … The Lebanese are renowned for their business acumen, after all, and this would fit with the tourism angle. We’ve killed two birds with one stone … and made it all much simpler. This way, we can approve the text … As for the third scene [he looks down at the screenplay], well … I don’t really think the film needs to be 120 pages long. So, now we’ve got it down to 20 pages. It’s great… Better than nothing, anyway, so roll with it!
Kareem But, sir, now it’s just a short film!
Captain Shadid Yes, but why not? My niece made a lovely short film and it was a big hit at all the festivals round the world. What do you have against short films?
Kareem Sir, it’s just… [Gets a bit flustered] … It’s just I … I don’t understand how you’ve got it down to 20 pages!
Captain Shadid Khalas, come now – no need to get all hot and bothered. Honestly, I get hundreds of scripts on my desk every day and I assure you, your screenplay is much better this way. It’d make a lovely short film. God grant you success!
Kareem But, Captain Shadid, I’ve spent three years working on this script! Can’t we come to a compromise? Can’t we see if there are any smaller changes we could make instead?
Captain Shadid [answering the telephone] Hello? Yes, Brigadier-General. Certainly, sir. Yes, sir. I’m looking into the matter right now, sir.
Captain Shadid gestures to Kareem to see himself out of his office.
Kareem leaves the room and sits down on a chair in Sergeant Da’ja’s office. Da’ja enters. Kareem raises his hand again.
Sergeant Da’ja What, are you still here?
Scene 5
Noha enters Captain Shadid’s office.
Captain Shadid Hi.
Noha Are you angry?
Captain Shadid Me? Why would I be angry? My wife criticises my job day in day out… and today she’s gone as far as mentioning me by name! What did you have to go and put my name in for? Why?
Noha Darling, you’re the one who’s forbidden her from putting on the play.
Captain Shadid What do you mean forbidden?
Noha Well, what else am I supposed to say?
Captain Shadid Hmmm … So … What, have you been to see this play, then?
Noha Of course. But I doubt you have?
Captain Shadid She gets naked in it!
Noha What makes you say that? Have you even seen it?
Captain Shadid No, I’ve not been to see it… But I’ve heard plenty about it from the others. What difference does it make if I’ve seen it? It contains nudity! But, anyway, nudity or not… you shouldn’t be meddling in my work!
Noha I’m just doing the same with my work as you do with yours. As a journalist, I just express my opinion about things… and then you go and meddle in my work.
Captain Shadid My job is to enforce the law.
Noha Yes, and who wrote that law?
Captain Shadid Who wrote the law? Who? The law is in the name of the Lebanese people!
Noha What, so don’t you think the Lebanese people want to go to see this play? Because there’s never an empty seat in the theatre whenever I go.
Captain Shadid Listen, I’m just doing my job… What do you want me to do? I’m your husband… So? What do you want from me? You want me to abolish censorship? Shut down the entire directorate? Sit at home and twiddle my thumbs? Give 200 soldiers the boot?
Noha Yeah, yeah, very funny.
Captain Shadid Well, it’s just not acceptable. Every day, it’s the same old story with you. Isn’t there anything else in the country you could write about besides me?
Noha I’m not the first to write about politics and have you censor it! You’re always saying, “Give it up, girl. You’re just banging your head against a brick wall.” Well, what else should I write about? First, no politics… and now art is banned as well. What should I write about, then? I may as well throw in the towel and sit at home. Is that what you’d rather? You’re always trying to censor me just like those naked women that pile up on your desk.
Captain Shadid Well, we need censorship. What would life be like without any kind of oversight? It’d be carnage… Are we back in the dark ages living in a forest? Children need oversight, society needs oversight.
Noha You said it! Children need oversight – but we’re not children! I’m not a child and I want to see the plays I want to see…Man, living in a forest in the dark ages would be better than living with you.
Captain Shadid What do you want? Shall I get your editor to censor you or shall I pull the plug on your magazine? I mean it… Do you understand?
