Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
 Judges include actor Noma Dumezweni; former Vanity Fair editor Tina Brown
Judges include actor Noma Dumezweni; former Vanity Fair editor Tina BrownA Zimbabwean pastor who was arrested by authorities last week for his #ThisFlag campaign, an Iranian Kurdish journalist covering his life as an interned Australian asylum seeker, one of China’s most notorious political cartoonists, and an imprisoned Russian human rights activist are among those shortlisted for the 2017 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards.
Drawn from more than 400 crowdsourced nominations, the shortlist celebrates artists, writers, journalists and campaigners overcoming censorship and fighting for freedom of expression against immense obstacles. Many of the 16 shortlisted nominees are regularly targeted by authorities or by criminal and extremist groups for their work: some face regular death threats, others criminal prosecution or exile.
“The creativity and bravery of the shortlist nominees in challenging restrictions on freedom of expression reminds us that a small act — from a picture to a poem — can have a big impact. Our nominees have faced severe penalties for standing up for their beliefs. These awards recognise their courage and commitment to free speech,” said Jodie Ginsberg, CEO of campaigning nonprofit Index on Censorship.
Awards are offered in four categories: arts, campaigning, digital activism and journalism.
Nominees include Pastor Evan Mawarire whose frustration with Zimbabwe’s government led him to the #ThisFlag campaign; Behrouz Boochani, an Iranian Kurdish journalist who documents the life of indefinitely-interned Australian asylum seekers in Papua New Guinea; China’s Wang Liming, better known as Rebel Pepper, a political cartoonist who lampoons the country’s leaders; Ildar Dadin, an imprisoned Russian opposition activist, who became the first person convicted under the country’s public assembly law; Daptar, a Dagestani initiative tackling women’s issues like female genital mutilation that are rarely discussed publicly in the country; and Serbia’s Crime and Corruption Reporting Network (KRIK), which was founded by a group of journalists to combat pervasive corruption and organised crime.
Other nominees include Hungary’s Two-tail Dog Party, a group of satirists who parody the country’s political discourse; Honduran LGBT rights organisation Arcoiris, which has had six activists murdered in the past year for providing support to the LGBT community and lobbying the country’s government; Luaty Beirão, a rapper from Angola, who uses his music to unmask the country’s political corruption; and Maldives Independent, a website involved in revealing endemic corruption at the highest levels in the country despite repeated intimidation.
Judges for this year’s awards, now in its 17th year, are Harry Potter actor Noma Dumezweni, Hillsborough lawyer Caiolfhionn Gallagher, former Vanity Fair editor Tina Brown, designer Anab Jain and music producer Stephen Budd.
Dumezweni, who plays Hermione in the stage play Harry Potter and the Cursed Child, was shortlisted earlier this year for an Evening Standard Theatre Award for Best Actress. Speaking about the importance of the Index Awards she said: “Freedom of expression is essential to help challenge our perception of the world”.
Winners, who will be announced at a gala ceremony in London on 19 April, become Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards Fellows and are given support for their work, including training in areas such as advocacy and communications.
“The GreatFire team works anonymously and independently but after we were awarded a fellowship from Index it felt like we had real world colleagues. Index helped us make improvements to our overall operations, consulted with us on strategy and were always there for us, through the good times and the pain,” Charlie Smith of GreatFire, 2016 Freedom of Expression Awards Digital Activism Fellow.
This year, the Freedom of Expression Awards are being supported by sponsors including SAGE Publishing, Google, Vodafone, media partner CNN, VICE News, Doughty Street Chambers, Psiphon and Gorkana. Illustrations of the nominees were created by Sebastián Bravo Guerrero.
Notes for editors:
For more information, or to arrange interviews with any of those shortlisted, please contact: Sean Gallagher on 0207 963 7262 or [email protected]. More biographical information and illustrations of the nominees are available at indexoncensorship.org/indexawards2017.
Luaty Beirão, Angola
Rapper Luaty Beirão, also known as Ikonoklasta, has been instrumental in showing the world the hidden face of Angolan President José Eduardo dos Santos’s rule. For his activism Beirão has been beaten up, had drugs planted on him and, in June 2015, was arrested alongside 14 other people planning to attend a meeting to discuss a book on non-violent resistance. Since being released in 2016, Beirão has been undeterred attempting to stage concerts that the authorities have refused to license and publishing a book about his captivity entitled “I Was Freer Then”, claiming “I would rather be in jail than in a state of fake freedom where I have to self-censor”.
Rebel Pepper, China
Wang Liming, better known under the pseudonym Rebel Pepper, is one of China’s most notorious political cartoonists. For satirising Chinese Premier Xi Jinping and lampooning the ruling Communist Party, Rebel Pepper has been repeatedly persecuted. In 2014, he was forced to remain in Japan, where he was on holiday, after serious threats against him were posted on government-sanctioned forums. The Chinese state has since disconnected him from his fan base by repeatedly deleting his social media accounts, he alleges his conversations with friends and family are under state surveillance, and self-imposed exile has made him isolated, bringing significant financial struggles. Nonetheless, Rebel Pepper keeps drawing, ferociously criticising the Chinese regime.
Fahmi Reza, Malaysia
On 30 January 2016, Malaysian graphic designer Fahmi Reza posted an image online of Prime Minister Najib Razak in evil clown make-up. From T-shirts to protest placards, and graffiti on streets to a sizeable public sticker campaign, the image and its accompanying anti-sedition law slogan #KitaSemuaPenghasut (“we are all seditious”) rapidly evolved into a powerful symbol of resistance against a government seen as increasingly corrupt and authoritarian. Despite the authorities’ attempts to silence Reza, who was banned from travel and has since been detained and charged on two separate counts under Malaysia’s Communications and Multimedia Act, he has refused to back down.
Two-tailed Dog Party, Hungary
A group of satirists and pranksters who parody political discourse in Hungary with artistic stunts and creative campaigns, the Two-tailed Dog Party have become a vital alternative voice following the rise of the national conservative government led by Viktor Orban. When Orban introduced a national consultation on immigration and terrorism in 2015, and plastered cities with anti-immigrant billboards, the party launched their own mock questionnaires and a popular satirical billboard campaign denouncing the government’s fear-mongering tactics. Relentlessly attempting to reinvigorate public debate and draw attention to under-covered or taboo topics, the party’s efforts include recently painting broken pavement to draw attention to a lack of public funding.
