18 Apr 2017 | Awards, Awards Update, News, Youth Board
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Beatrice Mtetwa is a noted Zimbabwean human rights attorney. She received the Bindmans Law and Campaigning Award from Index in 2006 for her efforts in protecting journalists arrested by Zimbabwe’s repressive regime, headed by President Robert Mugabe. Since receiving the award, she has continued in much the same vein and gone on to scale even greater heights – defending the human rights of Zimbabwean citizens at significant risk to her own liberty. Notable cases include defending, and securing the release of, two foreign journalists from The New York Times and The Telegraph in 2008.
In that case the two journalists, Barry Bearak and Stephen Bevam, were arrested in Harare as they attempted to cover the bitterly contested – and possibly rigged – presidential elections. The charges were based on the fact that they had practised journalism without being accredited – an act that did not amount to an offence under Zimbabwean law. Mtetwa was instrumental in securing the quick release of the journalists from an uncertain period of detention as political prisoners of the Mugabe regime. In 2009, she became the first African after Nelson Mandela, to receive the Ludovic-Trarieux International Human Rights Prize for her efforts at advancing human rights in Zimbabwe.
In her attempts to protect Zimbabweans from violations of the rule of law, she has also found herself at the receiving end of targeted prosecutions. Most recently, in 2013, she was charged with “obstructing justice” during a police raid. The state alleged that she made insulting statements to officers during the raid. The specific allegations in question? That Mtetwa shouted “at the top of her voice” that the raid was “unconstitutional, illegal, and unlawful” – statements that the court found did not warrant the charges that were brought against her.
Despite this arrest, Mtetwa has not been deterred from her indefatigable efforts to hold her government accountable. In 2016, she acted to secure the release of leaders of the war veterans association taken into custody by the Mugabe regime. She has also fought for and won several other critical human rights cases for people persecuted by the Mugabe regime.
With all the instability and uncertainty surrounding the rule of law in Zimbabwe, there is one constant. The world continues to watch Beatrice Mtetwa with admiration.
Tarun Krishnakumar is a member of Index on Censorship’s Youth Advisory Board. He graduated from the National Law School of India in Bangalore and currently works with a New Delhi-based law firm on public policy and regulatory affairs with a focus on technology.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”85476″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center” onclick=”custom_link” link=”https://www.indexoncensorship.org/2016/11/awards-2017/”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
Index on Censorship Freedom of Expression Awards
Seventeen years of celebrating the courage and creativity of some of the world’s greatest journalists, artists, campaigners and digital activists
2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”12″ style=”load-more” items_per_page=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1492506428504-2e169269-81a9-1″ taxonomies=”173″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
9 Feb 2017 | Mapping Media Freedom, News, Youth Board
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]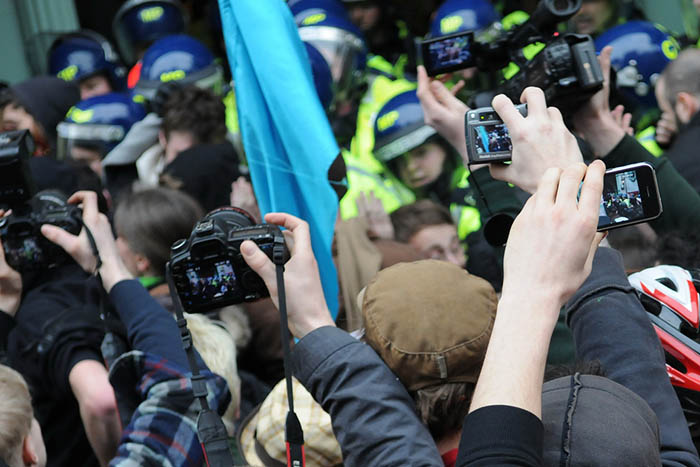
To highlight the most pressing concerns for press freedom in Europe in 2017, members Index’s outgoing youth board review the year gone by with some of our Mapping Media Freedom correspondents.
