2 Apr 2017 | Magazine, Magazine Contents, Volume 46.01 Spring 2017
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Contributors include Richard Sambrook, Dominic Grieve, Roger Law, Karim Miské, Mark Frary and Canan Coşkun”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
The spring issue of Index on Censorship magazine looks at how pressures on free speech are currently coming from many different angles, not just one. Richard Sambrook, former director of global news at the BBC, shows how journalists are in a bind, caught between what advertisers want and what readers want. Also looking at journalists, Duncan Tucker casts his eye on the grave situation in Mexico, where getting to the truth involves working against the government, violent cartels and even coworkers.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”88802″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
Meanwhile, in the Maldives Zaheena Rasheed shows how a mix of forces conspire against those who want to write anything beyond the usual tourist sale pitch.
But the squeezes on free expression don’t just concern journalists. Annemarie Luck reports from Japan, where penis festivals are popular, but women struggle to discuss their own bodies. Can they find a voice through art and manga? For musician Smockey from Burkina Faso, art should indeed be a way to confront truth and yet that’s not always the case. Expectations run high for him to not be “too political” in his lyrics.
Universities, normally the cradle of free expression, aren’t faring too well either, as two articles show. Jan Fox reports from the USA, where bias response teams are becoming a staple of US collegiate life. In South Africa Fees Must Fall has created a divide between right and left, writes Natasha Joseph, with neither side talking to each other and those in the middle being silenced altogether.
Outside of our special report, Roger Law, creator of the iconic TV satire Spitting Image, talks about the great fun he had with the series back in the day and questions whether the show would be able to air today. Alfonso Lázaro de la Fuente might say no. He was one of the Spanish puppeteers arrested last year for a show that referenced Basque-separatist organisation ETA. In an Index exclusive, he explains what the charges have meant for his personal and professional life.
Want to know how to spot fake news? Then read Reel-time news in which Index’s team of experienced global reporters offer tips on how to spot fake news from a mile/screen away. And don’t miss Martin Rowson‘s fake o’clock news, a hilarious – and sinister – take on what a future of alternative facts would look like.
Index also publish an interview with Turkish journalist Canan Coşkun, whose coworkers are currently in jail, and a pair of writers discuss the situation of free speech in Poland, which is tumbling down global charts following the election of the Law and Justice party. And in the UK, former attorney general Dominic Grieve reveals that MPs are avoiding hard talk in parliament.
Finally, the culture section includes a short story from award-winning French writer Karim Miské and original work from Vyacheslav Huk, a Crimean novelist who is unable to publish work in his mother tongue.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”SPECIAL REPORT: THE BIG SQUEEZE” css=”.vc_custom_1481731933773{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
The Big Squeeze: Freedom of speech under pressure
Fact-filled future? by Rachael Jolley: Journalists need to step up, and produce more detailed news coverage. The public needs it
Between a rock and a hard place, by Duncan Tucker: Mexico’s journalists face threats from cartels, the government and each other
Reality rapped, by Smockey: An award-winning musician from Burkina Faso explains why he won’t water down his lyrics to avoid rocking the boat, despite pressure to do so
Talking a tightrope, by
Kaya Genç: Despite the crackdown in Turkey, the post-Gezi spirit still survives among the determined
Taking the bait, by Richard Sambrook: The quest for instant gratification online is seriously compromising news reporting
Dangerous minds, by Natasha Joseph: Rather than creating an alliance, Fees Must Fall is limiting free speech at South Africa’s universities, leaving some early supporters disheartened
Japan’s Madonna complex, by Annemarie Luck: Japan’s contradictory attitudes include highly sexualised images of women and women not being allowed to talk about sex-related subjects
Squeezed in the closet, by Hannah Leung: Get married and be quiet are the messages China’s LGBT community is given
Degrees of separation, by Jan Fox: The author investigates units appearing on US campuses suggesting students should report lecturers who they feel are biased
Dying to tell a story, by Sadaf Saaz: The list of what Bangladesh writers cannot talk about is getting longer, but that isn’t stopping some from writing
Trouble in paradise, by Zaheena Rasheed: Behind the image of palm-lined beaches is a side of the Maldives the government doesn’t want you to see
Your cover is shown, by Mark Frary: Tech giants and governments are out to get your data. Soon it might be impossible to remain anonymous
Stripsearch cartoon, by Martin Rowson: Tune in to the fake o’clock news
Composing battle lines, by Steven Borowiec: Why have South Korean pop stars found themselves caught in crossfire between their country and China?