 Arcoiris, Honduras
Arcoiris, Honduras
Established in 2003, LGBT organisation Arcoiris, meaning ‘rainbow’, works on all levels of Honduran society to advance LGBT rights. Honduras has seen an explosion in levels of homophobic violence since a military coup in 2009. Working against this tide, Arcoiris provide support to LGBT victims of violence, run awareness initiatives, promote HIV prevention programmes and directly lobby the Honduran government and police force. From public marches to alternative awards ceremonies, their tactics are diverse and often inventive. Between June 2015 and March 2016, six members of Arcoiris were killed for this work. Many others have faced intimidation, harassment and physical attacks. Some have had to leave the country because of threats they were receiving.
Breaking the Silence, Israel
Breaking the Silence, an Israeli organisation consisting of ex-Israeli military conscripts, aims to collect and share testimonies about the realities of military operations in the Occupied Territories. Since 2004, the group has collected over 1,000 (mainly anonymous) statements from Israelis who have served their military duty in the West Bank and Gaza. For publishing these frank accounts the organisation has repeatedly come under fire from the Israeli government. In 2016 the pressure on the organisation became particularly pointed and personal, with state-sponsored legal challenges, denunciations from the Israeli cabinet, physical attacks on staff members and damages to property. Led by Israeli politicians including the prime minister, and defence minister, there have been persistent attempts to force the organisation to identify a soldier whose anonymous testimony was part of a publication raising suspicions of war crimes in Gaza. Losing the case would set a precedent that would make it almost impossible for Breaking the Silence to operate in the future. The government has also recently enacted a law that would bar the organisation’s widely acclaimed high school education programme.
Ildar Dadin, Russia
A long-term opposition and LGBT rights activist, Ildar Dadin was the first, and remains the only, person to be convicted under Russia’s 2014 public assembly law that prohibits the “repeated violation of the order of organising or holding meetings, rallies, demonstrations, marches or picketing”. Attempting to circumvent this restrictive law, Dadin held a series of one-man pickets against human rights abuses – an enterprise for which he was arrested and sentenced to three years imprisonment in 2015. In November 2016, website Meduza published a letter smuggled to his wife in which Dadin wrote that he was being tortured and abuse was endemic in Russian jails. The letter, a brave move for a serving prisoner, had wide resonance, prompting a reaction from the government and an investigation. Against his will, Dadin was transferred and disappeared within the Russian prison system until a wave of public protest led to his location being revealed in January 2017. Dadin was released on February 26 after a supreme court order.
Maati Monjib, Morocco
A well-known academic who teaches African studies and political history at the University of Rabat since returning from exile, Maati Monjib co-founded Freedom Now, a coalition of Moroccan human rights defenders who seek to promote the rights of Moroccan activists and journalists in a country ranked 131 out of 180 on the Reporters Without Borders Press Freedom Index. His work campaigning for press freedom – including teaching investigative journalism workshops and using of a smartphone app called Story Maker designed to support citizen journalism – has made him a target for the authorities who insist that this work is the exclusive domain of state police. For his persistent efforts, Monjib is currently on trial for “undermining state security” and “receiving foreign funds.”
 Jensiat, Iran
Jensiat, Iran
Despite growing public knowledge of global digital surveillance capabilities and practices, it has often proved hard to attract mainstream public interest in the issue. This continues to be the case in Iran where even with widespread VPN usage, there is little real awareness of digital security threats. With public sexual health awareness equally low, the three people behind Jensiat, an online graphic novel, saw an an opportunity to marry these challenges. Dealing with issues linked to sexuality and cyber security in a way that any Iranian can easily relate to, the webcomic also offers direct access to verified digital security resources. Launched in March 2016, Jensiat has had around 1.2 million unique readers and was rapidly censored by the Iranian government.
Bill Marczak, United States
A schoolboy resident of Bahrain and PhD candidate in computer science at the University of California, Berkeley, Bill Marczak co-founded Bahrain Watch in 2013. Seeking to promote effective, accountable and transparent governance, Bahrain Watch works by launching investigations and running campaigns in direct response to social media posts coming from activists on the front line. In this context, Marczak’s personal research has proved highly effective, often identifying new surveillance technologies and targeting new types of information controls that governments are employing to exert control online, both in Bahrain and across the region. In 2016 Marczak investigated several government attempts to track dissidents and journalists, notably identifying a previously unknown weakness in iPhones that had global ramifications.
#ThisFlag and Evan Mawarire, Zimbabwe
In May 2016, Baptist pastor Evan Mawarire unwittingly began the most important protest movement in Zimbabwe’s recent history when he posted a video of himself draped in the Zimbabwean flag, expressing his frustration at the state of the nation. A subsequent series of YouTube videos and the hashtag Mawarire used, #ThisFlag, went viral, sparking protests and a boycott called by Mawarire, which he estimates was attended by over eight million people. A scale of public protest previously inconceivable, the impact was so strong that private possession of Zimbabwe’s national flag has since been banned. The pastor temporarily left the country following death threats and was arrested in early February as he returned to his homeland.
Turkey Blocks, Turkey
In a country marked by increasing authoritarianism, a strident crackdown on press and social media as well as numerous human rights violations, Turkish-British technologist Alp Toker brought together a small team to investigate internet restrictions. Using Raspberry Pi technology they built an open source tool able to reliably monitor and report both internet shut downs and power blackouts in real time. Using their tool, Turkey Blocks have since broken news of 14 mass-censorship incidents during several politically significant events in 2016. The tool has proved so successful that it has begun to be implemented elsewhere globally.