Youth board member Sophia Smith Galer, from the UK, spoke to Ilcho Cvetanoski, Mapping Media Freedom correspondent for Croatia, Montenegro, Bosnia and Macedonia.
 According to Cvetanoski, a lot has improved in the region over the last 15 years. The era during which journalists were targeted and killed is long passed, but the media is still dogged by censorship and political divides. In fact, journalists are regularly threatened and vilified by political elites, often denounced as foreign mercenaries, spies and traitors. Cvetanoski reports that this has led to “physical threats, the atmosphere of impunity, media ownership and also verbal attacks amongst the journalists themselves”. He notes that techniques pressuring journalists have changed from “blatant physical assaults to more subtle ones”.
According to Cvetanoski, a lot has improved in the region over the last 15 years. The era during which journalists were targeted and killed is long passed, but the media is still dogged by censorship and political divides. In fact, journalists are regularly threatened and vilified by political elites, often denounced as foreign mercenaries, spies and traitors. Cvetanoski reports that this has led to “physical threats, the atmosphere of impunity, media ownership and also verbal attacks amongst the journalists themselves”. He notes that techniques pressuring journalists have changed from “blatant physical assaults to more subtle ones”.
The breaking up of the former Yugoslavia has undoubtedly been a historical burden on Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia. Cvetanoski describes this legacy as having left “deep scars in every aspect of the people’s lives, including the lives and the work of journalists”. Media workers are still remembered as having once been tools of the state. Nowadays, the opposite is happening; they’re being criticised by political elites as enemies of the state simply for scrutinising politicians’ behaviour.
It’s unsurprising that this has left many journalists in the region politicised, undermining professionalism and trust in the media. Conservative politicians court sympathisers in the media so that they can manipulate the angle and content of stories that are run. The fact that journalist salaries are low and that the economic situation is poor overall further imperils journalistic integrity in the face of bribes.
If the situation remains as it is – with limited and highly controlled sources for financing the media, a poor political culture and low media literacy among citizens – then Cvetanoski holds little hope for the future of press freedom in the region. News consumers aren’t equipped with the literacy levels to distinguish between professional versus sensational journalism, nor are the sources of media funding transparent or appropriate. “In this deadlock democracy, the first victims are the citizens who lack quality information to make decisions.”
Mapping Media Freedom is helping to change this. Making journalists feel less alone and offering a space for them to report threats to press freedom ensures that the hope for a free press throughout Europe is kept alive.
The youth board’s Constantin Eckner, from Germany, spoke with Zoltán Sipos, the MMF correspondent for Hungary, Romania and Bulgaria.
 As MMF illustrates, journalists in all three countries have to deal with constant pressure from authorities and various degrees of censorship. In 2016, 42 incidents were reported in Hungary, 21 in Romania and 7 in Bulgaria.
As MMF illustrates, journalists in all three countries have to deal with constant pressure from authorities and various degrees of censorship. In 2016, 42 incidents were reported in Hungary, 21 in Romania and 7 in Bulgaria.
Index on Censorship’s regional correspondent Zoltán Sipos, who is also the founder and editor of Romania’s investigative outlet Átlátszó Erdély, points out that the Hungarian government and its allies within the country follow a sophisticated plan to neutralise critical media outlets. Several newspapers that struggled financially have been purchased by rich business people or media moguls in recent history. “Just like in regards to any other part of society, prime minister Viktor Orbán seeks for a centralisation of the media industry,” Sipos says.
Yet, instead of simply controlling the media, Orbán and the reigning party Fidesz intend to use established outlets and broadcasters to construct narratives in favour of their agendas. Only a handful of independent outlets remain in Hungary.
In November 2016, Class FM, Hungary’s most popular commercial radio channel, was taken off the air. The Media Council of Hungaryʼs National Media refused to renew its licence as Class FM was owned by Hungarian oligarch Lajos Simicska, whose outlets became very critical towards the government after a quarrel between him and Orbán.
