Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
A major new global ranking index tracking the state of free expression published today (Wednesday, 25 January) by Index on Censorship sees the UK ranked as only “partially open” in every key area measured.
In the overall rankings, the UK fell below countries including Australia, Israel, Costa Rica, Chile, Jamaica and Japan. European neighbours such as Austria, Belgium, France, Germany and Denmark also all rank higher than the UK.
The Index Index, developed by Index on Censorship and experts in machine learning and journalism at Liverpool John Moores University (LJMU), uses innovative machine learning techniques to map the free expression landscape across the globe, giving a country-by-country view of the state of free expression across academic, digital and media/press freedoms.
Key findings include:
The countries with the highest ranking (“open”) on the overall Index are clustered around western Europe and Australasia – Australia, Austria, Belgium, Costa Rica, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Latvia, Lithuania, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Sweden and Switzerland.
The UK and USA join countries such as Botswana, Czechia, Greece, Moldova, Panama, Romania, South Africa and Tunisia ranked as “partially open”.
The poorest performing countries across all metrics, ranked as “closed”, are Bahrain, Belarus, Burma/Myanmar, China, Cuba, Equatorial Guinea, Eritrea, Eswatini, Laos, Nicaragua, North Korea, Saudi Arabia, South Sudan, Syria, Turkmenistan, United Arab Emirates and Yemen.
Countries such as China, Russia, Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates performed poorly in the Index Index but are embedded in key international mechanisms including G20 and the UN Security Council.
Ruth Anderson, Index on Censorship CEO, said:
“The launch of the new Index Index is a landmark moment in how we track freedom of expression in key areas across the world. Index on Censorship and the team at Liverpool John Moores University have developed a rankings system that provides a unique insight into the freedom of expression landscape in every country for which data is available.
“The findings of the pilot project are illuminating, surprising and concerning in equal measure. The United Kingdom ranking may well raise some eyebrows, though is not entirely unexpected. Index on Censorship’s recent work on issues as diverse as Chinese Communist Party influence in the art world through to the chilling effect of the UK Government’s Online Safety Bill all point to backward steps for a country that has long viewed itself as a bastion of freedom of expression.
“On a global scale, the Index Index shines a light once again on those countries such as China, Russia, Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates with considerable influence on international bodies and mechanisms – but with barely any protections for freedom of expression across the digital, academic and media spheres.”
Nik Williams, Index on Censorship policy and campaigns officer, said:
“With global threats to free expression growing, developing an accurate country-by-country view of threats to academic, digital and media freedom is the first necessary step towards identifying what needs to change. With gaps in current data sets, it is hoped that future ‘Index Index’ rankings will have further country-level data that can be verified and shared with partners and policy-makers.
“As the ‘Index Index’ grows and develops beyond this pilot year, it will not only map threats to free expression but also where we need to focus our efforts to ensure that academics, artists, writers, journalists, campaigners and civil society do not suffer in silence.”
Steve Harrison, LJMU senior lecturer in journalism, said:
“Journalists need credible and authoritative sources of information to counter the glut of dis-information and downright untruths which we’re being bombarded with these days. The Index Index is one such source, and LJMU is proud to have played our part in developing it.
“We hope it becomes a useful tool for journalists investigating censorship, as well as a learning resource for students. Journalism has been defined as providing information someone, somewhere wants suppressed – the Index Index goes some way to living up to that definition.”
Index’s new issue of the magazine looks at the importance of whistleblowers in upholding our democracies.
Featured are stories such as the case of Reality Winner, written by her sister Brittany. Despite being released from prison, the former intelligence analyst is still unable to speak out after she revealed documents that showed attempted Russian interference in US elections.
Playwright Tom Stoppard speaks to Sarah Sands about his life and new play title ‘Leopoldstatd’ and, 50 years on from the Pentagon Papers, the “original whistleblower” Daniel Ellsberg speaks to Index .

Daniels Ellsberg is a former US Government contractor who worked for Rand Corporation and exposed the country’s long-term involvement in Vietnam through the release of the Pentagon Papers in 1971.

Nerma Jelacic works for the Commission for International Justice and Accountability, which gathers war crimes evidence during ongoing conflicts.

Sir Tom Stoppard is a Czech-born British playwright and screenwriter who’s written for radio, stage and television.