Behrouz Boochani, Manus Island, Papua New Guinea/Australia (he is an Iranian refugee)
Iranian Kurdish journalist Behrouz Boochani fled the city of Ilam in Iran in May 2013 after the police raided the Kurdish cultural heritage magazine he had co-founded, arresting 11 of his colleagues. He travelled to Australia by boat, intending to claim asylum, but less than a month after arriving he was forcibly relocated to a “refugee processing centre” in Papua New Guinea that had been newly opened. Imprisoned alongside nearly 1000 men who have been ordered to claim asylum in Papua New Guinea or return home, Boochani has been passionately documenting their life in detention ever since. Publicly advertised by the Australian Government as a refugee deterrent, life in the detention centre is harsh. For the first 2 years, Boochani wrote under a pseudonym. Until 2016 he circumvented a ban on mobile phones by trading personal items including his shoes with local residents. And while outside journalists are barred, Boochani has refused to be silent, writing numerous stories via Whatsapp and even shooting a feature film with his phone.
Daptar, Dagestan, Russia
In a Russian republic marked by a clash between the rule of law, the weight of traditions, and the growing influence of Islamic fundamentalism, Daptar, a website run by journalists Zakir Magomedov and Svetlana Anokhina, writes about issues affecting women, which are little reported on by other local media. Meaning “diary”, Daptar seeks to promote debate and in 2016 they ran a landmark story about female genital mutilation in Dagestan, which broke the silence surrounding that practice and began a regional and national conversation about FGM. The small team of journalists, working alongside a volunteer lawyer and psychologist, also tries to provide help to the women they are in touch with.
KRIK, Serbia
Crime and Corruption Reporting Network (KRIK) is a new independent investigative website which was founded by a team of young Serbian journalists intent on exposing organised crime and extortion in their country which is ranked as having widespread corruption by Transparency International. In their first year they have published several high-impact investigations, including forcing Serbia’s prime minister to admit that senior officials had been behind nocturnal demolitions in a Belgrade neighbourhood and revealing meetings between drug barons, the ministry of police and the minister of foreign affairs. KRIK have repeatedly come under attack online and offline for their work –threatened and allegedly under surveillance by state officials, defamed in the pages of local tabloids, and suffering abuse including numerous death threats on social media.
Maldives Independent, Maldives
Website Maldives Independent, which provides news in English, is one of the few remaining independent media outlets in a country that ranks 112 out of 180 countries on the Reporters Without Borders Press Freedom Index. In August 2016 the Maldives passed a law criminalising defamation and empowering the state to impose heavy fines and shut down media outlets for “defamatory” content. In September, Maldives Independent’s office was violently attacked and later raided by the police, after the release of an Al Jazeera documentary exposing government corruption that contained interviews with editor Zaheena Rasheed, who had to flee for her safety. Despite the pressure, the outlet continues to hold the government to account.
Index recently appointed a new youth advisory board cohort. The eight young students and professionals, from countries including Hungary, Germany, India and the US, will hold their seats on the board until December.
Each month, board members meet online to discuss freedom of expression issues occurring around the world and complete an assignment that grows from that discussion. For their first task the board were asked to write a short bio and take a photo of themselves holding a quote that reflects their belief in free speech.
Sophia Smith-Galer 
I’m half English, half Italian, and was born and raised in London. I have just graduated from Durham University with a degree in Spanish and Arabic and will be studying for a Master’s in broadcast journalism at City University next year.
I have just returned from a trip to New York after winning a multilingual world essay prize which included speaking at the United Nations’ General Assembly. I was in the group of Arabic language winners and our speeches were about tackling climate change, which is one of the UN’s sustainable development goals for 2030. Now that I am embarking on a career in journalism I’m looking forward to continue supporting these goals in my work.
Freedom of expression is particularly important to me as several countries that speak both of the languages I have dedicated years of study to continue to be plagued by tyrants and censors. I’m particularly interested addressing censorship in Latin America and the Middle East, especially with regard to the arts, as I’m also a classical singer and keen art historian.
Shruti Venkatraman
Originally from Mumbai, I am currently a first year undergraduate studying law at the University of Edinburgh. As a law student, I am interested in advocacy in general, but I am particularly interested in advocating for fundamental human rights.
In today’s socio-political context, the phrase “freedom of expression” has gained importance and expanded in its meaning from it’s original intent to prevent minority persecution. Having lived in India and South Africa, I was able to grasp the importance of free speech in the context of regional history, and I learnt how human rights appeals have had local and global impacts and are inherently tied with social development. Index on Censorship’s admirable work to promote and defend freedom of expression highlights how important this cause is in our quest for social progress, justice and equality and how repression of these rights result in societal backwardness.
Niharika Pandit 
I am currently a master’s candidate at the Centre for Gender Studies at SOAS, University of London with South Asia as my focus area of gender research. I became interested in issues of censorship during my undergraduate studies in mass media with a specialisation in journalism from Bombay.
As a journalist and an active social media user in India, I was witness to numerous instances of online abuse, trolling and silencing of women politicians, journalists and activists who voiced opinions on political and social issues. As a response to the barrage of abuse in the online space, otherwise a liberating space to hear diversified opinions, I wrote a piece on Twitter trolls in India and the use of sexist abuse as a tool to muzzle women for Index on Censorship’s Young Writers’ Programme.
Within censorship, I am particularly interested in working on the intersections of social media, gender along with looking at censorship in militarised zones and its growing legitimacy in contemporary political ethos as part of my research.

