24 Feb 2017 | Croatia, Europe and Central Asia, Mapping Media Freedom, Montenegro, News and features
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Independent journalist Jovo Martinovic’s arrest with 13 other individuals during a joint Croatian and Montenegrin police operation on 22 October 2015 began an ongoing ordeal.
Martinovic was taken into custody “on reasonable suspicion that he committed criminal offence – creation of criminal organisation and unauthorised production, possession and distribution of narcotics”, according to Montenegro’s ministry of justice. Media reports explained the case more colloquially: Martinovic was detained for allegedly facilitating a meeting between drug dealers and buyers, and helping them to install a messaging app on their smartphones that is allegedly untraceable by the police.
Following Martinovic’s arrest, it took more than five months for the Special Prosecutor’s Office to raise an indictment against him. Then he spent an extra six months in pre-trial detention before the court case began on 27 October 2016. In total, Martinovic, who insists he is not guilty and the contacts with the suspects spent around one year in jail before the trial even took place. He was conditionally released on 4 January 2017. He remains under a travel ban and must report to police twice a month until the court’s final verdict is issued.
The length of Martinovic’s pre-trial detention provoked OSCE representative on freedom of the media Dunja Mijatovic and other watchdog organisations to call for a swift conclusion of his case. “Prolonged detention can have a detrimental impact on media freedom and a chilling effect on investigative journalism,” Mijatovic said.
The Committee to Protect Journalists, Human Rights Watch and Reporters Without Borders wrote a joint letter to Montenegrin prime minister Milo Djukanovic protesting the prolonged pre-trial detention and prosecution. The International Federation of Journalists wrote a letter to Djukanovic stating that they were “shocked by the gravity of his possible sentence being more than 10 years in prison”. Journalists who have worked with Martinovic wrote testimonies that in support of his professional integrity.
Martinovic has insisted that he is not guilty, adding that his contact with the two of the 13 suspects was linked to his journalistic work.
The main suspects, Dusko Martinovic (no relation) and Namik Selmanovic, who is co-operating with prosecutors, were helping the journalist in his reseatch for two documentaries, firstly a Vice documentary on the infamous Pink Panthers, a gang of gem thieves, and La Route de la Kalashnikov, a documentary about weapons smuggling commissioned by French production company CAPA Presse. The second programme, which exposed illegal smuggling of weapons from the Balkans into western Europe, was aired on the French television channel Canal+.
During one of the court sessions, Dusko Martinovic testified that met Martinovic for the first time in 2012 while he was serving time in prison for crimes related to his membership in the Pink Panthers. He also testified that the journalist had no involvement in illegal activities.
“Jovo did not take part in any drug smuggling operation,” Dusko Martinovic said in the court, Montenegrin daily Vijesti reported. In its coverage, the newspaper reported that Dusko Martinovic stressed that his contacts with Martinovic were strictly connected with the VICE documentary and later for a possible Hollywood movie about the Pink Panthers. Dusko Martinovic also said that he was offered a plea bargain by prosecutors if he testified “that Jovo was included in the drug smuggling”.
The one-year detention of Martinovic has raised questions about the country’s commitment to freedom of the press, Human Rights Watch associate director for program Fred Abrahams wrote: “The start of his trial last week did nothing to allay those concerns. To date, the evidence against Martinovic offered by deputy special prosecutor Mira Samardzic is weak, at best. She has allegedly incriminating statements from two of Martinovic’s co-accused, both of whom face jail sentences and have an incentive to co-operate with prosecutors. She also has recorded phone conversations between Martinovic and the alleged gang leader, Dusko Martinovic (no relation), but defence lawyers and others who have read the transcripts say they contain nothing to incriminate Jovo.”
Once free, it was much easier for Martinovic to tell his side of the story. Speaking to Mapping Media Freedom in a limited capacity about the ongoing case he said: “I do reject with indignation the charges laid against me. I was doing my job as a reporter and that is an undeniable fact.”
Martinovic said that until the trial ends he won’t be giving other statements.