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”IN FOCUS” css=”.vc_custom_1481731813613{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
We have no time for fear, by Canan Coşkun: A Turkish journalist on the perils of reporting in her country when fellow reporters are imprisoned
Reel-time news, by Natasha Joseph, Kaya Genç, Jemimah Steinfeld, Duncan Tucker, Abraham T Zere, Raymond Joseph: As “fake news” dominates headlines, Index’s global team of experienced journalists offers tips on how to spot falsehoods before you click and share
Singing from the same hymn sheet, by Suhrith Parthasarathy: Rising Indian nationalism is creating a repressive state where non-conformity is deemed unpatriotic
Poland: Special Focus, by Wojciech Przybylski, Marcin Król: Poland has gone from free speech hero to villain almost overnight. Two writers discuss the shift and why history is being rewritten
Shooting from the hip, by Irene Caselli: A new mayor in a Mexican border city believes he will make it less dangerous for journalists
Silence in the house, by Dominic Grieve: The former UK attorney general says MPs are shying away from tough topics in parliament
Puppet masters, by Roger Law: The creator of iconic TV satire Spitting Image on whether we still have our sense of humour
Drawing the line, by John Power: Australia is debating free speech, one cartoon at a time. Cartoonist Bill Leak interviewed just before he died
Puppet state, by Alfonso Lázaro de la Fuente: A Spanish puppeteer, arrested after terrorism charges related to a show, discusses the impact on his life
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”CULTURE” css=”.vc_custom_1481731777861{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
Novel take on terror, by
Karim Miské: The award-winning crime writer on why fiction and reality overlap. Plus his short story featuring a future where tech rules supreme. Interview by Sally Gimson
The war of the words, by Amira Hanafi: Translated extracts from an American-Egyptian writer’s project to capture the shifting linguistic landscape in Egypt since 2011. Interview by Sally Gimson
Crimean closedown, by Vyacheslav Huk: The Crimean novelist on being unable to publish in his mother tongue and a story of the narrator’s memories. Introduced and translated by Steve Komarnyckyj
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”COLUMNS” css=”.vc_custom_1481732124093{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
Index around the world, by
Kieran Etoria-King: What to look out for at Index’s Freedom of Expression Awards 2017, alongside news of other projects that Index has been working on in the last few months
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”END NOTE” css=”.vc_custom_1481880278935{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
Getting print out, by Jemimah Steinfeld: Self-publishing may be a new solution to censorship in China and other countries
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”SUBSCRIBE” css=”.vc_custom_1481736449684{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship magazine was started in 1972 and remains the only global magazine dedicated to free expression. Past contributors include Samuel Beckett, Gabriel García Marquéz, Nadine Gordimer, Arthur Miller, Salman Rushdie, Margaret Atwood, and many more.[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”76572″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]In print or online. Order a print edition here or take out a digital subscription via Exact Editions.
Copies are also available at the BFI, the Serpentine Gallery, MagCulture, (London), News from Nowhere (Liverpool), Home (Manchester), Calton Books (Glasgow) and on Amazon. Each magazine sale helps Index on Censorship continue its fight for free expression worldwide.
 SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row]
24 May 2016 | Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan News, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia, Croatia, Europe and Central Asia, France, Germany, Greece, Index Reports, Macedonia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News, Poland, Serbia, Spain, Turkey, Ukraine
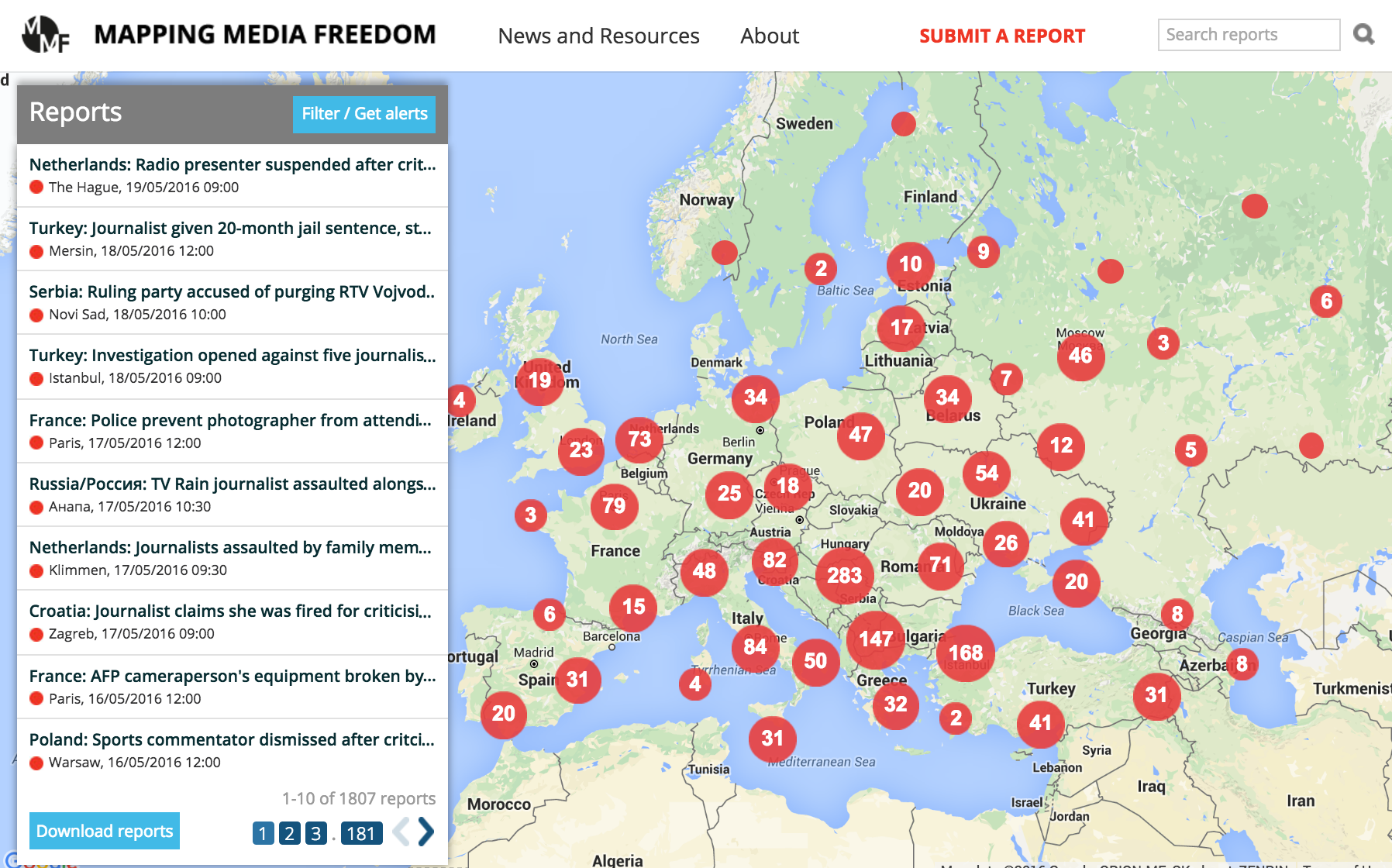
Mapping Media Freedom launched to the public on 24 May 2014 to monitor media censorship and press freedom violations throughout Europe. Two years on, the platform has verified over 1,800 media violations.
“The data the platform has collected over the last two years confirms that the state of press freedom across Europe is deplorable,” said Hannah Machlin, project officer for Mapping Media Freedom. “Media violations are occurring regularly in countries with strong democratic institutions and protective laws for journalists. Legislation limiting the press, violence across the continent and authoritarian governments are also fuelling this rapid and worrying decline. We hope that institutions and leaders take note of this information and take action swiftly.”