Layli Foroudi
It was studying literary works from the Soviet period during my undergraduate degree that highlighted the issue of censorship for me initially. Clearly this issue has outlived (and predates) the Soviet Union and is still of pressing concern in Russia today and globally. After graduating, I worked as a journalist on issues of freedom of expression and belief in Iran, and then in Russia at the Moscow Times. By pushing a state-sponsored version of the truth and punishing those at variance with it, these countries and others marginalise people and stifle innovation and creativity.
Freedom of expression and public debate underpin what society consists of and being denied this freedom is being denied the right to participation in society, as Hannah Arendt wrote: the polis is “the organisation of people as it arises out of acting and speaking together”. Historically, many have been denied the right to “act and speak”, based on ethnicity, gender, belief, immigration status, etc, and continue to be. I am interested in encouraging a diversity voices in the public sphere, something I have enjoyed exploring more this past year while undertaking an MPhil in race, ethnicity, and conflict at Trinity College Dublin and as a member of the youth advisory board since January.
Ian Morse 
I’m a student and journalist at Lafayette College in the US, but I have studied in Germany, Turkey and the UK. I really started studying news media when I lived in Turkey 18 months ago, because even then (much more so now) journalists and bloggers had a very tough time gathering and publishing good information. Since then, I’ve been a journalist in Turkey, the UK and Greece. I study history and mathematics-economics, but almost every project I do is focused on news media.
I’ve encountered freedom of expression violations in many fashions, from student pressures against speakers to petty government retaliation to Twitter blocking. There is quite a bit of nuance that is overlooked in many cases, but that nuance is needed to understand where the line needs to be drawn. Words have a lot of power in society – but it is often difficult to get the truth out when lies are louder or gags are stronger. I hope with Index that we can find ways to fix this.
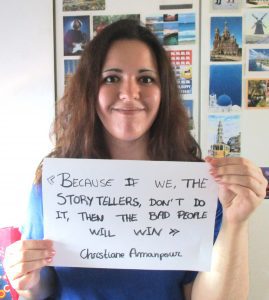
Anna Gumbau
I am a journalist living between Barcelona and Brussels. I am passionate about youth work, having volunteered for five years as member of AEGEE-Europe / European Students’ Forum, including a year as member of its international board. I have taken part in, and often led projects, run by students for other students all over Europe, on topics such as pluralism of media, election observation and media literacy. I am also involved in the field of internet governance, participating in the last two editions of the EuroDIG and joining the Youth Observatory of the Internet Society.
As a young media-maker who grew up listening to the stories of censorship in the times of the Spanish dictatorship, I believe strongly in free speech, a free press and media pluralism as essential pillars for democracy. I am fascinated by the power of words and freedom of expression to empower citizens and stand up to what they believe in. I also envision free media as a crucial element for better informed societies and, in extension, for more responsible individual citizens to participate in the public space.
Constantin Eckner 
I am originally from Germany. I graduated from University of St Andrews with a master’s degree in modern history. Currently, I am a Ph.D. candidate specialising in human rights, asylum policy and the history of migration. Moreover, I have worked as a writer and journalist since I was 17 years old, covering a variety of topics over the years. Longer stays in cities like Budapest and Istanbul have raised my awareness for pressures exerted upon freedom of expression.
In a perfect world journalists, as well as every citizen, would live without fear of state censorship and potentially facing repercussions for the words they write or speak, for the pictures they draw, for the photos they shoot or for music they play.
Freedom of expression and access to information are cornerstones of an enlightened society. Unfortunately, in 2016 the world is still challenged by undemocratic regimes and powers that intend to quash people, which is an oppressive situation that has to change. It is up to us to help those who cannot raise their voice fearlessly.
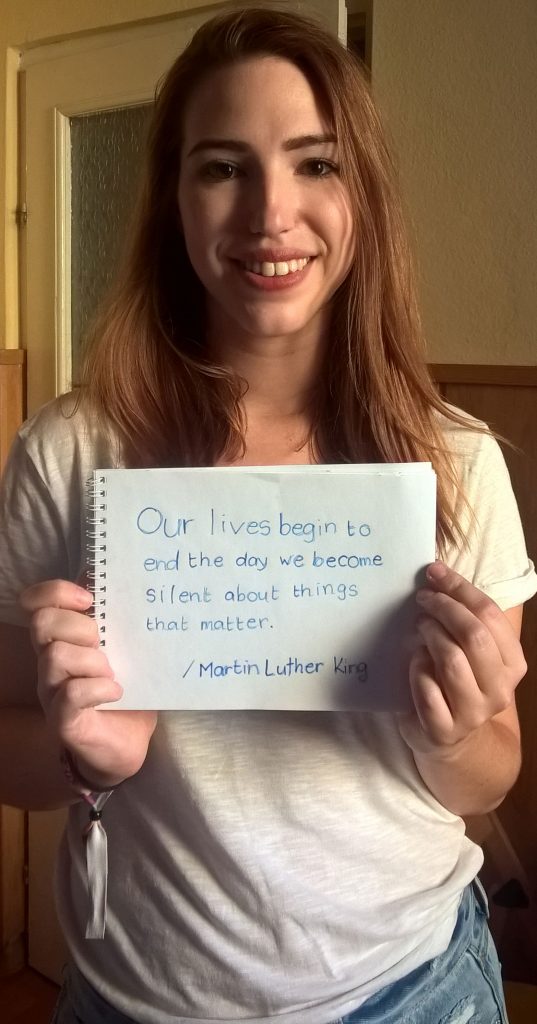 Fruzsina Katona
Fruzsina Katona
I was born and raised in Hungary, although I spent my pre-university years in a small town in eastern Hungary. Today I am a freelance journalist.
I always knew I wanted to be a journalist, since I was always interested in literally everything that surrounded me. The urge to publish became stronger at the age of 17, after I returned from Japan, where I spent a school year. That one year made me realise, that my home country is really far from the image I had of it. And the only way I can fight against corruption, abuses and narrow-mindedness – apart from voting – is to educate and inform the public. I took an internship at Hungary’s leading investigative journalism center, and 2015 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression award-winner, Atlatszo.hu. I have worked for them as a freelancer ever since, and I enjoy my work pretty much.
I recently received a graduate degree in communication and media studies, and supplemented my “official” studies with training, workshops and conferences across Europe.
In the future I would like to be a post-conflict reporter or a human rights journalist, specialising in freedom of expression and the press.
Free Word in partnership with Index on Censorship brought together three major cultural figures from Hungary, Poland and Turkey to compare their stories and ask: is Europe just a place, or a set of values that are rapidly unravelling?
Europe was a bastion of hope for more than a million refugees last year. What brought them? A hunger for safety and security? Dreams of freedom? The draw of liberal democracy with its ideals of free expression, equal opportunity and persecution for none?
But look within our own continent and you will see the cracks. In Hungary, Victor Orban’s administration looks increasingly autocratic. Poland’s new conservative government is making changes to its public media that critics have said amount to a takeover. How can we support neighbours like Turkey in their fight to avoid authoritarianism if we can’t fly the banner for freedom at home?

