Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_video link=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VpbIyNZ7WKI”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][three_column_post title=”You might also like to watch” category_id=”41199″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Attacks on press freedom in Europe are at serious risk of becoming a new normal, 14 international press freedom groups and journalists’ organisations including Index on Censorship warn today as they launch the 2020 annual report of the Council of Europe Platform to Promote the Protection of Journalism and the Safety of Journalists. The fresh assault on media freedom amid the Covid-19 pandemic has worsened an already gloomy outlook.
 The report analyses alerts submitted to the platform in 2019 and shows a growing pattern of intimidation to silence journalists in Europe. The past weeks have accelerated this trend, with the pandemic producing a new wave of serious threats and attacks on press freedom in several Council of Europe member states. In response to the health crisis, governments have detained journalists for critical reporting, vastly expanded surveillance and passed new laws to punish “fake news” even as they decide themselves what is allowable and what is false without the oversight of appropriate independent bodies.
The report analyses alerts submitted to the platform in 2019 and shows a growing pattern of intimidation to silence journalists in Europe. The past weeks have accelerated this trend, with the pandemic producing a new wave of serious threats and attacks on press freedom in several Council of Europe member states. In response to the health crisis, governments have detained journalists for critical reporting, vastly expanded surveillance and passed new laws to punish “fake news” even as they decide themselves what is allowable and what is false without the oversight of appropriate independent bodies.
These threats risk a tipping point in the fight to preserve a free media in Europe. They underscore the report’s urgent wake-up call on Council of Europe member states to act quickly and resolutely to end the assault against press freedom, so that journalists and other media actors can report without fear.
Although the overall response rate by member states to the platform rose slightly to 60 % in 2019, Russia, Turkey, and Azerbaijan – three of the biggest media freedom violators – continue to ignore alerts, together with Bosnia and Herzegovina.
2019 was already an intense and often dangerous battleground for press freedom and freedom of expression in Europe. The platform recorded 142 serious threats to media freedom, including 33 physical attacks against journalists, 17 new cases of detention and imprisonment and 43 cases of harassment and intimidation.
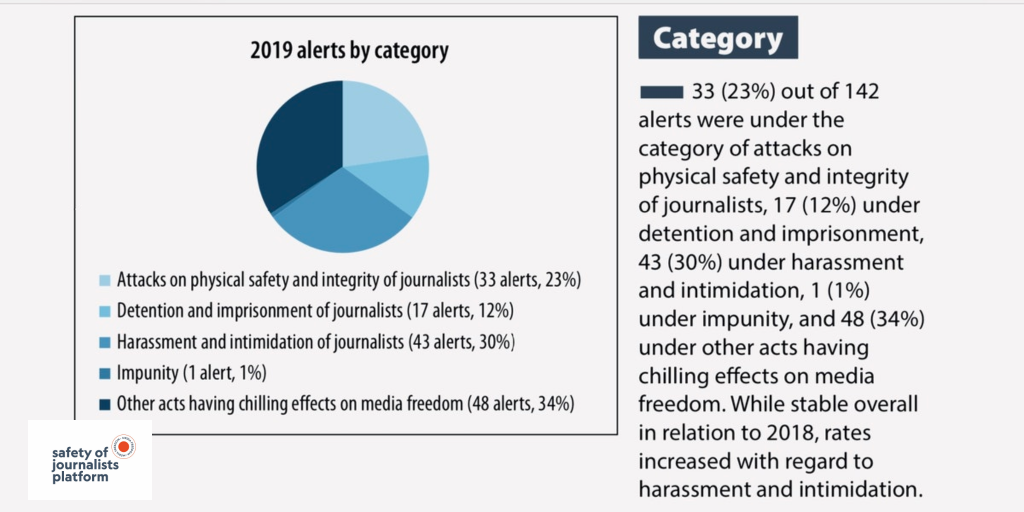
The physical attacks tragically included two killings of journalists: Lyra McKee in Northern Ireland and Vadym Komarov in Ukraine. Meanwhile, the platform officially declared the murders of Daphne Caruana Galizia (2017) in Malta and Martin O’Hagan (2001) in Northern Ireland as impunity cases, highlighting authorities’ failure to bring those responsible to justice. Only Slovakia showed concrete progress in the fight against impunity, indicting the alleged mastermind and four others accused of murdering journalist Ján Kuciak and his fiancée, Martina Kušnírová.
