19 Aug 2016 | Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan News, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, News, Russia, Serbia, Turkey
 Each week, Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project verifies threats, violations and limitations faced by the media throughout the European Union and neighbouring countries. Here are five recent reports that give us cause for concern.
Each week, Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project verifies threats, violations and limitations faced by the media throughout the European Union and neighbouring countries. Here are five recent reports that give us cause for concern.
16 August, 2016 – IMC TV reporter Gulfem Karatas and cameraman Gokhan Cetin were assaulted and detained while covering the police raid on the daily Ozgur Gundem. Footage of the attack was shared via IMC TV Twitter account, showing police grabbing the camera and physically assaulting the reporter, who is heard screaming in the footage.
Karatas and Cetin were detained along with journalists Günay Aslan, Reyhan Hacıoğlu, Ender Öndeş, Doğan Güzel, Ersin Çaksu, Kemal Bozkurt, Sinan Balık, Önder Elaldı, Davut Uçar, Zana Kaya, Fırat Yeşilçınar and Mesut Karnak.
In an official statement IMC TV said: “During the live broadcast, the police prevented Gulfem Karatas and Gokhan Cetin from reporting and detained them violently along with at least 21 Ozgur Gundem employees. We condemn this unacceptable treatment to our colleagues who were on duty and ask for their immediate release.”
16 August, 2016 – Journalist Vladimir Zivanovic and photographer Boris Mirko, who work for the daily Serbian Telegraph were threatened and insulted while reporting on the illegal construction of an aqua park in the capital Belgrade.
The journalists were in an area of the city where former professional football player Nikola Mijailovic is building the controversial aqua park. Mijailovic approached the journalists and shouted a series of insults about them and their families. He reportedly told them that they should be put in a gas chamber together.
Mijailovic also reportedly tried to bribe them. The journalists have reported the threats to the police and Serbia’s Independent Association of Journalists has condemned the incident.
15 August, 2016 – A court in Baku ruled to uphold a travel ban against investigative reporter Khadija Ismayilova. “Binagadi Court told me because I have no husband, kids or property, I might not be able to return if I leave the country,” Ismayilova said following the hearing in Baku.
Ismayilova was released from prison on 25 May on a suspended three-and-a-half-year sentence.
Also read: Azerbaijan’s long assault on media freedom
16 August, 2016 – The eighth administrative court in Istanbul ordered the closure of the newspaper Ozgur Gundem on the grounds of “producing terrorist propaganda”.
The court order described the closure as “temporary” although no duration appears to be specified in the text of the decision.
Later that day, Ozgur Gundem’s offices were raided by the police.
According to P24, the 23 members of staff were taken into custody. They are: Editor-in-Chief Zana Kaya, journalists Zana Kaya, Günay Aksoy, Kemal Bozkurt, Reyhan Hacıoğlu, Önder Elaldı, Ender Önder, Sinan Balık, Fırat Yeşilçınar, İnan Kızılkaya, Özgür Paksoy (DİHA news agency) , Zeki Erden, Elif Aydoğmuş, Bilir Kaya, Ersin Çaksu, Mesut Kaynar (DİHA), Sevdiye Gürbüz, Amine Demirkıran, Baryram Balcı, Burcu Özkaya, Yılmaz Bozkurt (member of the press office of the Istanbu Medical Chamber), Gülfem Karataş (İMC), Gökhan Çetin (İMC) and Hüseyin Gündüz (Doğu Publishing House).
Also read: Turkey’s continuing crackdown on the press must end
11 August, 2016 – Dmitri Remisov, the Rostov-on-Don regional correspondent for Rosbalt news agency, told the agency that he was repeatedly assaulted by police officers while being questioned at the regional Center for Counteracting Extremism.
According to Remisov, he was asked to come to the CCE to answer questions related to a criminal case “on the preparation of a terrorist act” in Rostov, a city in south-west Russia.
He reported that two police officers asked him whether he knew certain individuals, where most of the people he was asked about were opposition activists.
“Then they asked me if I knew a certain Smyshlayev. I said that I didn’t remember such a person,” Remizov said.“One officer started saying I did know this person in 2009, after which he struck my head three times. Afterwards, he began threatening me, saying he could prosecute me under the criminal law or could have some Nazis punish me.”
