Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
At 2.30pm on 19 December 2024, Ahmed Mohamed, editor-in-chief of the Syrian-Kurdish Hawar News Agency (ANHA), received a dispatch from two of his colleagues. An hour later, they were dead.
“They had just sent me a message saying ‘we’re coming back’,” Mohamed told Index.
Cihan Bilgin and Nazim Daştan, two Kurdish reporters, were reportedly targeted and killed by a Turkish airstrike as they returned from the Tishreen Dam near Aleppo, where they were covering ongoing clashes between the Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) and the Turkish-backed network of militias known as the Syrian National Army (SNA).
Indeed, Turkey, which is violently opposed to the Kurdish-led project due to its own domestic repression of the Kurdish cause, continues to target the region and journalists in particular, profiting from the chaos caused by the fall of former Syrian president, Bashar al-Assad. According to the Kurdish-run Firat News Agency (ANF), Turkey has killed 14 journalists and wounded seven others in the Iraqi Kurdistan and Syrian Kurdistan (Rojava) regions since 2019.
Journalists under attack
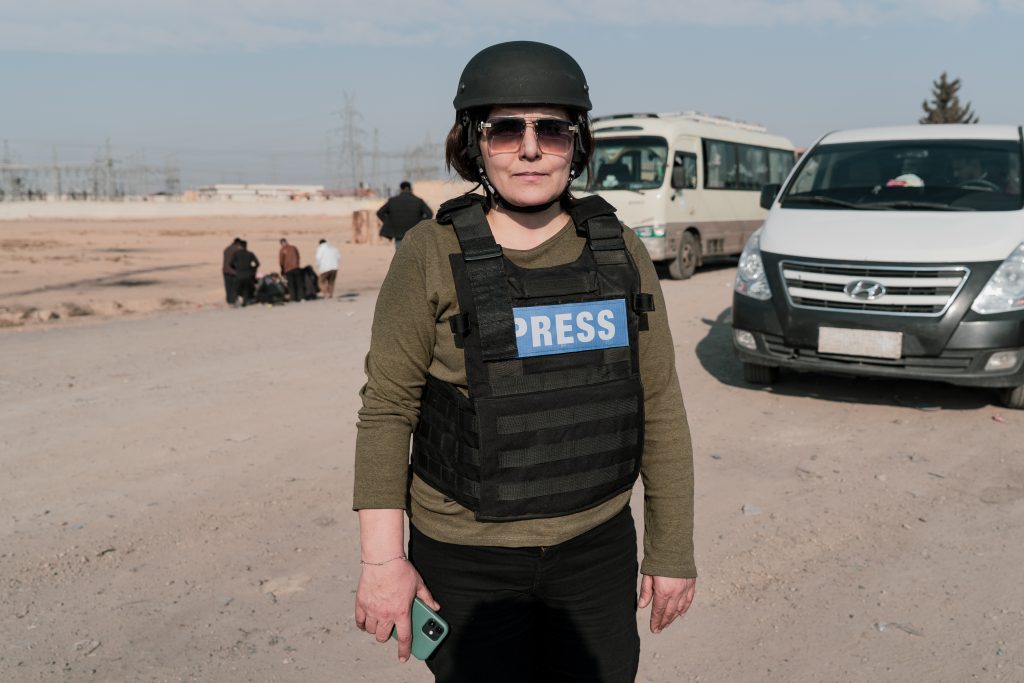

Sinem Adali, a journalist for Rojava TV, is preparing to go to the Tishreen dam front. Photo by Angeline Desdevises / Hans Lucas
In ANHA’s editorial offices in Qamishli, the de-facto Syrian Kurdish capital, a memorial showcases the microphones and cameras of journalists who died in the line of duty. Since 2017, six of ANHA’s journalists have been killed in the field: three reportedly in Turkish attacks, and three while covering the Kurds’ famous fight against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL).
Despite the recent ceasefire agreement between Syria’s new Turkish-linked president Ahmed al-Sharaa and SDF commander Mazloum Abdi, Turkish bombardments continue to target the Tishreen Dam, according to local monitor Rojava Information Center.
Leyla Abdi, a reporter for Ronahi TV, was wounded at the dam in January. Three days after her arrival at the dam, she was standing alongside civilians staging a protest on the crucial infrastructure, when she was hit by a bombardment. “That day, a dozen drones flew over us all day long. Turkey systematically strikes civilian convoys,” said Abdi, who is still recovering from her injuries.
