10 Mar 2014 | News, Uncategorized

(Image: GEO TV)
On 1 March an anti-terrorism court in Pakistan, found six men guilty of the murder of 28-year old journalist Wali Khan Babar. Four have been sentenced to life imprisonment, and two, in absentia, were sentenced to death.
The young reporter was shot dead on January 1, 2011, while working for GEO TV in the Liaquatabad area of Karachi. According to Committee to Protect Journalists, his was a work-related murder.
Convictions for attacks on journalists can be complicatd in Pakistan. Ahmed Omar Saeed Sheikh, who was convicted for the murder of US reporter, Daniel Pearl is the only previous journalist killer to have been sentenced to death. However, Pearl’s case remains in dispute and Sheikh has been incarcerated at the Hyderabad Central Jail for the last 12 years. His lawyers are appealing the conviction, saying he was framed. The confusion arose after Khalid Sheikh Mohmmad (currently being held in Guantanamo) confessed to the murder.
Therefore, Mazhar Abbas, former secretary general of the Pakistan Federal Union of Journalists (PFUJ) while terming this month’s conviction as an “important decision” remains sceptical that Babar’s family will get justice given the abysmally low conviction rate once the case goes to higher courts. “It may take years to get a decision if the case goes to the Sindh High Court for appeal,” he said pointing to deep-rooted “corruption” that prevailes in the judicial system.
But that is not the only reason for the delay in justice. Despite setting up anti-terrorist courts (ATCs) for speedy disposal of cases, the conviction rate has not made an appreciable difference. People like former prosecutor general of Sindh province, Shahadat Awan, links the high rate of acquittal (almost 73 percent), to weak investigation and witnesses retreating.
Since Babar’s trial began, six witnesses, a lawyer and two policemen linked to the investigation have been assassinated.
After these murders, and amid threats to the prosecutors and lawyers, the trial was shifted from Karachi to another city in Sindh, Shikarpur. “The case has been tried under extremely difficult circumstances and to that extent I am satisfied,” acknowledged Abbas.
However, not everyone is wholly satisfied.
According to Zohra Yusuf, chairperson of the independent Human Rights Commission of Pakistan (HRCP) “justice has not been fully served as two culprits are absconding and six witnesses and a prosecution lawyer were killed while the case was being heard.”
For Ambreen Agha, research assistant with New Delhi’s Institute for Conflict Management, the conviction was a welcome step but ensuring justice was equally important.
“It is a significant step in a place where a culture of impunity dominates” she said, citing the example of Malik Ishaq, a militant leader, who, despite his involvement in the massacre of minority Shias and his association with the defunct terrorist outfit, Lashkar e Jhangvi, “goes scot free”.
At the same time, a recent attack on the Islamabad courthouse showed how vulnerable those delivering justice were.
“Despite the threat that looms large on any functioning institution of Pakistan, the judiciary will have to stand strong and determined in bringing justice in this case. The onus lies on the judiciary despite the precarious times in Pakistan,” Agha emphasized.
Nevertheless, for the media community, the conviction of Babar’s killers is historic.
Media analyst, Adnan Rehmat, said the verdict was a “turning point in the battle for defence of beleaguered media practitioners” and Abbas termed it a “ray of hope” showing that Pakistan can improve its record on protecting journalists and pursuing their killers.
But Ambreen Agha warned that a sustained policy was required to “protect the media from the extreme intolerance of the militants and the political class”.
Further, she added: “The political lobby and its attempts to shrink spaces for freedom of expression by shutting down private TV channels, intimidating and blocking certain media outlets, has, in the past, emboldened the terrorists and opened the spaces for the perpetrators of violence.”
