Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
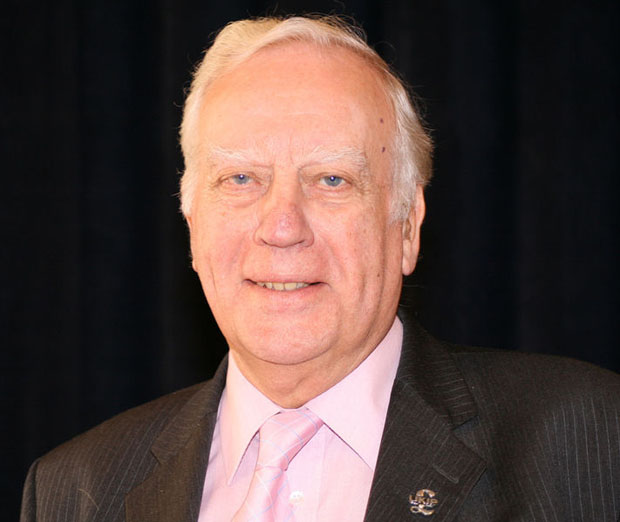

Derek Clark MEP (Image: Euro Realist Newsletter/Wikimedia Commons)
The UK Independence Party has promised it will ban the teaching of climate change in schools, if elected in May next year.
The party’s 2010 manifesto included a pledge to ban Al Gore’s Oscar-winning global warming documentary An Inconvenient Truth from schools.
But this week UKIP Education spokesman MEP Derek Clark has said the party will go even further. Clark told Index on Censorship:
We will still ban Al Gore’s video for use in schools if I’ve got anything to do with it. I will not have much opposition within the party. It is, of course, not just this video which needs banning; all teaching of global warming being caused in any way by carbon dioxide emissions must also be banned. It just is not happening.”
Dr Nick Eyre, Jackson Senior Research Fellow in Energy at the ECI and Oriel College Oxford and Co-Director of the UK Energy Research Centre, said of the proposal: “It is anti-scientific nonsense – as well as a worryingly repressive approach to education. The very strong link between climate change and anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions is overwhelmingly accepted by the global scientific community, and has been for at least 25 years.”
A recent IPCC report shows that scientists believe with 95% certainty that humans are the “dominant cause” of global warming. A 2013 study by UK Energy Research Centre, however, showed that 46% believe that climate change is ‘partly caused by human activity’, 22% believe that climate change is ‘mainly caused by human activity’ and another 6% believe that climate change is ‘entirely caused by human activity’. In total 74% of those surveyed believed that human activity is responsible for climate change.
This article was posted on 15 Jan 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
An earlier version of this article stated: “95% of scientists believe that humans are the ‘dominate cause’ of global warming.” It has been edited to: “scientists’ believe with 95% certainty that humans are the ‘dominate cause’ of global warming.
This article was amended to include the total number of people in the UK Energy Research Centre study who believe that human activity is responsible for climate change.
San Fransisco based Reddit.com made headlines when it allegedly banned climate change deniers from posting on the site.
UK-based freedom of speech advocate Brendan O’Neill, editor of Spiked magazine, claimed it had “shredded its own reputation” in a piece for The Telegraph, while James Delingpole, a right-wing commentator for The Spectator delivered a hot-blooded attack on the policy via Fox News website – “The greenies — and their many useful idiots in the liberal media — are terrified of open debate on climate-change because the real world evidence long ago parted company with their scientifically threadbare theory.”
Reddit is a huge online links directory and lively discussion board, with a reputation for scale, wit, lack of censorship and a strong sense of community. Over eighty million monthly unique visitors, two hundred and sixty million comments to date and a presence in one hundred and eighty countries are some of the stats that led Conde Nast to buy the company a year after it was launched in 2005. Last year, analysts valued it at over $200 million dollars. It’s no Facebook or Twitter in terms of publicity attracted, but it gets more traffic than CNN, and the Guardian.com’s monthly readership could fit into Reddit’s three times over.
It’s the famed lack of censorship that has lead opinion writers on both side of the Atlantic to point out this new policy on climate change denial.
For those who haven’t visited, the site is divided up into sub-reddits–links and discussions, which are classified according to themes, and run by unpaid volunteers.
“TIL,” shorthand for “Today I Learned,” offers obscure trivia and little known facts. “foreignpolicy” offers links and discussion on international relations, defence and diplomacy. “foodforthought” collates links to thought-provoking essays. There are subreddits for jokes, celebrity gossip, memes and funny videos – for agony aunts and video gaming.
In fact, rather than reddit.com having banned climate change skeptics, it’s the moderators of the “/r/science” reddit who have instigated the ban. Run by volunteers, it collects links about new research and scientific articles.