Kurdish journalists aren’t only targeted when working on the frontline. Repeated attacks have made the road along the Turkish border dangerous, if not impassable. It was here that, in August 2023, the vehicle of the women’s television channel Jin TV was destroyed. The driver, Necimedîn Sînan, was killed instantly, while journalist Delila Ağît lost an arm. Dijwar Iso, who also works at ANHA, said that press workers are now obliged to switch off their phones during missions to prevent the Turkish armed forces on the other side of the border from being able to track and target them.
These attacks are part of a wider drive to stifle the press from covering Turkey’s occupation of North and East Syria, which has killed hundreds and displaced hundreds of thousands of primarily Kurdish civilians to date. In November 2022, journalist Essam Abdallah was killed and another journalist Mohammad Al Jarada was injured in separate Turkish air raids on the same day.
In 2019, a civilian convoy accompanied by Kurdish journalists and a French television team was bombed by Turkish forces, killing two local journalists and injuring others. Several civilians were also killed in the strike.
Although journalists are protected by international law, Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdoğan’s administration is stepping up its attacks on journalists beyond its borders. In neighbouring Iraq, a drone strike in August last year killed two Kurdish media workers working for a local TV channel and wounded their colleague. Local sources say the drone was operated by the Turkish armed forces, which the Turkish defence ministry has denied. Human rights organisations and Kurdish media unions have called on the United Nations to investigate attacks on journalists, which they describe as “war crimes”.
Gypsy Guillén Kaiser, director of advocacy and communications at the Committee to Protect Journalists (CPJ) in New York, drew attention to the recent murder of Cihan Bilgin and Nazim Daştan, calling on the Turkish authorities to conduct a thorough investigation.
Psychological warfare
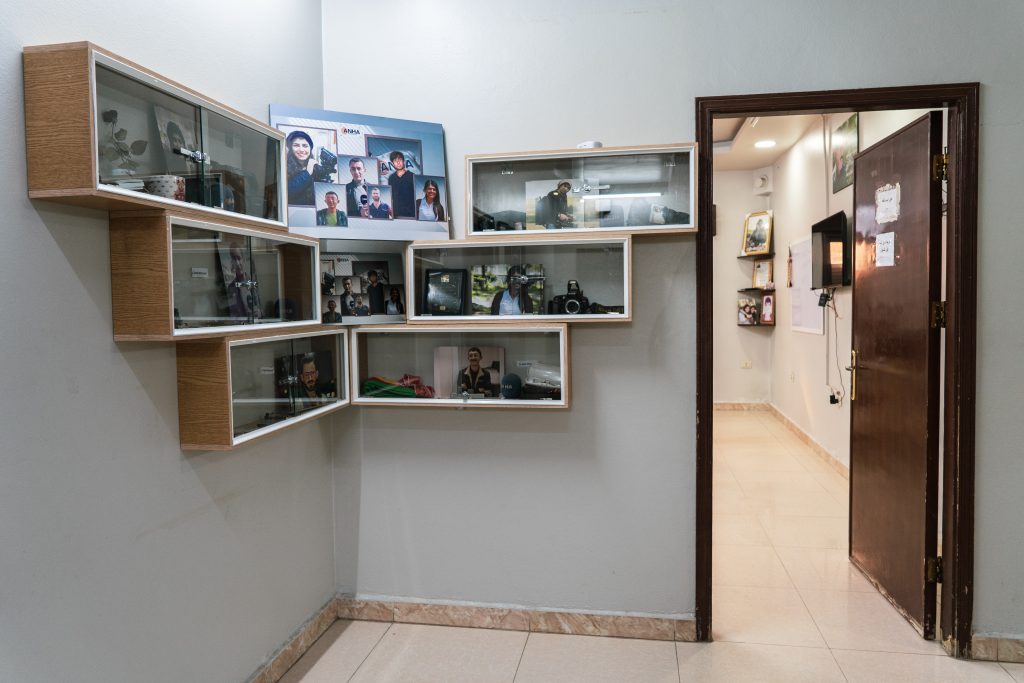

In ANHA’s offices, a memorial showcase displays the equipment and photos of six journalists who died while doing their job in north-eastern Syria. Photo by Angeline Desdevises / Hans Lucas
These constant attacks have created a climate of insecurity for all journalists in the region. Local journalist Loristan Derwish said: “As a woman, it was already hard to obtain the legitimacy to practise our profession and now we are confronted with attacks from Turkey and online harassment.” At the end of 2024, she was subjected to a wave of online harassment following a TV report she made interviewing female Kurdish fighters. Several Instagram accounts impersonating her were created, displaying fake pornographic photo montages. She believes the culprits are in Turkey.
