Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

A protester with a pride flag confronts the Hungarian national team before their Euro 2020 match with Germany. Jvºrgen Fromme/DPA/PA Images
In celebration of one of football’s biggest international tournaments, here is Index’s guide to the free speech Euros. Who comes out on top as the nation with the worst record on free speech?
It’s simple, the worst is ranked first.
We round up the last of the groups today with Group F, which played the deciding matches on Wednesday.
The recent Group F fixture between Germany and Hungary drew attention to Hungary’s poor record on free speech and censorship, when a protester carrying a pride flag ran on to the pitch. Hungary’s recent law, passed in June 2021, bans “the depiction or promotion of homosexuality to those under 18”. This includes teaching in schools and portrayals on television.
Prime Minister Victor Orbán was elected in 2010 and changed the constitution to take control of independent government institutions and initiated government policies to limit operations of opposition groups, journalists, and universities. According to non-profit Freedom House, the judiciary is unstable and controlled by the Prime Minister’s office, making it unusable in the struggle for free speech in Hungary. Reporters Without Borders (RSF) credit these policies for inspiring other European countries including Poland and Slovenia to institute similar restrictions on journalists.
Hungary’s coronavirus legislation gave the government almost unlimited power to handle the pandemic, a crisis which solidified Hungary as an information police-state where the prime minister can rule by decree without parliamentary oversight. Anti-scaremongering policies, meant to stop anyone “blocking the government’s anti-pandemic effort,” were used by Orbán to intimidate government critics and also temporarily suspended data protection policies. This fits with other incidents of government officials using their authority to suppress stories for their convenience.
Journalists who are caught conducting routine drone investigations in properties without express permission could get up to three years in prison under section 422 of the Hungarian criminal code, which focusses specifically on “illicit” data collection. Two journalists, Gabriella Horn and Balázs Gulyás, were threatened with this when investigating why military vehicles were present on land owned by businessman and friend of Orbán, Lőrinc Mészáros. It is a policy that shows the extent the government will go to, to side with government officials and oligarchs over journalists.
In May, journalist Júlia Halász appealed criminal charges of defamation and illegal recording for her publications after reporting on the harassment she endured while covering Hungarian diplomat, László Szabó.
Many journalists from the media company Magyar Hang reported government officials and their supporters harassing them for opposing Orbán’s reelection in 2018, and since the pandemic legislation, the head of the company, Csaba Lukács told the Committee to Protect Journalists, “reporting has become increasingly dangerous. This new legislation is a clear threat.”
In addition to government oppression, media publications face economic barriers in Hungary. Hungary’s government media council’s decisions have been criticised for being politicised because they prevented the consolidation of independent media companies while encouraging pro-government media outlets. Hungary’s largest independent newspaper closed in 2016, and the government oversaw the merger of hundreds of small media outlets in a major blow to Hungary’s media diversity.
France may have placed at the top of the group on Wednesday, but their free speech record is mediocre. Generally, France has an independent judiciary, fair and free elections, and free and independent media that protect free speech rights in France.
In recent years, political turmoil has given France a bad record of violence against journalists. RSF described it as an overall “hostile environment for reporters.” Anti-immigrant and anti-Muslim demonstrations in France have been increasingly violent, and while covering them, journalists are often arbitrarily detained with their equipment seized or subjected to teargas grenades, flashbangs, and baton beating. At least two journalists in 2020 were called before French police and claimed to have experienced harassment under questioning. Policies implemented in 2010 make it possible for the government to claim “overriding public interest” to force journalists to break source confidentiality.
Journalists are targets of police violence during the recent large-scale protests over France’s “Global Security Law”, which makes it illegal to “maliciously share” images that may lead to the identification of a police officer. The police response to the Gilets Jaunes – or “Yellow Vests” – movement has been widely criticised for putting bystanders and journalists in harm’s way.
Journalists were the target of the worst terrorist attacks in France. Nine Journalists were killed in 2015 during the Charlie Hebdo shooting which was an attack on the satirical publication Charlie Hebdo. The gunmen identified themselves as members of the Islamist group, Al-Qaeda, and five years later, a second stabbing attack outside Charlie Hebdo is also suspect to have an Islamist terrorist motive.