“I will fight in court to the utmost to defend my innocence”.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Click on the bubbles to view reports or double-click to zoom in on specific regions. The full site can be accessed at https://mappingmediafreedom.org/
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1490287936930-99f1d6d4-195c-1″ taxonomies=”256, 4612″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
2 Aug 2016 | Croatia, Europe and Central Asia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News and features
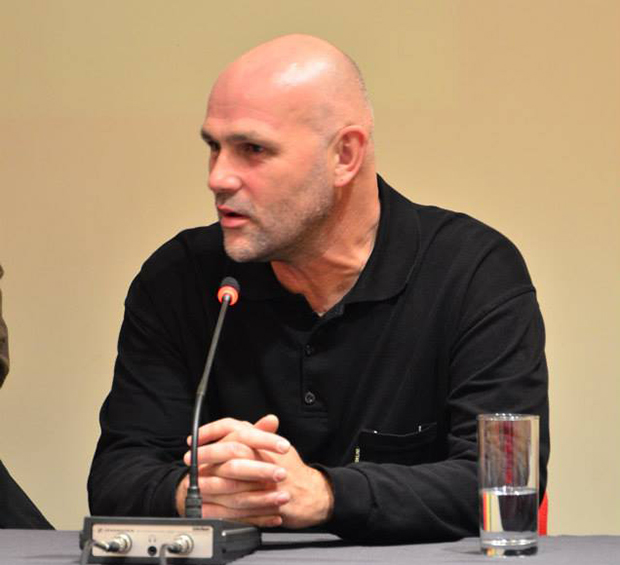

Sasa Lekovic, seen here at a Mediacentar Sarajevo event in 2013, spoke to Mapping Media Freedom about the changes at Croatia’s public broadcaster, HRT. (Photo: Mediacentar Sarajevo)
The cancellation of three radio programmes on 4 July by Croatia’s public broadcaster marks the latest in a line of sweeping changes the network has undergone since January 2016.
Two of the three shows — Audio.doc and Hidden Side of the Day — were produced by award-winning radio journalist Ljubica Letinic, while the third — Morning at Third — was considered to the Croatian Radio-Television’s (HRT) most popular. N1, a regional broadcaster, reported that the programmes will be replaced with new shows that are more appropriate to the ruling elite’s ideology, including one on Christian spirituality.
The changes at HRT have gathered momentum since Croatia’s new conservative government came to power in January 2016. More than 70 media workers at HRT have been demoted or fired and more than 10 TV and radio shows have been terminated, according to the Croatian Journalists’ Association, which has strongly condemned what it calls the deliberate destruction of HRT.
In a written response to the cancellations, CJA president Sasa Lekovic said Croatia’s minister of culture Zlatko Hasanbegovic is the force behind the “culturecide” at HRT and that the changes are motivated by the ideological differences between the conservative government and the liberal subdivisions at the public broadcaster.
In an interview with Mapping Media Freedom, Lekovic said that the purges at HRT were pre-announced, even before the conservative coalition government came to power.
“The latest developments were already announced,” Lekovic said, referring to two interviews. The first with the former Prime Minister Tomislav Karamarko from 2015, and the second with Hasanbegovic from 2013.
“Karamarko in his last year’s interview for weekly Globus announced how citizens, and especially journalist, will need to behave once he comes in power,” Lekovic said. After this it was reasonable to expect that Hasanbegovic will be in charge for media, especially after his statement that the public broadcaster’s channels are being used to enact a “post-modern, neo-Yugoslav deconstruction of Croatian national and cultural identity”.
The Croatian Writers’ Society (HDP) have also condemned the recent trend of deep and substantial changes in the public broadcaster accusing the actual government of “silencing critical voices”. Lekovic told Index on Censorship that the public broadcaster was totally devastated during Karamarko and Hasanbegovic’s brief tenure.
The coalition government between conservative center-right Croatian Democratic Union (HDZ) and the center party Most, a political platform comprised of independent local majors, was formed after more than two months of hard and erratic negotiations. By its nature it was an unstable and shaky coalition. Hasanbegovic as a high-ranking member of HDZ shortly after seated in the chair of the minister of culture. Immediately he became publicly known for series of scandals related to ideological and historical revisionism. One of the biggest scandals was revealed by the Croatian daily Novosti. They published an article that was written by Hasanbegovic during his student days in which he expressed sympathy for the fascist Ustasha regime in World War II Croatia.
After months of turbulence and scandals Karamarko resigned from the leader position at HDZ in June amid a corruption scandal that involved his wife. But briefly before his resignation, as a part of the intergovernmental power games, Karamarko and his party HDZ, which was the main party in the coalition, opted for a no-confidence vote for the government. The end result was Karamarko’s resignation from his position as the leader of the main ruling party, the failure of the coalition between HDZ and Most and snap elections were called for 11 September.