Noha Go ahead, then, censor it. Who’s going to rush out and buy it, anyway? You guys think it’s just “oversight”… but it’s not – it’s propaganda. And forbidding things just makes them more desirable.
Captain Shadid All right, enough. But just watch it, you. I can always divorce you!
Kareem is still waiting in Sergeant’s Da’ja’s office
Sergeant Da’ja So, your name’s Dalloum? Where are you from?
Kareem The Beqaa Valley.
Sergeant Da’ja Ah, Brigadier-General Dalloum is from Beqaa. Brigadier-General Damian Dalloum.
Kareem Damian Dalloum’s a great guy.
Sergeant Da’ja You know him?
Kareem He’s my father’s cousin.
Sergeant Da’ja Wallahi, no way! His cousin? His cousin? Gosh. Wait here a minute.
Da’ja enters the Captain’s office, stamps his foot on the ground and gives a military salute.
Sergeant Da’ja Er, excuse me, sir. The chap who’s just been in to see you this morning about the Indian film … from the Dalloum family.
Captain Shadid Yes, that’s all dealt with.
Sergeant Da’ja Yes, but he’s still here waiting … We’ve just been talking and it turns out that he’s a Dalloum Dalloum … He’s related to Brigadier-General Dalloum!
Captain Shadid Damian Dalloum?
Sergeant Da’ja Yes, sir…
Captain Shadid Well, why didn’t he say so?
Sergeant Da’ja I don’t know, sir, I don’t think he realised.
Captain Shadid What do you mean – he didn’t realise?
Sergeant Da’ja He didn’t realise that Brigadier-General Dalloum worked here in the directorate.
Captain Shadid How could he not know?
Sergeant Da’ja He might not have known. What would you like to do, sir?
Captain Shadid This film … we’ve had a look at it, right?
Sergeant Da’ja Yes … it’s a bit disrespectful in places, with some swearing … and the title’s rather strange …
Captain Shadid The film’s fine.
Sergeant Da’ja Yes, sir, there’s not really much to say about it.
Captain Shadid We could perhaps just change the title.
Sergeant Da’ja But it’s fine, otherwise.
Captain Shadid Yes, yes. What are you doing waiting out there? Show him in.
Sergeant Da’ja Yes, sir.
Da’ja steps back to his own office
Sergeant Da’ja The captain would like to see you.
Kareem stands up and enters Captain Shadid’s office
Captain Shadid Come in, Dalloum. Please, sit down. This is my wife, Noha. She writes for the Sun newspaper.
Kareem A pleasure to meet you. I always read your paper.
Captain Shadid Mr Kareem, your film is wonderful.
Kareem The short or the long version?
Captain Shadid No, the long version, of course! It’s a great film, wonderful!
Kareem But weren’t there a few things …?
Captain Shadid No, no. We’ve just gone back and had another look, and you were right: there’s not really anything to worry about. It’s very realistic, after all, and it’s got just the right amount of social and political criticism.
Kareem You mean, you’ll give me permission to film it?
Captain Shadid Yes, yes, of course. Don’t you fret! [To Noha] This film gets our full approval. You see: if it’s a great work of art, we approve it, and if it’s not, we don’t. It’s simple. Why do you always have to make such a mountain out of a molehill?
Captain Shadid God bless you, Mr Kareem. Go and see Sergeant Da’ja and he’ll sign it off.
Kareem Yes, captain. Thank you very much, sir!
Sergeant Da’ja Wallahi! So the captain has given you the go ahead?
Kareem steps back into Sergeant Da’ja’s office.
Kareem Yes, er …
Sergeant Da’ja He hasn’t changed the title?
Kareem No, it’s as it was.
Sergeant Da’ja It’s a wonderful film, very deep. It made a great impression on us all. I was the one who suggested that the captain had another look. So, I’ll just sign it off, and then you come back tomorrow for the permit – if it’s not too much trouble?
Kareem Not at all. It’s no trouble.