In April of 2021, French Journalist Nadiya Lazzouni received a death threat with sexist and anti-Muslim slurs and proof that the sender had been watching her. She filed a complaint with the Paris prosecutor’s office but has not heard anything in response as of 15 April. For some journalists in France, both extremists and the police can be a threat to their safety.
An active effort with constitutional safeguards to avoid repeating the country’s past has made Germany a stable democracy with well-protected civil liberties and political rights. Recent challenges with immigration have given a new rise to right-wing extremism and has created a more volatile environment for journalists. RSF’s 2021 report on Germany states “an independent judiciary ensures a favourable environment for journalists in Germany.” In recent years, the judiciary has been vital in preventing government policies that are harmful to journalists.
Despite the balanced government structure, Germany can still be a dangerous place for journalists. Extremists, mostly from the far right with some leftists, often use journalists as targets for violent attacks, and, especially during the Covid-19 pandemic, some politicians encouraged distrust in media outlets to promote populist agendas. In July of 2021, demonstrators protesting the Covid-19 lockdown physically blocked reporter’s cameras with their fists and shoved journalists while threatening them not to report on their protests. In May of 2021, Pro-Palestine demonstrators threw rocks and firecrackers at news crews in Berlin, and police used excessive force to prevent journalists from covering controversial evictions in October of 2020.
The Network Enforcement Act, a controversial law enacted in 2018, was brought in to regulate online hate speech and led to media companies deleting posts that would not have been considered hate speech. A majority of Germans, according to Freedom House, stated they are careful what they post online for fear of repercussions as a result.
Several government policies in response to extremism have been criticised for having unfair restrictions on journalism. In May of June 2021, their federal court ruled a law that was used to force journalists to reveal their sources was unconstitutional. Most recently in June 2021, a new law increased government surveillance and hacking power while removing judicial oversight and protections for Journalists during terrorism investigations, sparking concerns around protecting journalist sources from government retaliation.
Portugal has a long history of restricting press freedom, but following the Portuguese Constitution guaranteeing freedom of expression in 1978, it has grown to be ranked ninth-best in RSF’s World Press Freedom Index of 2021. Despite a vocal minority that criticises the extent to which freedom of expression is allowed, Portugal now has a decent free speech record, but journalists are hindered by the economic downturn’s effect on their media industry. With a near-perfect score from Freedom House, Portugal earned a 96/100 for its effective political system and balanced judiciary Portuguese media outlets struggled with funding during the pandemic, and in response, Prime Minister António Costa advanced what the state planned to pay in government advertising to support the industry. Generally, public broadcasters have and struggle against commercial television outlets, which gives diverse viewpoints but some risk of populism.
Wrongful surveillance of journalists by police has been an issue. In January 2021, police were allegedly surveilling journalists illegally, without a court order, attempting to uncover their sources, and the Lisbon prosecutor’s office was exposed using electronic surveillance on two journalists in an attempt to reveal their sources in 2018. If charged for “breaching judicial secrets”, the two journalists could face up to two years in prison.
Another challenge Portugal has been facing is recent corruption scandals. In September of 2020, 17 people, including three judges, were charged with corruption. Portuguese authorities, complying with the international effort identified those involved and froze their assets, but some concerns remain around the poor resources provided to investigators and the ineffective anti-corruption and whistleblower protection legislation passed in 2019.
Group E[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][three_column_post title=”You may also like to read” category_id=”8996″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”114690″ img_size=”full” add_caption=”yes”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]“The Hungarian public’s access to sources of balanced news and information is in greater danger than ever before.” This was the stark warning that Index on Censorship, alongside 15 other organisations, delivered to Executive Vice-President of the European Commission Margrethe Vestager today.
After a decade of Prime Minister Viktor Orban’s rule, Hungary’s media landscape is in turmoil. Last month, 70 of the approximately 90 journalists working at Index.hu – which had been considered one of the last major independent news outlets in Hungary – resigned after the editor-in-chief was fired by the company’s CEO.