The authorities in Romania and Bulgaria might not follow a well-wrought plan, but the situation for critical journalists is as severe. “The main problem is that most outlets can’t generate enough revenue from the market,” Sipos explains. “These outlets found themselves under constant pressure, as powerful business people are willing to purchase them and use them to promote their own political agendas.” Ultimately, this issue leads to the demise of independent reporting and weakens voices critical of the ruling parties and influential political players.
Sipos concludes that “these three countries have little to no tradition of independent journalism.” Although death threats towards, or even violence against journalists do not exist, the working conditions for critical reporters are difficult.
He recommends the investigative outlets Bivol.bg from Bulgaria, atlatszo.hu and Direkt36.hu from Hungary as well as RISE Project and Casa Jurnalistului from Romania as bastions of independent journalism. A few mainstream outlets that conduct critical reporting are 444.hu, index.hu, HotNews.ro and Digi24.
Layli Foroudi, a youth board member from the UK, interviewed Mitra Nazar, MMF correspondent for Serbia, Kosovo, Slovenia and the Netherlands.
 A Dutch national based in Belgrade, Serbia and the Netherlands are Nazar’s natural beats, and she also monitors media freedom in the nearby Balkan states of Slovenia and Kosovo.
A Dutch national based in Belgrade, Serbia and the Netherlands are Nazar’s natural beats, and she also monitors media freedom in the nearby Balkan states of Slovenia and Kosovo.
This year, Serbia has been the most intense of the four countries to cover. Serbian journalists have been subject to physical attacks and the government has maintained a smear campaign against independent media outlets in the country.
“This is a very organised campaign,” explains Nazar, “they’re being called foreign spies and foreign mercenaries.”
The “foreign spy” accusation has a real effect on the personal safety of journalists, whose pictures are often published alongside such accusations in the pro-government media. Nazar, who wrote a feature on the subject, says that this can cause such journalists to be branded as unpatriotic and anti-Serbian: “When the government accuses journalists of being “foreign spies”, it gives the impression that these independent journalists are against Serbia as a country.”
The ruling party of Serbia even went so far as to organise a touring exhibition called Uncensored Lies, where the work of independent media was parodied in an attempt to prove that the government does not censor, however, the exhibition also served to discredit these publications by calling the content “lies”.
“Can you imagine the ruling party organises an exhibition discrediting independent media,” says Nazar, shocked, “this is not indirect censorship, it is directly from the government.”
The media landscape in the Netherlands does not experience direct state-sponsored censorship, but there are other challenges. The Netherlands ranks 2nd in the 2016 RSF World Press Freedom Index, but Nazar has still reported a total of 49 incidents since the Mapping Media Freedom project started, from police aggression against journalists, to assaults on reporters during demonstrations, to broadcasters being denied access to public meetings.
For 2017, she is interested in looking into how the Dutch media deals with the rise of the far right and a growing anti-immigrant sentiment, especially in the upcoming elections which will see controversial far-right candidate Geert Wilders stand for office.
Last year, a Dutch tabloid De Telegraaf published an article about the arrival of refugees to the Netherlands with a sensational headline that generated a lot of debate in the Dutch media, which Nazar says is becoming increasingly politicised and polarised.
For Nazar, there is a line to be drawn with what legacy media outlets should and should not publish. “That line is representing and following the facts,” she says, “if you publish a headline that says there is a “migrant plague”, that is beyond facts – it is a political agenda.”
The youth board’s Ian Morse, from the USA, interviewed Vitalii Atanasov, the MMF correspondent for Ukraine.
In just the past two months in Ukraine, journalists have been assaulted, TV stations have been banned and governments on both sides of the country’s conflict with Russia have sought to limit public information and attack those who publicise.
Vitalii Atanasov is the correspondent who reported these incidents to the Mapping Media Freedom project. Drawing on sources from individual journalists to large NGOs, Atanasov monitors violations of media plurality and freedom in Ukraine for the project. To verify a story, he sometimes contacts media professionals directly, or crowdsources through social media, as he finds that all journalists publicise cases of violation of their rights, attacks, and incidents of violence.