Sergeant Da’ja And Brigadier-General Dalloum will be here tomorrow too, so you can say hello. I’ll take you to see him. So, please, mind how you go. And what else have I forgotten? Ah yes, here’s my phone number, just in case.
Kareem Your number?
Sergeant Da’ja Yes, come to me direct, if there’s anything at all you need!
Use of this translated script is copyrighted, please contact the magazine editor at Index about use of this material
Translated by Ruth Ahmedzai Kemp
Director and filmmaker Lucien Bourjeily brought interactive, improvised theatre to Lebanese audiences, introducing the first improvisational theatre troupe, ImproBeirut, to the Middle East in 2008. His hard-hitting play 66 Minutes in Damascus, which draws on journalists’ and activists’ descriptions of Syrian detention centres, showcased at the London International Festival of Theatre in summer 2012, receiving critical acclaim. With Kiki Bokassa, he is the co-founder of the Visual and Performing Arts Association, which advocates the use of creative arts to help resolve social issues. Bourjeily is the winner of the 2009 British Council’s Young Creative Entrepreneur Award; he won the title of best director at the 2008 Beirut International Film Festival for his debut film Taht El Aaricha; and was awarded a Fulbright Scholarship in 2010, graduating with a Master in Fine Arts in Film from Loyola Marymount University (Los Angeles). He is also the author of Index on Censorship’s Tripwires manual.
This article was originally published in the Winter 2013 print edition of Index on Censorship magazine. It was posted to indexoncensorship.org on February 12, 2014
29 Jan 2014 | News, United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates stand accused of blocking criticism over their human rights record, according to international monitoring group Human Rights Watch.
Each year the organisation publishes a global assessment of human rights. This year marked their 24th annual review and summarised key human rights issues in more than 90 countries and territories worldwide, drawing on events from the end of 2012 to November 2013. The work is available for free from their website.
The report contained a 1,400 word chapter about United Arab Emirates, criticising the country for abuses carried out against migrant workers, womens rights, use of torture, arbitrary detention, a poor justice system and lack of political freedom.
Following its publication online, Mohammed Ahmed Al Murr, Speaker of UAE’s Federal National Council (FNC), denounced the report, telling a government meeting:
“It involves many fallacies that are not based on any foundation and contradict several other international organisations’ statements, which testify to the significant progress achieved by the UAE and its honourable record in various areas of human rights.”
His criticisms were published by the state news agency on 22nd January 2014.
That same day, a press event in Dubai was cancelled unexpectedly, when staff at the Novotel hotel told Human Rights Watch that a government permit to hold the event had not been obtained.
“The staff were nervous, they’d been put in a difficult position,” explained Nick McGeehan, Middle East Researcher for Human Rights Watch, who was due to speak at the event.
“They told us that our event had to be cancelled, because a permit had not been obtained.”
“So I asked “If I get this permit, can we run the event?” Then they told me that the room had already been given away to someone else. That’s when we realised the event had probably been prevented from going ahead by someone in the government,” McGeehan told Index on Censorship.
The launch of the report had been accompanied by a series of press conferences, kicking off in Berlin then covering Moscow, London, Sao Paolo, Washington DC, Jakarta and Johanesburg, as well as Tripoli, Sanaa, Kuwait City and Amman. Dubai was the only location where the press conference was not allowed to take place.
Human Rights Watch say they’ve held several news conferences in Dubai since 2005, without any requirement for an advance government permit. They also say they haven’t been able to find information about such laws or permit requirements from their research.
In February 2012, at the last Human Rights Watch news conference in Dubai, people who identified themselves as UAE government employees interrupted the event, stating that a permit was required. Following this incident, Human Rights Watch wrote to Shaikh Mohammad bin Rashid al-Maktoum of Dubai to request clarification, but say they received no reply.
“Blocking Human Rights Watch from holding a news conference in the UAE sadly underscores the increasing threat to freedom of expression in the country,” said Sarah Leah Whitson, Middle East and North Africa director at Human Rights Watch, in a statement issued on Human Rights Watch website. She was preparing for a planned trip to Dubai in just a few days.
