28 Sep 2015 | Europe and Central Asia, Hungary, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News, Serbia
At least eight journalists were beaten and three detained as they covered a clash between refugees and the Hungarian police at the border with Serbia on 16 September.
Among those attacked were Swedish photographer Meli Petersson Ellafi, Jordan Davis, a journalist at Swiss RTS, and an entire film crew working for Radio Television of Serbia. They were covering events at the Horgoš-Röszke highway border crossing, which the Hungarian authorities had blocked the day before, leaving around 2,000 refugees stranded on the Serbian side.
On 16 September, at around 2:30 PM local time, refugees attempted to break through a gate into Hungary. While most were protesting peacefully, a small number threw stones and bottles across the fence at the Hungarian riot police. The police responded with tear gas, pepper spray and water cannons.
“At some point, the riot police retreated from the fence and the refugees managed to open the gate,” Timea Becková, who works for Slovakian newspaper Denník N, recalls. Confusion followed, with many refugees thinking the Hungarian authorities would let them in, so they walked towards the riot police on the Hungarian side. Several dozen journalists on the Serbian side followed the crowd.
At around 5:30 PM, TEK, the Hungarian anti-terror SWAT unit, equipped with sidearms, helmets and face masks, started pushing the refugees back towards Serbia.
“As I was moving backwards, I stopped for a moment to help an old man who fell and risked being trodden by riot police, which is when an officer hit me with a baton,” Becková said. She repeatedly told police in Hungarian that she is a journalist, but it made no difference.
“Suddenly the TEK guys, not the riot police, started running towards us — it was mayhem,” says Warren Richardson, an Australian photographer. Despite having two cameras, he was grabbed from behind by an officer.
“Clearly he was there to beat, not to ask questions,” Richardson told Index on Censorship, adding that he was standing on ‘no mans’ land’ between Serbia and Hungary. “From there they beat me into Hungary, then took me from the border to the police station illegally. They kidnapped me.”
“Law enforcement lost control of the situation,” Becková said. While she doesn’t hold a grudge against TEK, she says the events that followed were outrageous. She was forcefully brought back to the Hungarian side — with her hands tied tightly with a plastic wrap — where she was thrown to the ground.
She was later handed over to the regular police along with Richardson, who was kicked in the head and chest, and the Polish journalist, Jacek Tacik, who suffered a head wound. They were taken to a police station in Szeged along with a number of detained refugees.
There they were questioned on suspicion of having crossed the border illegally. In addition, Becková was accused of inciting rebellion and Tacik was told he had assaulted a policeman. However, this accusation did not emerge again during his interrogation, he told Index.
During questioning, Richardson refused to cooperate. “I stood up for myself. They were making up laws. They never took my name, personal address or fingerprints,” he said.
After interrogations that lasted up to 13 hours, the journalists were released and the charges were dropped.
In a statement, the Hungarian police denied beating the journalists. “The police — in accordance with the law — used necessary and proportional force against the members of an aggressive group that was using instruments that could cause serious harm to the police protecting the border of Hungary and the European Union. The media workers stayed at their own risk in an area where the police — after a proper warning — used coercive instruments.”
Hungarian government spokesman Zoltan Kovacs said it was a surprise to find journalists among the chaos. He said that in situations like this, the safety of journalists cannot be guaranteed, therefore they should stay away. A policeman is not in the position to judge who is a troublemaker and who represents the media, he added.
The European Federation of Journalists (EFJ) has denounced the attack. “It is incomprehensible to see an EU country like Hungary constantly violating press freedom and human rights. The European Commission and international institutions must take action against these serious violations,” EFJ President Mogens Blicher Bjerregaard said.
“It is a prerequisite for EU member states to respect the EU Charter on fundamental rights which sets out standards on media freedom and freedom of expression.”
The incident was also condemned by the Committee to Protect Journalists. “We are appalled by the police violence against journalists covering this world story,” CPJ Europe and Central Asia Program Coordinator Nina Ognianova said. “The Hungarian government must make a clear and unequivocal statement that it will not tolerate such behavior.”