This article was posted on March 10, 2014 at indexoncensorship.org
31 Dec 2013 | News, Politics and Society
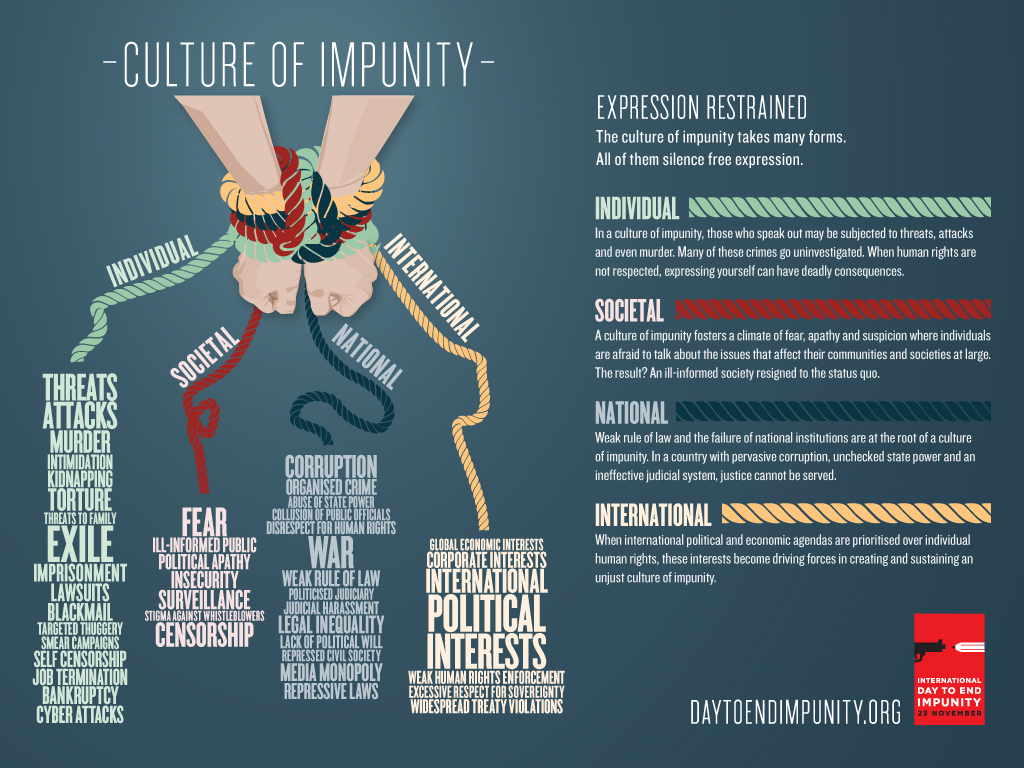
Journalists are known for uncovering the truth. What is less known is how these journalists gather these facts, often risking their jobs, and sometimes their lives, to discover information others are attempting to keep hidden from the world.
The Taksim Gezi Park Protest
The Gezi Park protest in Turkey made international news when, in May 2013, a sit-in at the park protesting plans to develop the area sparked violent clashes with police. What didn’t grab the attention of media workers worldwide was that at least 59 of their fellow journalists were fired or forced to quit over their reporting of the events.
The Turkish press have been long-time sufferers of the need to self-censor in an environment where the press is ultimately run by a handful of wealthy individuals. The Gezi Park protests saw a surge in the controlling influence of the Turkish media as 22 journalists were fired and a further 37 forced to quit due to their determination to cover the clashes for a national and international audience, as was their duty as journalists.
Turkey came in at 154th in the Reporters Without Borders Freedom of the Press Index 2013, a drop of six places from 2012.
Journalists imprisoned
2013 was the first year a detailed survey was carried out by Reporters Without Borders which looked into how many journalists had been imprisoned for their work; the result was shocking. One hundred and seventy eight journalists were spending time in jail for their actions, along with 14 media assistants. Perhaps more worrying was the statistic that 166 netizens had been imprisoned, those who actively supply the world with content often without being paid whilst gaining access to places that many ‘official’ journalists are banned from.
China handed out the most prison sentences during 2013 with 30 media personal serving time behind bars. Closely behind was Eritrea with 28 journalists imprisoned, Turkey with 27, and Iran and Syria handing out 20 sentences each.
Press freedom in Afghanistan
Murder, injuries, threats, beatings, closure of media organisations, and the dismissal for liking a Facebook post have all accounted towards the 62 cases of violence against the media and journalists working in Afghanistan over the past eight months. The Afghanistan Journalists Center, which collected the data from January to August 2013, has claimed that government officials and security forces, the Taliban, and illegal armed groups are behind the majority of attacks.
Of particular concern is the growing threat to female journalists who have been forced to quit their jobs after threats to their families.
According to the Afghanistan Media Law; every person has the right to freedom of thought and speech, which includes the right to seek, obtain and disseminate information and views within the limit of law without any interference, restriction and threat by the government or officials- a law Afghanistan does not appear to be upholding.
Exiled journalists
Some journalists are taking a risk every day that they go to work. They may not be killed for their reporting but that does not stop them facing imprisonment, violence, and harassment. Between June 2008 and May 2013 the CPJ found that 456 journalists were forced into exile as a means of protecting their families and themselves due to their determination to uncover the truth.