Online harassment is predominantly aimed at female journalists. Arîn Swed, spokesperson for the Syrian Kurdish Women’s Media Union (YRJ), said the union defends all female media workers against sexist and psychological attacks. “We supported Cîhan when she was threatened over the phone by MIT [Milli İstihbarat Teşkilatı – the Turkish secret service],” she said.
As of today, it is believed that at least five journalists, including Ciwana Cuma, a reporter for Ronahî TV, are being targeted. Cuma has covered the confrontations at the Tishreen Dam on several occasions. In a post on X (which has since been deleted) made by a Turkish account with more than 200,000 followers, the young woman was described as “another example like Cihan Bilgin”, “a terrorist”, and therefore identified as a potential future target.
The dehumanisation of journalists continues after their death. According to multiple sources, a photo of the decapitated body of reporter Vedat Erdemci, who was killed in a Turkish airstrike in 2019 in the Syrian city of Ras al-Ain, was sent to his mother. The Turkish state also refused to allow Cihan Bilgin and Nazim Daştan’s bodies to be handed over to their families in Turkey. They were finally buried in Qamishlo in January.
The West’s failure to respond to these crimes also creates negative psychological outcomes, local press workers say. “The death of a Kurdish journalist doesn’t cause a stir. The West creates a hierarchy among lives,” said Berîtan Ali, the regional head of a Kurdish TV station. Dilyar Cizîrî, co-chair of Free Press Union (YRA) organising in north-east Syria echoed her words: “Turkey’s attacks benefit from a sense of impunity, [caused] by the silence of international institutions.”
Destroying material resources
Beyond psychological attacks and online harassment, one of Turkey’s objectives is to shut down all means of expression for journalists in north and east Syria. Their social media accounts are frequently closed down by the platforms and their websites hacked. The ANHA website is the victim of roughly 7,000 cyber attacks per day, according to editor Mohamed. In 2019, hackers succeeded in replacing the homepage with a Turkish nationalist message, he said. Radio frequencies are also hijacked, the editor added, and overlaid with Turkish nationalist propaganda.
The media also face difficulties in obtaining the equipment they need to do their job, due to an embargo imposed on the region. “It is impossible to transport professional equipment legally across the Iraqi border. We have to find other ways,” said Mohamed. The workers are therefore forced to smuggle in protective equipment, such as bulletproof vests and helmets. ANHA only owns five vests for a team of 61 journalists, he said.
Fleeing domestic repression
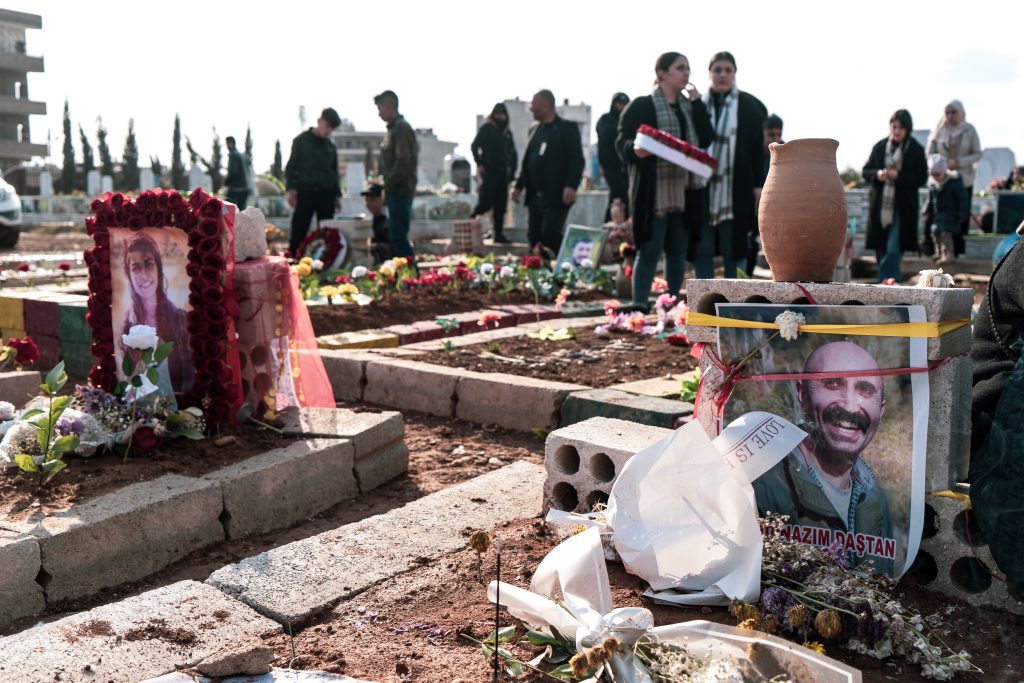

The bodies of the two Kurdish journalists Cihan Bilgin and Nazim Daştan are buried in Qamishli. Photo by Angeline Desdevises / Hans Lucas
In Turkey, attacks on opposition journalists have forced many into exile. Threatened with imprisonment for covering a demonstration near the Syrian border, Turkish-Kurdish journalist Dilan Dilok had to flee Turkey for Syria in 2017. “If I return to Turkey, I will either be arrested or killed,” she said. She adds that Turkish police are trying to intimidate her again: “My parents are often raided in the middle of the night and subjected to long interrogations.”