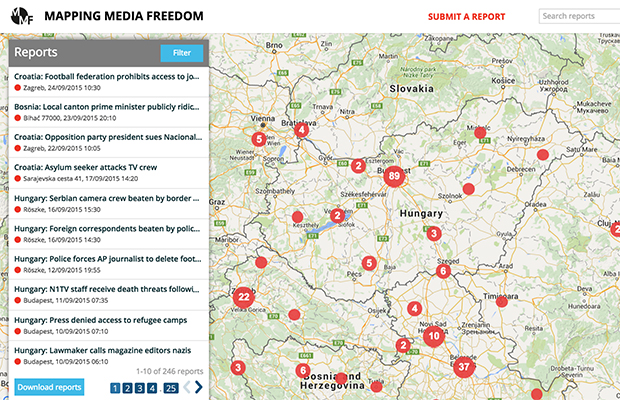
Mapping Media Freedom
Click on the bubbles to view reports or double-click to zoom in on specific regions. The full site can be accessed at https://mappingmediafreedom.org/
|
This article was published on 16 September 2015 at indexoncensorship.org
21 Sep 2015 | Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News, Serbia
Investigative journalist Ivan Ninic knew something was wrong when he saw the two young men reach down. “I saw they were getting two metal bars,” said Ninic, who is the latest victim of violence against journalists in Serbia. Two young men, in tracksuits and baseball caps, assaulted him on a Thursday evening in late August, in Serbia’s capital, Belgrade. “They attacked me and stuck me brutally,” he told UNS, a Serbian association for journalists. “I have a haematoma under my eye, bruises on the thigh bone and an injury to my shoulder.”
Just a week earlier, at a Jazz Festival in the southern city of Nis, local journalist Predrag Blagojevic was beaten by a police officer for — in the words of the officer — “acting smart”. “He grabbed me, bent my arm behind my back and repeated several times ‘Why are you acting smart?’ Then he hit me in the head with his hand. He hit me twice,” Blagojevic stated after the incident. Blagojevic had been approached by the officer and asked for his identity papers. Blagojevic had asked “why?” The police officer took him to his car and started beating him.
Media freedoms in Serbia are on the decline. The country has been cited in 93 verified violations against the media reported to Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project. A recent report by Human Rights Watch (HRW), painted a picture of journalists in several western Balkan countries, working in hostile environments whilst facing threats and intimidation.
“It’s certainly not going forward,” HRW researcher Lydia Gall said in an interview with Index on Censorship. “What in fact should be showing progress, is rather deteriorating.”
Gall interviewed over 80 journalists in Serbia, Kosovo, Macedonia, Montenegro and Bosnia-Herzegovina. The stories she heard were shocking.
“These are all countries that are transitioning,” she said. “They’re undergoing democratic development in, one would hope, a positive direction. But when you look at the documentation I’ve collected you’ll see a worrying picture unravel.”
The report contains examples of threats, beatings, and even the murder of several journalists. It also claims there is political interference, pressure and a lack of action by the authorities to investigate and prosecute those responsible for crimes against the media.
In Serbia alone Human Rights Watch reported 28 cases of physical attacks, threats, and other types of intimidation against journalists between January and August 2014.
NUNS (the Independent Journalists’ Association of Serbia) has documented a total of 365 physical and verbal assaults, and attacks, in the period from 2008 to 2014. This may be the tip of the iceberg since, according to NUNS, many media workers don’t report attacks.
Between May 2014 and June 2015, Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project has received 77 reports of violations against Serbian journalists and media workers.
Most of the targeted journalists investigate corruption and allegations of war crimes. Both Ivan Ninic and Predrag Blagojevic report on corruption on a regular basis. “These are not popular topics in the Balkans,” Lydia Gall said. “There are always people in power trying to get them not to write about them.”
Serbia has undergone incredible change over the past two decades. During the Federal Socialist Republic of Yugoslavia censorship was directly imposed by the state. Few forget the difficulties of reporting in Serbia during the darkest moments of the 1990s. Means and methods of pressure and censorship are very different nowadays.
“It’s not necessarily the state going after the journalist anymore,” Gall explained. “But it’s more the state neglecting to properly investigate crimes against journalists.”
“If it’s not physical interference or abuse, then it’s threats, or so-called friendly advice. In some cases journalists are being sued for civil libel and end up spending most of their time in courts instead of doing their work. It can be done in very subtle ways.”
This all contributes to a hostile environment for journalists to work in, the HRW report concludes. “You have to be a brave person to do this type of reporting in the Balkans,” said Gall.
Sometimes pressure on the media in Serbia is not even that subtle. Current Prime Minister Aleksandar Vucic, has been accused of being overly hostile against the media. He has publicly labeled Balkan Investigative Reporting Network (BIRN) foreign spies . The current government has also been accused by some journalists of involvement in several cyber attacks on critical online media portals, such as Pescanik.
