7 Feb 2017 | Awards, News, Press Releases
 Judges include actor Noma Dumezweni; former Vanity Fair editor Tina Brown
Judges include actor Noma Dumezweni; former Vanity Fair editor Tina Brown
- Sixteen courageous individuals and organisations who fight for freedom of expression in every part of the world
A Zimbabwean pastor who was arrested by authorities last week for his #ThisFlag campaign, an Iranian Kurdish journalist covering his life as an interned Australian asylum seeker, one of China’s most notorious political cartoonists, and an imprisoned Russian human rights activist are among those shortlisted for the 2017 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards.
Drawn from more than 400 crowdsourced nominations, the shortlist celebrates artists, writers, journalists and campaigners overcoming censorship and fighting for freedom of expression against immense obstacles. Many of the 16 shortlisted nominees are regularly targeted by authorities or by criminal and extremist groups for their work: some face regular death threats, others criminal prosecution or exile.
“The creativity and bravery of the shortlist nominees in challenging restrictions on freedom of expression reminds us that a small act — from a picture to a poem — can have a big impact. Our nominees have faced severe penalties for standing up for their beliefs. These awards recognise their courage and commitment to free speech,” said Jodie Ginsberg, CEO of campaigning nonprofit Index on Censorship.
Awards are offered in four categories: arts, campaigning, digital activism and journalism.
Nominees include Pastor Evan Mawarire whose frustration with Zimbabwe’s government led him to the #ThisFlag campaign; Behrouz Boochani, an Iranian Kurdish journalist who documents the life of indefinitely-interned Australian asylum seekers in Papua New Guinea; China’s Wang Liming, better known as Rebel Pepper, a political cartoonist who lampoons the country’s leaders; Ildar Dadin, an imprisoned Russian opposition activist, who became the first person convicted under the country’s public assembly law; Daptar, a Dagestani initiative tackling women’s issues like female genital mutilation that are rarely discussed publicly in the country; and Serbia’s Crime and Corruption Reporting Network (KRIK), which was founded by a group of journalists to combat pervasive corruption and organised crime.
Other nominees include Hungary’s Two-tail Dog Party, a group of satirists who parody the country’s political discourse; Honduran LGBT rights organisation Arcoiris, which has had six activists murdered in the past year for providing support to the LGBT community and lobbying the country’s government; Luaty Beirão, a rapper from Angola, who uses his music to unmask the country’s political corruption; and Maldives Independent, a website involved in revealing endemic corruption at the highest levels in the country despite repeated intimidation.
Judges for this year’s awards, now in its 17th year, are Harry Potter actor Noma Dumezweni, Hillsborough lawyer Caiolfhionn Gallagher, former Vanity Fair editor Tina Brown, designer Anab Jain and music producer Stephen Budd.
Dumezweni, who plays Hermione in the stage play Harry Potter and the Cursed Child, was shortlisted earlier this year for an Evening Standard Theatre Award for Best Actress. Speaking about the importance of the Index Awards she said: “Freedom of expression is essential to help challenge our perception of the world”.
Winners, who will be announced at a gala ceremony in London on 19 April, become Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards Fellows and are given support for their work, including training in areas such as advocacy and communications.
“The GreatFire team works anonymously and independently but after we were awarded a fellowship from Index it felt like we had real world colleagues. Index helped us make improvements to our overall operations, consulted with us on strategy and were always there for us, through the good times and the pain,” Charlie Smith of GreatFire, 2016 Freedom of Expression Awards Digital Activism Fellow.
This year, the Freedom of Expression Awards are being supported by sponsors including SAGE Publishing, Google, Vodafone, media partner CNN, VICE News, Doughty Street Chambers, Psiphon and Gorkana. Illustrations of the nominees were created by Sebastián Bravo Guerrero.
Notes for editors:
- Index on Censorship is a UK-based non-profit organisation that publishes work by censored writers and artists and campaigns against censorship worldwide.
- More detail about each of the nominees is included below.
- The winners will be announced at a ceremony at The Unicorn Theatre, London, on 19 April.
For more information, or to arrange interviews with any of those shortlisted, please contact: Sean Gallagher on 0207 963 7262 or [email protected]. More biographical information and illustrations of the nominees are available at indexoncensorship.org/indexawards2017.
Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards nominees 2017
Arts
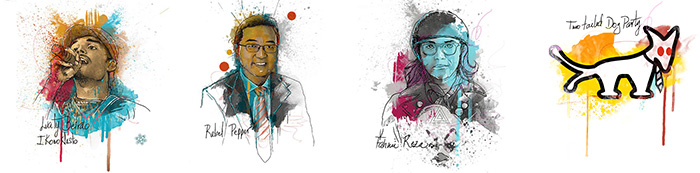
Luaty Beirão, Angola
Rapper Luaty Beirão, also known as Ikonoklasta, has been instrumental in showing the world the hidden face of Angolan President José Eduardo dos Santos’s rule. For his activism Beirão has been beaten up, had drugs planted on him and, in June 2015, was arrested alongside 14 other people planning to attend a meeting to discuss a book on non-violent resistance. Since being released in 2016, Beirão has been undeterred attempting to stage concerts that the authorities have refused to license and publishing a book about his captivity entitled “I Was Freer Then”, claiming “I would rather be in jail than in a state of fake freedom where I have to self-censor”.
Rebel Pepper, China
Wang Liming, better known under the pseudonym Rebel Pepper, is one of China’s most notorious political cartoonists. For satirising Chinese Premier Xi Jinping and lampooning the ruling Communist Party, Rebel Pepper has been repeatedly persecuted. In 2014, he was forced to remain in Japan, where he was on holiday, after serious threats against him were posted on government-sanctioned forums. The Chinese state has since disconnected him from his fan base by repeatedly deleting his social media accounts, he alleges his conversations with friends and family are under state surveillance, and self-imposed exile has made him isolated, bringing significant financial struggles. Nonetheless, Rebel Pepper keeps drawing, ferociously criticising the Chinese regime.
Fahmi Reza, Malaysia
On 30 January 2016, Malaysian graphic designer Fahmi Reza posted an image online of Prime Minister Najib Razak in evil clown make-up. From T-shirts to protest placards, and graffiti on streets to a sizeable public sticker campaign, the image and its accompanying anti-sedition law slogan #KitaSemuaPenghasut (“we are all seditious”) rapidly evolved into a powerful symbol of resistance against a government seen as increasingly corrupt and authoritarian. Despite the authorities’ attempts to silence Reza, who was banned from travel and has since been detained and charged on two separate counts under Malaysia’s Communications and Multimedia Act, he has refused to back down.
Two-tailed Dog Party, Hungary
A group of satirists and pranksters who parody political discourse in Hungary with artistic stunts and creative campaigns, the Two-tailed Dog Party have become a vital alternative voice following the rise of the national conservative government led by Viktor Orban. When Orban introduced a national consultation on immigration and terrorism in 2015, and plastered cities with anti-immigrant billboards, the party launched their own mock questionnaires and a popular satirical billboard campaign denouncing the government’s fear-mongering tactics. Relentlessly attempting to reinvigorate public debate and draw attention to under-covered or taboo topics, the party’s efforts include recently painting broken pavement to draw attention to a lack of public funding.
Campaigning
 Arcoiris, Honduras
Arcoiris, Honduras
Established in 2003, LGBT organisation Arcoiris, meaning ‘rainbow’, works on all levels of Honduran society to advance LGBT rights. Honduras has seen an explosion in levels of homophobic violence since a military coup in 2009. Working against this tide, Arcoiris provide support to LGBT victims of violence, run awareness initiatives, promote HIV prevention programmes and directly lobby the Honduran government and police force. From public marches to alternative awards ceremonies, their tactics are diverse and often inventive. Between June 2015 and March 2016, six members of Arcoiris were killed for this work. Many others have faced intimidation, harassment and physical attacks. Some have had to leave the country because of threats they were receiving.
Breaking the Silence, Israel
Breaking the Silence, an Israeli organisation consisting of ex-Israeli military conscripts, aims to collect and share testimonies about the realities of military operations in the Occupied Territories. Since 2004, the group has collected over 1,000 (mainly anonymous) statements from Israelis who have served their military duty in the West Bank and Gaza. For publishing these frank accounts the organisation has repeatedly come under fire from the Israeli government. In 2016 the pressure on the organisation became particularly pointed and personal, with state-sponsored legal challenges, denunciations from the Israeli cabinet, physical attacks on staff members and damages to property. Led by Israeli politicians including the prime minister, and defence minister, there have been persistent attempts to force the organisation to identify a soldier whose anonymous testimony was part of a publication raising suspicions of war crimes in Gaza. Losing the case would set a precedent that would make it almost impossible for Breaking the Silence to operate in the future. The government has also recently enacted a law that would bar the organisation’s widely acclaimed high school education programme.
