Index relies entirely on the support of donors and readers to do its work.
Help us keep amplifying censored voices today.
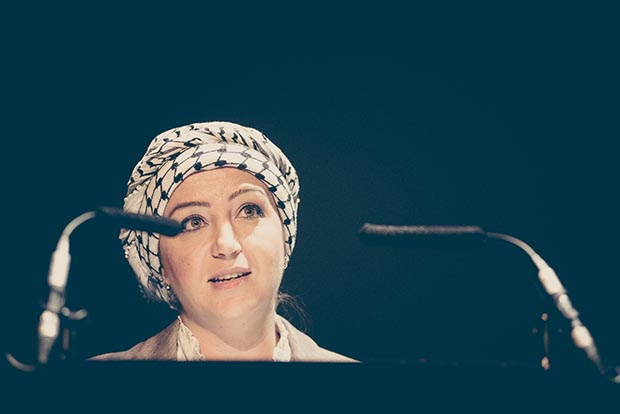

2016 Freedom of Expression Journalism Award winner Zaina Erhaim (Photo: Elina Kansikas for Index on Censorship)
Index on Censorship is appalled by the decision of UK border officials to confiscate the passport of Syrian journalist, Zaina Erhaim. The Syria coordinator for the Institute of War and Peace Reporting, Erhaim has been recognised by a number of organisations internationally for her work training citizen journalists to report on the conflict within Aleppo.
Index invited Erhaim, in her capacity as winner of this year’s Freedom of Expression Awards, to an event at Write on Kew Festival to speak about her experiences alongside veteran journalist Kate Adie.
When Erhaim arrived in the UK on Thursday 22 September for the event she was detained by the UK Border Agency (UKBA) and questioned for an hour before UKBA confiscated her passport. Erhaim was told that the passport had been reported by the Syrian authorities as stolen and therefore UKBA was compelled to retain it and return it to the Syrian government.
Erhaim had her old passport, which remains valid but is effectively unusable because the pages are filled, and was able to enter the UK for the debate. Further travel may be impossible, however, as Erhaim no longer has a passport with which to apply for a new visa to enter Europe.
When Erhaim challenged this decision, she was told to seek consular advice from the Syrian government in Damascus.
“We are extremely disappointed by the treatment of Zaina by border officials. It seems quite astonishing that the UK would accede to a request from a government whom it has only this weekend accused of being complicit in war crimes – especially when it is clear that the Syrian government is using tools, such as passport rescindments, to harass those who oppose or expose its behaviour,” Jodie Ginsberg, CEO of Index on Censorship, said.
Index will be raising the matter with the Home Office and Foreign and Commonwealth Office.
If you would like to write a letter in support of Zaina Erhaim, address your correspondence to:
Rt Hon Amber Rudd MP
Secretary of State for the Home Department
Direct Communications Unit
2 Marsham Street
London
SW1P 4DF
Rt Hon Boris Johnson MP
Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs
King Charles Street
London
SW1A 2AH
More about Zaina Erhaim
Women on the front line: Zaina Erhaim and Kate Adie on the challenges of war reporting
Zaina Erhaim: “I want to give this award to the Syrians who are being terrorised”
#IndexAwards2016: Zaina Erhaim trains Syrian women to report on the war
Each week, Index on Censorship’s Mapping Media Freedom project verifies threats, violations and limitations faced by the media throughout the European Union and neighbouring countries. Here are five recent reports that give us cause for concern.
France: In run up to elections France Télévisions delays airing documentary on Sarkozy funding https://t.co/W9iyZKk2fQ #mediafreedom #ECPMF
— Index on Censorship (@IndexCensorship) September 8, 2016
Former french president Nicolas Sarkozy is back on the campaign trail but fundraising from his 2012 run for office is raising questions. A new documentary investigating these finances was due to air on 29 September but following pressure from Michel Field, the head of news at France Télévisions, a French public national television broadcaster, it now won’t show until after the primary elections of Sarkozy’s Republicans party at the end of November.
On 6 September, the satirical and investigative newspaper Le Canard Enchaîné revealed that in mid-July, Field told Elise Lucet, the new director of Envoyé Special, that the documentary must be delayed. The publication also revealed that Field was in talks with Sarkozy, who had agreed to be the first guest on a new political programme by France Télé, but that Sarkozy’s team would prevent his appearance if the documentary was to air.
