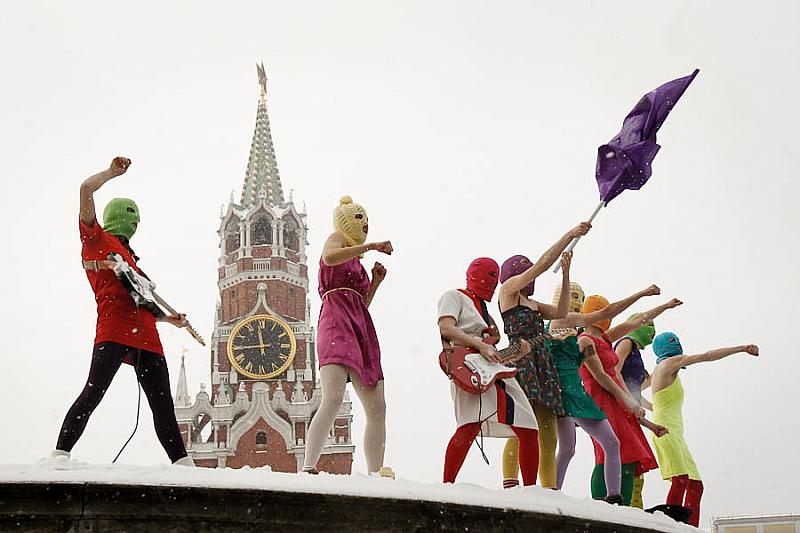8 Jul 2013 | Comment, Europe and Central Asia, News
 Global action is needed to counter Putin’s crackdown on civil society, says Yuri Dzhibladze, president of the Center for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights
Global action is needed to counter Putin’s crackdown on civil society, says Yuri Dzhibladze, president of the Center for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights
(more…)
2 Jul 2013 | Volume 42.02 Summer 2013
The current issue of Index on Censorship magazine features a special report on the shifting world power balance and the implications for freedom of expression.
“The multipolar world can be one where universal human rights and freedom of expression are kept firmly on the agenda, and increasingly respected, if these democracies hold themselves and each other to account — and are held to account — at home and internationally,” write Index CEO Kirsty Hughes and London School of Economics professor Saul Estrin.
The issue also looks at press freedom in Italy, Burma, Mexico, Columbia and India as well as violence against journalists and arrests of those who expose uncomfortable truths. “Worldwide, on average only one in ten cases of murders of journalists ends in a conviction,” says Guy Berger, author of an article on the threats and dangers journalists encounter around the world. Instead of being reassured that the rule of law will be upheld, “the take-away lesson for everyone is: journalists can be killed with impunity”.
From the current issue
Global view: Who has freedom of expression? | The multipolar challenge to free expression | Censorship: The problem child of Burma’s dictatorship | News in monochrome: Journalism in India
Also in this issue:
- John Lloyd on how party politics have skewed Italian journalism
- Yavuz Baydar says Turkey’s media moguls must defend free speech
- Htoo Lwin Myo tells what was it is like to work as a writer in Burma
- Bharat Bhushan on “paid-for” news and the absence of marginal voices in the Indian media
- Lawrence Freedman and Benedict Wilkinson on the opportunities — and limits — of online activism
- A new play from Turkmenistani writer-in-exile Farid Tukhbatullin, whose wit offers a glimpse of life inside one of the world’s most closed and repressive countries.
- Find out more here | Subscribe now
Did you know you can read the magazine on your iPhone/iPad? Download for FREE then upgrade to a 30 day subscription for only £1.79.
22 Jun 2013 | News, Russia
Index’s Padraig Reidy speaks to two members of the Russian feminist punk group on a secret trip to the UK
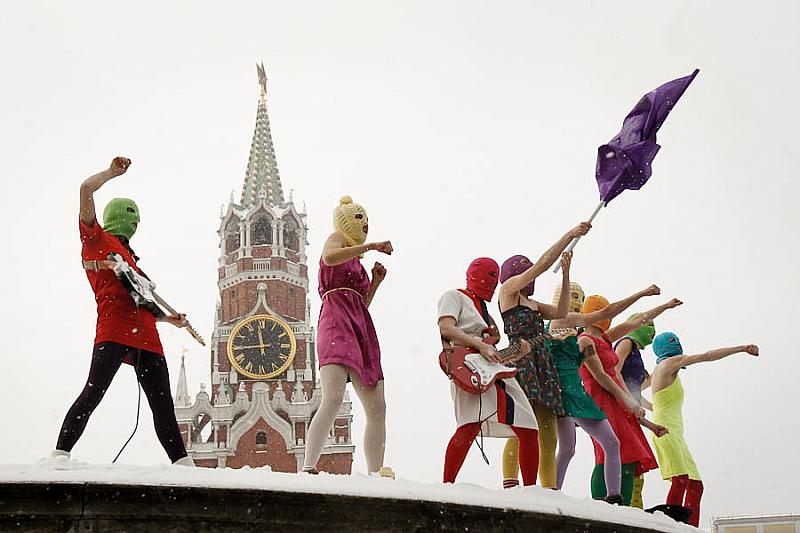
Pussy Riot members perform in Moscow
(more…)
21 Jun 2013 | Events
Date: 18 July, 6:30-8pm at ECFR
Venue: European Council on Foreign Relations, London
Tickets: Free, but space is limited. Email [email protected] if you’d like to attend.
Index, in partnership with the European Council on Foreign Relations, is holding a timely debate on the shifting world order and its impact on rights and freedoms. The event will also launch the latest issue of Index on Censorship magazine, including a special report on the multipolar world.
The balance of economic, political and social power is shifting across the world; in this debate we will ask how this might affect individuals’ rights and freedoms. In the last two months we have seen protests across the world as citizens challenge their governments. Meanwhile news of US internet companies being tapped by the NSA continue to hit the headlines. Discussions of who is tapping whom continue to be uncovered. From nations to companies, who has the power now?
The expert panelists include: Index CEO Kirsty Hughes, ECFR Senior Policy Fellow Anthony Dworkin, and Turkish journalist and writer Ece Temelkuran.


 Global action is needed to counter Putin’s crackdown on civil society, says Yuri Dzhibladze, president of the Center for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights
Global action is needed to counter Putin’s crackdown on civil society, says Yuri Dzhibladze, president of the Center for the Development of Democracy and Human Rights