“If the UAE wants to call itself a global media center, it needs to show that it respects freedom of speech and the open expression of critical ideas, not shut down media events,” she added.
Her statement was issued on 22 January – two days later she was barred from entering the country when she landed at Dubai airport for the start of a two day tour.
Whitson has traveled to the UAE on numerous occasions. An ex-Goldman Sachs lawyer who attended Harvard Law School in the same class as Barack Obama, she has conducted several human rights missions in the Middle East, including examining the impact of war and sanctions on the Iraqi civilian population, elections in Kurdish-controlled northern Iraq, and human rights issues in southern Lebanon.
Whitson’s boss, Kenneth Roth, stepped in when he heard news of her rejection at the border.
“These petty tactics by the UAE authorities only demonstrate the government’s intolerance of free speech and fear of critical discussion,” he said.
“Human Rights Watch will continue to document abuses in the UAE and to urge the government to comply with its most basic human rights obligations.”
In contrast to her reception in Dubai – Whitson went on to Yemen, where she meet with the transition government and had, according to the state news agency, a “fruitful” meeting. Human Rights Watch also levelled strong criticism at the Yemeni authorities in their annual report, accusing them of “failing to address multiple human rights challenges.”
Unable to hold the event as planned, Nick McGeehan stayed on for a day to was pulled aside by customs officials as he left Dubai, and told he had been permanently “blacklisted.” His colleague Tamara Alrifai, Advocacy and Communications director for the Middle East and North Africa division, who had also been scheduled to speak at the event, was told the same. The parting words from the customs officials, polite but firm, were allegedly “You are not welcome in my country.”
Human Rights Watch is an independent, nongovernmental organization, supported by contributions from private individuals and foundations worldwide. It accepts no government funds, directly or indirectly, and although based in the US, has been fiercely critical over issues such as Guantanamo Bay and the “war on drugs.” It also maintains offices all over the world and works closely with local activists.
This article was published on 29 January 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
15 Jan 2014 | Europe and Central Asia, European Union, Index Reports, News, Politics and Society
This article is part of a series based on our report, Time to Step Up: The EU and freedom of expression
Beyond its near neighbourhood, the EU works to promote freedom of expression in the wider world. To promote freedom of expression and other human rights, the EU has 30 ongoing human rights dialogues with supranational bodies, but also large economic powers such as China.
The EU and freedom of expression in China
The focus of the EU’s relationship with China has been primarily on economic development and trade cooperation. Within China some commentators believe that the tough public noises made by the institutions of the EU to the Chinese government raising concerns over human rights violations are a cynical ploy so that EU nations can continue to put financial interests first as they invest and develop trade with the country. It is certainly the case that the member states place different levels of importance on human rights in their bilateral relationships with China than they do in their relations with Italy, Portugal, Romania and Latvia. With China, member states are often slow to push the importance of human rights in their dialogue with the country. The institutions of the European Union, on the other hand, have formalised a human rights dialogue with China, albeit with little in the way of tangible results.
