Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”Index on Censorship has dedicated its milestone 250th issue to exploring the increasing threats to reporters worldwide. Its special report, Truth in Danger, Danger in Truth: Journalists Under Fire and Under Pressure, is out now.”][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”76283″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”SPECIAL REPORT: DANGER IN TRUTH, TRUTH IN DANGER” css=”.vc_custom_1483444455583{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”IN FOCUS” css=”.vc_custom_1481731813613{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”CULTURE” css=”.vc_custom_1481731777861{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”COLUMNS” css=”.vc_custom_1481732124093{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”END NOTE” css=”.vc_custom_1481880278935{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-top: 15px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_custom_heading text=”SUBSCRIBE” css=”.vc_custom_1481736449684{margin-right: 0px !important;margin-left: 0px !important;border-bottom-width: 1px !important;padding-bottom: 15px !important;border-bottom-color: #455560 !important;border-bottom-style: solid !important;}”][vc_column_text]Index on Censorship magazine was started in 1972 and remains the only global magazine dedicated to free expression. Past contributors include Samuel Beckett, Gabriel García Marquéz, Nadine Gordimer, Arthur Miller, Salman Rushdie, Margaret Atwood, and many more.[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”76572″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]In print or online. Order a print edition here or take out a digital subscription via Exact Editions.
Copies are also available at the BFI, the Serpentine Gallery, MagCulture, (London), News from Nowhere (Liverpool), Home (Manchester), Calton Books (Glasgow) and on Amazon. Each magazine sale helps Index on Censorship continue its fight for free expression worldwide.
![]() SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row]
SUBSCRIBE NOW[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row]
Mapping Media Freedom launched to the public on 24 May 2014 to monitor media censorship and press freedom violations throughout Europe. Two years on, the platform has verified over 1,800 media violations.
“The data the platform has collected over the last two years confirms that the state of press freedom across Europe is deplorable,” said Hannah Machlin, project officer for Mapping Media Freedom. “Media violations are occurring regularly in countries with strong democratic institutions and protective laws for journalists. Legislation limiting the press, violence across the continent and authoritarian governments are also fuelling this rapid and worrying decline. We hope that institutions and leaders take note of this information and take action swiftly.”
To mark the anniversary, we asked our correspondents to pick a key violation that stood out to them as an example of the wider picture in their region.
Russia / 113 verified reports
Several journalists and human rights activists attacked in Ingushetia
“The brutal attack on a minibus carrying six journalists and several human rights activists near the border between Ingushetia and Chechnya on the 9 March 2016 demonstrates the dangers faced by media professionals working in Russia’s North Caucasus. No suspects have been established so far. This case stands out due to its extreme violence but also supports a common trend: the reluctance of the local authorities to ensure that the journalists’ rights are respected.” – Ekaterina Buchneva
Italy / 190 verified reports
97 journalists accused of breaking the law in mafia investigation
“This was a very relevant investigation, with no precedent, that took place in October, a few weeks away from the start of the trial known as Mafia Capitale, which concerns the scandal that involved the government of the city of Rome. It is a collective intimidation because it involved 97 journalists, who were denounced for violating the secret on the ongoing investigations. It is a really serious form of intimidation because it was activated within the field of law and thus is not punishable.” – Rossella Ricchiuti
Turkey / 57 verified reports
Zaman newspaper seized by authorities