According to Le Canard, Field also tried to have a heavily-edited version of the documentary air 8 September, which Lucet refused to comply with. Lucet accused Field of censorship and the director of France Télévisions, Delphine Ernotte Cunci, is taking some time to decide whether to air the documentary or not.
On 7 September, France Télévisions confirmed that the documentary would be aired “before the end of the year”.
On 5 September a court in Chechnya sentenced journalist Zhalaudi Geriev to three years in prison on drug possession charges. Geriev, who worked for the independent regional website Kavkazski Uzel, which covers politics and human rights issues, claims he was forced to give a confession.
In court, Geriev said that on 16 April he was kidnapped from a public bus on his way to Grozny. He added that he was taken to the woods, where he was beaten and tortured, and then taken to a local cemetery. There, according to the prosecutors, he was arrested for possession of 160 grams of marijuana and admitted he was guilty.
Kavkazski Uzel issued a statement saying that they believe that the case against Geriev is fabricated and motivated by his professional activities.
The House of Lords debated the so-called Snooper’s Charter on 5 September. Part of the Investigatory Powers Bill introduced by Prime Minister Theresa May when she was still Home Office secretary, it would allow police and intelligence agencies to intercept, gather and store the communications of tens of millions of people including whistleblowers, journalists and sources.
If passed, this law would allow the “relevant public authorities” to obtain journalists’ communications data with the aim of identifying or confirming the identity of anonymous sources.
On 4 September the studios of national Ukrainian TV channel Inter were set on fire by unknown assailants.
The news agency Unian, citing the State Emergency Services division, reported: “At 16:31 on Sept. 4, Kyiv Emergency Situations Service operators received a call about a fire that had broken out at a building of a TV channel at 26 Schuseva Street. Upon arrival at the scene, firefighters discovered two piles of tyres had been set ablaze during a rally outside the building and an external source of ignition brought [into the building] had caused a fire on the first floor…and second floor.”
Thirty people were evacuated and one journalist suffered a broken leg and smoke inhalation.
Can Dündar’ın eşi Dilek Dündar’ın yurt dışına çıkışına izin verilmedi https://t.co/ZQmQN9hn0W pic.twitter.com/6jE351HToZ
— ANADOLU AJANSI (@anadoluajansi) September 3, 2016
Dilek Dundar, the wife of prominent Turkish journalist and former editor-in-chief of Cumhuriyet newspaper Can Dundar was prevented from leaving the country at the Ataturk International airport on 3 September. She was on her way to Berlin, Germany, when airport officials confiscated her passport and informed her that it had been cancelled.
Can Dundar said of the situation: “This … is an excellent example of authoritarian rule. The new legal order … treats the whole family as criminals.”
Also read:
Can Dündar: Turkey is “the biggest prison for journalists in the world”
Mapping Media Freedom
|
Index recently appointed a new youth advisory board cohort. The eight young students and professionals, from countries including Hungary, Germany, India and the US, will hold their seats on the board until December.
Each month, board members meet online to discuss freedom of expression issues occurring around the world and complete an assignment that grows from that discussion. For their first task the board were asked to write a short bio and take a photo of themselves holding a quote that reflects their belief in free speech.
Sophia Smith-Galer 
I’m half English, half Italian, and was born and raised in London. I have just graduated from Durham University with a degree in Spanish and Arabic and will be studying for a Master’s in broadcast journalism at City University next year.
I have just returned from a trip to New York after winning a multilingual world essay prize which included speaking at the United Nations’ General Assembly. I was in the group of Arabic language winners and our speeches were about tackling climate change, which is one of the UN’s sustainable development goals for 2030. Now that I am embarking on a career in journalism I’m looking forward to continue supporting these goals in my work.
Freedom of expression is particularly important to me as several countries that speak both of the languages I have dedicated years of study to continue to be plagued by tyrants and censors. I’m particularly interested addressing censorship in Latin America and the Middle East, especially with regard to the arts, as I’m also a classical singer and keen art historian.