Bazid Erven, a reporter for Kurdish news agency Ajansa Welat, and 10 other journalists were allegedly arrested on 20 December 2024 in Van, Turkey, for protesting against the assassination of their colleagues. “These arrests are nothing new, they are routine for us,” Erven said. The day after his own arrest, seven other journalists were detained in Istanbul for several weeks. “There is state and police repression against Kurdish journalists,” he added. It therefore comes as no surprise that Turkey is ranked 158 out of 180 countries in Reporters Without Borders’ worldwide press freedom ranking.
A future for the Syrian press
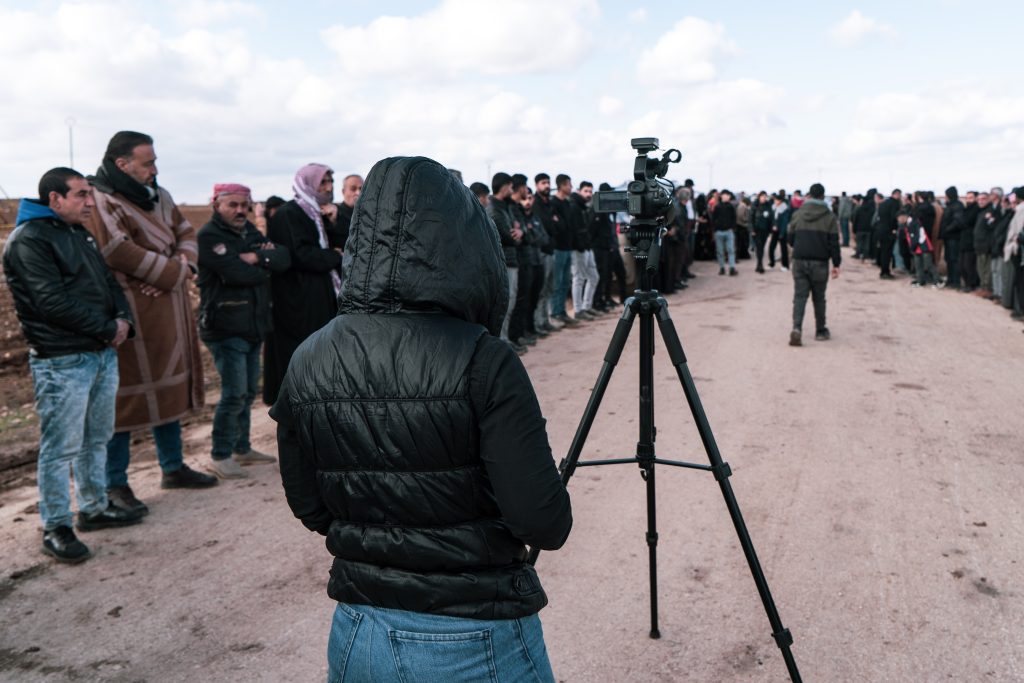

A Jin TV journalist reports on the funeral of two Kurdish political figures killed by a Turkish drone strike in Iraq. Photo by Angeline Desdevises / Hans Lucas
Since the fall of Assad’s regime, the ANHA agency has opened several offices across Syria. Its journalists, who previously worked underground in other regions of the country, can now operate openly. However, there is still concern for Syrian news professionals in view of the rampant insecurity in the country, a reality brought home by recent massacres committed by forces of the new government, targeting the Alawite minority.