“These attacks and actions taken by the government against independent media in Turkey attest to the shrinking space of independent media overall. In addition, it illustrates the shifting power dynamic within the ruling government in Turkey where once upon a time friends, are turned into enemies by the regime. As the paper wrote itself, Turkey is headed through its ‘darkest and gloomiest days in terms of freedom of the press.'” – MMF’s Turkey correspondent
Azerbaijan/ 5 verified reports
Writer banned from leaving country
“Aylisl’s 12-hour interrogation at the airport and later charges of hooliganism were just as absurd as the claim that a 79-year-old man, suffering from a heart condition and other health issues would attack an airport employee to such an extent that it would cause hemorrhage. I chose this example to illustrate the absurdity of charges brought against individuals in Azerbaijan but also the extent to which the regime is ready to go in order to muzzle those voices who different.” – MMF’s Azerbaijan correspondent
Macedonia / 59 verified reports
Deputy Prime Minister attacks journalist
“This incident best demonstrates the division in society as a whole and among journalists as a professional guild. This is a clear example of how politicians and elites look upon and treat the journalist that are critical towards their policies and question their authority.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Bosnia / 56 verified reports
Police raid Klix.ba offices
“This was the most serious incident over the last two years in Bosnia regarding the state’s misuse of institutions to gag free media and suppress investigative journalism. In this specific incident, the state used its mechanisms to breach media freedoms and send a chilling message to all other media.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Croatia / 64 verified reports
Journalist threatened by disbanded far-right military group
“After the centre-right government in Croatia came to power in late 2015, media freedom in the country rapidly deteriorated. Since then around 70 media workers in the public broadcaster were replaced or removed from their posts. This particular case of the prominent editor-in-chief of the weekly newspaper Novosti receiving a threatening letter from anonymous disbanded military organisation demonstrates the polarisation in the society and its affect on media freedom.” – Ilcho Cvetanoski
Greece / 34 verified reports
Golden Dawn members assault journalists covering demonstration
“This was the second attack against journalists by Golden Dawn members within one month. With more than 50,000 asylum seekers and migrants trapped in Greece, the tension between members of the far-right group and anti-fascist organisations is rising.” – Christina Vasilaki
Poland / 35 verified reports
Over 100 journalists lose jobs at public broadcasters
“This report highlights the extent of the ongoing political cleansing of the public media since the new media law was passed in early January.” – Martha Otwinowski
Germany / 74 verified reports
Journalist stops blogging after threats from right-wing extremists
“The MMF platform lists numerous incidents where German journalists have been threatened or physically assaulted by right-wing extremists over the last two years. This incident stands out as a case of severe intimidation that resulted in silencing the journalist altogether.” – Martha Otwinowski
Belgium / 19 verified reports
Press asked to respect lockdown during anti-terrorism raids
“On 22 November 2015, the Belgian authorities asked the press to refrain from reporting while a big anti-terrorist raid was taking place in Brussels. While understandable, this media lock-down raised questions for press freedom and underlined the difficulties of reporting on terror attacks and anti-terror operations.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Luxembourg / 2 verified reports
Investigative journalist on trial for revealing Luxleaks scandal
“This Luxleaks-related case is the only violation we have become aware in Luxembourg over the period (which is not to say that no other cases occurred). Along with two whistleblowers, a journalist was prosecuted by PricewaterhouseCoopers and accused of manipulating a whistleblower into leaking documents. This is a good example of the threat the notion of trade secrets can represent to journalism.” – Valeria Costa-Kostritsky
Ukraine / 127 verified reports
Website leaks personal information of more than 4,000 journalists