“Some cases are complicated, and the information about them is very contradictory,” Atanasov tells Index. “So I’m trying to trace the background of the conflict that led to the violation of freedom of expression and media.”
Many of the violations that occur in Ukraine are either individual attacks on media workers by separatists in the east or Ukrainian officials attempting to control the media through regulation and licensing.
Of about a dozen and a half reports since he began working with MMF, Atanasov says many reports stick out, such as the “blatant” attempts of authorities to influence the work of major TV channels such as Inter and 1+1 channels. Most recently, Ukraine banned the independent Russian station Dozhd from broadcasting in Ukraine. While TV has recently been the target, problems with media freedom have come from almost everywhere.
“The sources of these threats can be very different,” Atanasov says, “for example, representatives of the authorities, the police, intelligence agencies, politicians, private businesses, third parties, criminals, and even ordinary citizens.”
Atanasov and MMF build off the work of other groups working in Ukraine, such as the Institute of Mass information, Human Rights Information Center, Detector Media, and Telekritika.ua.
Click on the bubbles to view reports or double-click to zoom in on specific regions. The full site can be accessed at https://mappingmediafreedom.org/
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_basic_grid post_type=”post” max_items=”4″ element_width=”6″ grid_id=”vc_gid:1486659943480-96bea7cd-9879-6″ taxonomies=”6514, 6564″][/vc_column][/vc_row]
21 Sep 2016 | Magazine, mobile, News, Volume 45.02 Summer 2016 Extras, Youth Board
In the latest issue of Index on Censorship magazine, The Unnamed: Does anonymity need to be defended?, Index’s contributing editor for Turkey, Kaya Genç, explores anonymous artists in Turkey. In the piece the artists discuss how vital anonymity is in allowing them to complete their more controversial work. The Index on Censorship youth advisory board have taken inspiration from this piece for their latest task, in which they investigate anonymous art around the world.
Keizer by Constantin Eckner

Ants feature in Keizer’s work to sybolise “the forgotten ones, the silenced, the nameless, those marginalised by capitalism”. Image: Keizer
Prior to the January 25 Revolution political street art was anything but common in Egypt, yet it has proliferated in public spaces in the aftermath of the revolution. One of the most productive street artists in Cairo is Keizer, who has gained popularity and notoriety in recent years. Like Banksy and other street artists, he uses the well-known stencil technique to empower his fellow countrymen, and people in general, with his thought-provoking work. He likens people to ants, which are featured in most of his graffiti. Keizer explains on his Facebook account that the ant “symbolises the forgotten ones, the silenced, the nameless, those marginalised by capitalism. They are the working class, the common people, the colony that struggles and sacrifices blindly for the queen ant and her monarchy.”
Asked about the reason for protecting his identity, Keizer said: “I am very concerned over my safety and the repercussions of street art which I’ve already had a taste of, especially with this current regime. Including death threats,

Egyptian street artist Keizer has gained popularity in recent years. Image: Keizer
my twitter account was hacked twice. In the past five years of working on the street I’ve been caught once. I came out of it with a few bumps and bruises, nothing major. I consider myself lucky that I came out one day later.
“You can imagine that being caught here is very different than being caught in Europe. There is no proper procedure and that makes you a victim of the person handling you, and the uncertainty of what comes next. Graffiti is a grey area here, they don’t have any definition or classification for it in the books, so they make it up as they go along, taking you for the fear ride. It’s all under vandalism, so they can make it look small or escalate it to exaggerated levels. For instance, you can be dubbed as a political traitor; it can be considered racketeering; they can glue your name to any political movement unpopular with the people…etc.”
Tall walls, low profiles: Icy and Sot by Layli Foroudi
Icy and Sot describe themselves as stencil artists from Tabriz, Iran. As for their identities, they reveal only that they are brothers, born in 1985 and 1991. Their work is created under pseudonyms in countries around the world, including Iran, USA, Germany, Norway, and China, on legal and illegal walls as well as in galleries.