To mark the anniversary, we asked our correspondents to pick a key violation that stood out to them as an example of the wider picture in their region.
Russia / 113 verified reports
Several journalists and human rights activists attacked in Ingushetia
“The brutal attack on a minibus carrying six journalists and several human rights activists near the border between Ingushetia and Chechnya on the 9 March 2016 demonstrates the dangers faced by media professionals working in Russia’s North Caucasus. No suspects have been established so far. This case stands out due to its extreme violence but also supports a common trend: the reluctance of the local authorities to ensure that the journalists’ rights are respected.” – Ekaterina Buchneva
Italy / 190 verified reports
97 journalists accused of breaking the law in mafia investigation
“This was a very relevant investigation, with no precedent, that took place in October, a few weeks away from the start of the trial known as Mafia Capitale, which concerns the scandal that involved the government of the city of Rome. It is a collective intimidation because it involved 97 journalists, who were denounced for violating the secret on the ongoing investigations. It is a really serious form of intimidation because it was activated within the field of law and thus is not punishable.” – Rossella Ricchiuti
Turkey / 57 verified reports
Zaman newspaper seized by authorities
“These attacks and actions taken by the government against independent media in Turkey attest to the shrinking space of independent media overall. In addition, it illustrates the shifting power dynamic within the ruling government in Turkey where once upon a time friends, are turned into enemies by the regime. As the paper wrote itself, Turkey is headed through its ‘darkest and gloomiest days in terms of freedom of the press.'” – MMF’s Turkey correspondent
Azerbaijan/ 5 verified reports
Writer banned from leaving country
“Aylisl’s 12-hour interrogation at the airport and later charges of hooliganism were just as absurd as the claim that a 79-year-old man, suffering from a heart condition and other health issues would attack an airport employee to such an extent that it would cause hemorrhage. I chose this example to illustrate the absurdity of charges brought against individuals in Azerbaijan but also the extent to which the regime is ready to go in order to muzzle those voices who different.” – MMF’s Azerbaijan correspondent
Macedonia / 59 verified reports
Deputy Prime Minister attacks journalist
“This incident best demonstrates the division in society as a whole and among journalists as a professional guild. This is a clear example of how politicians and elites look upon and treat the journalist that are critical towards their policies and question their authority.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Bosnia / 56 verified reports
Police raid Klix.ba offices
“This was the most serious incident over the last two years in Bosnia regarding the state’s misuse of institutions to gag free media and suppress investigative journalism. In this specific incident, the state used its mechanisms to breach media freedoms and send a chilling message to all other media.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Croatia / 64 verified reports
Journalist threatened by disbanded far-right military group
“After the centre-right government in Croatia came to power in late 2015, media freedom in the country rapidly deteriorated. Since then around 70 media workers in the public broadcaster were replaced or removed from their posts. This particular case of the prominent editor-in-chief of the weekly newspaper Novosti receiving a threatening letter from anonymous disbanded military organisation demonstrates the polarisation in the society and its affect on media freedom.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Greece / 34 verified reports
Golden Dawn members assault journalists covering demonstration
“This was the second attack against journalists by Golden Dawn members within one month. With more than 50,000 asylum seekers and migrants trapped in Greece, the tension between members of the far-right group and anti-fascist organisations is rising.” – Christina Vasilaki
Poland / 35 verified reports
Over 100 journalists lose jobs at public broadcasters
“This report highlights the extent of the ongoing political cleansing of the public media since the new media law was passed in early January.” – Martha Otwinowski
Germany / 74 verified reports
Journalist stops blogging after threats from right-wing extremists