The top countries from which journalists fled included Somalia, Ethiopia and Sri Lanka with Iran topping the table having forced a total of 82 journalists into exile. Although a majority of these journalists claim sanctuary in countries like Sweden, the U.S and Kenya, only 7% of those exiled since 2008 have been able to return home.
Impunity
Murder is a crime for which those involved should be punished. Yet in the case of the killing of journalists nine out of 10 killers go free. Put another way, in only five percent of cases for the murder of a journalist does the defendant receive a sentence of full justice. The most likely reason to kill a journalist is to silence them from speaking the truth to others.
IFEX, global freedom of expression network behind the International Day to End Impunity campaign said: “When someone acts with impunity, it means that their actions have no consequences. Intimidation, threats, attacks and murders go unpunished. In the past 10 years, more than 500 journalists have been killed. Murder is the ultimate form of censorship, and media are undoubtedly on the frontlines of free expression.”
27 Nov 2013 | News, Politics and Society, United Nations

The UN has officially recognised 2 November as the International Day to End Impunity for crimes against journalists. As reported by Index, a draft resolution calling for this was put to a vote on 26 November. Co-sponsored by 80 organisations across 48 countries, it was passed by the Third Committee, which deals with human rights issues.
Index on Censorship, as part of the IFEX network, has welcomed the decision. Annie Game, IFEX Executive Director, stated: “There has never been a more dangerous time for journalists. They are being killed and imprisoned worldwide in record numbers. They face daily threats, attacks and intimidation from private individuals, non-state actors, and government officials who seek to silence them. The overwhelming majority of these crimes are committed with impunity.”
“We welcome the resolution’s call to proclaim November 2 as the International Day to End Impunity for crimes against journalists. With complete impunity in nine out of 10 cases of journalist murders worldwide, this decision does not come too soon. This is a crucial step toward guaranteeing that individual journalists can continue to work in the public interest without fear of reprisal, and that those who seek to silence them with violence are brought to justice.”
26 Nov 2013 | News, Politics and Society, United Nations

The UN has been urged to officially recognise the International Day to End Impunity for Crimes against Journalists as the Third Committee, dedicated to dealing with human rights issues, will today be asked to vote on a draft resolution.
The resolution, backed by at least 48 countries, is based on the UN Plan of Action on the Safety of Journalists and the Issue of Impunity, approved on 12 April 2012, which saw United Nations agencies work with member states towards a free and safe working environment for journalists. If successful, the UN Secretary General will present a report on the implementation of the resolution at the next General Assembly 2014, with 2 November officially being recognised as the official UN International Day to End Impunity.
Co-sponsored by 80 organisations and backed by countries including the United States — and even Azerbaijan and Colombia — the draft resolution calls for the acknowledged ‘condemnation of all attacks and violence against journalists and media workers, such as torture, extrajudicial killings, enforced disappearances and arbitrary detention, as well as intimidation and harassment in both conflict and non-conflict situations’.
Index on Censorship as a founding member of IFEX has been supporting the International Day to End Impunity since its launch in 2010 which has seen the 23 November recognised as the day for campaign. Annie Game, IFEX Executive Director, stated: “This is a positive move forward because IFEX members acknowledged that making the International Day to End Impunity an official UN day can help to raise the global profile of the issue. Every year, a growing number of IFEX members and concerned individuals take part in this campaign that strikes at the very roots of the problem. Having the UN acknowledge the importance of this issue will help us broaden our reach and turn up the volume on the call to end impunity.”
The draft resolution also:
• acknowledges ‘the specific risks faced by women journalists in the exercise of their work, and underlining, in this context, the importance of taking a gender-sensitive approach when considering measures to address the safety of journalists’;
• the acknowledgement that ‘journalism is continuously evolving to include inputs from media institutions, private individuals and a range of organisations that seek, receive and impart information and ideas of all kinds, online as well as offline, in the exercise of freedom of opinion and expression, in accordance with article 19 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights’;
• and ‘urges Member States to do their utmost to prevent violence against journalists and media workers, to ensure accountability through the conduct of impartial, speedy and effective investigations into all alleged violence against journalists and media workers falling within their jurisdiction, and to bring the perpetrators of such crimes to justice and to ensure that victims that access to appropriate remedies’.
The full draft resolution can be seen here.
This article was originally published on 26 Nov 2013 at indexcensorship.org