Despite the fact that the government lost the confidence vote, the changes at HRT continue as the broadcaster is under HDZ influence. In March, while still in power, the centre-right government installed Sinisa Kovacic, then-head of the parallel journalist association HNIP, as an acting head of HRT. Since then he has continued to implement Hasanbegovic’s vison for HRT and to reshape the broadcaster’s programmes. Since Kovacic was supposed to be in that position for maximum six months, a period that is long overdue, negotiations on his successor are underway.
Letinic said she is skeptical about the future of Croatian journalism. “It doesn’t look good, both for journalism and journalists. The paradox is that even such journalism serves this country. It was the weekly Nacional that provoked the fall of HDZ-MOST government.”
6 Jun 2016 | Croatia, Europe and Central Asia, European Union, Hungary, News and features
Since the 1920s, generations of western Europeans got used to the monopoly of public radio and later public television. These broadcasters developed strategies to better serve audiences and distance themselves from governments. The arrival of private broadcasters, in many cases taking place only in the 1970’s, was generally viewed as a complimentary service aimed at entertaining the public. Although public service broadcasting lost market share, it remained a respected institution in society; necessary to bring up youth, to get an objective picture of the world and cater to the interests of minorities.
Eastern Europeans also got used to the monopoly of state radio and television. Those broadcasters served the communist parties and were administered and financed by governments. Their political bankruptcy came with the collapse of communist ideology, underlined in particular by the plurality of private broadcasters that came on to the scene in the early 1990s.
These private media – with plentiful Western programming – was indeed television, for so long hidden from the viewers by totalitarian regimes. Politicians flocked to their studios to take part in talk shows, abandoning once-mighty state television. Thus, in the east, the public perception of public broadcasting was predominantly sceptical, if not negative. A discussion on its development was of tangential interest, at least during the saturation process of the new private media.
Abandoned by politicians and the public, the slow and clumsy transformation of the state broadcasters into public ones was guided by the bureaucrats, almost by themselves. The driving force behind the transformation was almost exclusively the activity of Strasbourg and Brussels. We all know that in the words of European institutions “public service broadcasting is a vital element of democracy in Europe.” Transformation of state television into a public one was a condition precedent of new democracies becoming member states of the Council of Europe in some cases. The authenticity of the transformation has been important to become a candidate for entry into the European Union and even sometimes to NATO.
Developments in younger EU member states show the importance of public service broadcasters for the development of democracy – and how they can be misused.
In December 2015, Poland‘s parliament adopted a law giving the treasury minister the mandate to appoint and dismiss members of management and supervisory boards. Since the law came into effect in January, reportedly more than 100 journalists in public media have lost their jobs, allegedly for not being government-friendly.
In March, the Croatian parliament dismissed the director general of Croatian Radio-Television. A week later, the government also proposed that parliament reject a regular report from the independent media regulator, both events raising serious concerns about the overall media freedom situation in the country.
Hungary was probably the first example in the EU where public service broadcasting was practically turned back into state broadcasting, going against international standards calling for independence. New media laws in 2010 and the restructuring of the media landscape led, within a matter of one year, to all public service media being subordinated to political decisions. The new system introduced and cemented the political dependence of public service media; the governing party had nominated all new heads of public service media and the Media Authority now controls the budget of all public service media. The law vested unusually broad powers in the politically homogeneous Media Authority and Media Council, enabling them to control content of all media.
The battle to establish credible public service broadcasters in transitional democracies has been even more difficult to wage.
The latest example is the steering board of Bosnian Radio and Television which last month decided to suspend operation of all programming at the end of this month. This decision, a wrong one for several reasons, follows years of political and financial wrangling over control of the operation.
Throughout the western Balkans, significant issues are pending affecting the independence and financial stability of public broadcasting.
A bureaucratic response to the need to establish public service broadcasters has brought predictable results. The newly established broadcasters were visibly underfunded, with formal and informal administrative links – if not strings – to governments and no clear commitments to the public. Once established, it was unclear what to do with them. Most governments viewed them as an element of bureaucracy itself, a burden to carry on the road to a united Europe. If possible and convenient, they tried to make use of them through a carrot-and-stick policy.