“The MMF platform lists numerous incidents where German journalists have been threatened or physically assaulted by right-wing extremists over the last two years. This incident stands out as a case of severe intimidation that resulted in silencing the journalist altogether.” – Martha Otwinowski
Belgium / 19 verified reports
Press asked to respect lockdown during anti-terrorism raids
“On 22 November 2015, the Belgian authorities asked the press to refrain from reporting while a big anti-terrorist raid was taking place in Brussels. While understandable, this media lock-down raised questions for press freedom and underlined the difficulties of reporting on terror attacks and anti-terror operations.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Luxembourg / 2 verified reports
Investigative journalist on trial for revealing Luxleaks scandal
“This Luxleaks-related case is the only violation we have become aware in Luxembourg over the period (which is not to say that no other cases occurred). Along with two whistleblowers, a journalist was prosecuted by PricewaterhouseCoopers and accused of manipulating a whistleblower into leaking documents. This is a good example of the threat the notion of trade secrets can represent to journalism.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Ukraine / 127 verified reports
Website leaks personal information of more than 4,000 journalists
“This incident shows how fragile the media freedom and personal data of journalists are in armed conflict. Even after a great international scandal, the site continues to break the legislation and publishes new lists. It has been operating for two years already and those involved in its activities go unpunished. It seems that the post-Maidan Ukraine has simply ‘no political will’ for this.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
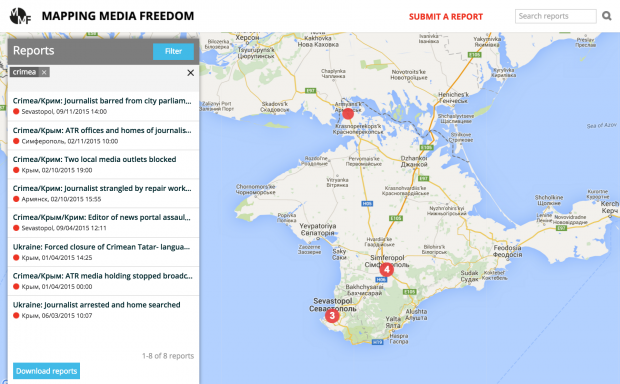
Crimea / 18 verified reports
Journalists’ homes searched, criminal case filed
“This report shows the everyday life of independent journalists working on the peninsula. Only a few critical voices are still remaining in Crimea while the majority of independent journalists were forced to leave the profession or to leave Crimea and continue their work on the mainland Ukraine.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
Spain / 49 verified reports
Journalist fined for publishing photos of arrest
“The latest issue for the Spanish media is the Public Security Law, introduced in June 2015, which among other things limits space for reporters. The law prohibits the publication of photo and video material where police officers may be identified, unless official state permission is obtained. This was the first case of a journalist being fined by the new law.” – Miho Dobrasin
Belarus / 47 verified reports
Journalist beaten by police, detained and fined for filming police attacks
“The story has ended in impunity: a criminal case was not even filed against the police officers who had beaten the journalist.” – Volha Siakhovich
Latvia / 12 verified reports
Latvia and Lithuania ban Russian-language TV channels
“This was the beginning of a disturbing tendency to react with rather futile gestures against Russian television channels. The bans are not so much against the media, as telling the audience that the authorities, not the public, will decide what Latvian viewers may or may not see or hear.” – Juris Kaža
Serbia / 110 verified reports
Investigative journalists victim of smear campaign
“You have to be very brave to launch a new investigative journalism portal in Serbia and expose corruption and organised crime involving government officials. That is why the launch of KRIK in early 2015 has been so important for media freedom, but at the same time so dangerous for its journalists. Smear campaigns like this by pro-government tabloid Informer are a relatively new but common method in the Balkans to scare journalists off.” – Mitra Nazar
18 May 2016 | Bosnia, Europe and Central Asia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News, Russia, Turkey, United Kingdom

Each week, Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project verifies threats, violations and limitations faced by the media throughout the European Union and neighbouring countries. Here are five recent reports that give us cause for concern.
The Russian state media regulator Roskomnadzor began blocking Krym Realii, the Сrimean edition of Radio Free Europe / Radio Liberty on Saturday 14 May.
A representative of Roskomnadzor confirmed that the regulator had blocked a page, which contains an interview with a leader of the Tatar Mejlis, at the request of the general prosecutor office. “Currently, Roskomnadzor is implementing measures for blocking and closing this website,” criminal prosecutor Natalia Poklonskaya told Interfax.