The EU has a Strategic Partnership with China. This partnership includes a political dialogue on human rights and freedom of the media on a reciprocal basis.[1] It is difficult to see how effective this dialogue is and whether in its present form it should continue. The EU-China human rights dialogue, now 14 years old, has delivered no tangible results.The EU-China Country Strategic Paper (CSP) 2007-2013 on the European Commission’s strategy, budget and priorities for spending aid in China only refers broadly to “human rights”. Neither human rights nor access to freedom of expression are EU priorities in the latest Multiannual Indicative Programme and no money is allocated to programmes to promote freedom of expression in China. The CSP also contains concerning statements such as the following:
“Despite these restrictions [to human rights], most people in China now enjoy greater freedom than at any other time in the past century, and their opportunities in society have increased in many ways.”[2]
Even though the dialogues have not been effective, the institutions of the EU have become more vocal on human rights violations in China in recent years. For instance, it included human rights defenders, including Ai Weiwei, at the EU Nobel Prize event in Beijing. The Chinese foreign ministry responded by throwing an early New Year’s banquet the same evening to reduce the number of attendees to the EU event. When Ai Weiwei was arrested in 2011, the High Representative for Foreign Affairs Catherine Ashton issued a statement in which she expressed her concerns at the deterioration of the human rights situation in China and called for the unconditional release of all political prisoners detained for exercising their right to freedom of expression.[3] The European Parliament has also recently been vocal in supporting human rights in China. In December 2012, it adopted a resolution in which MEPs denounced the repression of “the exercise of the rights to freedom of expression, association and assembly, press freedom and the right to join a trade union” in China. They criticised new laws that facilitate “the control and censorship of the internet by Chinese authorities”, concluding that “there is therefore no longer any real limit on censorship or persecution”. Broadly, within human rights groups there are concerns that the situation regarding human rights in China is less on the agenda at international bodies such as the Human Rights Council[4] than it should be for a country with nearly 20% of the world’s population, feeding a perception that China seems “untouchable”. In a report on China and the International Human Rights System, Chatham House quotes a senior European diplomat in Geneva, who argues “no one would dare” table a resolution on China at the HRC with another diplomat, adding the Chinese government has “managed to dissuade states from action – now people don’t even raise it”. A small number of diplomats have expressed the view that more should be done to increase the focus on China in the Council, especially given the perceived ineffectiveness of the bilateral human rights dialogues. While EU member states have shied away from direct condemnation of China, they have raised freedom of expression abuses during HRC General Debates.
The Common Foreign and Security Policy and human rights dialogues
The EU’s Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) is the agreed foreign policy of the European Union. The Maastricht Treaty of 1993 allowed the EU to develop this policy, which is mandated through Article 21 of the Treaty of the European Union to protect the security of the EU, promote peace, international security and co-operation and to consolidate democracy, the rule of law and respect for human rights and fundamental freedom. Unlike most EU policies, the CFSP is subject to unanimous consensus, with majority voting only applying to the implementation of policies already agreed by all member states. As member states still value their own independent foreign policies, the CFSP remains relatively weak, and so a policy that effectively and unanimously protects and promotes rights is at best still a work in progress. The policies that are agreed as part of the Common Foreign and Security Policy therefore be useful in protecting and defending human rights if implemented with support. There are two key parts of the CFSP strategy to promote freedom of expression, the External Action Service guidelines on freedom of expression and the human rights dialogues. The latter has been of variable effectiveness, and so civil society has higher hopes for the effectiveness of the former.
The External Action Service freedom of expression guidelines
As part of its 2012 Action Plan on Human Rights and Democracy, the EU is working on new guidelines for online and offline freedom of expression, due by the end of 2013. These guidelines could provide the basis for more active external policies and perhaps encourage a more strategic approach to the promotion of human rights in light of the criticism made of the human rights dialogues.
The guidelines will be of particular use when the EU makes human rights impact assessments of third countries and in determining conditionality on trade and aid with non-EU states. A draft of the guidelines has been published, but as these guidelines will be a Common Foreign and Security Policy document, there will be no full and open consultation for civil society to comment on the draft. This is unfortunate and somewhat ironic given the guidelines’ focus on free expression. The Council should open this process to wider debate and discussion.
The draft guidelines place too much emphasis on the rights of the media and not enough emphasis on the role of ordinary citizens and their ability to exercise the right to free speech. It is important the guidelines deal with a number of pressing international threats to freedom of expression, including state surveillance, the impact of criminal defamation, restrictions on the registration of associations and public protest and impunity against human right defenders. Although externally facing, the freedom of expression guidelines may also be useful in indirectly establishing benchmarks for internal EU policies. It would clearly undermine the impact of the guidelines on third parties if the domestic policies of EU member states contradict the EU’s external guidelines.