After he was questioned another policeman threatened him with physical punishment, saying “we will meet [with you] once again”.
The Rosbalt correspondent received medical care after the questioning. He also filed a complaint against police officers, Rosbalt reported.
12 Aug 2016 | Belarus, Germany, Mapping Media Freedom, mobile, Netherlands, News, Romania, Turkey
Each week, Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project verifies threats, violations and limitations faced by the media throughout the European Union and neighbouring countries. Here are five recent reports that give us cause for concern.
5 August, 2016 – Twelve journalists were arrested on terror charges following a court order, independent press agency Bianet reported.
According to Bianet: “The court on duty has ruled to arrest Alaattin Güner, Şeref Yılmaz, Ahmet Metin Sekizkardeş, Faruk Akkan, Mehmet Özdemir, Fevzi Yazıcı, Zafer Özsoy, Cuma Kaya and Hakan Taşdelen on charges of “being a member of an armed terrorist organisation” and Mümtazer Türköne, columnist of the now closed Zaman Daily on charges of “serving the purposes of FETÖ (Fethullahist Terrorist Organisation)” and Hüseyin Turan and Murat Avcıoğlu on charges of “aiding a [terrorist] organization as non-member”.
Warrants for the detainment of all 13 Zaman newspaper journalists were issued on 27 July 2016 by Turkish authorities.
Also read: 200 Turkish journalists blacklisted from parliament
4 August, 2016 – Monica Gubernat, a member and chairperson of the National Audiovisual Council of Romania, cut off the live transmission of a council debate, news agency Mediafax reported.
An ordinance says that all meetings of the council must be broadcasted live on its website.
The institution has recently purchased equipment to broadcast debates, which was set to go live on 4 August, 2016. A member of the council, Valentin Jucan, even issued a press statement about the live broadcast.
The chairperson, Monica Gubernat was opposed to it, saying that she was not informed about the broadcast, and asked for a written notification about the transmission.
ActiveWatch and the Centre for Independent Journalism announced they would inform the supervisory bodies of the National Audiovisual Council of Romania and the culture committees of the Parliament about the “abusive behavior of a member of the council” and asked for increased transparency within this institution.
The National Audiovisual Council of Romania is the only regulator of the audiovisual sector in Romania. Their job is to ensure that Romania’s TV channels and radio stations operate in an environment of free speech, responsibility and competitiveness. In practice, the council’s activity is often criticised for its lack of transparency and their politicised rulings.
2 August, 2016 – British blogger Graham Phillips and freelance journalist Billy Six, forcibly entered the offices of non-profit investigative journalism outlet Correctiv, filmed without permission and accused staff of spreading lies, the outlet reported on its Facebook page on Wednesday 3 August.
According to Correctiv’s statement, Phillips had been seeking to confront Marcus Bensmann, the author of a Correctiv article which claimed that Russian officers had shot down the passenger airplane crossing over Ukraine in July 2014.
Phillips maintains the Ukrainian military is responsible for the crash.
2 August, 2016 – Police officers prevented freelance journalist Dzmitry Karenka from filming near the Central Election Commission office located in the Belarusian Government House in Minsk, the Belarusian Association of Journalists reported.
The journalist reported intended to film a video on the last day when candidates for the House of Representatives, Belarusian lower chamber, could register.
At 6am he was approached by police officers who told him that administrative buildings in Belarus can be filmed “only for the news” and asked him to show his press credentials which he didn’t have as he is a freelance journalist.
Karenka told the Belarusian Association of Journalists that he spoke with the police for over an hour before he was released and advised not to film administrative buildings.
Also read: Belarus: Government uses accreditation to silence independent press
1 August, 2016 – The website of the Dutch edition of Turkish newspaper Zaman Today was hit by a DDoS attack, broadcaster RTL Nieuws reported.
The website, known to be critical of the Erdogan government, was offline for about an hour.
An Erdogan supporter reportedly announced an attack on the website earlier via Facebook. Zaman Today said it will be pressing charges against him.