Krym Realii was established following the annexation of Crimea to Russia. Materials on the site are published in Russian, Ukrainian and Crimean Tatar languages.
Several editors at RBC media holding lost their jobs on 13 May following a meeting between top management with journalists. They include RBC editor-in-chief Elizaveta Osetinskaya, editor-in-chief of the RBC business newspaper Maksim Solyus, and RBC deputy chief editor Roman Badanin.
In a press release, RBC underlined that the dismissals were finalised as a mutual agreement of both parties, but sources from TV-Dozhd and Reuters claim managers have bowed to political pressure from the Kremlin.
The pressure against RBC began following investigations that have reportedly “irked the Kremlin“, including one on the assets of Vladimir Putin’s alleged daughter, Ekaterina Tikhonova.
Petar Panjkota, a journalist for the Croatian commercial national broadcaster RTL, was physically assaulted after he had finished a segment from the Bosnian town Banja Luka on 14 May.
Panjkota was reporting on parallel rallies in Banja Luka, the administrative centre of Bosnia’s Serb-dominated of Republika Srpska. He was reporting on protests organised by the ruling and opposition parties of the Bosnian Serbs. When he went off air, Panjkota was punched in the head by an unidentified individual, leaving bruises.
RTL strongly condemned the attack, calling it another attack on media freedom. No information has surfaced on the identity of the assailant.
On 12 May, the long-awaited white paper on the future of the BBC was unveiled. The BBC Trust is to be abolished and replaced by a new governing board including ministerial appointees. The board will be comprised of 12 to 14 members: the chair, deputy chair and members for each of the four nations of the UK will be appointed by the government and the remaining seats will be appointed by the BBC.
“It is vital that this appointments process is clear, transparent and free from government interference to ensure that the body governing the BBC does not become simply a mouthpiece for the government,” Jodie Ginsberg, CEO of Index on Censorship, said.
“Independence from government is essential for the BBC and these proposals don’t quite offer that,” Richard Sambrook, director of the Centre for Journalism at Cardiff School of Journalism, Media and Cultural Studies and former BBC journalist, told Index on Censorship. “There is no reason the board can’t be appointed by an arms length, independent panel. Currently the plans are too close to a state broadcasting model.”
Two reporters working for Dicle News Agency (DİHA) reporters were detained in the eastern city of Van on 12 May. Nedim Türfent and Şermin Soydan were allegedly detained within the scope of an on-going investigation and taken to the anti-terror branch in the central Edremit district of Van.
Both were detained separately. According to Bestanews website, Nedim Türfent was detained when his car was stopped by state forces at the entrance of Van. Şermin Soydan was detained on her way to cover news in the city of Van.
7 Dec 2015 | Europe and Central Asia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News, Russia
Russia’s takeover of Crimea has been accompanied by an ongoing process that is shrinking the space for media and freedom of speech on the peninsula. As the clampdown progressed, a majority of the independent journalists either left the disputed territory or stopped openly criticising Russian policy. At the same time, the number of alternative sources of information declined significantly.
Russian and Crimean authorities have used red tape, paramilitary violence and threats to silence independent voices and media. They have stifled freedom of information and jeopardised journalist safety.
Journalists and media professionals dubbed Crimea “fear peninsula”.
Curtailing broadcast TV

As Russia took over, television stations opposed to the annexation were one of the first targets. In March 2014, Chornomorska, the largest local TV and radio company, and all Ukrainian stations had their analogue broadcasts terminated. This was followed two months later, in June 2014, by the dropping of Ukrainian cable TV channels in some cable networks.
Applying Russia’s extremism law in Crimea
Soon after the annexation, Russia began implementing its overly broad and vague 2002 law, On Countering Extremist Activity, which led to a surge in warnings against the media. In summer 2014, Shevket Kaybullaev, the editor-in-chief of the Crimean Tatar newspaper Avdet , was summoned to the office of public prosecution in Simferopol. Kaybullaev was interrogated because of a complaint against the paper that challenged coverage of the mood of the Tatar community in the run-up to local elections. The complainant accused the paper of “radicalism and extremism”.