On 6 February, interim prime minister Mohammed al-Bashir ordered the dissolution of the Syrian Journalists‘ Union (SJU). The Free Press Union (YRA)’s Cizîrî strongly condemned this decision: “The SJU was controlled by the former regime, but the solution should have been to restructure it.” The International Federation of Journalists also sent a letter to Al-Bashir and Syrian president Al-Sharaa, condemning the dissolution of the union and calling on them to uphold international law.
North and East Syria’s YRA says it is ready to help establish a new nationwide independent union and has just set up a Security Advisory and Risk Management Unit in order to provide “support and assistance to all Syrian journalists and media workers”. It seeks to pressure armed groups so that they abide by international law and wants to “contribute to efforts toward accountability and justice”.
In Qamishlo, the latter are yet to be found. Women’s Media Union (YRJ) president Swed is moved when she talks about her colleagues who have been killed in the field. But above all, she is determined to fight for their legacy: “As soon as [Cihan’s death] was announced, the women of the union took over. Today, if ANHA’s media coverage of Tishreen continues, it is thanks to the other women journalists.”
Football is a colossal business in Turkey. The billion-dollar industry constitutes Europe’s sixth largest football economy. No wonder the so-called “beautiful game” wields such enormous cultural and political influence on Turks, many of whom define themselves by their loyalty to football clubs Galatasaray, Fenerbahçe and Beşiktaş.
All based in Istanbul, they’re known as “the big three”, but since the nationalist-Islamist AK Party came to power in 2002, a flurry of other teams, from Trabzonspor to Başakşehir, have risen to prominence, winning national cups and increasingly defining what modern Turkish football is. Unsurprisingly, these teams are government-supported – a prerequisite for any successful business in autocrat President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan’s “New Turkey”.
Just a decade ago, though, anti-government sentiment defined Turkish football. During the opening ceremony of Galatasaray’s fancy new stadium in 2011, Erdoğan greeted fans, expecting gratitude for his role in building the new venue. Instead, boos rose from the terraces.
“It’s a key moment in modern AK Party-era Turkish football,” said Patrick Keddie, who chronicled the tale of Turkish football in his 2018 book The Passion: Football and the Story of Modern Turkey.
“He expected to be welcomed and thought he would bask in fame, but ended up getting booed… It was around this time that things began to turn. There was this shift from the liberal early-era AK Party to something much more authoritarian and repressive.” Turkish football in those years, Keddie noticed, was “utterly politicised on every level”, from activists using the game’s national prominence to voice their political anger, to Erdoğan talking up his semi-professional football background for political gain. “There was this mythology of him as a former player.”
That 2011 incident, so crushing for an ex-footballer, marked the culmination point of several changes that began in 2002. Acting
out of financial self-interest, the government started knocking down stadiums in city centres and replacing them with enormous new ones, subsequently building a dozen more, in the suburbs, in association with Toki, Turkey’s public housing body.
Despite such tactics, cronies of the AK Party noticed how impenetrable the “big three” culture remained. Defending the republic’s ideals, fans of those teams largely hated the party’s oppressive project of Islamist nationalism. So the government began criminalising, imprisoning and demonising dissident fans and managers through a flurry of court cases.
First came the “match-fixing scandal”. In the summer of 2011, Erdoğan’s prosecutors began investigating football matches they
accused of being fixed. On 10 July 2012, a state court ordered the arrest of 61 people. Among the managers and national team players held was Aziz Yıldırım, the strictly secularist president of Fenerbahçe – the club Turkey’s founder Mustafa Kemal Atatürk supported and which symbolises his modernising legacy. (A retrial process that began in 2015 cleared Fenerbahçe from all the charges; Yıldırım’s case was dropped in 2020.) Week after week, Fenerbahçe fans rushed to courts and, after sentencing, to prisons to show solidarity.
But it was the Beşiktaş fans – particularly the Çarşı group, named after the marketplace where Beşiktaş fans used to gather before matches for a drink – who played a crucial role in 2013’s Gezi uprising.
These Istanbul protests started as a movement against the development of the area, but quickly became a focal point of wider anti-government sentiment. Alongside environmentalists, leftists, liberals and other progressive millennials, Beşiktaş fans filled public squares and fought with the police.
Haldun Açıksözlü, an actor and author, wrote two books on Çarşı. “While growing up as a leftist in my youth, my passion for Beşiktaş grew, too,” he told Index. “I was part of Çarşı right from its inception.”