Ildar Dadin, Russia
A long-term opposition and LGBT rights activist, Ildar Dadin was the first, and remains the only, person to be convicted under Russia’s 2014 public assembly law that prohibits the “repeated violation of the order of organising or holding meetings, rallies, demonstrations, marches or picketing”. Attempting to circumvent this restrictive law, Dadin held a series of one-man pickets against human rights abuses – an enterprise for which he was arrested and sentenced to three years imprisonment in 2015. In November 2016, website Meduza published a letter smuggled to his wife in which Dadin wrote that he was being tortured and abuse was endemic in Russian jails. The letter, a brave move for a serving prisoner, had wide resonance, prompting a reaction from the government and an investigation. Against his will, Dadin was transferred and disappeared within the Russian prison system until a wave of public protest led to his location being revealed in January 2017. Dadin was released on February 26 after a supreme court order.
Maati Monjib, Morocco
A well-known academic who teaches African studies and political history at the University of Rabat since returning from exile, Maati Monjib co-founded Freedom Now, a coalition of Moroccan human rights defenders who seek to promote the rights of Moroccan activists and journalists in a country ranked 131 out of 180 on the Reporters Without Borders Press Freedom Index. His work campaigning for press freedom – including teaching investigative journalism workshops and using of a smartphone app called Story Maker designed to support citizen journalism – has made him a target for the authorities who insist that this work is the exclusive domain of state police. For his persistent efforts, Monjib is currently on trial for “undermining state security” and “receiving foreign funds.”
Digital Activism
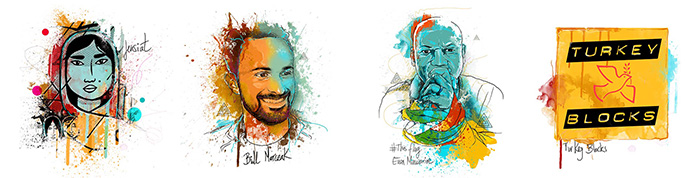 Jensiat, Iran
Jensiat, Iran
Despite growing public knowledge of global digital surveillance capabilities and practices, it has often proved hard to attract mainstream public interest in the issue. This continues to be the case in Iran where even with widespread VPN usage, there is little real awareness of digital security threats. With public sexual health awareness equally low, the three people behind Jensiat, an online graphic novel, saw an an opportunity to marry these challenges. Dealing with issues linked to sexuality and cyber security in a way that any Iranian can easily relate to, the webcomic also offers direct access to verified digital security resources. Launched in March 2016, Jensiat has had around 1.2 million unique readers and was rapidly censored by the Iranian government.
Bill Marczak, United States
A schoolboy resident of Bahrain and PhD candidate in computer science at the University of California, Berkeley, Bill Marczak co-founded Bahrain Watch in 2013. Seeking to promote effective, accountable and transparent governance, Bahrain Watch works by launching investigations and running campaigns in direct response to social media posts coming from activists on the front line. In this context, Marczak’s personal research has proved highly effective, often identifying new surveillance technologies and targeting new types of information controls that governments are employing to exert control online, both in Bahrain and across the region. In 2016 Marczak investigated several government attempts to track dissidents and journalists, notably identifying a previously unknown weakness in iPhones that had global ramifications.
#ThisFlag and Evan Mawarire, Zimbabwe
In May 2016, Baptist pastor Evan Mawarire unwittingly began the most important protest movement in Zimbabwe’s recent history when he posted a video of himself draped in the Zimbabwean flag, expressing his frustration at the state of the nation. A subsequent series of YouTube videos and the hashtag Mawarire used, #ThisFlag, went viral, sparking protests and a boycott called by Mawarire, which he estimates was attended by over eight million people. A scale of public protest previously inconceivable, the impact was so strong that private possession of Zimbabwe’s national flag has since been banned. The pastor temporarily left the country following death threats and was arrested in early February as he returned to his homeland.
Turkey Blocks, Turkey
In a country marked by increasing authoritarianism, a strident crackdown on press and social media as well as numerous human rights violations, Turkish-British technologist Alp Toker brought together a small team to investigate internet restrictions. Using Raspberry Pi technology they built an open source tool able to reliably monitor and report both internet shut downs and power blackouts in real time. Using their tool, Turkey Blocks have since broken news of 14 mass-censorship incidents during several politically significant events in 2016. The tool has proved so successful that it has begun to be implemented elsewhere globally.