Human rights dialogues
Another one of the key processes for the EU to raise concerns over states’ infringement of the right to freedom of expression as part of the CFSP are the human rights dialogues. The guidelines on the dialogues make explicit reference to the promotion of freedom of expression. The EU runs 30 human rights dialogues across the globe, with the key dialogues taking place in China (as above), Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Georgia and Belarus. It also has a dialogues with the African Union, all enlargement candidate countries (Croatia, the former Yugoslav republic of Macedonia and Turkey), as well as consultations with Canada, Japan, New Zealand, the United States and Russia. The dialogue with Iran was suspended in 2006. Beyond this, there are also “local dialogues” at a lower level, with the Heads of EU missions, with Cambodia, Bangladesh, Egypt, India, Israel, Jordan, Laos, Lebanon, Morocco, Pakistan, the Palestinian Authority, Sri Lanka, Tunisia and Vietnam. In November 2008, the Council decided to initiate and enhance the EU human rights dialogues with a number of Latin American countries.
It is argued that because too many of the dialogues are held behind closed doors, with little civil society participation with only low-level EU officials, it has allowed the dialogues to lose their importance as a tool. Others contend that the dialogues allow the leaders of EU member states and Commissioners to silo human rights solely into the dialogues, giving them the opportunity to engage with authoritarian regimes on trade without raising specific human rights objections.
While in China and Central Asia the EU’s human rights dialogues have had little impact, elsewhere the dialogues are more welcome. The EU and Brazil established a Strategic Partnership in 2007. Within this framework, a Joint Action Plan (JAP) covering the period 2012-2014 was endorsed by the EU and Brazil, in which they both committed to “promoting human rights and democracy and upholding international justice”. To this end, Brazil and the EU hold regular human rights consultations that assess the main challenges concerning respect for human rights, democratic principles and the rule of law; advance human rights and democracy policy priorities and identify and coordinate policy positions on relevant issues in international fora. While at present, freedom of expression has not been prioritised as a key human rights challenge in this dialogue, the dialogues are seen by both partners as of mutual benefit. It is notable that in the EU-Brazil dialogue both partners come to the dialogues with different human rights concerns, but as democracies. With criticism of the effectiveness and openness of the dialogues, the EU should look again at how the dialogues fit into the overall strategy of the Union and its member states in the promotion of human rights with third countries and assess whether the dialogues can be improved.
[1] It covers both press freedom for the Chinese media in Europe and also press freedom for European media in China.
[2] China Strategy Paper 2007-2013, Annexes, ‘the political situation’, p. 11
[3] “I urge China to release all of those who have been detained for exercising their universally recognised right to freedom of expression.”
[4] Interview with European diplomat, February 2013.
8 Jan 2014 | News, Volume 42.04 Winter 2013
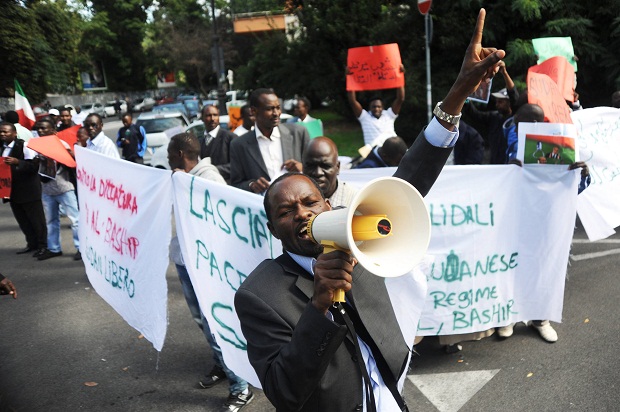
Dozens of protesters in front of the Sudanese Embassy in Rome October 2013 to protest of the alleged human rights abuses in Sudan (Image Marco Zeppetella/Demotix)
In the latest magazine issue of Index on Censorship the Bishop of Bradford Nick Baines reflects on his first visit to Sudan, a country whose leader strongly believes in one religion and one language for all.