Rooted in the Ottoman Empire, Turkish football’s story begins with English residents of Salonica introducing the sport to Turks. The first matches were played in 1875. A football league was established in Istanbul in 1904, which soon extended into regional leagues in Anatolian cities and eventually the formation of the nationwide professional league. While Fenerbahçe and Galatasaray were known as teams of the bourgeoise and aristocracy, Beşiktaş was the team of cab drivers and the working classes.
Çarşı fans, Açıksözlü says, are famed for their cosmopolitanism and because they have a vital element of dissent. He said: “The group’s founders, from the early 1980s, were all leftists. Çarşı was a fan group that tilted football spectators toward leftist politics in the aftermath of the coup trauma of 12 September 1980. This leftist, communitarian perspective influenced me.”
But things turned when Beşiktaş’s 70-year-old stadium, İnönü (named after Atatürk’s closest ally in founding the republic), was demolished in 2013. “They made a mess of İnönü Stadium in the name of rebuilding it,” said Açıksözlü.
Erdoğan, who hates İnönü’s secularist politics, ended up excising the name of Turkey’s second president from Istanbul with this gesture.
Around this time, “the police and security forces began terrorising Beşiktaş fans”, said Açıksözlü. “Perhaps that was why Çarşı played such a prominent role in Gezi. The reaction creates reaction: the unnecessary use of tear gas by the police, their assault on Çarşı fans while they walked on streets with their families – these inevitably pushed Çarşı to the side of the sensitive people of Gezi.”
Açıksözlü describes Çarşı’s involvement in Gezi as an “incredible tale worthy of movies”. It began simply: 50 people walked from Beşiktaş to the nearby Akaretler neighbourhood. Their number grew to 100 at first and then grew to 1,000. When they walked up the hill and reached Gezi Park, the group numbered 2,500. “People heard their chants on the streets and joined in. Anyone who said they wouldn’t accept [living] under a one-man regime, wouldn’t accept state-intervention in their lives, sided with Çarşı,” he said.
Before Gezi, what Keddie – the British journalist – knew about Turkish football was clichéd: that it had crazy fans, that the big three Istanbul clubs hated each other. “I was surprised to see how prominent those fans were in the protests,” Keddie said. “They were on the forefront, fighting the police, manning the barricades.”
Still, the “big three” culture proved hard to penetrate for Keddie, who struggled with mingling with fans. “I think they’re insular and clannish and suspicious of outsiders – especially journalists.”
By the time Beşiktaş opened its new stadium on 10 April 2016, Keddie had noticed that Turkey’s political equation had changed dramatically. On the opening day, when Erdoğan sprinted and kicked a ball on the pitch, the stands were free of spectators. Even if they wanted to, nobody could boo him now.
When he visited the new stadium, Açıksözlü saw “airplane seats with special monitors attached to them”, and decided the old spirit of Çarşı was gone.
“There was this period, from 2011 to 2014, when the protest movement was quite intense,” Keddie said, “but by April 2016, most of the protests had died down or got more subtle for various reasons. Turkey didn’t have these major events, these major triggers, anymore. The biggest recent scandal of European football, the match-fixing case, 2013’s massive Gezi Park protests, and its aftermath – all of that had faded. With some exceptions, all forms of protest were essentially banned in Turkey.”
A significant factor behind the demise of Turkey’s protest culture was Passolig, an electronic ticket system the government introduced in 2014. “The electronic fan card Passolig was introduced as part of the country’s efforts to tackle hooliganism and violence in football,” announced the AK Party-run Anadolu Agency. “The new practice aims at a better identification of fans involved in violence in stadiums.”
In reality, Passolig was a cunningly conceived mechanism to detain dissident football fans. “Bringing in the Passolig card cowed many fans, and it made them think twice about protesting and even chanting because that system came with a whole load of security protocol and surveillance systems,” said Keddie.
It was much easier to identify anti-government protesters, ban them from stadiums and even charge and imprison them. “It was a response, the authorities said, to hooliganism and disorder, but most fans considered it a way to control them politically. It also gentrified the sport, making it more manageable, more middle class.”
Açıksözlü pointed to the formation of the 1453 group, a nationalist fans’ group, as another form of secret state intervention. “Specially assigned people were sent to Galatasaray’s Aslan Pençesi fan group and the Tek Yumruk group of Fenerbahçe. Their job was to stop fans looking at events from a leftist perspective.”
Anger soon melted into silence. Concern for security triumphed. Today, most fans wonder why they should risk their safety under an oppressive regime: Erdoğan sued more than 38,000 Turks for defamation between 2015 and 2021. Besides, for many devoted fans, it’s costly to go to matches at big clubs now. After Beşiktaş relocated, Çarşı had a much less prominent place in the new stadium. And outside the glossy new venues, Keddie observed, “the police are deployed in heavy numbers and they are happy to use violence whenever they need to”.