At the end of 2019, the platform recorded 105 cases of journalists behind bars in the Council of Europe region, including 91 in Turkey alone. The situation has not improved in 2020. Despite the acute health threat, Turkey excluded journalists from a mass release of inmates in April 2020, and second-biggest jailer Azerbaijan has made new arrests over critical coverage of the country’s coronavirus response.
2019 saw a clear increase in judicial or administrative harassment against journalists, including meritless SLAPP cases, and spurious and politically motivated legal threats. Prominent examples were the false drug charges filed against Russian investigative journalist Ivan Golunov and the continued imprisonment of journalists in Ukraine’s Russia-controlled Crimea. The Covid-19 crisis has strengthened officials’ tools to harass journalists, with dangerous new “fake news” laws in countries such as Hungary and Russia that threaten journalists with jail for contravening the official line.
Other serious issues identified by 2019 alerts included expanded surveillance measures threatening journalists’ ability to protect their sources, including in France, Poland and Switzerland, as well political attempts to “capture” media through ownership and market manipulation, most conspicuously of all in Hungary. These threats, too, are exacerbated by the actions taken by several governments under the health crisis, which further include arbitrary limitations on independent reporting and on journalists’ access to official information about the pandemic.
Jessica Ní Mhainín, Index’s policy research and advocacy officer, says, “There is a growing pattern of intimidation aimed at silencing journalists in Europe. The situation in Eastern Europe – especially in Hungary, Poland, and Bulgaria – is particularly concerning. But the killing of Lyra McKee shows that we cannot take the safety of journalists for granted anywhere – not even in countries that are seen to be safe for journalists. This report provides an opportunity for us all to come to grips with the serious situation that is facing European media and to remind ourselves of the vital role that the media play in holding power to account.”
Index and the other platform partners call for urgent scrutiny of action taken by governments to claim extraordinary powers related to freedom of expression and media freedom under emergency legislation that are not strictly necessary and proportionate in response to the pandemic. Uncontrolled and unlimited state of emergency laws are open to abuse and have already had a severe chilling effect on the ability of the media to report and scrutinise the actions of state authorities.
While the platform welcomes an increased focus on press freedom by European institutions, including both the Council of Europe and European Union institutions, the ongoing crisis demands more urgent and stringent responses to protect media freedom and freedom of expression and information, and to support the financial sustainability of independent professional journalism. In the age of emergency rule, protecting the press as the watchdog of democracy cannot wait.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]

Index on Censorship’s Monitoring and Advocating for Media Freedom project monitors threats, limitations and violations related to media freedom in Azerbaijan, Belarus, Russia, Turkey and Ukraine. Previously these countries were also included in the Mapping Media Freedom project, which Index incubated and managed between 2014 – 2018.
This report summarises policy recommendations based on analysis since April, 2019. The recommendations are based on research by in-country correspondents and Index staff. Country reports published by the project since April are available on the project webpage.
After a brief background section, the report sets out key policy recommendations that apply to all the project countries, followed by key recommendations for each project country.
Background
It is essential that media freedom groups and international organisations continue to monitor, verify and document threats, limitations and violations related to media freedom in Azerbaijan, Belarus, Russia, Turkey and Ukraine, continue to raise awareness about the challenges and to advocate for change. Media freedom is severely restricted in all these countries and journalists are under great pressure.