Also read: Turkey’s media crackdown has reached the Netherlands
11 Aug 2016 | Europe and Central Asia, mobile, News, Turkey, Turkey Uncensored
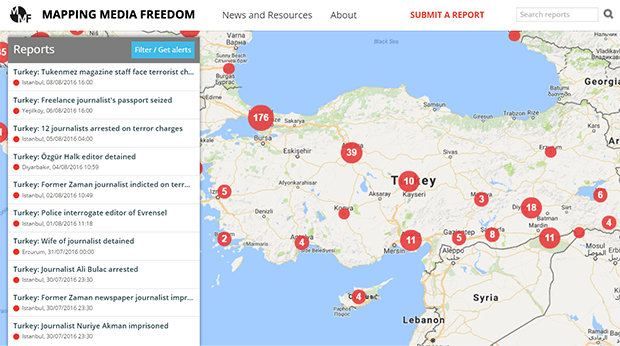
The number of threats to media freedom in Turkey have surged since the failed coup on 15 July.
One of the most vital duties of a journalist — in any democracy — is to report on the day-to-day operations of a country’s parliament. Journalism schools devote much time to teaching the deciphering budgets and legal language, and how to report fairly on political divides and debates.
I recalled these studies when I read an email Wednesday morning from an Ankara-based colleague. I smiled bitterly. The message included a link to an article published in the Gazete Duvar, which informed that 200 journalists had been barred from entering the home of the Grand National Assembly of Turkey. Security controls at the two entrances of the failed-coup-damaged building had been intensified and journalists were checked against a list as they tried to enter.
The reason for the bans? Most of those who were blocked worked for shuttered or seized outlets alleged to be affiliated with the Gülenist movement.
Parliament, though severely damaged by bombing during the night of the coup attempt, is still open. For any professional colleague, these sanctions mean only one thing: journalism is now at the absolute mercy of the authorities who will define its limits and content.
Many pro-government journalists do not think the increasingly severe controls are alarming. “It is democracy that matters,” they argue on the social media. “Only the accomplices of the putschists in the media will be affected, not the rest.”
If only that were true. Reality proves the opposite. Along with the closures of more than 100 media outlets, a wide-scale clampdown on Kurdish and leftist media is underway. Outlets deemed too critical of government policies have come under post-coup pressure.
Late Tuesday, pro-Kurdish IMC TV reported that the official twitter accounts of three major pro-Kurdish news sources — the daily newspaper Özgür Gündem and news agencies DIHA and ANF — were banned. Some Kurdish colleagues interpret the sanctions as part of an upcoming security operation in the southeastern provinces of Diyarbakır and Şırnak.
What I see is a new pattern: in the past three-to-four days, many Twitter accounts of critical outlets and individual journalists have been silenced. An “agreement” appears to have been reached between Ankara and Twitter, but no explanation has yet been given.
For days now, many people have been kept wondering about the case of Hacer Korucu. Her husband, Bülent Korucu, former chief editor of weekly Aksiyon and daily Yarına Bakış, is sought by police after an arrest order issued on him about “aiding and abetting terror organisation”, among other accusations. She was arrested nine days ago as police had told the family that “she would be kept until the husband shows up”.
The Platform for Independent Journalism provided more insight on Hacer Korucu’s detention and subsequent arrest. The motive? She had taken part in the activities of the schools affiliated with Gülen Movement and attended the Turkish Language Olympiade.
Hacer Korucu’s case, without a doubt, shows how arbitrary law enforcement has become in Turkey. As a result no citizen can feel safe any longer.
“She is a mother of five,” was the outcry of Rebecca Harms, German MEP. “A crime to be married to a journalist?”
How do we now expect an honest Turkish or Kurdish journalist to answer this question? By any measure of decency, the snapshot of Turkey in the post-putsch days leaves little suspicion: emergency rule gives a free reign to authorities who feel empowered to block journalists from covering the epicenter of any democratic activity — parliament — and let relatives of journalists suffer.
Meanwhile, we are told on a daily basis that democracy was saved from catastrophe on that dreadful July evening and it needs to be cherished.
But, like this? How?
A version of this article originally appeared on Suddeutsche Zeitung. It is posted here with the permission of the author.

Turkey Uncensored is an Index on Censorship project to publish a series of articles from censored Turkish writers, artists and translators.