As such, the new public service broadcasters immediately became subject to criticism by almost anyone who wanted to speak about them. Left to survive in the monstrous buildings of brutal architecture that once belonged to powerful state television, they had to sell airtime to advertisers, beg for Western donations and save on everything.
The advance of the internet and other new technologies almost killed the whole idea of television and radio, including public service broadcasting. It was saved by the transformation process – from public service broadcasting to public service media. In the West, the BBC and other companies have struggled to make use of the changing trends in media consumption. They went online, launched smartphone applications, became interactive, archived in order to engage fragmented audiences where and when required by the viewers.
Unfortunately this is not the case in the East. Public service broadcasters at best try to appeal to the older and well-educated audiences, traditional in their use of public service media. For our children, today’s debate is not only irrelevant, it is beyond their understanding.
Is there a future?
In my view we are losing the battle and might soon lose the war. To reverse the trend, we should do the following:
Give public service broadcasters a clear-cut mandate and obligation to program for the public which, in turn, should have effective feedback and control over content. There should be programmes that cater to minorities; there should be objective news, calm and matter-of-fact debates, educational and children’s programmes.
Public service broadcasters should function independently of the government. Buffer boards, meaning councils should be established to guarantee that only an abuse of a clear-cut mandate may serve to reprimand or dismiss an editor; only mismanagement and corruption may lead to firing executive directors.
And, finally, licence fees should be introduced or increased to heighten a feeling of public ownership. We can talk about other methods of independent funding, but none of them may bring this feeling of owning an institution that serves you.
Recent columns:
Dunja Mijatović: Chronicling infringements on internet freedom is a necessary task
Dunja Mijatović: Propaganda is ugly scar on face of modern journalism
Dunja Mijatović: There is hope that justice can be served in Serbia
24 May 2016 | Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan News, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia, Croatia, Europe and Central Asia, France, Germany, Greece, Index Reports, Macedonia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News and features, Poland, Serbia, Spain, Turkey, Ukraine
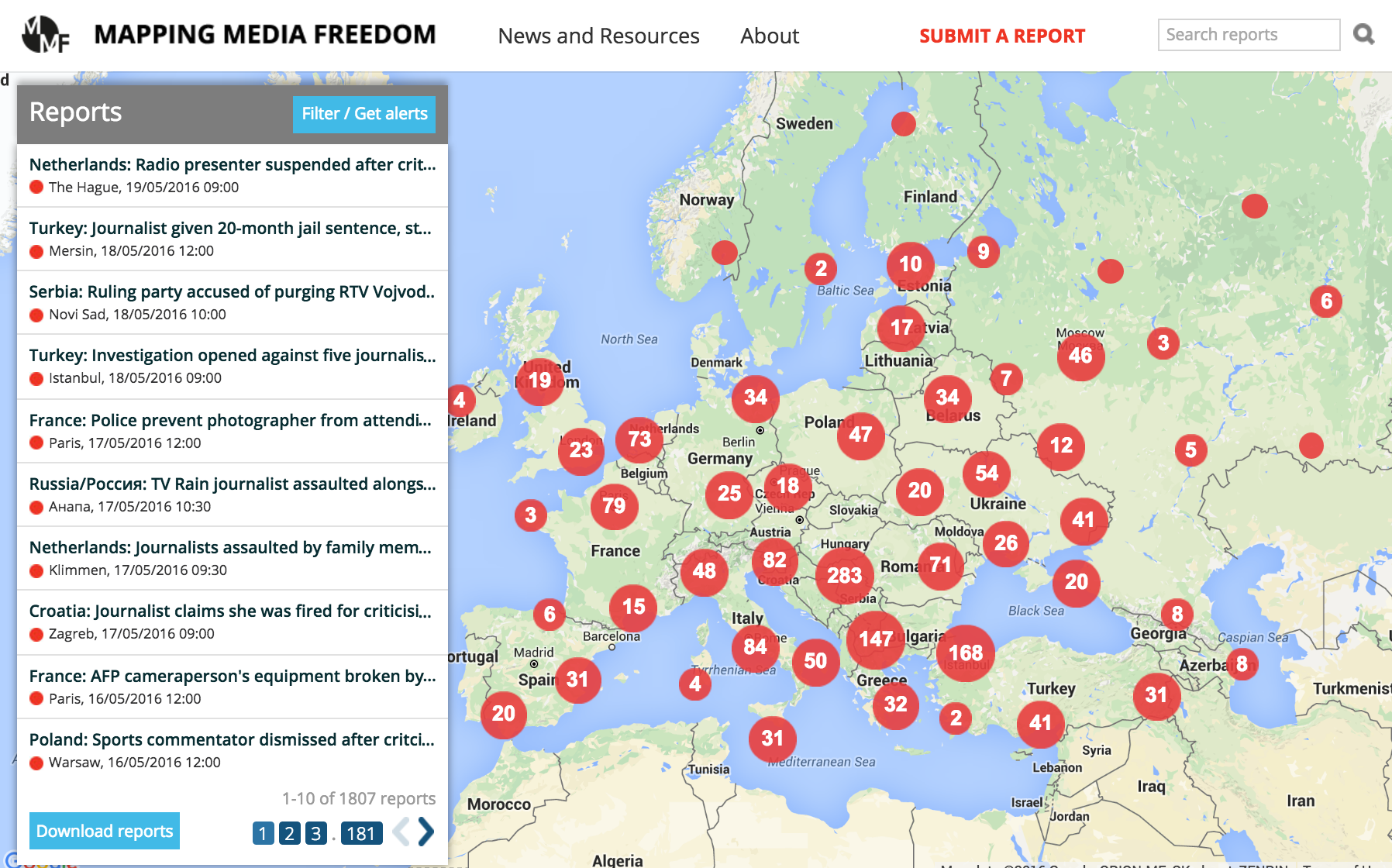
Mapping Media Freedom launched to the public on 24 May 2014 to monitor media censorship and press freedom violations throughout Europe. Two years on, the platform has verified over 1,800 media violations.
“The data the platform has collected over the last two years confirms that the state of press freedom across Europe is deplorable,” said Hannah Machlin, project officer for Mapping Media Freedom. “Media violations are occurring regularly in countries with strong democratic institutions and protective laws for journalists. Legislation limiting the press, violence across the continent and authoritarian governments are also fuelling this rapid and worrying decline. We hope that institutions and leaders take note of this information and take action swiftly.”
To mark the anniversary, we asked our correspondents to pick a key violation that stood out to them as an example of the wider picture in their region.
Russia / 113 verified reports
Several journalists and human rights activists attacked in Ingushetia