Journalism

Behrouz Boochani, Manus Island, Papua New Guinea/Australia (he is an Iranian refugee)
Iranian Kurdish journalist Behrouz Boochani fled the city of Ilam in Iran in May 2013 after the police raided the Kurdish cultural heritage magazine he had co-founded, arresting 11 of his colleagues. He travelled to Australia by boat, intending to claim asylum, but less than a month after arriving he was forcibly relocated to a “refugee processing centre” in Papua New Guinea that had been newly opened. Imprisoned alongside nearly 1000 men who have been ordered to claim asylum in Papua New Guinea or return home, Boochani has been passionately documenting their life in detention ever since. Publicly advertised by the Australian Government as a refugee deterrent, life in the detention centre is harsh. For the first 2 years, Boochani wrote under a pseudonym. Until 2016 he circumvented a ban on mobile phones by trading personal items including his shoes with local residents. And while outside journalists are barred, Boochani has refused to be silent, writing numerous stories via Whatsapp and even shooting a feature film with his phone.
Daptar, Dagestan, Russia
In a Russian republic marked by a clash between the rule of law, the weight of traditions, and the growing influence of Islamic fundamentalism, Daptar, a website run by journalists Zakir Magomedov and Svetlana Anokhina, writes about issues affecting women, which are little reported on by other local media. Meaning “diary”, Daptar seeks to promote debate and in 2016 they ran a landmark story about female genital mutilation in Dagestan, which broke the silence surrounding that practice and began a regional and national conversation about FGM. The small team of journalists, working alongside a volunteer lawyer and psychologist, also tries to provide help to the women they are in touch with.
KRIK, Serbia
Crime and Corruption Reporting Network (KRIK) is a new independent investigative website which was founded by a team of young Serbian journalists intent on exposing organised crime and extortion in their country which is ranked as having widespread corruption by Transparency International. In their first year they have published several high-impact investigations, including forcing Serbia’s prime minister to admit that senior officials had been behind nocturnal demolitions in a Belgrade neighbourhood and revealing meetings between drug barons, the ministry of police and the minister of foreign affairs. KRIK have repeatedly come under attack online and offline for their work –threatened and allegedly under surveillance by state officials, defamed in the pages of local tabloids, and suffering abuse including numerous death threats on social media.
Maldives Independent, Maldives
Website Maldives Independent, which provides news in English, is one of the few remaining independent media outlets in a country that ranks 112 out of 180 countries on the Reporters Without Borders Press Freedom Index. In August 2016 the Maldives passed a law criminalising defamation and empowering the state to impose heavy fines and shut down media outlets for “defamatory” content. In September, Maldives Independent’s office was violently attacked and later raided by the police, after the release of an Al Jazeera documentary exposing government corruption that contained interviews with editor Zaheena Rasheed, who had to flee for her safety. Despite the pressure, the outlet continues to hold the government to account.
4 Oct 2016 | Asia and Pacific, Awards, China, Fellowship, Fellowship 2016, mobile, News

In April 2016 the US government called China’s Great Firewall a barrier to trade. This came just months after the US criticised China for cyber spying on American companies, or what the Justice Department called the “great brain robbery”.
“Obama keeps saying that if China continues employing its hacking units to attack US companies, America will tear down the Great Firewall,” Charlie Smith, co-founder of GreatFire, the anonymous group of individuals who work towards circumventing China’s Great Firewall and winners of the 2016 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Award for digital activism, told Index. “Great – so tear it down, let’s go.”
But it’s not happening, Smith added.
Over on the other side of America’s political spectrum, US senator Ted Cruz has been busy over the last month trying to get the US Congress to act to “prevent the Obama administration from giving the internet” to China. Cruz failed in his mission, as on 1 October the US gave up its remaining control over the internet, with the California-based Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) no longer under the direction of the Department of Commerce.
There are now fears that the change will open the door for authoritarian governments, including China’s, to get control of the network of networks, leading to greater censorship.
In Cruz’s first letter to ICANN, kicking off his attempt to stop the move, the former presidential hopeful quoted GreatFire’s research into internet censorship in China.
“I then reached out to them and said: ‘Hey, we’re GreatFire, what more do you want to know?’” Smith said. “ICANN has a representative in Beijing and that representative sits in the Cyberspace Administration office, which is censorship central, so Cruz’s campaign was very interested in that.”