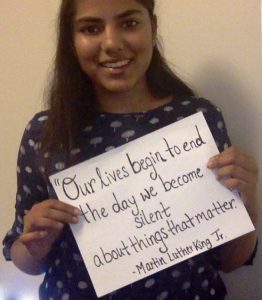
Shruti Venkatraman
Originally from Mumbai, I am currently a first year undergraduate studying law at the University of Edinburgh. As a law student, I am interested in advocacy in general, but I am particularly interested in advocating for fundamental human rights.
In today’s socio-political context, the phrase “freedom of expression” has gained importance and expanded in its meaning from it’s original intent to prevent minority persecution. Having lived in India and South Africa, I was able to grasp the importance of free speech in the context of regional history, and I learnt how human rights appeals have had local and global impacts and are inherently tied with social development. Index on Censorship’s admirable work to promote and defend freedom of expression highlights how important this cause is in our quest for social progress, justice and equality and how repression of these rights result in societal backwardness.
Niharika Pandit 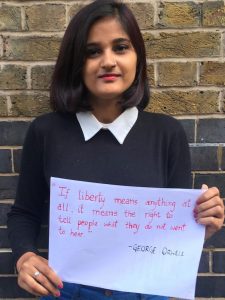
I am currently a master’s candidate at the Centre for Gender Studies at SOAS, University of London with South Asia as my focus area of gender research. I became interested in issues of censorship during my undergraduate studies in mass media with a specialisation in journalism from Bombay.
As a journalist and an active social media user in India, I was witness to numerous instances of online abuse, trolling and silencing of women politicians, journalists and activists who voiced opinions on political and social issues. As a response to the barrage of abuse in the online space, otherwise a liberating space to hear diversified opinions, I wrote a piece on Twitter trolls in India and the use of sexist abuse as a tool to muzzle women for Index on Censorship’s Young Writers’ Programme.
Within censorship, I am particularly interested in working on the intersections of social media, gender along with looking at censorship in militarised zones and its growing legitimacy in contemporary political ethos as part of my research.

Layli Foroudi
It was studying literary works from the Soviet period during my undergraduate degree that highlighted the issue of censorship for me initially. Clearly this issue has outlived (and predates) the Soviet Union and is still of pressing concern in Russia today and globally. After graduating, I worked as a journalist on issues of freedom of expression and belief in Iran, and then in Russia at the Moscow Times. By pushing a state-sponsored version of the truth and punishing those at variance with it, these countries and others marginalise people and stifle innovation and creativity.
Freedom of expression and public debate underpin what society consists of and being denied this freedom is being denied the right to participation in society, as Hannah Arendt wrote: the polis is “the organisation of people as it arises out of acting and speaking together”. Historically, many have been denied the right to “act and speak”, based on ethnicity, gender, belief, immigration status, etc, and continue to be. I am interested in encouraging a diversity voices in the public sphere, something I have enjoyed exploring more this past year while undertaking an MPhil in race, ethnicity, and conflict at Trinity College Dublin and as a member of the youth advisory board since January.
Ian Morse 
I’m a student and journalist at Lafayette College in the US, but I have studied in Germany, Turkey and the UK. I really started studying news media when I lived in Turkey 18 months ago, because even then (much more so now) journalists and bloggers had a very tough time gathering and publishing good information. Since then, I’ve been a journalist in Turkey, the UK and Greece. I study history and mathematics-economics, but almost every project I do is focused on news media.
I’ve encountered freedom of expression violations in many fashions, from student pressures against speakers to petty government retaliation to Twitter blocking. There is quite a bit of nuance that is overlooked in many cases, but that nuance is needed to understand where the line needs to be drawn. Words have a lot of power in society – but it is often difficult to get the truth out when lies are louder or gags are stronger. I hope with Index that we can find ways to fix this.
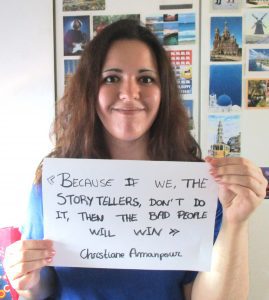
Anna Gumbau
I am a journalist living between Barcelona and Brussels. I am passionate about youth work, having volunteered for five years as member of AEGEE-Europe / European Students’ Forum, including a year as member of its international board. I have taken part in, and often led projects, run by students for other students all over Europe, on topics such as pluralism of media, election observation and media literacy. I am also involved in the field of internet governance, participating in the last two editions of the EuroDIG and joining the Youth Observatory of the Internet Society.