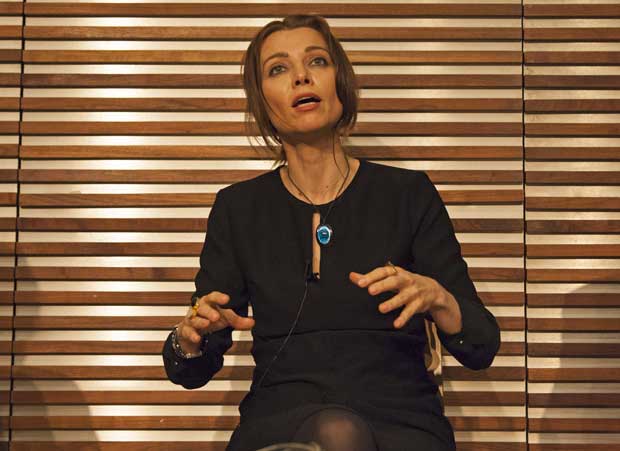
Agnes Heller, Elif Shafak and Adam Zagajewski
Photos: Sean Gallagher/Index on Censorship
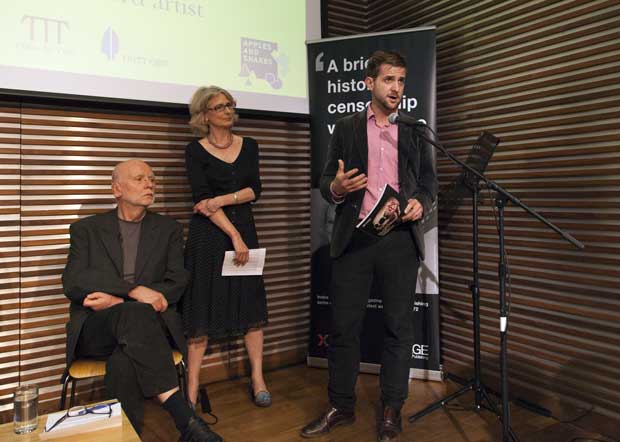