Freedom of expression is of universal importance, but its absence is sometimes more easily seen through the lens of a different culture. The familiar landscape of “home” can sometimes hinder a proper appreciation of the absence of freedoms, being outside of one’s comfort zone can heighten awareness of reality. In this article I want to approach the matter from the outside in.
Early in 2013 I visited Sudan for the first time. The diocese of Bradford has had a partnership with Sudan for 30 years, and I was linked for a decade with Anglican dioceses in Zimbabwe (in my previous post as Bishop of Croydon). I thought I could easily switch attention from one African country to another. The reality was different.
Zimbabwe is ruled by Robert Mugabe, a man so corrupt that even his own demise will not clear the path to a golden new age – there are too many people who need to be protected by power well into the future. Sudan is governed by Omar al Bashir, a man committed to the project of creating a single nation (Sudan) with a single ethnicity (Arab), a single language (Arabic) and a single religion (Islam). There is a degree of shameful incompetence about Mugabe’s manipulation of power and the consequent destruction of the Zimbabwean economy and the country’s political culture. But al Bashir knows exactly what he is doing. And he does it in the face of a serious indictment by the International Criminal Court (ICC) for genocide in Darfur: he feels untouchable
Since 99 per cent of southerners voted in 2011 for the division of Sudan into two independent states, Sudan and South Sudan, al Bashir has chosen to make the secessionists take responsibility for their choice – to some extent understandably. If they are so keen on having their own country, then they can go there… and then apply for visas to come to Sudan as foreigners. Harsh? Yes, but he could be seen to be compelling the South Sudanese to live with the consequences of their actions. Democratic choices bring consequences.
However, the real experience of this is the expulsion from Sudan of anyone deemed to originate in the south – even several generations ago. Those who remain – often because they are married to Sudanese – are prohibited from working. Apart from the human cost of this policy, the effect on the Anglican church (the Episcopal Church of Sudan, which has not divided along with the states) is an exodus of leaders, an increased dependency of those who remain on the goodwill and generosity of other Sudanese Christians. And this is happening alongside the ongoing genocide in Darfur, government violence in South Kordofan and Blue Nile state. Khartoum has had to absorb destitute migrants on an unimaginable scale.
Those displaced are almost exclusively African. They speak African languages (derogatorily referred to as “twittering” by the Arabs). They are mostly (but not exclusively) Christian.
My visit to Khartoum earlier this year ended when my wife and I left a Christian-owned guesthouse at 1am in order to get to the airport for the flight back to Manchester. Within an hour the guesthouse had been raided by the security services, all property confiscated, and all residents and guests taken in for questioning. Foreign guests were deported and the family that ran the guesthouse was removed; the father of the family is now prohibited from working. This might not sound too dramatic – especially in the light of reports from parts of the Middle East and South Asia where Christians are being targeted for violence or forced to convert to Islam – but it comes as part of a deliberate policy on the part of government to exclude Christians and force them to leave for the South. This necessarily puts pressure on Christians to keep quiet, but the bishops (in particular) continue to be unafraid to engage courageously with “the powers”.
It seems that al Bashir blames the international community for refusing to welcome him back into the fold by removing the ICC indictment after the peaceful transition to two states. Foreigners are to be removed, even when they provide essential services that cannot be provided locally. We met European medical personnel who had spent their working lives developing medical facilities in local communities, and who now found themselves thrown out, leaving medical provision severely weakened.
Why destroy social, educational and medical infrastructure simply in order to save face? Riots in September 2013 in Khartoum (initially about the removal of fuel subsidies) demonstrated that economic matters do not always serve the interests of the government of the day.
But there is a bigger question relevant beyond Sudan. How do we understand and clearly define the categories in which and through which we see political, religious and cultural phenomena? Getting the category wrong leads inevitably to miscomprehension, to a potentially dangerous misapplication of rhetoric/language… and this has political consequences.