Although GreatFire would not align themselves with a political party, Smith added that if Cruz really believes what he is saying and GreatFire can help, the organisation will support him on this issue.
GreatFire’s own efforts to put a hole in China’s firewall took a new turn in July 2016 with the launch of its groundbreaking new site to test virtual private networks within the country, Circumvention Central. “Stable circumvention is a difficult thing to find in China so this new site a way for people to see what’s working and what’s not working,” Smith told Index at the time.
Speaking three months on, Smith told us that although the site works and customers are overwhelmingly pleased with the service, it isn’t making as many sales as he’d hoped it would. In August the platform sold a few dozen subscriptions but Smith was really hoping to see numbers in the hundreds by this stage.
“Maybe we’re not getting enough people to the site,” Smith said. “I guess it’s timing too; people have other subscriptions that haven’t yet expired, so they’re not ready.”
“What we have done, however, is engaged with some VPN firms like a paid consultancy service and helped them improve what they are doing,” Smith added. “It’s actually been quite revealing because we can see the volatility in the market and how one service may work really well this month and next month it will basically be useless.”
GreatFire is working closely with VPN services Hide My Ass and AnchorFree, both of whom have been introductions from Index on Censorship.
The Chinese government has taken notice of Circumvention Central, sending an email to all VPN providers listed on the site asking them not to stop operating in China but to cease working with GreatFire specifically.
One reads: “Please immediately stop working with GreatFire.org. GreatFire.org is an anti-China website as declared by the Cyberspace Administration of China. We hereby express our strong concern and request you stop working with GreatFire at the earliest time possible.”
“So there’s no real serious threat from the government there,” Smith said, adding that although Chinese authorities are constantly trying to take down or attack the site, they have been wholly unsuccessful.
GreatFire is also working on its free internet browser that allows users to access content that’s behind China’s firewall. The browser is currently available in English and Chinese, but will soon be available in traditional Chinese, Arabic, Spanish, Croatian and Persian.
“We’re currently looking for publications in those languages that are blocked so we can help provide access,” said Smith.
The main focus for the future, however, is the VPN service. “We believe we have the best circumvention tool on the market and we want to show people how it works and drive adoption.”
Also read:
Smockey: “We would like to trust the justice of our country”
Zaina Erhaim: Balancing work and family in times of war
Artist Murad Subay worries about the future for Yemen’s children
Nominations are now open for 2017 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards. You can make yours here.
19 Sep 2016 | Magazine, Volume 45.03 Autumn 2016
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]

Autumn 2016 magazine cover
Anonymity is out of fashion. There are plenty of critics who want it banned on social media. It’s part of a harmful armoury of abuse, they argue.
Certainly, social media use seems to be doing its best to feed this argument. There are those anonymous trolls who sent vile verbal attacks to writers such as US author Lindy West. She was confronted by someone who actually set up a fake Twitter account under the name of her dead father.
Anonymity has been used in other ways by the unscrupulous. Earlier this year, a free messaging app called Kik was the method two young men used to get in touch with a 13-year-old girl, with whom they made friends online and then invited her to meet. They were later charged with her murder. Participants who use Kik to chat do not have to register their real names or phone numbers, according to a report on the court case in the New York Times, which cited other current cases linked to Kik activity including using it to send child pornography.
So why do we need anonymity? Why does it matter? Why don’t we just ban it or make it illegal if it can be used for all these harmful purposes? Anonymity is an integral part of our freedom of expression. For many people it is a valuable way of allowing them to speak. It protects from danger, and it allows those who wouldn’t be able to speak or write to get the words out.
“If anonymity wasn’t allowed any more, then I wouldn’t use social media,” a 14-year-old told me over the kitchen table a few weeks ago. He uses forums on the website Reddit to have debates about politics and religion, where he wants to express his view “without people underestimating my age”.
Anonymity to this teenager is something that works for him; lets him operate in discussions where he wants to try out his arguments and gain experience in debates. Anonymity means no one judges who he is or his right to join in.
For others, using a fake or pen name adds a different layer of security. Writers for this magazine worry about their personal safety and sometimes ask for their names not to be carried on articles they write. In the current issue, an activist who works helping people find ways around China’s great internet wall is one of our authors who can’t divulge his name because of the work he does.