“/r/science is not the beginning or the end of internet discussion”, defends Carl Ellstrom from Sweden – a reddit user, scientist and moderator of the science subreddit. “Users who are banned from /r/science are not banned from reddit, and can discuss their opinions in other subreddits.”
While it’s not the beginning or the end, /r/science still attracts millions of visitors each month. So the decision to ban climate change scepticism is of note.
Typical of their profession–other moderators backed up the decision by citing research–97% of climate scientists agree that man is changing the planet, according to a report from the respected Institute of Physics.
The move principally revolved around aggressive and repeated comments, which a small group of malicious users were posting on every article or piece of research concerned with climate change. Their allegations generally focused on conspiracy theories, didn’t address the article with constructive, focused criticism, were repetitive and, critically, had a disproportionate silencing effect on any discussion.
“These problematic users were not the common ‘internet trolls’ looking to have a little fun upsetting people,” explains Nathan Allen, a PhD chemist with a major chemical company and reddit moderator who wrote for The Guardian.
“These people were true believers, blind to the fact that their arguments were hopelessly flawed, the result of cherry-picked data and conspiratorial thinking. They had no idea that the smart-sounding talking points from their preferred climate blog were, even to a casual climate science observer, plainly wrong. They were completely enamoured by the emotionally charged and rhetoric-based arguments of pundits on talk radio and Fox News.”
Expanding on that last point Allen says the same comparison could be made with the climate change denial lobby in general, and their disproportionate influence on the press.
“Like our commenters, professional climate change deniers have an outsized influence in the media and the public. And like our commenters, their rejection of climate science is not based on an accurate understanding of the science but on political preferences and personality.”
He ends his piece with a deliberate challenge to the editors of the world’s largest websites
“If a half-dozen volunteers can keep a page with more than 4 million users from being a microphone for the antiscientific, is it too much to ask for newspapers to police their own editorial pages as proficiently?”
If Allen’s suggestion was ever to be noticed and accepted by editors–he ramifications for freedom of speech and media censorship would be radical. Editors might be forced to ignore lobbying from certain spheres of belief, or might miss out on important stories.
But UK research published earlier in the year, shows the disproportionate effect on distorting the truth that having a free and open press creates.
On average, Brits think teenage pregnancies are twenty five times higher than official estimates. The public think 31% of the population are immigrants–the reality is closer to ten percent. Welfare benefit fraud is thought to be 34 times higher than it actually is.
All of the misconceptions covered by IPSOS Mori, the polling company that undertook the research, have been central to political party manifestos and been aggressively pushed by their PR companies.
Or that journalists are too readily being made tools of political parties who want to get elected, who want the issues that they care most about continually in the press, hotly discussed and “on the agenda.” Perhaps we, as journalists, need to remain ever vigilant to the briefing of misinformation and our responsibility to the truth.
This article was published on 3 Jan 2014 at indexoncensorship.org

(Photo Illustration: Shutterstock)
The continuing advance of climate science, as reflected in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s recently released Fifth Assessment Report, points ever more strongly to the need for an expedited phase-out of carbon emissions from fossil fuels. Only a fundamental transformation of the current energy system during the coming decades may make it possible to avert disastrous impacts of global climatic disruption.
Carrying out such a transformation would be a political, economic, and technological challenge under the best of circumstances. But it is made especially difficult by corporate and ideologically driven opposition — most notably, by pressure from fossil fuel production interests to protect their strategic position and set the terms for government policymaking.
The United States and Canada exemplify the power of the dominant energy interests. The governments of both countries strongly support the expansion of domestic fossil energy extraction, production, and export. But the collision between climate science and energy politics, and threats to freedom of communication, are playing out differently in the two countries.
With the Harper government in Canada, for years we have witnessed an ongoing repression of climate and environmental science communication by government scientists, along with systematic cutbacks of environmental research and data collection. “Harper’s attack on science: No science, no evidence, no truth, no democracy“, an excellent review and discussion in the May 2013 issue of the Canadian journal Academic Matters, itemized a series of moves by the Harper government to control or prevent the free flow of scientific information across Canada, particularly when that information highlights the undesirable consequences of industrial development. The free flow of information is controlled in two ways: through the muzzling of scientists who might communicate scientific information, and through the elimination of research programs that might participate in the creation of scientific information or evidence.
It appears that the issues on which government scientists are subjected to the tightest political control of communications include climate change, the Alberta tar sands, the oil and gas industry, and Arctic wildlife. In other words, issues on which free communication of scientific evidence could pose problems for corporate energy development interests.
The situation in Canada has driven government scientists to hold public protest rallies twice in the last year. In September, rallies in major city centers and on university campuses were held across the country.