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
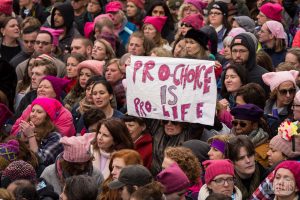
A Women's March in 2017. Credit: Mark Dixon/Flickr
“I had a second trimester abortion,” tweeted Erica Goldblatt Hyatt, a Canadian living in the USA. “Our son never formed an airway. Had he survived birth he would have been brain dead. That wasn’t the life I wanted for him. It was the first true parenting decision I ever made.”
Goldblatt Hyatt’s story was included in a CNN article, along with stories from a mother of two who didn’t want more children and a woman who got pregnant at 16 with no family support, about the reasons women have abortions.
Since the passing of Roe v Wade in the Supreme Court in 1973, abortion has been enshrined in law in the USA. Some states have restrictions on access to abortion, but the ruling that it is a legal right has remained in place.
The passing of Ruth Bader Ginsburg in September, and her replacement by Amy Coney Barrett, has fuelled the fire of panic in women that this right could soon be snatched away, a panic they have felt since 2016 when Donald Trump said that if he is able to select enough justices for the bench, over-turning Roe v Wade “will happen automatically”.
The USA is not the only country where reproductive rights are being dismantled. Mass protests have broken out in Poland over the last few weeks after the constitutional court ruled that, even in the case of severe foetal abnormalities, women will be forced by law to carry the pregnancy to term. This is a further encroachment on reproductive freedom in a country that already has some of the most restrictive abortion laws in Europe.
The women of Northern Ireland are also facing barriers to reproductive freedom. Despite abortion being decriminalised in October 2019, access to clinics is severely lacking, prompting the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists to write a letter, sections of which were published by the Independent on 26 October, warning of the risks to women.
“There have already been at least two cases of attempted suicide by women in Northern Ireland unable to access care,” it says, adding that there has been a dramatic increase in women “turning to unregulated methods of abortion during the pandemic.”
Reproductive rights are a freedom of expression issue. We do not only express ourselves verbally and artistically, we express ourselves through the choices we make about how we live our lives and what happens to our bodies. The decisions about when, if ever, to become a mother, and to how many children, are some of the biggest a woman can make. When states take control of this decision, they are taking control of our self-expression.
This is not to say that these decisions cannot be discussed and debated. Debate is at the heart of freedom of expression and that extends to the topic of abortion. People should be allowed to talk about the questions surrounding it, such as “when does life start?” For some it starts at the moment of conception, meaning abortion at any stage, even the very early weeks, would constitute ending a life. But this is not a consensus. And even if life does start at conception, that would not necessarily mean that abortion should be banned. After all, there are all kinds of practises that we allow as a society even if we question them morally because we believe banning them would ultimately go against freedom and autonomy.
Pro-life advocates must of course have their right to this view respected, and no one should force them to abort. But equally people attempting to force their beliefs on others, and control their actions to be in line with these beliefs, is when the defenders of freedom of expression must step in.
It should go without saying that the consequences of being forced to have a child are far-reaching. There’s the toll on mental health for one. According to research by scientists at King's College London one in four pregnant women suffer from mental health problems. This can be even more extreme for those in unwanted pregnancies. In 2017 a young woman, who became known as Ms Y, sued the official health service in Ireland after she was not only denied an abortion but held against her will and forced medication to prolong the pregnancy. She had arrived in Ireland in 2014 seeking asylum and soon discovered she was pregnant. She said she'd been raped and was suicidal because of the pregnancy.
Research also shows that having a baby can hold a woman’s career back six years. Inflicting career disruptions on women by forcing them to continue with unwanted pregnancies is an infringement on their self-expression in the workplace that can have long-spanning repercussions. And then there are all the negative impacts it can have on relationships, finances, social support networks – the list could go on. None of these are trivial matters. Rather they’re all choices that are part of our free expression.
The Polish ruling also highlights that many abortions are because either the baby or the mother, or both, are seriously ill. Abortion is not always a lifestyle choice. It is often a very traumatic decision a woman is forced to make about an intended pregnancy. Heart-breaking as these decisions undoubtedly are, the most profound forms of expression are often the choices we make about our health and that of our families.
Incidentally, as is often the case with censoring behaviour, removing someone’s choice can actually be counter-productive. A study by the National Library of Medicine concluded that women who had had an abortion were more likely to have an intended pregnancy within the next five years than women forced to continue with an unwanted pregnancy. Diane Greene Foster, one of the academics who conducted the study, concluded: “Being able to access abortion gives women the opportunity to have a child later with the right partner, at the right time”. She added that a woman who is denied an abortion is likely to “face diminished opportunities to achieve other life goals, gain secure financial footing, and have a child she can cherish and support”.