Violence against journalists; misuse of counter-terror and security legislation to silence journalists; travel bans that isolate journalists and impact them professionally; failure to investigate violent crimes against journalists and silencing and punishing journalists through defamation and insult laws – all these are familiar tactics and increasingly common. In more recent years the introduction of restrictive internet-related legislation, such as in Russia, has opened a new frontline in the fight to safeguard media freedom.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR ALL PROJECT COUNTRIES
Governments and multilateral groups, in particular the European Union (EU), must take a strong stand in defence of media freedom and journalists, both in their bilateral relations with the project countries and in multilateral processes. Governments and the EU should ensure that issues such as proposed or existing legislation that restricts media freedom, violence against journalists and failures to investigate crimes against journalists, form part of the agenda in strategic bilateral and multilateral discussions.
Countries that have a version of the Magnitsky Act (in the EU, this includes Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania and The Netherlands) should consider making use of this legislation in cases where media freedom and the safety of journalists are at stake. Countries that have not yet introduced such legislation should consider doing so. The UK should put its Magnitsky amendment into use.

A man lays flowers near the picture of murdered journalist Anna Politkovskaya, during a rally in Moscow, Russia, 7 October 2009. CREDIT: EPA / Alamy Stock Photo
Impunity is a major challenge in all the project countries. In Azerbaijan, the death of freelance journalist Rafic Tagi, who died in hospital after a stabbing in 2011, has never been investigated properly. Belarussian cameraman Dzmitry Zavadski disappeared in 2000 on his way to meet journalist Pavel Sheremet, later killed in Ukraine in 2016. Zavadski’s body was never found.
The instigator of the 2006 contract killing of investigative journalist Anna Politkovskaya in Russia is still not known, nor is the motive. In 2018 the European Court of Human Rights found that the Russian authorities had failed to carry out an effective investigation into her killing. Turkey failed to investigate the death of editor Rohat Aktaş, killed when he was covering hostilities between Kurdish separatists and Turkish forces in 2016.
Ukrainan journalist Pavel Sheremet was killed by a car bomb in Kyiv in 2016 and, despite statements from the authorities that the case is a priority, there has been no progress. All the project countries should commit to investigating unsolved killings of journalists and should implement the guidelines in recommendation CM/Rec(2016)4 of the Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe.
In relation to impunity, the guidelines envisage that when investigations and prosecutions have not resulted in justice member states can consider establishing special inquiries or independent specialised bodies, and that the latter could involve participation by respected media and/or civil society figures.
 Council of Europe member states must engage fully with the platform for journalism
Council of Europe member states must engage fully with the platform for journalismCouncil of Europe member states must engage more actively with the Council of Europe’s Platform for the protection of journalism and safety of journalists. The partner organisations of the platform, which include Index on Censorship, should continue to use the platform to raise awareness of media freedom violations and threats to journalists. This should include advocating for states to respond to all alerts communicated to the platform.
The overall response rate from states in 2018 was only 39%. It is also important that states provide substantive replies to alerts and engage in follow-up dialogue with the partner organisations. The platform is an underused mechanism, with potential to achieve more. Partner organisations can also be of assistance to member states that are willing to engage fully.
Belarus is not a member of the Council of Europe, but other international organisations and processes, such as the special procedures of the United Nations human rights council, should be engaged to follow up cases and issues in Belarus.

Azerbaijan must halt its use of travel bans for journalists including Khadija Ismayilova
The EU must use its influence to defend media freedom and journalists in Azerbaijan. Negotiations on an agreement to replace the EU-Azerbaijan Partnership and Cooperation Agreement, in place since 1999, are at an advanced stage and will need to be brought to a conclusion by the new European Commission. It is extremely important that the EU raises media freedom and human rights in these negotiations.
In 2018, the European Parliament adopted a resolution which recommended that the EU should make deepening of relations with Azerbaijan conditional on respecting democratic values and human rights, and that it should ensure that Azerbaijan frees its political prisoners (including journalists such as Afgan Mukhtarli) before the negotiations on a new partnership agreement are concluded. Mukhtarli remains imprisoned.