“Improving media freedom is an important condition in Serbia’s negotiation process with the European Union for membership. But EU’s pressure on Serbia is too weak,” said Gall.
“They’re mainly looking at the legislative framework. On paper it looks great. The problem comes to light when you look on the ground. When you speak to journalists, who are living this reality every day.”
Meanwhile the Serbian journalist associations, NUNS and UNS, are trying to put pressure on the authorities to track down the attackers of Ivan Ninic.
Ninic is known for his investigations into corruption within high levels of government. He founded the Center for the Rule of Law, an NGO, and is planning to launch a website to publish investigative reports.
He believes the attack is a warning: “I expect the police will find and punish not only the attackers, but also the masterminds, so that I know who is sending me this message,” he said in a statement.
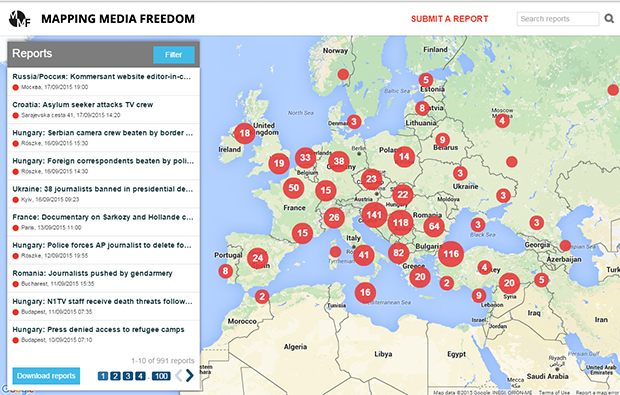
Mapping Media Freedom
Click on the bubbles to view reports or double-click to zoom in on specific regions. The full site can be accessed at https://mappingmediafreedom.org/
|
This article was published on 16 September 2015 at indexoncensorship.org
18 Sep 2015 | Bosnia, Croatia, Macedonia, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, Montenegro, News, Serbia
“Media has a significant role in the theatre of the absurd,” a participant in a conference on the security and protection of journalists in western Balkan countries claimed.
Media workers and representatives from journalists’ associations in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Serbia and Montenegro joined representatives of international organisations in Sarajevo in June 2015 to debate key issues facing the media in the region: attacks on journalists, impunity, the effectiveness of the legal system and institutional mechanisms to create a safe environment to work in.
Conference participants said media freedom is deteriorating and assigned responsibility for the decline on governments in the region, local media ownership and, especially, international institutions and organisations.
Goran Miletic, programme director for the western Balkans at Civil Rights Defenders, an NGO working in the area, said that in 2004 some of the international organisations decided to withdraw funding from local media to focus on other projects. Miletic said that reduced level of funding for media was a lost opportunity to prevent human rights abuses and further democratise the region.
International funding is vital to professionalising the media, which cannot rely on local government support. “If we analyse research on what people think of human rights defenders or journalists, they are often characterised as spies, foreign mercenaries, or enemies of the state,” said Miletic.
A lack of media plurality and news illiteracy were identified as concerns that have had a detrimental effect on the advancement of press freedom and professionalism in the region.
“Media freedom is once again one of the key challenges for the region,” said Andy McGuffie, head of the communication office of the Delegation of the European Union to Bosnia and Herzegovina and a European Union Special Representative.
Presidents of journalists’ associations focused on attacks on journalists and the effectiveness of the legal system and institutional components. Addressing the current situation in Croatia, Zdenko Duka, then president of the Croatian Journalists’ Association, underlined that “fortunately, [in recent months], there have not been too many physical assaults. Comparing assaults and threats against journalists to other countries in the region, the situation in Croatia is better.”
Croatia has a checkered history on media freedom. During the 1990s journalists were widely targeted and were under surveillance by the secret service. In the 2000s, the journalist Ivo Pukanic, was assassinated in a bomb attack at his Zagreb office. Though a court convicted six men for the murder, the person who ordered the crime has not been brought to justice.
Duka emphasised two 2014 physical assaults: an incident in Rijeka in which football club officials attacked a journalist and a photographer and the brutal attack on journalist Domagoj Margetic who was assaulted by several people near his home in Zagreb. Margetic sustained head injuries as a result of the attack, for which he received medical treatment.