“This incident shows how fragile the media freedom and personal data of journalists are in armed conflict. Even after a great international scandal, the site continues to break the legislation and publishes new lists. It has been operating for two years already and those involved in its activities go unpunished. It seems that the post-Maidan Ukraine has simply ‘no political will’ for this.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
Crimea / 18 verified reports
Journalists’ homes searched, criminal case filed
“This report shows the everyday life of independent journalists working on the peninsula. Only a few critical voices are still remaining in Crimea while the majority of independent journalists were forced to leave the profession or to leave Crimea and continue their work on the mainland Ukraine.” – Tetiana Pechonchyk
Spain / 49 verified reports
Journalist fined for publishing photos of arrest
“The latest issue for the Spanish media is the Public Security Law, introduced in June 2015, which among other things limits space for reporters. The law prohibits the publication of photo and video material where police officers may be identified, unless official state permission is obtained. This was the first case of a journalist being fined by the new law.” – Miho Dobrasin
Belarus / 47 verified reports
Journalist beaten by police, detained and fined for filming police attacks
“The story has ended in impunity: a criminal case was not even filed against the police officers who had beaten the journalist.” – Volha Siakhovich
Latvia / 12 verified reports
Latvia and Lithuania ban Russian-language TV channels
“This was the beginning of a disturbing tendency to react with rather futile gestures against Russian television channels. The bans are not so much against the media, as telling the audience that the authorities, not the public, will decide what Latvian viewers may or may not see or hear.” – Juris Kaža
Serbia / 110 verified reports
Investigative journalists victim of smear campaign
“You have to be very brave to launch a new investigative journalism portal in Serbia and expose corruption and organised crime involving government officials. That is why the launch of KRIK in early 2015 has been so important for media freedom, but at the same time so dangerous for its journalists. Smear campaigns like this by pro-government tabloid Informer are a relatively new but common method in the Balkans to scare journalists off.” – Mitra Nazar
Mapping Media Freedom
|
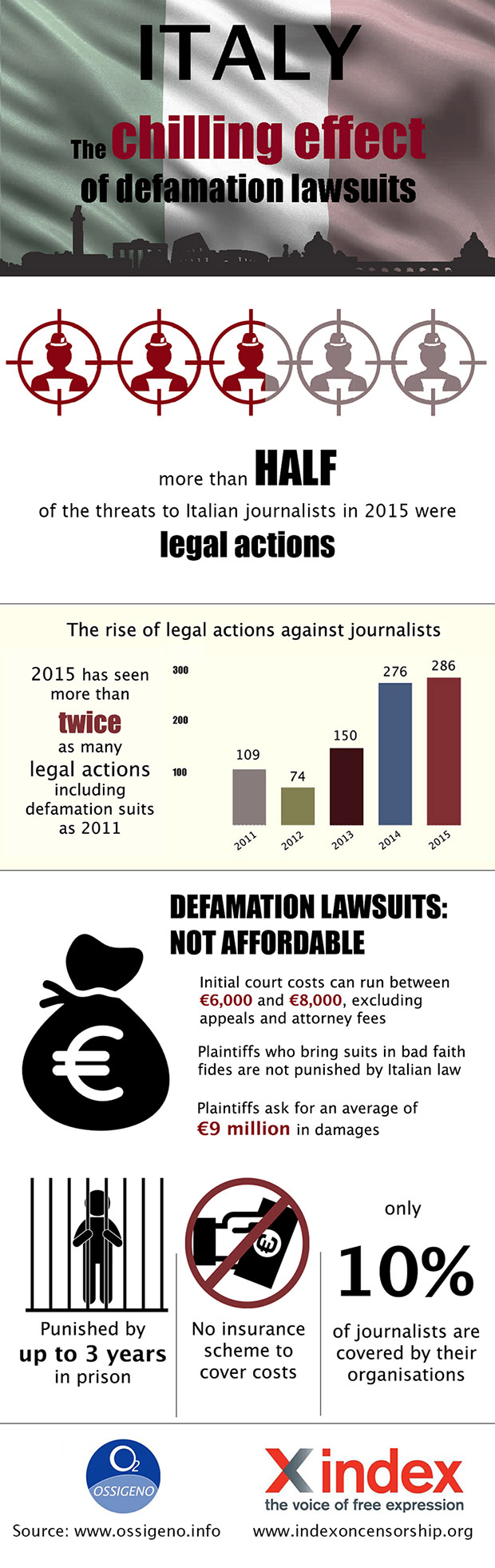
Italy might soon introduce fines against vexatious defamation lawsuits against journalists, as part of a large-scale reform being discussed by the parliament.
On 10 March, the chamber of deputies passed a set of recommendations to reform civil proceedings, which would include penalties to discourage the use of libel suits to intimidate journalists.
The recommendations, called delegation to the government with instructions on the efficiency of civil proceeding and sponsored by ministry of justice Andrea Orlando (Democratic Party) and vice-president of the justice committee Franco Vazio, of the same party, would punish plaintiffs who are proved to be in mala fides, i.e. knowing their claims to be false, by making them reimburse journalists an amount between two and five times the trial’s expenses.
The recommendations are what Italian law calls a “delegated law”. With them, the parliament delegates the government to legislate in its place – but only following a set of restrictions and recommendations, which are what the chamber of deputies approved on 10 March.
Before the government turns them into law, the recommendations now need to be approved by the Italian senate, which has not yet released a timeline for debating the recommendations.
If the senate approves the recommendations, the government will have an 18-month window to enforce them. However, according to Italian law, no individual minister is in charge of the measure, and there won’t be a backlash against the government if it fails to take action.
Nevertheless, president of the National Federation of Italian Press Giuseppe Giulietti has expressed satisfaction about the recommendations, saying in a statement it is a “relevant first step in the right direction”.
Alberto Spampinato, director of Ossigeno per l’Informazione, an Italian organisation that monitors threats to journalists, also thinks that although the measures aren’t a major step forward, they are a good start.
“The fines would drive down the number of vexatious defamation lawsuits brought against journalists,” Spampinato told Index.
According to data by Ossigeno, defamation lawsuits have become the most used tool to silence journalists in the country.