Poland, Hungary and Turkey come up on Index’s radar far too often at the moment, says @DBetzH, introducing tonight’s panelists #fweurope
— Index on Censorship (@IndexCensorship) June 15, 2016

In Turkey people cite Singapore as example of having economic success without democracy. Says @Elif_Safak #fweurope
— Index on Censorship (@IndexCensorship) June 15, 2016

‘Liberal democracy is majority decision but not majority rule.’ #AgnesHeller #FWEurope
— Free Word (@FreeWordCentre) June 15, 2016

In Hungary, the question isn’t whether you should criticise the government, but whether you have the means to do so. #FWEurope
— Eleanor Paton (@eleanorpea) June 15, 2016

People cannot express their dissatisfaction with the government without a political language and discussion #AgnesHeller #FWEurope
— Free Word (@FreeWordCentre) June 15, 2016

‘People internalise totalitarian values without realising it’ @Elif_Safak #FWEurope
— Free Word (@FreeWordCentre) June 15, 2016

‘Writers have to defend political freedom but also the magic of imagination’ #AdamZagajewski #FWEurope
— Free Word (@FreeWordCentre) June 15, 2016

.@Elif_Safak says politics is everywhere. Adam Zagajewski says too much politics in creative writing inhibits imagination #fweurope
— Index on Censorship (@IndexCensorship) June 15, 2016

‘Limits of political correctness should be moral and not legislative’ #AgnesHeller #FWEurope
— Free Word (@FreeWordCentre) June 15, 2016

I’m bolder when writing fiction [than an op-ed] because I live in it. Later, when I send to editor, I get nervous @Elif_Safak #fweurope
— Index on Censorship (@IndexCensorship) June 15, 2016

‘All interpretations of ‘Freedom’ should exist simultaneously’ #AgnesHeller #FWEurope
— Free Word (@FreeWordCentre) June 15, 2016