Açıksözlü said “industrial football” had destroyed the pleasures of the game. “Did you hear anything about Çarşı in the past five years? Did you read anything about other fan groups? Because of Passolig, the fan groups no longer influence Turkish football.” Still, the protest culture lives on, despite going underground. Fans can still be heard chanting about Atatürk, and when they sing the famed Izmir March, with lyrics including “Long live Atatürk! Your name will be written on a precious stone”, it’s a message directed at the Islamists.
Opposition politicians are playing ball, too. After a match between Galatasaray and the government-funded Başakşehir ended 2-0, the leader of the İYı Party, Meral Akşener, tweeted: “Galatasaray 2 -Erdoğan 0.” Many in Turkey call Başakşehir “Erdoğanspor”.
When another member of the opposition, Ekrem İmamoğlu, won Istanbul’s mayoral elections in 2019 but was refused the mandate after Erdoğan accused him of being a “terrorist”, a “liar” and a “thief”, the young politician, an ex-goalkeeper, visited football stadiums for support.
“Football is a big part of İmamoğlu’s brand,” Keddie said. “He was a goalie in his youth. So after the election was cancelled, he went to stadiums of the big three, pointedly avoiding smaller clubs, especially Başakşehir. Fans at those stadiums were chanting, ‘Give him the mandate’.” Once he was re-elected as mayor, İmamoğlu pledged to defend the interests of the big three.
Meanwhile, the “artificial success” of Başakşehir, Keddie said, may prove temporary. “I don’t see Başakşehir as really having power because they’re not an authentic, grassroots project. They don’t have many fans… It’s like a top-down project team; after all those years of investment and success in winning the league, they still get terrible attendances. It’s a cultural thing. Every other team sneers at them. Even people who support the government and support Beşiktaş or Galatasaray sneer at them.”
The AK Party may play dirty again, reject the results of next year’s presidential elections and invite their hardline supporters to
the streets to terrorise people. But then Turkey’s oppressed football fans can make a return, too, and protect Atatürk’s legacy.
“I spoke to a lot of people from Çarşı,” Keddie recalled, “and they said: ‘Yes, we’re against the government, and if something like Gezi happened again, we’d be there in a heartbeat.’”
Kaya Genç is Index’s contributing editor for Turkey. He is based in Istanbul.
This article appears in the autumn 2022 issue of Index on Censorship. To subscribe click here
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]On 5 July 2017, human rights defenders from a number of different organisations gathered on the island of Büyükada for a workshop on the protection of digital information.
On the third day of the workshop, ten of the attendees were arrested at gunpoint and later charged with aiding the Fethullah Gülen Terrorist Organization, which President Erdoğan blames for 2016’s failed military coup.
The Istanbul 10, as they became known, were released on bail on October 25th 2017, after 113 days in detention but then faced three years of court hearings.
On 3 July 2020, former Amnesty Turkey chair Taner Kılıç was convicted of membership of the Fethullah Gülen Terrorist Organization and sentenced to 6 years 3 months in prison.
Meanwhile, Özlem Dalkıran, İdil Eser and Günal Kurşun were convicted of assisting the organization and sentenced to 25 months, pending an appeals process which could last years.