Throughout history journalists have worked with sources who want to see important information exposed, but do not want their own identity to be made public. Look at the Watergate exposé or the Boston Globe investigation into child sex abuse by priests. Anonymous sources can provide essential evidence that helps keep an investigation on track.
That right, to keep sources private, has been the source of court actions against journalists through the years. And those who choose to work with journalists, often rely on that long held practice.
Pen names, pseudonyms, fake identities have all have been used for admirable and understandable purposes over the centuries: to protect someone’s life; to blow a whistle on a crime; for a woman to get published at a period when only men did so, and on and on. Those who fought for democracy, the right to protest and other rights, often had operate under the wire, out of the searching eyes of those who sought to stop them. Thomas Paine, who wrote the famous pamphlet Common Sense “Addressed to Inhabitants of America”, advocating the independence of the 13 states from Britain, first published his words in 1776 anonymously.
From the early days of Index on Censorship, when writing was being smuggled across borders and out of authoritarian countries, the need for anonymity was paramount.
Over the years it has been argued that anonymity is a vital component in the machinery of freedom of expression. In the USA, the American Civil Liberties Union argues that anonymity is a First Amendment right, given in the Constitution. As far back as 1996, a legal case was taken in Georgia, USA, to restrict users from using pseudonyms on the internet.
Today, in India, the world’s largest democracy, there are discussions about making anonymity unlawful. Our article by lawyer and writer Suhrith Parthasarathy considers why if minister Maneka Gandhi does go ahead with plans to remove anonymity on Twitter it could have ramifications for other forms of writing. As Anja Kovacs of the Internet Democracy Project told Index, “democracy virtually demands anonymity. It’s crucial for both the protection of privacy rights and the right to freedom of expression”.
We must make sure that new systems aimed at tackling crime do not relinquish our right to anonymity. Anonymity matters, let’s remember it has a role to play.
Order your full-colour print copy of our anonymity magazine special here, or take out a digital subscription from anywhere in the world via Exact Editions (just £18* for the year). Each magazine sale helps Index on Censorship fight for free expression worldwide.
*Will be charged at local exchange rate outside the UK.
Copies will be available at the BFI, the Serpentine Gallery, MagCulture, (London), News from Nowhere (Liverpool), Home (Manchester), Carlton Books (Glasgow) and on Amazon. Each magazine sale helps Index on Censorship continue its fight for free expression worldwide.
The full contents of the magazine can be read here.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”From the Archives”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”89160″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422011400799″][vc_custom_heading text=”Going local” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422011400799|||”][vc_column_text]March 2011
If the US’s internet freedom agenda is going to be effective, it must start by supporting grassroots activists on their own terms, says Ivan Sigal.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”89073″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422013512242″][vc_custom_heading text=”On the ground” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422013512242|||”][vc_column_text]December 2013
Attacked by the government and the populist press alike, political bloggers and Twitter users in Greece struggle to make their voices heard.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”89161″ img_size=”213×289″ alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0306422011409641″][vc_custom_heading text=”Meet the trolls” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:http%3A%2F%2Fjournals.sagepub.com%2Fdoi%2Fpdf%2F10.1177%2F0306422011409641|||”][vc_column_text]June 2011
Whitney Phillips reports on a loose community of anarchic and anonymous people is testing the limits of free speech on the internet.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_separator][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”The unnamed” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:%20https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2F2017%2F09%2Ffree-to-air%2F|||”][vc_column_text]The autumn 2016 Index on Censorship magazine explores topics on anonymity through a range of in-depth features, interviews and illustrations from around the world.
With: Valerie Plame Wilson, Ananya Azad, Hilary Mantel[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_single_image image=”80570″ img_size=”medium” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2016/11/the-unnamed/”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/3″][vc_custom_heading text=”Subscribe” font_container=”tag:p|font_size:24|text_align:left” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fwww.indexoncensorship.org%2Fsubscribe%2F|||”][vc_column_text]In print, online. In your mailbox, on your iPad.
Subscription options from £18 or just £1.49 in the App Store for a digital issue.
Every subscriber helps support Index on Censorship’s projects around the world.
 SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
19 Sep 2016 | Magazine, Magazine Contents, mobile, Volume 45.03 Autumn 2016
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Does anonymity need to be defended? Contributors include Hilary Mantel, Can Dündar, Valerie Plame Wilson, Julian Baggini, Alejandro Jodorowsky and Maria Stepanova “][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2”][vc_column_text]
The latest issue of Index on Censorship explores anonymity through a range of in-depth features, interviews and illustrations from around the world. The special report looks at the pros and cons of masking identities from the perspective of a variety of players, from online trolls to intelligence agencies, whistleblowers, activists, artists, journalists, bloggers and fixers.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”78078″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
Former CIA agent Valerie Plame Wilson writes on the damage done when her cover was blown, journalist John Lloyd looks at how terrorist attacks have affected surveillance needs worldwide, Bangladeshi blogger Ananya Azad explains why he was forced into exile after violent attacks on secular writers, philosopher Julian Baggini looks at the power of literary aliases through the ages, Edward Lucas shares The Economist’s perspective on keeping its writers unnamed, John Crace imagines a meeting at Trolls Anonymous, and Caroline Lees looks at how local journalists, or fixers, can be endangered, or even killed, when they are revealed to be working with foreign news companies. There are are also features on how Turkish artists moonlight under pseudonyms to stay safe, how Chinese artists are being forced to exhibit their works in secret, and an interview with Los Angeles street artist Skid Robot.
Outside of the themed report, this issue also has a thoughtful essay by novelist Hilary Mantel, called Blot, Erase, Delete, about the importance of committing to your words, whether you’re a student, an author, or a politician campaigner in the Brexit referendum. Andrey Arkhangelsky looks back at the last 10 years of Russian journalism, in the decade after the murder of investigative reporter Anna Politkovskaya. Uzbek writer Hamid Ismailov looks at how metaphor has taken over post-Soviet literature and prevented it tackling reality head-on. Plus there is poetry from Chilean-French director Alejandro Jodorowsky and Russian writer Maria Stepanova, plus new fiction from Turkey and Egypt, via Kaya Genç and Basma Abdel Aziz.
There is art work from Molly Crabapple, Martin Rowson, Ben Jennings, Rebel Pepper, Eva Bee, Brian John Spencer and Sam Darlow.
You can order your copy here, or take out a digital subscription via Exact Editions. Copies are also available at the BFI, the Serpentine Gallery, MagCulture, (London), News from Nowhere (Liverpool), Home (Manchester), Calton Books (Glasgow) and on Amazon. Each magazine sale helps Index on Censorship continue its fight for free expression worldwide.
Index on Censorship magazine was started in 1972 and remains the only global magazine dedicated to free expression. Past contributors include Samuel Beckett, Gabriel García Marquéz, Nadine Gordimer, Arthur Miller, Salman Rushdie, Margaret Atwood, and many more.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”SPECIAL REPORT: THE UNNAMED” css=”.vc_custom_1483445324823{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
Does anonymity need to be defended?
Anonymity: worth defending, by Rachael Jolley: False names can be used by the unscrupulous but the right to anonymity needs to be defended
Under the wires, by Caroline Lees : A look at local “fixers”, who help foreign correspondents on the ground, can face death threats and accusations of being spies after working for international media
Art attack, by Jemimah Steinfeld: Ai Weiwei and other artists have increased the popularity of Chinese art, but censorship has followed
Naming names, by Suhrith Parthasarathy: India has promised to crack down on online trolls, but the right to anonymity is also threatened
Secrets and spies, by Valerie Plame Wilson: The former CIA officer on why intelligence agents need to operate undercover, and on the damage done when her cover was blown in a Bush administration scandal
Undercover artist, by Jan Fox: Los Angeles street artist Skid Robot explains why his down-and-out murals never carry his real name
A meeting at Trolls Anonymous, by John Crace: A humorous sketch imagining what would happen if vicious online commentators met face to face
Whose name is on the frame? By Kaya Genç: Why artists in Turkey have adopted alter egos to hide their more political and provocative works
Spooks and sceptics, by John Lloyd: After a series of worldwide terrorist attacks, the public must decide what surveillance it is willing to accept
Privacy and encryption, by Bethany Horne: An interview with human rights researcher Jennifer Schulte on how she protects herself in the field
“I have a name”, by Ananya Azad: A Bangladeshi blogger speaks out on why he made his identity known and how this put his life in danger
The smear factor, by Rupert Myers: The power of anonymous allegations to affect democracy, justice and the political system
Stripsearch cartoon, by Martin Rowson: When a whistleblower gets caught …
Signing off, by Julian Baggini: From Kierkegaard to JK Rowling, a look at the history of literary pen names and their impact
The Snowden effect, by Charlie Smith: Three years after Edward Snowden’s mass-surveillance leaks, does the public care how they are watched?
