Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
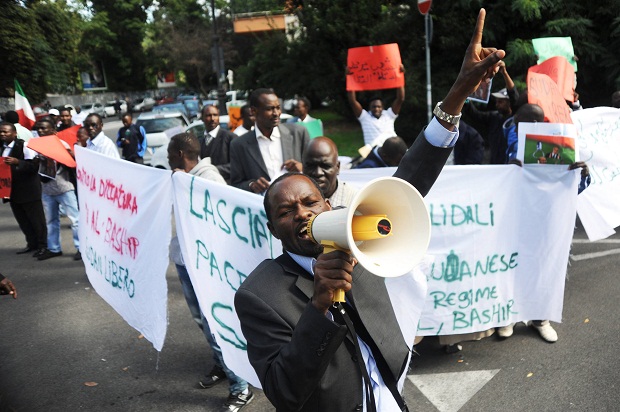
Dozens of protesters in front of the Sudanese Embassy in Rome October 2013 to protest of the alleged human rights abuses in Sudan (Image Marco Zeppetella/Demotix)
In the latest magazine issue of Index on Censorship the Bishop of Bradford Nick Baines reflects on his first visit to Sudan, a country whose leader strongly believes in one religion and one language for all.
Freedom of expression is of universal importance, but its absence is sometimes more easily seen through the lens of a different culture. The familiar landscape of “home” can sometimes hinder a proper appreciation of the absence of freedoms, being outside of one’s comfort zone can heighten awareness of reality. In this article I want to approach the matter from the outside in.
Early in 2013 I visited Sudan for the first time. The diocese of Bradford has had a partnership with Sudan for 30 years, and I was linked for a decade with Anglican dioceses in Zimbabwe (in my previous post as Bishop of Croydon). I thought I could easily switch attention from one African country to another. The reality was different.
Zimbabwe is ruled by Robert Mugabe, a man so corrupt that even his own demise will not clear the path to a golden new age – there are too many people who need to be protected by power well into the future. Sudan is governed by Omar al Bashir, a man committed to the project of creating a single nation (Sudan) with a single ethnicity (Arab), a single language (Arabic) and a single religion (Islam). There is a degree of shameful incompetence about Mugabe’s manipulation of power and the consequent destruction of the Zimbabwean economy and the country’s political culture. But al Bashir knows exactly what he is doing. And he does it in the face of a serious indictment by the International Criminal Court (ICC) for genocide in Darfur: he feels untouchable
Since 99 per cent of southerners voted in 2011 for the division of Sudan into two independent states, Sudan and South Sudan, al Bashir has chosen to make the secessionists take responsibility for their choice – to some extent understandably. If they are so keen on having their own country, then they can go there… and then apply for visas to come to Sudan as foreigners. Harsh? Yes, but he could be seen to be compelling the South Sudanese to live with the consequences of their actions. Democratic choices bring consequences.
However, the real experience of this is the expulsion from Sudan of anyone deemed to originate in the south – even several generations ago. Those who remain – often because they are married to Sudanese – are prohibited from working. Apart from the human cost of this policy, the effect on the Anglican church (the Episcopal Church of Sudan, which has not divided along with the states) is an exodus of leaders, an increased dependency of those who remain on the goodwill and generosity of other Sudanese Christians. And this is happening alongside the ongoing genocide in Darfur, government violence in South Kordofan and Blue Nile state. Khartoum has had to absorb destitute migrants on an unimaginable scale.
Those displaced are almost exclusively African. They speak African languages (derogatorily referred to as “twittering” by the Arabs). They are mostly (but not exclusively) Christian.
My visit to Khartoum earlier this year ended when my wife and I left a Christian-owned guesthouse at 1am in order to get to the airport for the flight back to Manchester. Within an hour the guesthouse had been raided by the security services, all property confiscated, and all residents and guests taken in for questioning. Foreign guests were deported and the family that ran the guesthouse was removed; the father of the family is now prohibited from working. This might not sound too dramatic – especially in the light of reports from parts of the Middle East and South Asia where Christians are being targeted for violence or forced to convert to Islam – but it comes as part of a deliberate policy on the part of government to exclude Christians and force them to leave for the South. This necessarily puts pressure on Christians to keep quiet, but the bishops (in particular) continue to be unafraid to engage courageously with “the powers”.
It seems that al Bashir blames the international community for refusing to welcome him back into the fold by removing the ICC indictment after the peaceful transition to two states. Foreigners are to be removed, even when they provide essential services that cannot be provided locally. We met European medical personnel who had spent their working lives developing medical facilities in local communities, and who now found themselves thrown out, leaving medical provision severely weakened.
Why destroy social, educational and medical infrastructure simply in order to save face? Riots in September 2013 in Khartoum (initially about the removal of fuel subsidies) demonstrated that economic matters do not always serve the interests of the government of the day.