“Political correctness is partly stupid, partly vital. Trump abolishing decency,” says Adam. But he’s free to do that, adds Agnes #fweurope
— Index on Censorship (@IndexCensorship) June 15, 2016
Electrifying performance from #AlixAlixandra on freedom #FWEurope
— Free Word (@FreeWordCentre) June 15, 2016
Watch the event in full here:
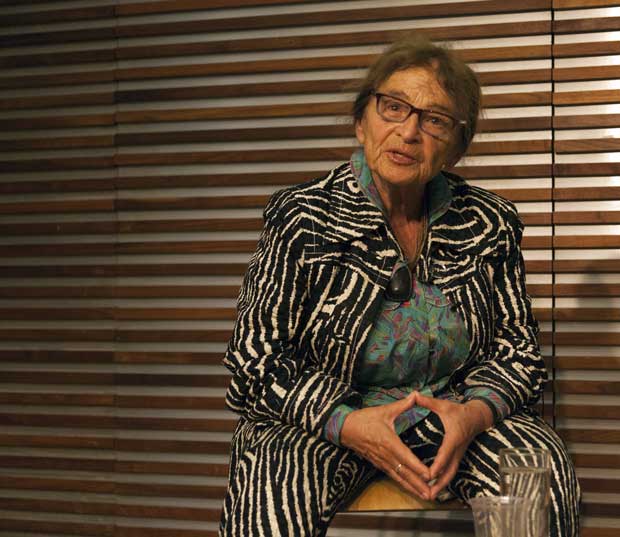
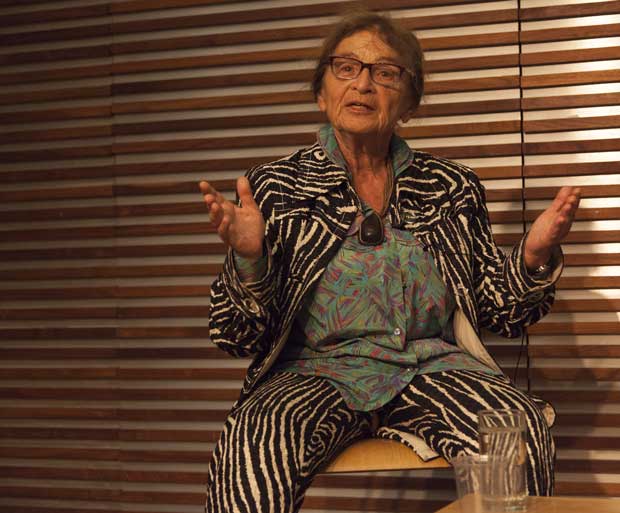
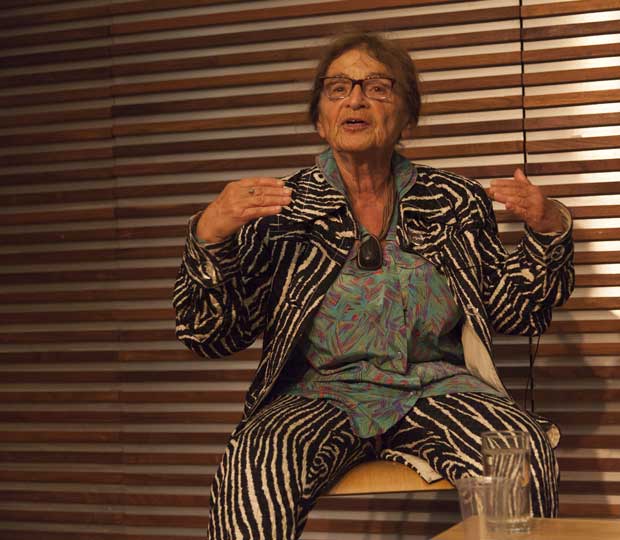
Agnes Heller was born in 1929 and is one of the leading thinkers to come out of the tradition of critical theory. Her broad intellectual range and publications include ethics, philosophical anthropology, political philosophy and a theory of modernity and its culture. Hungarian by birth, she was one of the best-known dissident Marxists in central Europe in the 1960s and 1970s. She has held visiting lectureships all over the world and has been the Hannah Arendt Professor of Philosophy at the New School in New York. She now lives in Budapest and is one of the most popular and outspoken critics of the current regime.
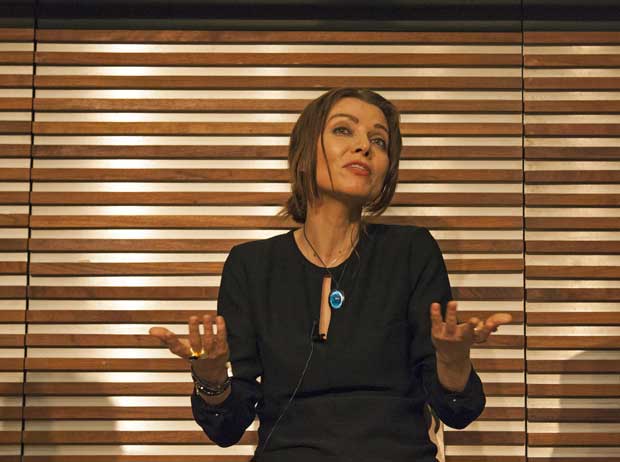
Elif Shafak was born in Strasbourg, France, in 1971. She is an award-winning novelist and the most widely read woman writer in Turkey. Critics have named her as “one of the most distinctive voices in contemporary Turkish and world literature”. Her books have been published in more than 40 countries and she was awarded the honorary distinction of Chevalier of the Order of Arts and Letters. Elif has published thirteen books, nine of which are novels. She writes fiction in both Turkish and English. Elif blends Western and Eastern traditions of storytelling, bringing out the myriad stories of women, minorities, immigrants, subcultures, youth and global souls. Her work draws on diverse cultures and literary traditions, as well as a deep interest in history, philosophy, Sufism, oral culture, and cultural politics. Elif’s writing breaks down categories, clichés, and cultural ghettoes. She also has a keen eye for black humour.
Adam Zagajewski is an award-winning poet, novelist, translator and essayist. Born in Lwow in 1945, he first became well-known as one of the leading poets of the Generation of ‘68’ or the Polish New Wave (Nowa Fala). His poems and essays have been translated into many languages. Among his honors and awards are a fellowship from the Berliner Kunstlerprogramm, the Kurt Tucholsky Prize, a Prix de la Liberté, and a Guggenheim Fellowship. Since 1988, he has served as visiting associate professor of English in the Creative Writing Programme at the University of Houston. In 2010, he was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature. Adam is currently co-editor of Zeszyty Literackie (Literary Review). He lives in Krakow.
Since the 1920s, generations of western Europeans got used to the monopoly of public radio and later public television. These broadcasters developed strategies to better serve audiences and distance themselves from governments. The arrival of private broadcasters, in many cases taking place only in the 1970’s, was generally viewed as a complimentary service aimed at entertaining the public. Although public service broadcasting lost market share, it remained a respected institution in society; necessary to bring up youth, to get an objective picture of the world and cater to the interests of minorities.
Eastern Europeans also got used to the monopoly of state radio and television. Those broadcasters served the communist parties and were administered and financed by governments. Their political bankruptcy came with the collapse of communist ideology, underlined in particular by the plurality of private broadcasters that came on to the scene in the early 1990s.
These private media – with plentiful Western programming – was indeed television, for so long hidden from the viewers by totalitarian regimes. Politicians flocked to their studios to take part in talk shows, abandoning once-mighty state television. Thus, in the east, the public perception of public broadcasting was predominantly sceptical, if not negative. A discussion on its development was of tangential interest, at least during the saturation process of the new private media.
Abandoned by politicians and the public, the slow and clumsy transformation of the state broadcasters into public ones was guided by the bureaucrats, almost by themselves. The driving force behind the transformation was almost exclusively the activity of Strasbourg and Brussels. We all know that in the words of European institutions “public service broadcasting is a vital element of democracy in Europe.” Transformation of state television into a public one was a condition precedent of new democracies becoming member states of the Council of Europe in some cases. The authenticity of the transformation has been important to become a candidate for entry into the European Union and even sometimes to NATO.