“For years, we’ve been saying that there are two conditions for the independent operation of Index: that there be no external influence on the content we publish or the structure and composition of our staff. Firing Szabolcs Dull has violated our second condition. His dismissal is a clear interference in the composition of our staff, and we cannot regard it any other way but as an overt attempt to apply pressure on Index.hu,” the departing journalists wrote in an open letter.
“Index was the most widely read news website in Hungary,” explained András Pethő in an interview with Index on Censorship. Pethő is co-founder and senior editor at Direkt36, a small investigative journalism outlet that focuses on reporting abuses of power. “It was one of the few remaining independent news websites in Hungary. It was a kind of hub on the Hungarian internet: a lot of people started their day by checking Index.”
“The organisation, the outlet itself is still here. The whole staff resigned but they hired new people. There’s a new leadership and we’ll see what that looks like, how they will cover news, and how independent they will be,” said Pethő. “What happened is bad for basically everyone who is interested in independent journalism in Hungary.”
Before founding Direkt36, Pethő had been a reporter and editor at Origo.hu, one of the largest online news outlets alongside Index. But in 2014, Origo.hu’s editor-in-chief was abruptly replaced after an investigation was published about lavish expenses claimed by Orban’s chief of staff. “Basically we went through a pretty similar story [to Index],” said Pethő. “The whole project – Direckt36 – was born as a response to the negative environment.”
What happened at Index and Origo are just two examples of the Hungarian government’s efforts to undermine independent media in the country. Index on Censorship has reported regularly on Orban’s attacks on the media and has been particularly concerned by events of the last six months fearing that the Covid-19 crisis is being used as a distraction to further curtail media freedom. In this period, we have received reports of journalists being barred from press conferences, alongside other attacks that we have documented on our map.
But despite the government’s ongoing and strategic efforts to punish critical media and reward government mouthpieces, the EU has yet to meaningfully intervene. As highlighted by the signatories of today’s letter to Vestager, such efforts have included the misuse of state aid, which has resulted in two complaints being logged with the European Commission in 2016 and 2018 respectively. The first complaint relates to Hungary’s public service broadcaster which, despite having long ceased to meet international standards due to its clear pro-government bias, continues to receive state funding. The second relates to the distribution of state advertising to media outlets in Hungary.
Although it was a market leader, Index.hu had received virtually no state advertising in the years prior to the mass resignations. At the same time, its main competitor – the now pro-government Origo.hu, benefitted heavily. As stated in today’s letter, “the goal of these efforts is clear: to financially weaken independent media and hamper the production and dissemination of critical news.”
Pethő says that Direkt36 are among the organisations feeling the squeeze. “When we launched it in 2015 and when we had a bigger story, those stories were often picked up by several online news outlets, a couple of TV channels, radio stations… so it could travel quite widely in the Hungarian media,” he said.
“That space has been shrinking gradually more and more and now when we publish a bigger piece maybe it’s picked up by a couple of news websites, maybe there is a radio interview, maybe one TV channel. But it’s much less than what we had three, four or five years ago.”[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

Richard Patterson/Flickr