But there is a bigger question relevant beyond Sudan. How do we understand and clearly define the categories in which and through which we see political, religious and cultural phenomena? Getting the category wrong leads inevitably to miscomprehension, to a potentially dangerous misapplication of rhetoric/language… and this has political consequences.
My own diocese of Bradford has a high percentage of Muslims from south Asia. Immigration began in the mid-20th century in order to staff the textile mills of West Yorkshire. Many of Bradford’s Muslims originate from the region of Kashmiri Mirpur in Pakistan. This concentration necessarily affects how the community lives and organises in Bradford, how it is influenced by (and, in turn, influences) events back in Pakistan, and how it is understood by the non-Pakistani population in the city.
One of the first lessons I had to learn when I came to Bradford nearly three years ago was not to confuse ethnicity with religion. What might appear to be a phenomenon rooted in religious identity (certain modes of dress, for example) might actually be more appropriately understood as a cultural phenomenon that coincidentally becomes associated with religious identity. To confuse the two can be dangerous. What I have in mind here is where violence (in particular) is attributed to religion, when religious tagging is clearly a tribal badging designed to hide more cultural (or other) identity.
Examples of this can be seen in the Northern Ireland of the Troubles or the sectarian destructiveness of Lebanon. Although the categories cannot easily be extricated from one another, at least those who observe or comment on such events should have the intelligence to dig a little deeper into the categorisation of such phenomena before simplistically eliding culture and religion as if they were synonymous.
The point is that there are two dangers here: (a)that category errors lead to poor communication and confusion, and (b)that people might be reluctant to speak out on serious matters simply because they fear being accused of racism or simply getting it wrong. This doesn’t help anyone where honest and frank conversation is needed and mutual critique is essential to good relationships.
This takes us back to Sudan. It is not a simple matter – capable of easy explication or distinction – to work out what can be attributed to which category. Al Bashir’s policy seems clearly to create a political, ethnic, religious and cultural identity in which there is no place for diversity. One can assume that he is aiming at a myth of solidarity – that if everyone claims the same identity, they will buy into the same projects, have the same friends and enemies, defend the same categories and communicate in the same way. Of course, this fails to take into account the complex reality of human identity construction and how complex and diverse people interrelate and self-identify.
In one sense all this should not need to be articulated. If Muslim is blowing up Muslim in Pakistan or Afghanistan, then there is clearly more going on than mere “religion” or religious identity. Simply reporting atrocities as if they were political or cultural events (without reference to religious allegiance) is as naïve as to report on religion without reference to the ethnic, political, economic, social or cultural identities that shape religious expression.
This is not a plea for obfuscation or mitigation of religiously motivated violence. On the contrary, it is a plea for the sort of literacy that seeks to comprehend in order to know how to think about and respond to phenomena that might all-too-easily be capable of simplistic categorisation.
Language goes to the heart of this. Not only the language of explanation or reportage, but the ways in which language is (or particular languages are) seen to be totems of identities that are deemed to be inconvenient. In Zimbabwe identity is tied up inextricably with language: the Shonaspeaking government has demonstrated in past violence what it thinks of the Ndebelespeaking Matabele. In Sudan African languages – mostly spoken by Christians of African (rather than Arabic) origin – are being derided and squeezed out. This is one reason why some churches in Sudan put such high value on keeping their own languages alive, teaching them to both children and adults, working hard (with pitiful resources) to reserve their means of communication as an integral element of cultural and religious identity. Language is as much part of individual and common identity as is skin colour, and nobody should be compelled to lose their native tongue.
One of the most penetrating verses of the Old Testament is found in the book of Proverbs. Seized upon by opponents of Hitler during the 1930s and 1940s in Germany, it demands that we “open our mouths for the dumb” – that is, that those who have a voice must keep alive the songs and language of people whose voice is silenced by the exercise of corrupt power. The moral demands of this are clear here also. But, for that voice to be heard and understood, it is essential that intelligent consideration is given to ensuring that the categories of speech and identification are kept as accurate as possible.
Responding to religious phenomena as if they were merely “cultural” is as dangerous and misplaced as eliding all cultural phenomena as merely “religious” – and runs the risk of stopping people speaking truthfully and accurately when religion is the root of violence or cultural violence seeks to hide behind a religious facade. The world is more complex than that. We can and must do better.
From mid-June to early August this year, Sudan has witnessed nationwide protests directly calling for regime change, sparked by an alarming increase in prices. The protests were met with a massive crackdown on civil liberties, and a wave of arrests by National Intelligence and Security Services (NISS), Sudan’s security apparatus. While journalists were not disproportionately impacted by the crackdown, what they have experienced during the past few weeks helps paint a picture of a country on the brink of economic collapse and escalating political turmoil.