Sanja Mikleusevic-Pavic, a journalist from Zagreb, agreed with Duka. “Croatia is in a much better situation than other countries,” she said. Key reasons for this include the Trade Union and the Journalists’ Association, which are very well organised and powerful, but most of all, the key role played by the public broadcaster HRT. “HRT is a strong, independent and professional public broadcaster,” said Mikleusevic-Pavic.
From her point of view, the main threat to independence and professionalism are pressures from tycoons and politicians, which, in her experience, are significant. The case of Croatian TV broadcaster RTL, which was found guilty of slander for airing a live show during which Croatian Prime Minister Zoran Milanovic accused Zagreb Mayor Milan Bandic of corruption, sets a negative precedent, particularly because another TV station that aired the same statement was not charged. As punishment, RTL has been ordered to pay 6,500 euros to the mayor.
Croatia’s new criminal code presents another obstacle to media freedom. It includes Article 148, introduced in 2013, which establishes an offence of “humiliation”, “shaming” or “vilification”. Osservatorio Balcani e Caucaso said the article would allow judges to sentence a journalist if the information published is not considered being in the public interest and “for the court, it is of little importance that the information is correct – it is enough for the principal to state that he felt humbled by the publication of the news.”
In April 2014, Jutarnji List journalist Slavica Lukic became the first Croatian journalist to be prosecuted under the article. She was found guilty of vilification. Lukic reported that a company had economic problems despite the substantial public funding it received. The company stated it felt “humiliated” and the judge fined her 4,000 Euros.
Dunja Mijatovic, OSCE Representative on Freedom of the Media, said in a letter to the Croatian officials that the current legal definitions of “insult” and “shaming” are “vague, open to individual interpretation and, thus, prone to arbitrary application.”
Duka said that there are more than 40 criminal insult cases pending against journalists in the country and this is clear evidence that “truth can be punishable.” Furthermore, he believes judges are not well prepared for defamation, slander and libel cases. Defamation in Croatia has not been decriminalised as it has been in Montenegro, Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina.
“The situation in Serbia is alarming. As long as there is a brutal assault on journalists, we cannot talk about freedom of speech and media freedom,” Vukasin Obradovic, president of the Independent Journalists’ Association of Serbia (NUNS), said in a speech at the conference.
From 2008 to 2014, Serbia has seen a total of 365 physical and verbal assaults, intimidation and attacks on the property of media professionals. Since May 2014 alone, Index’s European Union-funded Mapping Media Freedom project has received over 48 reports of violations against Serbian media, including attacks to property, intimidation and physical violence.
In his talk, Obradovic described several incidents to illustrate the media situation in Serbia. On 14 April 2007 a bomb exploded outside the apartment of journalist Dejan Anastasijevic. No one was injured. In a statement to international media, Anastasijevic said: “It was just before 3 am on Saturday when a hand grenade went off outside the bedroom window of my Belgrade apartment, filling the room with smoke and shards of glass, leaving shrapnel holes on the ceiling and walls — some only inches above the bed. Despite the damage, we were lucky: When the police arrived, they found a second unexploded grenade on the sidewalk nearby.”
Anastasijevic was targeted because of his investigative reporting on crimes in the former Yugoslavia and criminal syndicates in Serbia, local media reported. The most recent attack followed Anastasijevic’s criticism of a lenient verdict for members of Serb paramilitaries called “Scorpions,” journalists associations said. The case has still not been resolved.
Obradovic emphasised that attacks on journalists in Belgrade often get more attention than violations that take place outside the capital.
Vladimir Mitric, a journalist from the town of Loznica, has been under police protection since October 2005 after being subjected to a brutal assault. He was attacked as he entered his apartment and struck with a blunt instrument from behind several times. He ended up with a broken hand and was very badly bruised all over his body. He is disabled as a result of that attack.
“I live under police protection that I was granted by court, not police, at my request, which is important,” said Mitric in an interview with SEEMO. A former police officer was identified as the attacker and was sentenced to six months in jail by the Loznica Basic Court. The Belgrade Court of Appeal later doubled the sentence.
However, a few months after the trial, Tomislav Nikolic, the president of Serbia, granted amnesty to the attacker and the remainder of his sentence was vacated. Threats against Mitric continue despite 24-hour police protection. Human Rights Watch reported: “The person making the threats was accompanied by a police officer who had been responsible for Mitric’s protection. The person making the threats was charged with minor offences in September, but at this writing the police officer had not been disciplined.”