As a young media-maker who grew up listening to the stories of censorship in the times of the Spanish dictatorship, I believe strongly in free speech, a free press and media pluralism as essential pillars for democracy. I am fascinated by the power of words and freedom of expression to empower citizens and stand up to what they believe in. I also envision free media as a crucial element for better informed societies and, in extension, for more responsible individual citizens to participate in the public space.
Constantin Eckner 
I am originally from Germany. I graduated from University of St Andrews with a master’s degree in modern history. Currently, I am a Ph.D. candidate specialising in human rights, asylum policy and the history of migration. Moreover, I have worked as a writer and journalist since I was 17 years old, covering a variety of topics over the years. Longer stays in cities like Budapest and Istanbul have raised my awareness for pressures exerted upon freedom of expression.
In a perfect world journalists, as well as every citizen, would live without fear of state censorship and potentially facing repercussions for the words they write or speak, for the pictures they draw, for the photos they shoot or for music they play.
Freedom of expression and access to information are cornerstones of an enlightened society. Unfortunately, in 2016 the world is still challenged by undemocratic regimes and powers that intend to quash people, which is an oppressive situation that has to change. It is up to us to help those who cannot raise their voice fearlessly.
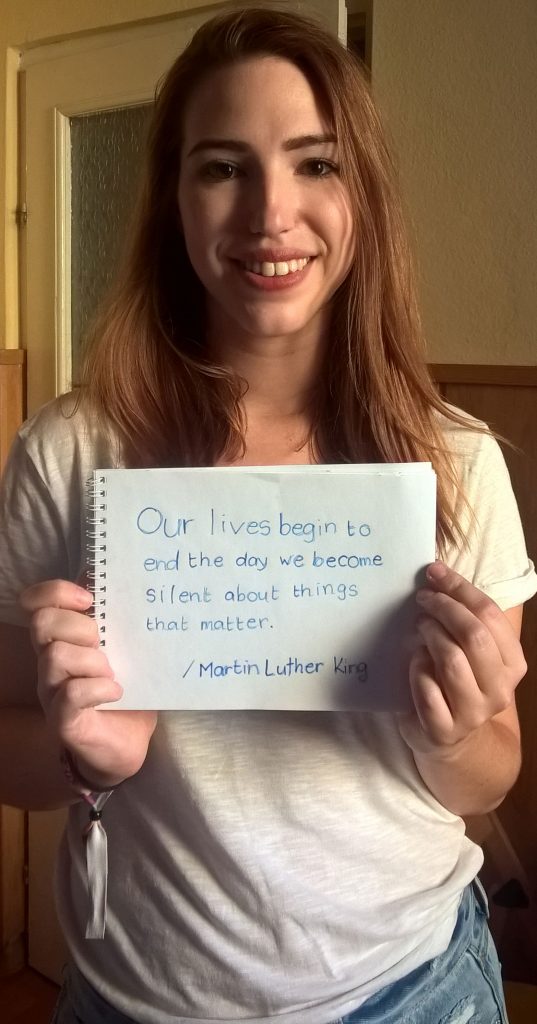 Fruzsina Katona
Fruzsina Katona
I was born and raised in Hungary, although I spent my pre-university years in a small town in eastern Hungary. Today I am a freelance journalist.
I always knew I wanted to be a journalist, since I was always interested in literally everything that surrounded me. The urge to publish became stronger at the age of 17, after I returned from Japan, where I spent a school year. That one year made me realise, that my home country is really far from the image I had of it. And the only way I can fight against corruption, abuses and narrow-mindedness – apart from voting – is to educate and inform the public. I took an internship at Hungary’s leading investigative journalism center, and 2015 Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression award-winner, Atlatszo.hu. I have worked for them as a freelancer ever since, and I enjoy my work pretty much.
I recently received a graduate degree in communication and media studies, and supplemented my “official” studies with training, workshops and conferences across Europe.