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
[streamquiz id=”6″][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]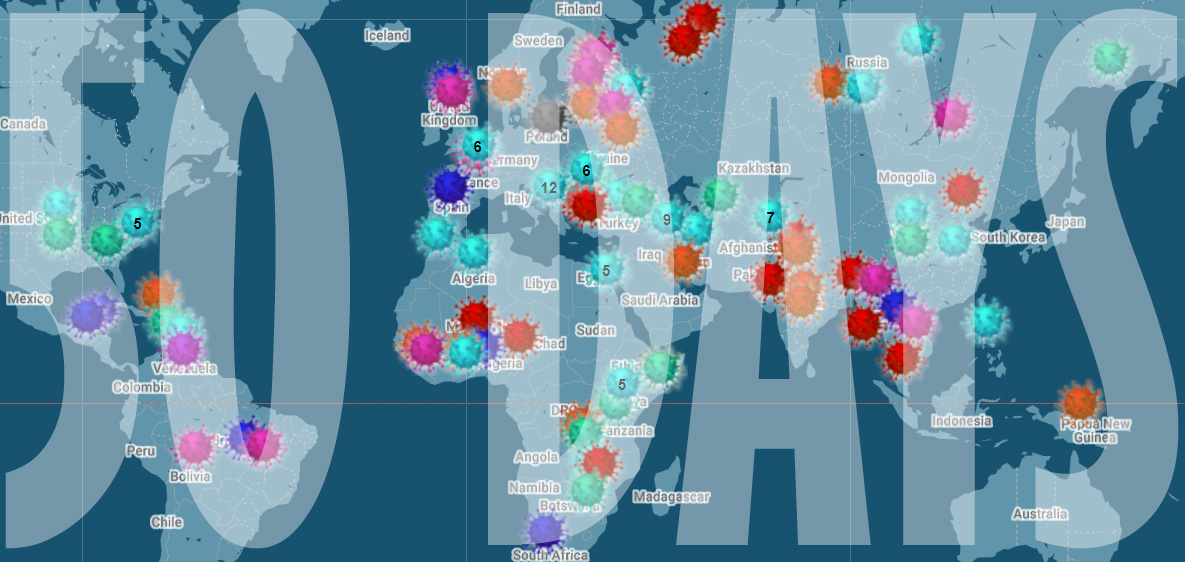
As we mark 50 days since we first started collating attacks on media freedom related to the coronavirus crisis, we’re horrified by the number of attacks we have mapped – over 150 in what is ultimately a short period of time.
We know that in times of crisis media attacks often increase – just look at what happened to journalists after the military coup in Egypt in 2013 and the failed coup against Recep Tayyip Erdogan in Turkey in 2016. The extent of the current attacks, in democratic as well as authoritarian countries, has been a shock.
Our network of readers, correspondents, Index staff and our partners at the Justice for Journalists Foundation have helped collect the more than 150 reports media attacks.
But these incidents are likely to be the very tip of the iceberg. When the world is in lockdown, finding out about abuses of power is harder than ever. Journalists are struggling to do their job even before harassment. How many more attacks are happening that we don’t yet know about? It’s a scary thought.
Rachael Jolley, editor-in-chief of Index on Censorship, said: “We are alarmed at the ferocity of some of the attacks on media freedom we are seeing being unveiled. In some states journalists are threatened with prison sentences for reporting on shortages of vital hospital equipment. The public need to know this kind of life-saving information, not have it kept from them. Our reporting is highlighting that governments around the world are tempted to use different tactics to stop the public knowing what they need to know.”
Index is alarmed that the attacks are not coming from the usual suspects. Yes, there have been plenty of incidents reported in Russia and the former Soviet Union, Turkey, Hungary and Brazil. At the same time there have been many incidents in countries you would not expect to see – Spain, New Zealand, Germany and the UK.
The most common incident we have recorded on the map are attacks on journalists – whether physical or verbal – and cases where reporters have been detained or arrested. There have been more than 30 attacks on journalists, with the source of many of these being the US President Donald Trump. He has a history of being combative with the press and decrying fake news even where the opposite is the case and the crisis has seen a ramped up attempt at excluding the media. During the crisis, he has refused to answer journalists’ questions, attacked the credentials of reporters and walked out from press conferences when he doesn’t like the direction they are taking.
We have also seen reporters and broadcasters detained and charged just for trying to tell the story of the crisis, including Dhaval Patel, editor of the online news portal Face of Nation in Gujarat, Mushtaq Ahmed in Bangladesh and award-winning investigative journalist Wan Noor Hayati Wan Alias in Malaysia.
Since we started the mapping project, we have highlighted other specific trends. Orna Herr has written about how coronavirus is providing pretext for Indian prime minister Narendra Modi to increase attacks on the press and Muslims. Jemimah Steinfeld wrote about how certain leaders are dodging questions while we have also looked at how freedom of information laws are being suspended or deadlines for information extended.
Although the map does not tell the whole story it does act as a record of these attacks. When this crisis is finally all over, it will allow us to ask questions about why these attacks happened and to make sure that any restrictions that have been introduced are reversed, giving us back our freedom.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_btn title=”Report an incident” shape=”round” color=”danger” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fforms.gle%2Fhptj5F6ZvxjcaGLa7|||” css=”.vc_custom_1589455005016{border-radius: 5px !important;}”][/vc_column][/vc_row]