“The brutal attack on a minibus carrying six journalists and several human rights activists near the border between Ingushetia and Chechnya on the 9 March 2016 demonstrates the dangers faced by media professionals working in Russia’s North Caucasus. No suspects have been established so far. This case stands out due to its extreme violence but also supports a common trend: the reluctance of the local authorities to ensure that the journalists’ rights are respected.” – Ekaterina Buchneva
Italy / 190 verified reports
97 journalists accused of breaking the law in mafia investigation
“This was a very relevant investigation, with no precedent, that took place in October, a few weeks away from the start of the trial known as Mafia Capitale, which concerns the scandal that involved the government of the city of Rome. It is a collective intimidation because it involved 97 journalists, who were denounced for violating the secret on the ongoing investigations. It is a really serious form of intimidation because it was activated within the field of law and thus is not punishable.” – Rossella Ricchiuti
Turkey / 57 verified reports
Zaman newspaper seized by authorities
“These attacks and actions taken by the government against independent media in Turkey attest to the shrinking space of independent media overall. In addition, it illustrates the shifting power dynamic within the ruling government in Turkey where once upon a time friends, are turned into enemies by the regime. As the paper wrote itself, Turkey is headed through its ‘darkest and gloomiest days in terms of freedom of the press.'” – MMF’s Turkey correspondent
Azerbaijan/ 5 verified reports
Writer banned from leaving country
“Aylisl’s 12-hour interrogation at the airport and later charges of hooliganism were just as absurd as the claim that a 79-year-old man, suffering from a heart condition and other health issues would attack an airport employee to such an extent that it would cause hemorrhage. I chose this example to illustrate the absurdity of charges brought against individuals in Azerbaijan but also the extent to which the regime is ready to go in order to muzzle those voices who different.” – MMF’s Azerbaijan correspondent
Macedonia / 59 verified reports
Deputy Prime Minister attacks journalist
“This incident best demonstrates the division in society as a whole and among journalists as a professional guild. This is a clear example of how politicians and elites look upon and treat the journalist that are critical towards their policies and question their authority.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Bosnia / 56 verified reports
Police raid Klix.ba offices
“This was the most serious incident over the last two years in Bosnia regarding the state’s misuse of institutions to gag free media and suppress investigative journalism. In this specific incident, the state used its mechanisms to breach media freedoms and send a chilling message to all other media.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Croatia / 64 verified reports
Journalist threatened by disbanded far-right military group
“After the centre-right government in Croatia came to power in late 2015, media freedom in the country rapidly deteriorated. Since then around 70 media workers in the public broadcaster were replaced or removed from their posts. This particular case of the prominent editor-in-chief of the weekly newspaper Novosti receiving a threatening letter from anonymous disbanded military organisation demonstrates the polarisation in the society and its affect on media freedom.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Greece / 34 verified reports
Golden Dawn members assault journalists covering demonstration
“This was the second attack against journalists by Golden Dawn members within one month. With more than 50,000 asylum seekers and migrants trapped in Greece, the tension between members of the far-right group and anti-fascist organisations is rising.” – Christina Vasilaki
Poland / 35 verified reports
Over 100 journalists lose jobs at public broadcasters
“This report highlights the extent of the ongoing political cleansing of the public media since the new media law was passed in early January.” – Martha Otwinowski