10 Aug 2016 | Academic Freedom, Campaigns -- Featured, Europe and Central Asia, mobile, News, Turkey, Turkey Uncensored
The stream may be small right now, a trickle, but it is unmistakable. Turkey’s academics and secular elite are quietly and slowly making their way for the exits.
Some months ago, in the age before Turkey’s post-coup crushing of academia, a respected university lecturer told me she was seeking happiness outside Turkey. She was teaching economics at one of Istanbul’s major universities, but neither her nor her husband, who is also in the financial sector, had a desire to remain in the country any longer. They simply packed up and left for Canada.
The growing unease about the future is now accelerating among the academics and mainly secular elite in the country. This well-educated section of society is feeling the pressure more than any other, and as the instability mounts the urge to join the “brain drain” will only increase.
Some of them, particularly those academics who have been fired and those who now face judicial charges for signing a petition calling for a return to peace negotiations with the Kurdish PKK, no longer see a future for their careers. With the government further empowered by emergency rule decrees, the space for debate and unfettered learning is shrinking.
One of the petition’s signatories, the outspoken sociologist Dr Nil Mutluer, has already moved to a role at the well-respected Humboldt University in Berlin to teach in a programme devoted to scholars at risk.
You only have to look at the numbers to realise why more are likely to follow in the footsteps of those who have already left Turkey. In the days after the failed coup that struck at the country’s imperfect democracy, the government of president Recep Tayyip Erdogan swept 1,577 university deans from their posts. Academics who were travelling abroad were ordered to return to the country, while others were told they could not travel to conferences for the foreseeable future. Some foreign students have even been sent home. The pre-university educational system has been hit particularly hard: the education ministry axed 20,000 employees and 21,000 teachers working at private schools had their teaching licenses revoked.
Anyone with even the whiff of a connection to FETO — the Erdogan administration’s stalking horse for the parallel government supposedly backed by the Gulenist movement — is in the crosshairs. Journalists, professors, poets and independent thinkers who dare question the prevailing narrative dictated by the Justice and Development Party will hear a knock at the door.
It appears that the casualty of the coup will be the ability to debate, interrogate and speak about competing ideas. That’s the heart of academic freedom. The coup and the president’s reaction to it have ripped it from Turkey’s chest.
But it’s not just the academics who are starting to go. The secular elite and people of Kurdish descent that are also likely to vote with their feet.
Signs are, that those who are exposed to, or perceive, pressure, are already doing this. Scandinavian countries have noted an increase in the exodus of the Turkish citizens. Deutsche Welle’s Turkish news site reported that 1719 people sought asylum in Germany in the first half of this year. This number already equals the total of Turkish asylum seekers who registered during the whole of 2015. Not surprisingly, 1510 of applications in 2016 came from Kurds, who are under acute pressure from the government.
The secular (upper) middle class is also showing signs of moving out. The economic daily Dünya reported on Monday that the number of inquiries into purchasing homes abroad grew four-to-five times the pre-coup level. Many real estate agencies, the paper reported, are expanding their staff to meet the demand. Murat Uzun, representing Proje Beyaz firm, told Dünya:
“The demand is growing since July 15 by every day. Emergency rule has also pushed up the trend. These people are trying to buy a life abroad. Ten to twelve people visit our office every day….Many ask about the citizenship issues.”
Adnan Bozbey, of Coldwell Banker, told the paper that people were asking him: “Is Turkey becoming a Middle Eastern country?”
According to Dünya, the USA, Ireland, Portugal, Greece, Malta and Baltic countries are popular among those who want to seek life prospects elsewhere.
In short, the unrest is spreading. Unless the dust settles and the immense political maneuvering about the course Turkey is on reverses, it would be realistic to presume that a significant demographic shift will take place in the near future.
A version of this article originally appeared on Suddeutsche Zeitung. It is posted here with the permission of the author.

Turkey Uncensored is an Index on Censorship project to publish a series of articles from censored Turkish writers, artists and translators.
 Each week, Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project verifies threats, violations and limitations faced by the media throughout the European Union and neighbouring countries. Here are five recent reports that give us cause for concern.
Each week, Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project verifies threats, violations and limitations faced by the media throughout the European Union and neighbouring countries. Here are five recent reports that give us cause for concern.