Azerbaijan must refrain from targeting journalists’ online activities, including through call hacking, internet blocking and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. In October, internet blockages and disruption to mobile phone services were reported in central Baku in connection with ongoing protests. Several journalists were also detained or subjected to physical violence during the protests. Social media platforms such as YouTube should respect Azerbaijani users’, including journalists’ right to seek, receive and impart information. Platforms should implement terms and conditions consistently and transparently, including when dealing with harassment of journalists by alleged state-sponsored trolls.
Azerbaijan must halt its use of travel bans for journalists. For example, the well known journalist Khadija Ismayilova is currently under a travel ban. OSCE Media Freedom Representative Harlem Désir has stated that it is a serious hindrance to her work as a professional journalist.
Belarus must amend the law on mass media. The legislation currently requires journalists, including freelancers, who work for media outlets registered outside Belarus to obtain accreditation from the foreign affairs ministry. This has led to journalists being fined repeatedly. At a very minimum, Belarus must urgently establish procedures that enable journalists to appeal rejected accreditation requests.
Other governments must make it clear to Belarus that restrictive and repressive actions against journalists will not be tolerated. This applies to the requirements for accreditation for journalists working for non-Belarussian media outlets above, but also to the practice of detaining journalists for short periods. Some observers have credited Belarus’ tendency to impose fines on journalists or to detain them for short periods – rather than sentence and imprison them – as an attempt to build alliances in the West at a time when relations with Russia are weak. Other governments need to signal clearly it is not acceptable.
In the case of Belarus, which is not a member of the Council of Europe, it is important that support and training aimed at enabling journalists to defend their rights includes training on other international organisations and processes, such as the special procedures of the United Nations human rights council, including the special rapporteur on the situation of human rights in Belarus.

Russia must investigate cases of trumped-up charges against journalists such as Ivan Golunov
Russia must refrain from finalising the legislative changes that would extend the scope of “foreign agent” to individual journalists. Existing problematic legislation already requires media outlets that receive funds from abroad to register as foreign agents. At the time of writing the Duma has approved changes that would extend this to individual journalists, including freelance journalists and bloggers. Any one of these receiving payments for services, or a salary from abroad, would need to register with the ministry of justice. All published work would need to display a “foreign agent” label. This legislation should not proceed, and existing legislation that labels media outlets as foreign agents should be reviewed.
Access to court proceedings is a frequent problem for journalists. As stated in Opinion No. 8 of the Consultative Council of European Prosecutors: “Transparency in the performance of the prosecutor’s duties is an essential component of the rule of law, and one of the important guarantees of a fair trial. Not only must justice be done, but it must also be seen to be done. In order for this to be possible, the media should be able to provide information on judicial, criminal or other proceedings” (paragraph 30). The authorities must review existing processes for compliance with international standards.
The authorities must thoroughly investigate cases of trumped-up charges against journalists and ensure that the instigators are brought to justice. Recent incidents include the high-profile case of Ivan Golunov, arrested for possession and trafficking of drugs, and what appears to be a fake letter sent in the name of Nikita Telizhenko with the aim of discrediting him.