As the sentences were announced, Index’s editor-in-chief Rachael Jolley spoke with Özlem Dalkıran.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_video link=”https://youtu.be/jFAojAdwiQk”][/vc_column][/vc_row]
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]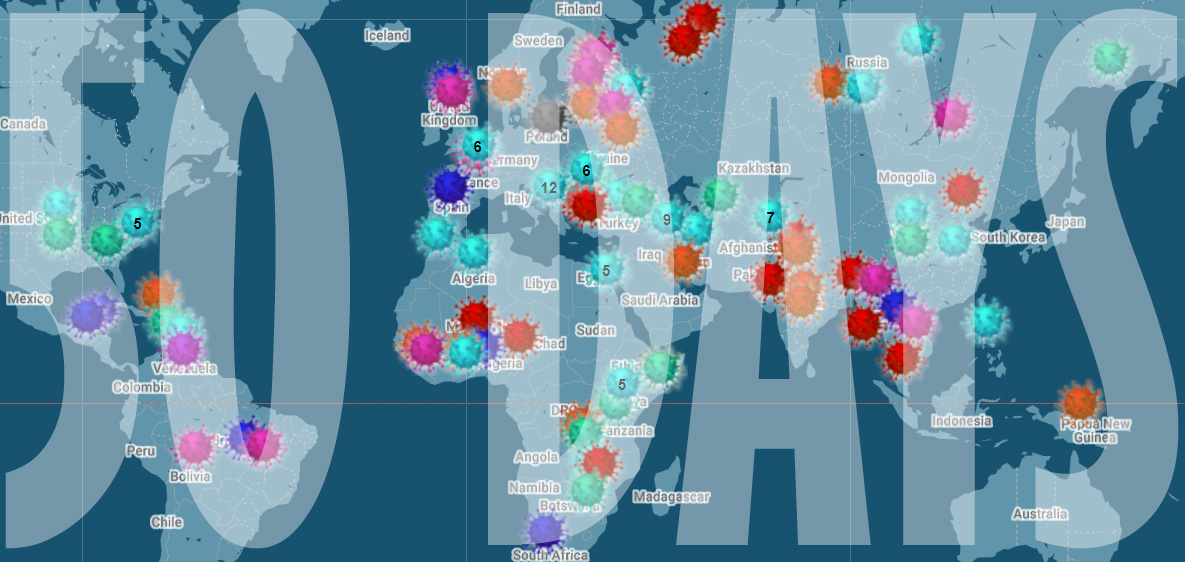
As we mark 50 days since we first started collating attacks on media freedom related to the coronavirus crisis, we’re horrified by the number of attacks we have mapped – over 150 in what is ultimately a short period of time.
We know that in times of crisis media attacks often increase – just look at what happened to journalists after the military coup in Egypt in 2013 and the failed coup against Recep Tayyip Erdogan in Turkey in 2016. The extent of the current attacks, in democratic as well as authoritarian countries, has been a shock.
Our network of readers, correspondents, Index staff and our partners at the Justice for Journalists Foundation have helped collect the more than 150 reports media attacks.
But these incidents are likely to be the very tip of the iceberg. When the world is in lockdown, finding out about abuses of power is harder than ever. Journalists are struggling to do their job even before harassment. How many more attacks are happening that we don’t yet know about? It’s a scary thought.
Rachael Jolley, editor-in-chief of Index on Censorship, said: “We are alarmed at the ferocity of some of the attacks on media freedom we are seeing being unveiled. In some states journalists are threatened with prison sentences for reporting on shortages of vital hospital equipment. The public need to know this kind of life-saving information, not have it kept from them. Our reporting is highlighting that governments around the world are tempted to use different tactics to stop the public knowing what they need to know.”
Index is alarmed that the attacks are not coming from the usual suspects. Yes, there have been plenty of incidents reported in Russia and the former Soviet Union, Turkey, Hungary and Brazil. At the same time there have been many incidents in countries you would not expect to see – Spain, New Zealand, Germany and the UK.
The most common incident we have recorded on the map are attacks on journalists – whether physical or verbal – and cases where reporters have been detained or arrested. There have been more than 30 attacks on journalists, with the source of many of these being the US President Donald Trump. He has a history of being combative with the press and decrying fake news even where the opposite is the case and the crisis has seen a ramped up attempt at excluding the media. During the crisis, he has refused to answer journalists’ questions, attacked the credentials of reporters and walked out from press conferences when he doesn’t like the direction they are taking.
We have also seen reporters and broadcasters detained and charged just for trying to tell the story of the crisis, including Dhaval Patel, editor of the online news portal Face of Nation in Gujarat, Mushtaq Ahmed in Bangladesh and award-winning investigative journalist Wan Noor Hayati Wan Alias in Malaysia.
Since we started the mapping project, we have highlighted other specific trends. Orna Herr has written about how coronavirus is providing pretext for Indian prime minister Narendra Modi to increase attacks on the press and Muslims. Jemimah Steinfeld wrote about how certain leaders are dodging questions while we have also looked at how freedom of information laws are being suspended or deadlines for information extended.
Although the map does not tell the whole story it does act as a record of these attacks. When this crisis is finally all over, it will allow us to ask questions about why these attacks happened and to make sure that any restrictions that have been introduced are reversed, giving us back our freedom.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_btn title=”Report an incident” shape=”round” color=”danger” link=”url:https%3A%2F%2Fforms.gle%2Fhptj5F6ZvxjcaGLa7|||” css=”.vc_custom_1589455005016{border-radius: 5px !important;}”][/vc_column][/vc_row]