Journalists have no access to insurance schemes to cover defamation trials expenses in Italy, and only 10% of them can rely on their organisations to cover the costs, making it hard for journalists to afford to be sued for libel.
Ossigeno argues that even the threat of legal action has a chilling effect on the media.
According to Spampinato, an older law had already established fines for these cases. However, as it failed to specify the amount of the fines, judges have been unable to impose any at all.
“It’s important that the parliament has begun to address the issue,” he says.
The vote came just after the chamber of deputies ratified a parliamentary report on the protection of journalists on 3 March.
The report, titled Report on the State of Information and on the Condition of Journalists threatened by Organised Crime, was sponsored by MP Claudio Fava and backed by the anti-mafia parliamentary committee, and it calls for further measures to protect journalists from intimidation.
The report recommends differentiating between malicious falsehood and defamation, and to make it “a criminal offence to punish any threat, pressure, and violent or damaging behaviour to limit the press’s freedom”.
Ossigeno’s Spampinato says both would be important measures.
“Just like when a patient dies, we don’t always blame the surgeon for it, we must be able to distinguish between a journalist’s mistakes and the cases in which he disseminates falsehood intentionally,” he said.
He also agreed with the report that in most cases it should be a criminal offence to limit press freedom. He argued that the right to be informed is the only fundamental human right not protected by criminal law – not just in Italy but also in other European countries.
The report was approved by the chamber unanimously but isn’t a binding resolution.
However, Ossigeno thinks it is an important milestone, calling it a “historic vote” on its website.
“The vote on the committee’s report paves the way for other proposals,” explained Spampinato. “MPs will introduce new measures to protect journalists.”
This article was originally posted at Index on Censorship
Two Italian journalists are being prosecuted by The Vatican for revealing confidential information and could face up to eight years in prison.
Emiliano Fittipaldi and Gianluigi Nuzzi are being tried in the so-called “Vatileaks II” case for publishing leaked documents in their books detailing financial misdeeds involving The Holy See. Fittipaldi is the author of Avarice and Nuzzi’s is entitled Merchants in the Temple.
The criminal trial by the Vatican justice against the reporters is a serious one. The journalists are accused of violating “Crimes against the Fatherland” in the Vatican penal code, specifically a 2013 amendment that added section 116, which says “whoever procures illegally or reveals information or documents whose disclosure is forbidden, shall be punished with imprisonment from six months to two years or with a fine from thousand to five thousand euro”. But “if the conduct has related to information or documents concerning the fundamental interests or diplomatic relations of the Holy See and the State, punishment of imprisonment is implemented from four to eight years”.
Fittipaldi and Nuzzi are not the only people standing trial in the case. The alleged sources of the internal Vatican documents — Lucio Vallejo Balda, secretary of Cosea, the commission that conducted the survey on the finances of the Vatican, and Francesca Immacolata Chaouqui, a member the commission — are also in the dock. A fifth person, Nicola Maio, a former contributor to Cosea, is also being prosecuted. Balda, Chaouqui and Maio are also accused of criminal association.
So far, there have been three hearings as part of the trial. The first on 24 November ended with a decision by the court to reject requests for deferral submitted by the defendants, who said they didn’t have enough times to organise their defence, having received court documents only the day before. The second hearing on 30 November lasted only 13 minutes, during which the court deferred the trial until 7 December. On that day, the court admitted all the witnesses requested by the defence.
“I am a journalist, and when a reporter has some news and verifies it, he must publish it”, Fittipaldi said of the Vatican’s decision to prosecute. After the second hearing, Nuzzi said: “It is a Kafkian process, in which the elements of surrealism occasionally fall on the stage of the case. I do not share the codes of this process, we are talking about a process to press freedom.”
Press freedom organisations have been quick to express solidarity with the journalists and called on the Vatican to end the proceedings. The FNSI (National Federation of Press in Italy) called the disputed allegations “paradoxical”. Dunja Mijatović, the OSCE Representative on Freedom of the Media, asked the Vatican, which is a member of the OSCE, to withdraw the criminal charges set against the reporters. The CPJ (Committee to Protect Journalists) called on Vatican to drop the charges against Nuzzi and Fittipaldi. EFJ (European Federation of Journalists) said: “Journalists must be free to investigate and report about the use of public money. The protection of their sources is also part of the ethical code of journalists.”
The next hearing of the case has yet to be scheduled.
Mapping Media Freedom
|