Developments in younger EU member states show the importance of public service broadcasters for the development of democracy – and how they can be misused.
In December 2015, Poland‘s parliament adopted a law giving the treasury minister the mandate to appoint and dismiss members of management and supervisory boards. Since the law came into effect in January, reportedly more than 100 journalists in public media have lost their jobs, allegedly for not being government-friendly.
In March, the Croatian parliament dismissed the director general of Croatian Radio-Television. A week later, the government also proposed that parliament reject a regular report from the independent media regulator, both events raising serious concerns about the overall media freedom situation in the country.
Hungary was probably the first example in the EU where public service broadcasting was practically turned back into state broadcasting, going against international standards calling for independence. New media laws in 2010 and the restructuring of the media landscape led, within a matter of one year, to all public service media being subordinated to political decisions. The new system introduced and cemented the political dependence of public service media; the governing party had nominated all new heads of public service media and the Media Authority now controls the budget of all public service media. The law vested unusually broad powers in the politically homogeneous Media Authority and Media Council, enabling them to control content of all media.
The battle to establish credible public service broadcasters in transitional democracies has been even more difficult to wage.
The latest example is the steering board of Bosnian Radio and Television which last month decided to suspend operation of all programming at the end of this month. This decision, a wrong one for several reasons, follows years of political and financial wrangling over control of the operation.
Throughout the western Balkans, significant issues are pending affecting the independence and financial stability of public broadcasting.
A bureaucratic response to the need to establish public service broadcasters has brought predictable results. The newly established broadcasters were visibly underfunded, with formal and informal administrative links – if not strings – to governments and no clear commitments to the public. Once established, it was unclear what to do with them. Most governments viewed them as an element of bureaucracy itself, a burden to carry on the road to a united Europe. If possible and convenient, they tried to make use of them through a carrot-and-stick policy.
As such, the new public service broadcasters immediately became subject to criticism by almost anyone who wanted to speak about them. Left to survive in the monstrous buildings of brutal architecture that once belonged to powerful state television, they had to sell airtime to advertisers, beg for Western donations and save on everything.
The advance of the internet and other new technologies almost killed the whole idea of television and radio, including public service broadcasting. It was saved by the transformation process – from public service broadcasting to public service media. In the West, the BBC and other companies have struggled to make use of the changing trends in media consumption. They went online, launched smartphone applications, became interactive, archived in order to engage fragmented audiences where and when required by the viewers.
Unfortunately this is not the case in the East. Public service broadcasters at best try to appeal to the older and well-educated audiences, traditional in their use of public service media. For our children, today’s debate is not only irrelevant, it is beyond their understanding.
Is there a future?
In my view we are losing the battle and might soon lose the war. To reverse the trend, we should do the following:
Give public service broadcasters a clear-cut mandate and obligation to program for the public which, in turn, should have effective feedback and control over content. There should be programmes that cater to minorities; there should be objective news, calm and matter-of-fact debates, educational and children’s programmes.
Public service broadcasters should function independently of the government. Buffer boards, meaning councils should be established to guarantee that only an abuse of a clear-cut mandate may serve to reprimand or dismiss an editor; only mismanagement and corruption may lead to firing executive directors.
And, finally, licence fees should be introduced or increased to heighten a feeling of public ownership. We can talk about other methods of independent funding, but none of them may bring this feeling of owning an institution that serves you.
Recent columns:
Dunja Mijatović: Chronicling infringements on internet freedom is a necessary task
Dunja Mijatović: Propaganda is ugly scar on face of modern journalism
Dunja Mijatović: There is hope that justice can be served in Serbia