Sladjana Novosel, a journalist from Novi Pazar, was targeted three times between September 2010 and March 2013. Novosel was subjected to verbal attacks, shaming and bullying. Police have, so far, failed to pursue investigations of these threats.
In another incident, Davor Pasalic, the editor-in-chief of FoNet, was attacked twice early in the morning of 3 July 2014 as he made his way home from his office. The two attacks left him with cuts and bruises, and four of his teeth were broken or knocked out. After seven months of investigation and zero progress, Pasalic sarcastically said that his case is “no big deal.” But he added that the assault has had no impact on his work.
Obradovic finished his talk by saying that “the impunity and recklessness of institutions obviously encourage attacks.”
Branislava Opranovic, member of the executive board of the Independent Journalists’ Association of Vojvodina (NDNV), focused on economic issues and ownership transparency in the media. She described the lack of ownership transparency in the media, sharing her personal experience. “I have been working for the daily Dnevnik for years and years, but still don’t know who the owner of the newspaper is.” She also mentioned other cases, including one where a man in his twenties wanted to buy nine media outlets in Vojvodina, or the episode where her coworkers were waiting patiently in a line to collect bonuses of 5 Euros despite having not received their salaries.
Though Bosnia and Herzegovina was the first country from the region to decriminalise defamation, in 1999, the situation is no better than in Serbia. Borka Rudic, Secretary General of the BH Journalists Association, said: “The raid of the Klix.ba offices in late December 2014 just proves this conclusion.”
In that incident, police entered and searched Klix.ba’s Sarajevo offices for a recording of a phone call in which the Republika Srpska Prime Minister Željka Cvijanović talks about “buying off” politicians. Local media reported that police were copying material from the newsroom’s computers. The police also seized computers, documents, notes and other items from the offices, according to media reports.
Despite positive developments in the law over the past 15 years, the situation has shown little improvement, as institutions are failing to properly implement new legislation, meaning protection on journalists is weak. Between 2006 and 2014, there have been approximately 400 registered cases of media rights violations, including 40 physical assaults and 17 death threats.
Bosnian journalists use a name and shame strategy, in which the identity of every person who threatens or attacks a journalist is publicised. Rudic said that the most serious incident was the attack of Professor Slavo Kukic, a prominent writer and columnist, who was severely beaten with a baseball bat in his office at the University of Mostar, on 23 June 2014.
Marko, a journalist present at the event, shared his and a colleague’s personal experiences. While working for a public broadcaster they were both victims of constant harassment by one of their deputy editors, receiving no support from senior editors or directors. This resulted in them both being admitted to a psychiatric hospital for mental health issues.
Montenegrin TV host and journalist, Darko Ivanovic, told how one of his country’s prominent politicians stated: “it is customary law to hit journalists,” when asked why he slapped a journalist.
Over the last few years Ivanovic has had his car vandalised on a number of occasions, though only one incident resulted in the arrest of a suspect, who admitted the vandalism. However, when interviewed by Ivanovic, the suspect admitted that the police gave him 5 Euros so he confessed to the crime. “There is always someone found guilty, but usually they’re not the real perpetrators. And this puts into the question the effectiveness of the system,” Ivanovic said.
Marijana Camovic, President of the Trade Union of Media of Montenegro, said at the conference “the mindset of local politicians is that for them it is impossible that a journalist could be impartial and professional.”
Tabloids in Montenegro are used for smear campaigns. Civil rights activist Vanja Calovic became the victim of just such a campaign by Informer, a daily newspaper. The tabloid’s mid-June attack against the head of the MANS NGO began with the release of a video recording that, according to the paper, proved that Calovic was “an animal abuser” and alleged that she had sexual relations with her dogs.
The NGO Human Rights Action (HRA) highlighted the perilous state of journalism in its report, “Prosecution of Attacks on Journalists in Montenegro”. The HRA outlined 30 cases of threats, violence and assassinations of journalists as well as attacks on media property between May 2004 and January 2014. “Most of these attacks have not been clarified to date. In most cases certain patterns can be observed, for example: victims are the media or individuals willing to criticise the government or organised crime,” the report said.
One-third of all incidents happened in the the last year, which to the HRA shows the atmosphere of impunity is escalating. “Such an atmosphere of impunity threatens journalists in particular, who are often victims of unresolved attacks. If the state treats these attacks passively, it becomes responsible for the suppression of freedom of speech, the rule of law and democracy.”