In the future I would like to be a post-conflict reporter or a human rights journalist, specialising in freedom of expression and the press.

Rt Hon Boris Johnson
Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs
Foreign and Commonwealth Office
King Charles Street Whitehall
London SW1A 2AH
15 August 2016
Dear Mr Johnson,
First, may we congratulate you on your recent appointment as Secretary of State for Foreign and Commonwealth Affairs.
We write to raise our deep concern over the current ambassador from the Kingdom of Bahrain to the UK, Sheikh Fawaz bin Mohammad Al Khalifa, on his recent statements and record on press freedom, and urge you to raise the concerns set out below to the Government of Bahrain.
Last month, on 20 July, the Bahrain embassy in the UK released a statement in support of the actions of the Information Affairs Authority (IAA), which brought a case against Bahraini journalist Nazeeha Saeed. Ms. Saeed has worked as correspondent for France24 for seven years, and for Radio Monte Carlo Doualiya for 12 years. She was charged with working for international media outlets without a license. Her case is just the latest in a series of regressive actions targeting critical journalists, creating an environment where a free fourth estate cannot function.
The Bahrain embassy’s statement reported that the IAA had lodged a legal complaint against Ms. Saeed for illegally working as a foreign correspondent, that Ms. Saeed’s foreign correspondence license expired ‘over 150 days’ ago, and that she was warned of legal action.1 None of this is true. The undersigned NGOs have seen a letter by the IAA from June 2016 denying her license renewal, which she had applied for at the end of March 2016 (some 110 days earlier to the embassy’s statement, not 150). The IAA did not in fact warn her of legal action in the letter.
It is not innocuous that Sheikh Fawaz, as ambassador to the United Kingdom, had the embassy publish this statement in support of the IAA and we see this statement as a reflection of Bahrain’s antipathy towards a free press, and as Sheikh Fawaz’s direct role in antagonising the press.
The IAA is the government body that regulates the press, issues journalist licenses, and operates Bahrain News Agency and the state-run Bahrain TV. Sheikh Fawaz Al Khalifa, prior to becoming ambassador, was the first president of the IAA between 2010 and 2012, overseeing the institution during the Arab Spring. In that time, the government systematically cracked down on political and civil freedoms. The IAA was responsible for suspending the only independent newspaper, aiding in the censorship of the press and the deportation of foreign-national journalists, and in spreading hate speech through IAA-controlled TV stations.
Journalists interviewed by the Bahrain Institute for Rights and Democracy have told us that press relations were calmer before Sheikh Fawaz’s 2010-2012 presidency of the IAA. Sheikh Fawaz’s appointment as media chief in July 2010 coincided with the arrest and torture of opposition politicians and activists in the lead-up to Bahrain’s November 2010 General Elections, actions which precipitated the Arab Spring protests. Journalists state that government censorship of the press increased substantially with the formation of the IAA under Sheikh Fawaz.
In May 2011, Ms. Saeed was summoned to a police station in connection to the police killing of a protester she had witnessed. There, police detained her and tortured her into signing a confession, as reported by Human Rights Watch.2 To date Ms. Saeed has been denied justice by Bahrain’s courts.3 The IAA, despite its responsibilities to protect journalists, did not support her. Soon after Ms. Saeed’s detention, BBC Arabic interviewed Sheikh Fawaz, then-IAA president, asking him: “Why is a journalist who has come to report these events treated in this way?” He replied: “She does not have any license to report for the French news agency.”4 In fact, Ms. Saeed had a license at that time, and has done throughout her career, until the IAA’s refusal of her latest renewal in April 2016. Sheikh Fawaz not only failed to protect a vulnerable journalist, he intentionally spread falsehoods justifying her mistreatment.