“It isn’t the way science is supposed to be. It’s not the way science used to be, the way I remember it in the federal government,” IPCC vice-chair and retired Environment Canada scientist John Stone told The Guardian.
So the Harper government can be said to be following in the footsteps — even surpassing — the record of the former Bush-Cheney administration in the U.S., whose alignment with energy industry interests led them to misrepresent climate science intelligence and impede forthright communication by federal climate scientists.
In the U.S., the Obama administration presents a complex picture that differs from Canada in significant ways, but also suggests the problematic nature of government support for expanded fossil energy extraction and production. The administration appears susceptible to industry pressure aimed at playing down the environmental and societal consequences of fossil energy resource extraction and use.
After several years of near-silence on climate change at the highest levels of U.S. political leadership, in June President Obama finally gave a major public address on climate change (the first by an American president) and laid out a multifaceted Climate Action Plan. The plan focuses on actions that can be taken by the White House and Executive Branch in the absence of action by a Congress that is tied in knots, largely subservient to corporate energy interests, and with much of the Republican Party aligned with the global warming denial machine.
Under Obama, we see a more straightforward acknowledgement of climate science and assessments by the most credible experts, and more straightforward communication on climate by federal research agencies. The forthcoming National Climate Assessment, scheduled for release next spring, will address the implications of climatic disruption for the U.S., across geographical regions and socioeconomic and resource sectors (public health, water resources, food production, coastal zones, and so forth). The importance of national assessments for public discourse was underscored when the Bush administration, in collusion with nongovernmental global warming denialists, suppressed official use of and references to the first National Climate Assessment, which had been completed in 2000.
Yet, despite the numerous constructive action items in Obama’s Climate Action Plan, there appears to be a contradiction at the heart of Obama’s policy, as indicated by the administration’s adoption of what they call an ‘all of the above’ approach to energy development. Obama points to increased U.S. fossil energy extraction as a major accomplishment. U.S. energy development includes ‘mountaintop removal’ coal mining in Appalachia, large-scale coal strip-mining on public lands in the West, and increased coal exports; deepwater drilling for oil in the Gulf of Mexico, even in the wake of the BP oil blowout disaster in 2010, and quite possibly drilling in the Arctic Ocean off the coast of Alaska; and a dramatic increase during the past five years in natural gas production using directional drilling technology and hydraulic fracturing of shale deposits that cover a number of large areas across the country.
Natural gas from ‘fracking’ appears to be an essential component of the administration’s climate policy, i.e., relying on the ongoing trend of substitution of natural gas for coal in power plants in order to meet a 2020 goal for reducing U.S. carbon emissions. The Department of the Interior has proposed to open 600 million acres of public land to fracking. But fracking is controversial, raising concerns about contamination of drinking water in affected areas by chemicals used in fracking, large-scale use of water in drilling, air pollution, leaking methane greenhouse gas emissions, and industrial degradation of rural landscapes. Environmental groups have protested at the White House, calling for a moratorium on fracking on public lands.
There are sIgns that the administration may be allowing political pressure from the natural gas industry to compromise investigations by the Environmental Protection Agency into fracking contamination incidents. The EPA has pulled back from several high-profile investigations in a manner that raises questions about whether this indicates a pattern of failure to act on scientific evidence. When the EPA’s scientists found evidence that fracking was contaminating water supplies, the EPA stopped or slowed down their work in in Pennsylvania, Texas, and Wyoming.
“Not only does this pattern of behavior leave impacted residents in the lurch, but it raises important questions as to whether the agency is caving to pressure from industry, antagonistic members of Congress and/or other outside sources,” Kate Sinding at the Natural Resources Defense Council notes. “This trend also calls into serious question the agency’s commitment to conducting an impartial, comprehensive assessment of the risks fracking presents to drinking water—a first-of-its-kind study that is now in its fourth year, with initial results now promised in 2014.” The EPA recently announced that it has delayed the expected final date of this study until 2016 — Obama’s eighth and final year in office. Meanwhile, industry continues to create a fait accompli of radically expanded fracking operations.
Obama has adopted a forward-looking position on climate change. But his ‘all of the above’ energy policy, and particularly his full-speed-ahead support for shale gas fracking, raises the question of whether politics is impeding freedom of communication by government experts — and whether the EPA is thereby being impeded in doing its job of protecting the public against the environmental dangers of fossil fuel development.
This article was originally published on 8 Oct 2013 at indexoncensorship.org
A controversial climate change sculpture was removed after it upset donors from the energy industry in the US. Kevin Smith asks whether corporate sponsorship by companies like BP and Shell has an affect on artistic freedom in the UK
(more…)