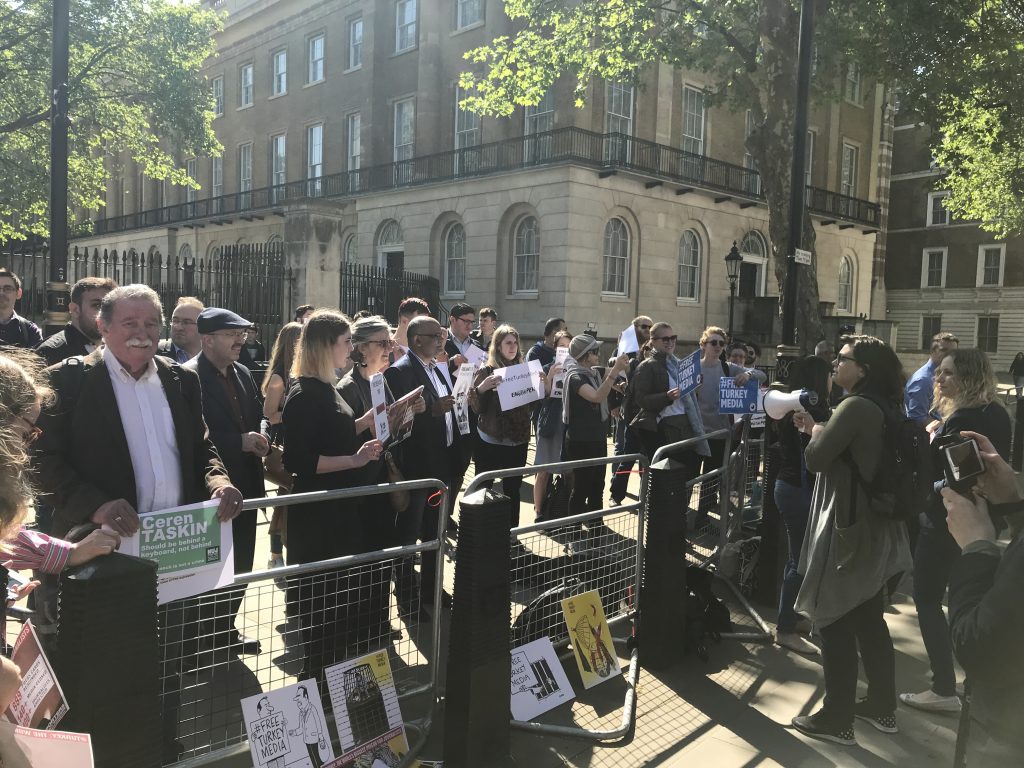

Index on Censorship magazine editor Rachael Jolley leads chants in support of Turkey’s jailed journalists ahead of Turkish President Erdogan’s visit to Downing Street in May 2018
The judicial reform strategy (JRS), launched in May, 2019, will not achieve any meaningful change, at least not in its current form. Turkey’s judicial system is not independent: it is overloaded with cases, many which concern journalists, and it has been undermined through the large-scale dismissal of judges. It is extremely important that other countries and international organisations scrutinise the judicial reform strategy, and make it clear that in its current form it is completely inadequate when it comes to addressing the enormous structural problems of the judiciary.
In May 2019, the United Nations special rapporteur on the promotion and protection of the right to freedom of opinion and expression published a follow-up report to an earlier visit to Turkey in 2016. The rapporteur had made a series of recommendations in 2016, which included releasing jailed journalists and reversing the closure of media outlets. The follow-up report found that Turkey had either failed to implement or had contravened all the recommendations, with the exception of one (lifting the state of emergency). Turkey should urgently implement all the recommendations made by the United Nations special rapporteur.
Diplomatic representations and international organisations, including the EU, need to support observation of trials that involve journalists and media outlets. High-profile trials in central locations can be well-attended by observers, but coverage of trials in remote locations is more limited. Support can include sending representatives to follow trials and/or financial support for organisations that monitor trials.

Ukraine President Volodymyr Zelenskiy must engage with the media. Photo: Wikimedia
The government needs to undertake an independent and transparent review of state support, including financial support for far-right groups associated with extremism. The review should involve international experts. It should include investigating the possibility of state security force collusion with paramilitary and extremist organisations and thorough investigations of alleged involvement in violence against journalists, such as the unsolved murder of Oles Buzina.
President Volodymyr Zelenskiy reportedly held a 14-hour press conference in October, attended by 300 journalists. Whether it signals a new era in the relationship between Ukraine’s elected representatives and the media remains to be seen. The failure of the president and lawmakers to engage meaningfully with the media in the past has been a challenge for journalists and this needs to change.