Leave no trace, by Mark Frary: Five ways to increase your privacy when browsing online
Goodbye to the byline, by Edward Lucas: A senior editor at The Economist explains why the publication does not name its writers in print
What’s your emergency? By Jason DaPonte: How online threats can lead to armed police at your door
Yakety yak (don’t hate back), by Sean Vannata: How a social network promising anonymity for users backtracked after being banned on US campuses
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”IN FOCUS” css=”.vc_custom_1481731813613{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
Blot, erase, delete, by Hilary Mantel: How the author found her voice and why all writers should resist the urge to change their past words
Murder in Moscow: Anna’s legacy, by Andrey Arkhangelsky: Ten years after investigative reporter Anna Politkovskaya was killed, where is Russian journalism today?
Writing in riddles, by Hamid Ismailov: Too much metaphor has restricted post-Soviet literature
Owners of our own words, by Irene Caselli: Aftermath of a brutal attack on an Argentinian newspaper
Sackings, South Africa and silence, by Natasha Joseph: What is the future for public broadcasting in southern Africa after the sackings of SABC reporters?
“Journalists must not feel alone”, by Can Dündar: An exiled Turkish editor on the need to collaborate internationally so investigations can cross borders
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”CULTURE” css=”.vc_custom_1481731777861{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
Bottled-up messages, by Basma Abdel Aziz: A short story from Egypt about a woman feeling trapped. Interview with the author by Charlotte Bailey
Muscovite memories, by Maria Stepanova: A poem inspired by the last decade in Putin’s Russia
Silence is not golden, by Alejandro Jodorowsky: An exclusive translation of the Chilean-French film director’s poem What One Must Not Silence
Write man for the job, by Kaya Genç: A new short story about a failed writer who gets a job policing the words of dissidents in Turkey
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”COLUMNS” css=”.vc_custom_1481732124093{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
Global view, by Jodie Ginsberg: Europe’s right-to-be-forgotten law pushed to new extremes after a Belgian court rules that individuals can force newspapers to edit archive articles
Index around the world, by
Josie Timms: Rounding up Index’s recent work, from a hip-hop conference to the latest from Mapping Media Freedom
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”END NOTE” css=”.vc_custom_1481880278935{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
What ever happened to Luther Blissett? By Vicky Baker: How Italian activists took the name of an unsuspecting English footballer, and still use it today
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”SUBSCRIBE” css=”.vc_custom_1481736449684{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship magazine was started in 1972 and remains the only global magazine dedicated to free expression. Past contributors include Samuel Beckett, Gabriel García Marquéz, Nadine Gordimer, Arthur Miller, Salman Rushdie, Margaret Atwood, and many more.[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”76572″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]In print or online. Order a print edition here or take out a digital subscription via Exact Editions.
Copies are also available at the BFI, the Serpentine Gallery, MagCulture, (London), News from Nowhere (Liverpool), Home (Manchester), Calton Books (Glasgow) and on Amazon. Each magazine sale helps Index on Censorship continue its fight for free expression worldwide.
 SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1483444808560-b79f752f-ec25-7″ taxonomies=”8927″ exclude=”80882″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1483444808560-b79f752f-ec25-7″ taxonomies=”8927″ exclude=”80882″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
 Judges include actor Noma Dumezweni; former Vanity Fair editor Tina Brown
Judges include actor Noma Dumezweni; former Vanity Fair editor Tina Brown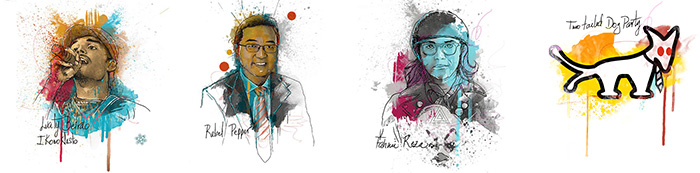
 Arcoiris, Honduras
Arcoiris, Honduras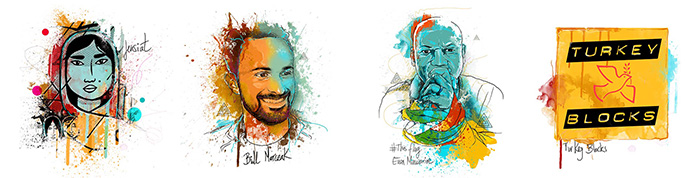 Jensiat, Iran
Jensiat, Iran