The anonymous duo, who paint on themes like human rights, censorship, and justice, say that charges against artists in Iran make going public risky.
“Pseudonyms help us to keep a low profile,” the brothers explained in an interview with ArtInfo, “Being arrested in Iran is completely different, because they charge you with crimes that you have not even committed, like Satanism or political crimes.”
Their work often uses striking human faces in black and white to make statements about politics and the environment, to call for peace, and to direct messages at the government of Iran. In 2015, Icy and Sot used their art to protest for freedom of expression in Iran, prompted by the arrest and 18-month imprisonment of Atena Farghadani, an Iranian artist who was detained for publishing a cartoon that satirised the Iranian government as animals. In solidarity, they stenciled a tribute piece depicting Farghadani with a backdrop of protesters on a wall in Brooklyn.
Maeztro Urbano’s fight to change a criminal image by Ian Morse.
In the most recent data, Honduras has the highest homicide rate in the world, with 84 intentional homicides per 100,000 people in 2013. The prominence of drug trafficking and ubiquity of poverty does not improve its reputation.
To some Hondurans, their country’s international image has done nothing but hurt citizen’s attempts to improve daily life in the country’s bustling cities and lively cultural centers. Maeztro Urbano and his friends became the face of an urban street art project to disrupt the atmosphere of crime and reveal another side of the country outside of the headlines.
His projects range from adjusting street signs promoting gender equality to vandalising billboards with corrupt politicians, to wall graffiti showing the effect of violence on children. Working his day shifts in the advertising industry, Maeztro Urbano said he wants to contribute more to his country than proliferating consumerism.
“Change should start within society. With each individual,” El Maestro – as he is also called – told The Creators Project. “To have respect for the lives of others, to respect the right to sexual diversity, to a better education.”
“If we don’t change that as a society and as individuals, we will never be able to change as a country.”
Assailants in Honduras have not been very hospitable to those reporting on crime or those wishing to express their identity. Faced with police harassment and shootings from unknown attackers, Maeztro Urbano chooses to wear a mask while he works to spread messages of hope around the country.
Bleeps.gr: Over a decade of political artivism in Athens by Anna Gumbau.
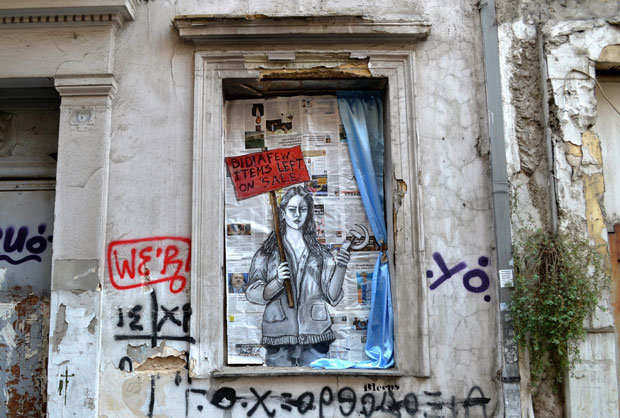

Bleeps.gr is one of Greece’s most prominent street artists, having painted murals on the streets of Athens for over 10 years. Image: Bleeps.gr
“I have been radically oriented to the political discourse, utilising the public sphere, and I am not afraid or discouraged”, Bleeps.gr, one of the most prominent Greek street artists, told Index.
Bleep.gr has been designing murals, that are mostly critical of the austerity policies imposed to Greece, on the streets of Athens for over 10 years. The Greek social turmoil has had a strong influence on his artwork, not only in his scenes, but even in his methods. “I buy very cheap materials and can’t afford those impressive equipment to create a mural”, he said in an interview with Street Art Europe.