Ms. Saeed’s case is not the only one in which Sheikh Fawaz has played a role. The Bahrain Independent Commission of Inquiry, the accepted record of rights violations during 2011, notes (para. 1611) how Sheikh Fawaz’s Deputy Assistant at the IAA summoned an Iraqi journalist working for the only independent newspaper, Al Wasat, for a meeting in April 2011 during an imposed State of Emergency. When the journalist arrived at the IAA offices, police arrested, beat and threatened him, then deported him that same evening.5
Al Wasat newspaper was subjected to a smear campaign led by the IAA itself. On 2 April 2011, the IAA-operated Bahrain TV broadcast a two-hour live show antagonising Al Wasat and immediately afterwards, the IAA suspended the newspaper, only allowing it to resume publication after the resignation of its senior editorial staff.6 The newspaper was not alone suffering this crackdown on free expression: Bahrain TV broadcast programmes identified and vilified celebrity protestors throughout the Arab Spring period. Athletes, including national football team players, who called on live broadcasts to defend their appearance at protests, were arrested and subjected to torture within days of doing so.7 The IAA-run Bahrain TV, which we reiterate would have been executing policy set by the president, Sheikh Fawaz, has never been held to account for its role inciting hatred against legitimate political protest and the targeting of specific persons.
Journalism as a whole was under threat during Sheikh Fawaz’s leadership of the IAA. The repression of independent journalists and media under his watch was on a scale similar to that seen in countries like Turkey and Egypt, which are known for state censorship of the press.
A sure indicator of this is in the Reporters Without Borders Press Freedom Index, which ranks each country on press freedom, with the 1st country having the freest press. Bahrain’s ranking, which stood at 119th in 2009, the year before Sheikh Fawaz’s IAA presidency, fell by 46 rungs to 165th by 2012, the year his presidency ended. This was the greatest fall in rankings Bahrain ever saw.
Bahrain’s ranking currently sits at 162 (with this latter rise in rank due mainly to the addition of countries ranked below Bahrain). As a point of comparison, the 2016 Press Freedom Index 2016 respectively ranked Turkey and Egypt at 151 and 159. The rankings reflect Sheikh Fawaz’s devastating leadership of the state media body and the long shadow left on press freedom.
It was for these reasons that the community of press freedom activists, rights defenders and NGOs greeted Sheikh Fawaz’s appointment as ambassador to the United Kingdom with alarm. His embassy’s latest statements on the case of Ms. Nazeeha Saeed, for which the history extends back to his IAA presidency in 2011, calls back his direct role in repressing Bahrain’s press and journalists. His role in allowing the incitement of hatred against pro-democracy protesters on his watch, and his continued public attempts to mislead on the cases of journalists like Ms. Saeed, are indications that neither he nor the country he represents share the key British values of the right to free speech and individual liberty, nor in the universally recognised right to freedom of expression, as protected under Article 19 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. The Kingdom of Bahrain’s choice of a person with a key role in repressing freedom of speech as their ambassador to the United Kingdom reflects Bahrain’s unchanged, poor attitudes towards freedom of speech and human rights more generally.
We therefore urge you to address this promptly and raise these issues surrounding Sheikh Fawaz’s past and current involvement in the violations of press freedom with the Government of Bahrain.
Yours sincerely,
Bahrain Institute for Rights and Democracy
Index on Censorship
Reporters Without Boarders
1 Bahrain Embassy in London, Press Release: Information Affairs Authority Clarifies Regulation for Foreign Correspondents Related to Nazeeha Saeed, 20 July 2016, http://us12.campaign- archive1.com/?u=adae2d71fee280549ad890919&id=79fd8c6d53.
2 Human Rights Watch, Criminalizing Dissent, Entrenching Impunity: Persistent Failures of the Bahraini Justice System Since the BICI Report, 28 May 2014, https://www.hrw.org/report/2014/05/28/criminalizing-dissent- entrenching-impunity/persistent-failures-bahraini-justice.
3 Reporters Without Borders, RSF Demands Justice for Bahraini Journalists Tortured in 2011, 20 November 2015, https://rsf.org/en/news/rsf-demands-justice-bahraini-journalist-tortured-2011.
4 Bahrain TV on Youtube, IAA President Interview on BBC Arabic – 27 May 2011, 27 May 2011, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SDlClo2AIuE.
5 Bahrain Independent Commission of Inquiry (BICI), Report of the Bahrain Independent Commission of Inquiry, November 2011, para. 1611, http://www.bici.org.bh/BICIreportEN.pdf.
6 BICI, Report of the BICI, para. 1592.
7 ESPN (mirror), ESPN E:60: Athletes of Bahrain, 8 November 2011, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wfhPWwhWlJU.