The assassination of Editor-in-chief of the Daily Dan, Dusko Jovanovic, who was killed in a drive-by shooting on the evening of 27 May 2004, has not been solved nine years later. Damir Mandic, the only defendant in the recent trial, claims he is innocent and accused the police of planting evidence, Balkan Insight reported. Mandic said he was in prison for 10 years although he was innocent, and his human rights had been violated. He remains the only perpetrator to be convicted.
Seven years after the brutal attack that nearly took the life of journalist Tufik Softic, Montenegrin police detained two men suspected of involvement in his attempted murder. For media unions and observers, the detentions were long overdue, but emblematic of the atmosphere of impunity in Montenegro. In November 2007, Softic was brutally beaten in front of his home by two hooded assailants wielding baseball bats. Then in August 2013, an explosive device was thrown into the yard of his family home. The journalist has been provided with constant police security since February 2014.
Besides this atmosphere of impunity that threatens journalists, Camovic spoke of other phenomena. Approximately 80 per cent of all active media workers in Montenegro are not members of any journalist’s association. When asked why they’re not active in the organisations, they had no answer.
In summing up the situation, Ivanovic said that states and political parties deliberately tolerate grey or criminal activities of media owners so they can control them easily.
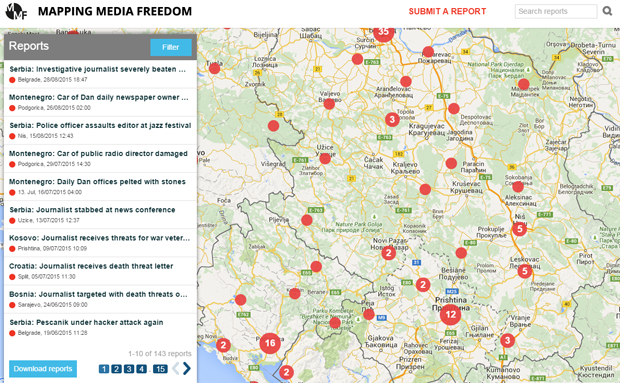
Mapping Media Freedom
Click on the bubbles to view reports or double-click to zoom in on specific regions. The full site can be accessed at https://mappingmediafreedom.org/
|
17 Sep 2015 | Campaigns, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News
Ukrainian President Petro Poroshenko signed a decree on Wednesday 16 September banning at least 38 international journalists and bloggers from Ukraine for one year. The decree, published on the presidential website, says those listed are banned for being “actual or potential threat to national interests, national security, sovereignty and territorial integrity of Ukraine.”
Poroshenko said the people targeted were involved in Russia’s 2014 annexation of Crimea and the current aggression in eastern Ukraine.
“This ban is a serious blow to media freedom,” Index senior advocacy officer Melody Patry said. “There is no explanation whatsoever on what press coverage constitutes an actual or potential threat to national security. We appreciate that the situation in eastern Ukraine is sensitive but preventing journalists from reporting from within the country is not the solution and it’s undermining freedom of information.”
The Committee to Protect Journalists reports that the 34 journalists and seven bloggers named in the ban come from Bulgaria, Estonia, Germany, Hungary, Israel, Kazakhstan, Latvia, Macedonia, Moldova, Poland, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, Spain, Switzerland and the United Kingdom.
The original list included three BBC media staff members – Moscow correspondent Steve Rosenberg, producer Emma Wells and cameraman Anton Chicherov – who were later removed from the ban list, media reported.
“We cannot accept that kind of censorship”, said Mogens Blicher Bjerregård, president of the European Federation of Journalists. Censorship is never the right answer, even to counter propaganda or to sanction journalists who allegedly crossed the Russian-Ukrainian border illegally. The ban is simply inappropriate. Peace and Development of our democracies need press freedom not banning journalists. We and the international society must firmly urge the Ukraine government to lift immediately the ban on named journalists.”
Over 380 people in total have been banned, including activists and Russian officials.
This measure was added to the Mapping Media Freedom platform, which monitors and map threats and violations to media freedom in Europe, including Ukraine and Russia.
The environment for media freedom in Ukraine has been deteriorating against the backdrop of the conflict in the eastern part of the country, making it one the the deadliest countries for journalists, with at least eight media workers killed since the beginning of 2014.
This statement was updated to reflect the later removal of three BBC journalists from the ban list.
Mapping Media Freedom
Click on the bubbles to view reports or double-click to zoom in on specific regions. The full site can be accessed at https://mappingmediafreedom.org/
|