My own diocese of Bradford has a high percentage of Muslims from south Asia. Immigration began in the mid-20th century in order to staff the textile mills of West Yorkshire. Many of Bradford’s Muslims originate from the region of Kashmiri Mirpur in Pakistan. This concentration necessarily affects how the community lives and organises in Bradford, how it is influenced by (and, in turn, influences) events back in Pakistan, and how it is understood by the non-Pakistani population in the city.
One of the first lessons I had to learn when I came to Bradford nearly three years ago was not to confuse ethnicity with religion. What might appear to be a phenomenon rooted in religious identity (certain modes of dress, for example) might actually be more appropriately understood as a cultural phenomenon that coincidentally becomes associated with religious identity. To confuse the two can be dangerous. What I have in mind here is where violence (in particular) is attributed to religion, when religious tagging is clearly a tribal badging designed to hide more cultural (or other) identity.
Examples of this can be seen in the Northern Ireland of the Troubles or the sectarian destructiveness of Lebanon. Although the categories cannot easily be extricated from one another, at least those who observe or comment on such events should have the intelligence to dig a little deeper into the categorisation of such phenomena before simplistically eliding culture and religion as if they were synonymous.
The point is that there are two dangers here: (a)that category errors lead to poor communication and confusion, and (b)that people might be reluctant to speak out on serious matters simply because they fear being accused of racism or simply getting it wrong. This doesn’t help anyone where honest and frank conversation is needed and mutual critique is essential to good relationships.
This takes us back to Sudan. It is not a simple matter – capable of easy explication or distinction – to work out what can be attributed to which category. Al Bashir’s policy seems clearly to create a political, ethnic, religious and cultural identity in which there is no place for diversity. One can assume that he is aiming at a myth of solidarity – that if everyone claims the same identity, they will buy into the same projects, have the same friends and enemies, defend the same categories and communicate in the same way. Of course, this fails to take into account the complex reality of human identity construction and how complex and diverse people interrelate and self-identify.
In one sense all this should not need to be articulated. If Muslim is blowing up Muslim in Pakistan or Afghanistan, then there is clearly more going on than mere “religion” or religious identity. Simply reporting atrocities as if they were political or cultural events (without reference to religious allegiance) is as naïve as to report on religion without reference to the ethnic, political, economic, social or cultural identities that shape religious expression.
This is not a plea for obfuscation or mitigation of religiously motivated violence. On the contrary, it is a plea for the sort of literacy that seeks to comprehend in order to know how to think about and respond to phenomena that might all-too-easily be capable of simplistic categorisation.
Language goes to the heart of this. Not only the language of explanation or reportage, but the ways in which language is (or particular languages are) seen to be totems of identities that are deemed to be inconvenient. In Zimbabwe identity is tied up inextricably with language: the Shonaspeaking government has demonstrated in past violence what it thinks of the Ndebelespeaking Matabele. In Sudan African languages – mostly spoken by Christians of African (rather than Arabic) origin – are being derided and squeezed out. This is one reason why some churches in Sudan put such high value on keeping their own languages alive, teaching them to both children and adults, working hard (with pitiful resources) to reserve their means of communication as an integral element of cultural and religious identity. Language is as much part of individual and common identity as is skin colour, and nobody should be compelled to lose their native tongue.
One of the most penetrating verses of the Old Testament is found in the book of Proverbs. Seized upon by opponents of Hitler during the 1930s and 1940s in Germany, it demands that we “open our mouths for the dumb” – that is, that those who have a voice must keep alive the songs and language of people whose voice is silenced by the exercise of corrupt power. The moral demands of this are clear here also. But, for that voice to be heard and understood, it is essential that intelligent consideration is given to ensuring that the categories of speech and identification are kept as accurate as possible.
Responding to religious phenomena as if they were merely “cultural” is as dangerous and misplaced as eliding all cultural phenomena as merely “religious” – and runs the risk of stopping people speaking truthfully and accurately when religion is the root of violence or cultural violence seeks to hide behind a religious facade. The world is more complex than that. We can and must do better.