Bleeps.gr chooses to use a pseudonym as an attempt to challenge “the institutionalised perception of the identity”, he told Index. While he is not afraid of the state authorities, he points at art institutions, such as galleries, exhibitions and festivals, who reject and exclude his art. “Most of the censorship I have received has come from other artists, especially the ones related to systemic initiatives, who in the past years have removed all of my works from the city center” he said. Greek political street artists often suffer from the exclusion of art galleries and exhibitors; in the summer of 2013, the CRISIS? WHAT CRISIS? street art festival in Athens, which celebrates the value of street art in the current political happenings, invited 20 artists from different European countries but failed to invite any Greek artists.
Nevertheless, Bleeps.gr stresses the fact that the internet “has provided a virtual field of allocation”, and most of the political street art discourse happens there.
Bleeps.gr highlights the mechanisms of such institutions to “absorb street artists” and make them become part of the art “business”, adding: “the majority of them nowadays serve gentrification policies and turn policies and turn political art into a spectacle for tourist pleasure”.
King of Spades by Sophia Smith-Galer.
When it comes to anonymous artists, the art tends to speak far louder than any speculation into the artist themselves. This anonymous artist in Lebanon is no Arab Banksy that lurks tantalisingly close to the limelight; this artist could quite literally be anyone, and the lack of anybody claiming the piece as their own is revelatory of the grave reality of artists in developing countries that test the patience of despots and tyrants.
Despite its tired and no longer relevant label “Paris of the Middle East”, even the dazzlingly artistic city of Beirut, Lebanon, can’t quite get away with hanging something like this banner, depicting the late Saudi Arabian monarch King Abdullah bin Abdul Aziz as a brutal King of Spades. Shortly after its creation in 2013, the Lebanese state prosecutor ordered an investigation to reveal the source of these posters after complaints from Saudi Ambassador Ali Awad Asiri.
It seems that nobody got caught, and nor do I particularly want to dwell on what would have happened to the artist if they had. But in the Middle East, such a daring artistic expression must be forbidden fruit in a region of gagged political artistry; demonstrated no better than in this mysterious artist who gambled with the assumed impunity of that gentleman with the bloodied scimitar.
Dede Bandaid by Shruti Venkatraman.
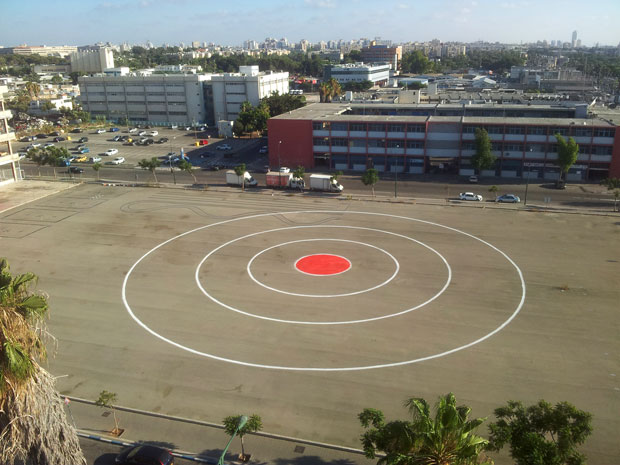

One of Dede Bandaid’s most well known works, a missile target painted in the middle of a large car park, a reference to the Gaza conflict in 2014. Image: Dede Bandaid / Wikicommons
Dede Bandaid is an anonymous Israeli artist who has added colour to Tel Aviv’s streets with thought provoking and politically relevant street art. His artistic career began in 2000 during his compulsory military service, and most of his earlier pieces demonstrated a clear anti-establishment sentiment. His more recent works, following the end of his stint in the military, aim to communicate social and political messages. One of his most well known works is a missile target painted in the middle of a large car park, a reference to the Gaza conflict in 2014.
Dede enjoys using public spaces as a canvas as this approach allows freer and more controversial expression, while also being accessible to and viewable by a larger audience especially when the street art is photographed and its images are circulated online. He also makes use of traditional symbols of peace, like the white dove, and frequently incorporates Band-Aids that represent healing and remedy in his artwork, with “Bandaid” being the pseudonym he signs on all his pieces. Over time, Dede’s style has evolved from stencilling to free-hand painting and collage and he interestingly also exhibits certain pieces in galleries across the world.