Germany / 74 verified reports
Journalist stops blogging after threats from right-wing extremists
“The MMF platform lists numerous incidents where German journalists have been threatened or physically assaulted by right-wing extremists over the last two years. This incident stands out as a case of severe intimidation that resulted in silencing the journalist altogether.” – Martha Otwinowski
Belgium / 19 verified reports
Press asked to respect lockdown during anti-terrorism raids
“On 22 November 2015, the Belgian authorities asked the press to refrain from reporting while a big anti-terrorist raid was taking place in Brussels. While understandable, this media lock-down raised questions for press freedom and underlined the difficulties of reporting on terror attacks and anti-terror operations.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Luxembourg / 2 verified reports
Investigative journalist on trial for revealing Luxleaks scandal
“This Luxleaks-related case is the only violation we have become aware in Luxembourg over the period (which is not to say that no other cases occurred). Along with two whistleblowers, a journalist was prosecuted by PricewaterhouseCoopers and accused of manipulating a whistleblower into leaking documents. This is a good example of the threat the notion of trade secrets can represent to journalism.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Ukraine / 127 verified reports
Website leaks personal information of more than 4,000 journalists
“This incident shows how fragile the media freedom and personal data of journalists are in armed conflict. Even after a great international scandal, the site continues to break the legislation and publishes new lists. It has been operating for two years already and those involved in its activities go unpunished. It seems that the post-Maidan Ukraine has simply ‘no political will’ for this.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
Crimea / 18 verified reports
Journalists’ homes searched, criminal case filed
“This report shows the everyday life of independent journalists working on the peninsula. Only a few critical voices are still remaining in Crimea while the majority of independent journalists were forced to leave the profession or to leave Crimea and continue their work on the mainland Ukraine.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
Spain / 49 verified reports
Journalist fined for publishing photos of arrest
“The latest issue for the Spanish media is the Public Security Law, introduced in June 2015, which among other things limits space for reporters. The law prohibits the publication of photo and video material where police officers may be identified, unless official state permission is obtained. This was the first case of a journalist being fined by the new law.” – Miho Dobrasin
Belarus / 47 verified reports
Journalist beaten by police, detained and fined for filming police attacks
“The story has ended in impunity: a criminal case was not even filed against the police officers who had beaten the journalist.” – Volha Siakhovich
Latvia / 12 verified reports
Latvia and Lithuania ban Russian-language TV channels
“This was the beginning of a disturbing tendency to react with rather futile gestures against Russian television channels. The bans are not so much against the media, as telling the audience that the authorities, not the public, will decide what Latvian viewers may or may not see or hear.” – Juris Kaža
Serbia / 110 verified reports
Investigative journalists victim of smear campaign
“You have to be very brave to launch a new investigative journalism portal in Serbia and expose corruption and organised crime involving government officials. That is why the launch of KRIK in early 2015 has been so important for media freedom, but at the same time so dangerous for its journalists. Smear campaigns like this by pro-government tabloid Informer are a relatively new but common method in the Balkans to scare journalists off.” – Mitra Nazar