Remaining childless, or having children with the right partner when it is the right time to do so, is an umbrella of self-expression under which so many other forms of expression shelter; expression through work, through lifestyle choices, through parenting ability. It is a form of expression which must remain in the hands of individuals and be kept out of the grips of the state.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship has filed an alert to the Council of Europe about a defamation action that is being taken against the Dublin Inquirer, its co-founder Sam Tranum and reporter Laoise Neylon. The Council of Europe has formally notified Ireland of the legal action.
The alert is the first media freedom alert on Ireland since the Council of Europe’s alert platform was launched in 2015. The platform catalogues threats to media freedom in the Council of Europe’s 47 member states.
On the back of the alert, Index on Censorship and seven other media freedom organisations have also written to justice minister, Helen McEntee, and foreign affairs minister, Simon Coveney, to express their concerns over the lawsuit.
“We believe that this legal action is a Strategic Lawsuit against Public Participation (Slapp), intended to intimidate and silence an independent media outlet that is reporting in the public interest,” they wrote.
“The aim of a Slapp is not to succeed in court, but to drain their targets of money, time, and energy in an effort to discourage them from reporting further on a particular person or issue,” the letter explains.
The organisations urge the government to pursue reform of Irish defamation law and to support the creation of anti-Slapps legislation at EU level. “We call on you to get behind such measures in order to bring about concrete protections – including an anti-Slapps directive – for freedom of expression, access to information, and ultimately our democracies.”
Click here to read our report on the rise of Slapps.
Read below the letter to McEntee and Coveney in full:
8 September 2020
Dear Minister Helen McEntee TD, Minister for Justice
Dear Minister Simon Coveney TD, Minister for Foreign Affairs and Trade
Cc: Permanent Representation of Ireland to the EU
Index on Censorship, alongside the undersigned press freedom organisations, are writing to raise our concern about legal action that is being taken against the independent news outlet, the Dublin Inquirer, its co-founder Sam Tranum, and its reporter Laoise Neylon.
As outlined in the media freedom alert that was issued by the Council of Europe today, the Dublin Inquirer is facing a defamation lawsuit for an article it published on its website on 26 August, which reported on an eviction that had taken place in Glasnevin the previous week. Tranum, Neylon, and the Dublin Inquirer, were served with summons on 31 August.
We believe that this legal action is a Strategic Lawsuit against Public Participation (SLAPP), intended to intimidate and silence an independent media outlet that is reporting in the public interest. The aim of a SLAPP is not to succeed in court, but to drain their targets of money, time, and energy in an effort to discourage them from reporting further on a particular person or issue.
The SLAPP that the Dublin Inquirer is facing is just one example of a phenomenon that has become widespread in Europe in recent years: at the time of her death in 2017, Maltese journalist Daphne Caruana Galizia had 47 vexatious lawsuits filed against her. This year, the Council of Europe Platform for the Protection of Journalism and Safety of Journalists has recorded SLAPPs in Belgium, Malta, France, Bulgaria, Poland, and Romania – and we have reason to believe that these are just the tip of the iceberg.
The lengthy process and extremely high costs associated with defending a defamation case means that Ireland’s draconian defamation laws are an ideal tool with which to threaten and intimidate. Because of the arduousness of exhausting domestic measures, the European Court of Human Rights provides little practical protection to Irish journalists and media outlets. This means that small media outlets, like the Dublin Inquirer, could face closure when targeted with such legal threats and actions.
We therefore urge you, not only to pursue the long overdue reform of Irish defamation law, but to support the creation of robust anti-SLAPPs legislation at EU level. The European Commission has committed to considering suitable anti-SLAPP measures as part of its upcoming European Democracy Action Plan. We call on you to get behind such measures in order to bring about concrete protections – including an anti-SLAPPs directive – for freedom of expression, access to information, and ultimately our democracies.
Thank you in advance for your consideration of our concerns. We look forward to your response and would be glad to schedule a meeting to discuss in more detail.
Kind regards,
Index on Censorship
European Centre for Press and Media Freedom (ECPMF)
The Daphne Caruana Galizia Foundation
Irish Council for Civil Liberties (ICCL)
Free Press Unlimited (FPU)
Article 19
Reporters Without Borders (RSF)
Committee to Protect Journalists (CPJ)[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]