In the highly divisive media landscape, the role of the public broadcaster is extremely important. Ukraine’s public broadcasting company is severely underfunded and currently has a very small audience. As Index on Censorship outlined in its Demonising the Media report a year ago, a significant but underreported trend in the region is the threat to public broadcasters. A number of national broadcasters in the EU and neighbouring countries were brought under closer government control in 2014-18. Ensuring both sufficient funding and editorial independence are crucial in ensuring the public’s right to know is defended.
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_custom_heading text=”3 Incidents” use_theme_fonts=”yes”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
19 October 2019 – Multiple media outlets reported the arrest and assault of journalists during an unsanctioned rally against corruption and low wages in Baku.
Journalists detained during the rally included Gulnaz Gambarli, Nurlan Libre (Gahramanli), Farid Ismayilov, Mehin Kerimi, Abulfat Bakhshali, Vugar Mirzabay and Fatima Movlamli, as well as blogger Mehman Huseynov. All were released shortly after.
According to the independent reporter Ulviyya Ali, Nurlan Libre was assaulted in the police car after being detained at the rally. At least three journalists were reported to have sustained minor injuries as a result of police actions: Sevinc Vagifqizi sustained bruises on her arms, while Ramin Deko and Shahla Abbasova also sustained minor injuries. Journalist Tazakhan Miralamli was held at the police station for more than four hours. None of the journalists filed complaints against the police.

More than 80 people were reportedly arrested during the protests in October, including at least eight journalists.
Limitation to media freedom: arrest/detention/interrogation; property damage; physical assault
Source of violation: public/state security;
Links: https://twitter.com/UlviyyaAli/status/1185478151754924032?s=20
https://www.rferl.org/a/police-arrest-opposition-activists-ahead-of-baku-rally/30225138.html
17 October 2019 – Meydan TV journalist Seymur Hezi was arrested while leaving his house in Baku two days before a scheduled protest, Hezi’s wife Nigar told the Committee to Protect Journalists. He was sentenced to 15 days in administrative detention for alleged hooliganism and noncompliance with police orders. Hazi was reportedly intending to cover the protests, which were due to take place on 19 October.
The arrest came less than two months after the journalist was released from prison, where he served 5 years on charges of hooliganism. Hazi was recognized as a prisoner of conscience by Amnesty International. The European Court of Human Rights had ruled that his detention was illegal.
Updates:
29 October 2019 – Azadliq Radio reported that Seymur Hezi was sentenced to an additional 15 days in administrative detention.
17 November 2019 – Azadliq Radio reported that Seymur Hezi was released.
Limitation to media freedom: arrest/detention/interrogation;
Source of violation: court/judicial
Links: https://cpj.org/2019/10/azerbaijani-journalist-seymur-hazi-detained-in-run.php
https://eurasianet.org/azerbaijan-detains-opposition-leader-and-reportedly-many-more
https://www.azadliq.org/a/otuz-gunluk-hebs-muddeti-basha-chatan-seymur-hezi-azadliqda/30275204.html
https://turkustan.info/2019/10/29/seymur-h%C9%99zinin-h%C9%99bs-mudd%C9%99ti-uzadildi/
http://teref.az/hadise/132289-seymur-hezinin-hebs-muddeti-uzadildi.html
16 October 2019 – Online news site Sozcu.az reported that 7gun.az’s editor, Javid Shiraliyev, was the victim of an attempted arson attack. His house was set on fire in the early hours of 16 October. 7gun.az had previously published a series of stories about corruption in Azerbaijan.
Shiraliyev said that despite the family being at home at the time of the incident, no one was injured. He had reported the incident to the police.
Shiraliyev said he believed that the attack was in retaliation for the series of stories his outlet published about corruption and local governance violations in Masalli administrative district.
https://sozcu.az/masallida-jurnalistin-evini-yandirmaq-ist-yibl-r/
Limitation to media freedom: property damage;
Source of violation: unknown[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1574783884308-a5185785-918d-4″ taxonomies=”8996″][/vc_column][/vc_row]