Verbal accusations against journalists have also become day-to-day practice. The Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) and prosecutor’s offices demanded the removal of “extremist materials” from media outlets. Crimean Tatar TV channel ATR received two warnings about the “violation of legislation aimed at countering extremist activity”. The station management was reminded that the formation of an anti-Russian public opinion could be considered a violation of the extremist law.
Criminal penalties for “incitement to separatism”
On 9 May 2014, amendments were made to Russia’s Criminal Code. A new article, 280.1, states that “public calls for action aimed at violating the territorial integrity of the Russian Federation” is punishable by up to five years imprisonment. The words “annexation” and “occupation” are de facto banned in Crimea when referring to recent events.
The amended code has been used to target Crimean journalists. In March 2015, two journalists, the Center for Investigative Journalism’s Anna Andrievska and Natalia Kokorina, had their apartments searched. Kokorina was interrogated for six hours. The FSB opened the criminal case against Andrievska on charges of “incitement to separatism” based on her reporting on individuals providing support for the Crimea volunteer battalion fighting in Donbas, in eastern Ukraine.
Searches and seizure of property
Russian authorities are using searches and property seizure as a way to intimidate and pressurise media companies. In August 2014, the work of Chornomorska TV and Radio Company and the Center for Investigative Journalism were blocked after the seizure of their broadcasting equipment. The broadcaster wasn’t able to retrieve its equipment until five months later.
In September 2014, a search was conducted at the office of the Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People, a representative body for the ethnic group. Because it shares the building with the Mejlis, the offices of the Avdet newspaper were also raided. Following the probe, the paper was ordered to vacate its offices within 24 hours.
In January 2015, a search was carried out at the ATR TV channel, which disrupted the station’s broadcasts and prevented newsroom staffers from reporting.
Using paramilitaries to put pressure on journalists
Paramilitary groups have also been used to target journalists. So-called Crimean self-defense groups have been found to have illegally detained, assaulted and tortured journalists, as well as confiscations of and damage to property. From 15 to 19 May, 2014, ten cases of journalists’ rights violations were recorded and documented by the Crimea Field Mission on Human Rights. The situation has been worsened by the fact that to date not all the documented attacks on journalists by self-defense group members have been investigated by Crimean authorities. This has created an atmosphere of fear and impunity.
Problems with registration and re-registration of Crimean media
After the Russian annexation, Crimean authorities demanded that all active media outlets re-register according to Russian legislation. As a result, mass media that was considered disloyal — including News Agency QHA and TV Channel ATR, among others — did not receive legal permission to continue their work on the peninsula. In February 2015, all Crimean independent radio companies were silenced after losing their frequencies during a bidding process that was carried out opaquely. Beginning on 1 April 2015, the Federal Service for Supervision of Communications, Information Technologies and Mass Communications (Roskomnadzor) stopped recognising Crimean media outlets with Ukrainian registrations, making their work in the annexed territory illegal.
Making media accreditation more difficult
New rules for accreditation in Crimea make it possible to selectively restrict media access to the authorities. The State Council of the Republic of Crimea issued new regulations that make “biased coverage” one of the reasons journalists could lose accreditation. Kerch City Council, for instance, prohibits journalists without accreditation from even entering the city hall.
Blocking access to the online media
In October 2015, media freedom in Crimea came under renewed pressure when websites were blocked. Roskomnadzor carried out a request by the general prosecutor to restrict access to the Center for Investigative Journalism and Events Crimea websites in Crimea and Russia. Roskomnadzor said that the information on the sites “contains calls for riots, realisation of extremist activity and/or participation in mass (public) events held in violation of the established order”.
These internet media outlets became the first Crimean mass media whose content are officially blocked on the territory of Crimean peninsula.
Mapping Media Freedom
Click on the bubbles to view reports or double-click to zoom in on specific regions. The full site can be accessed at https://mappingmediafreedom.org/
|
![]() SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row]