Cabbage Walker in Kashmir by Niharika Pandit.
A pheran-clad man walks around with a cabbage on a leash in the neighbourhoods of Srinagar, Kashmir. This performance act that he presents is inspired by Chinese artist Han Bing’s “Walking the Cabbage” social intervention work. While Bing chose to walk the cabbage to reflect on the changing values in the Chinese society, where once cabbage was a subsistence food product but is now only embraced by the poor, in Kashmir, this anonymous artist aims to normalise the cabbage walking to show the absurdity of militarisation in the region. Both the performances employ cabbage as an element of satire to expose the irony inherent in what how elitism and militarisation come to be normalised in societies across the world.
The Kashmiri Cabbage Walker writes on his blog, “I as a Kashmiri am willing to recognise walking the cabbage as part of the Kashmiri landscape but I will never accept the check posts, the bunkers, the army camps, the torture centers, the barbed wire, the curfews, the arrests, the toxic environment of conflict and war, as part of the same.”
This performance artist chooses to remain anonymous as it helps in focusing on the message and not the messenger. The Kashmiri Cabbage Walker says that he represents all Kashmiri lives under militarisation thereby revealing the artist’s identity becomes unimportant here.
Cracked pavements in Budapest by Fruzsina Katona.
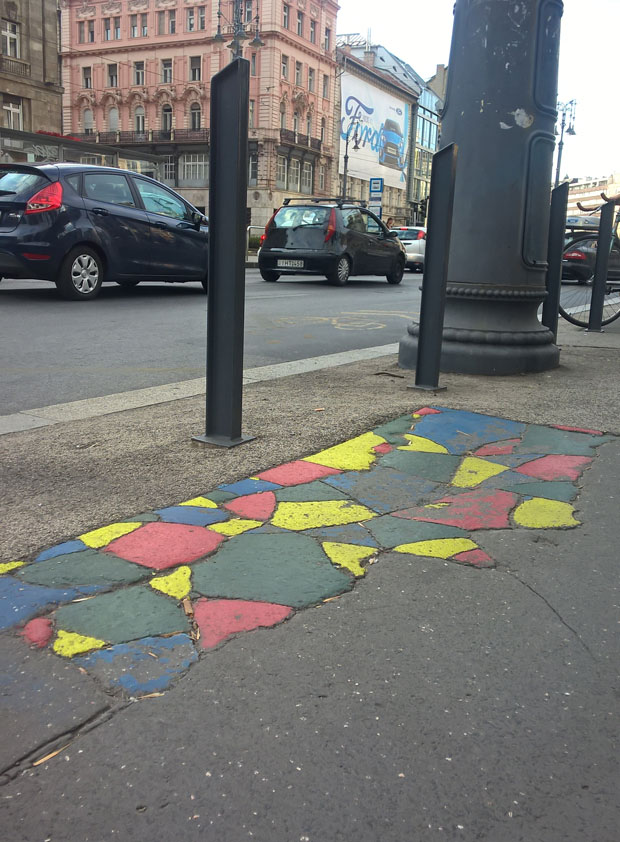

Anonymous volunteers have joined the satirial political party the Two-Tailed Dog party (MKKP) to paint cracked pavement on the streets of Budapest. Image: Fruzsina Katona
Anonymity does not necessarily mean that one is trying to hide his or her identity. Sometimes the identity of the person is utterly irrelevant. In Budapest, several anonymous volunteers are painting the streets of the city.
The pavement on the streets of the Hungarian capital are falling apart, ruining the image of the city and endangering those who walk on it. Authorities are known to do very little to fix the problem, but something had to be done. Hungary’s satiric political party, the Two-Tailed Dog party (MKKP) called for action and its artsy, anonymous volunteers started colouring the cracked pavement pieces resulting in dozens of cheerful spots across the city.
Unfortunately, there are some who find quarrels in a straw, and the police were called on the ad-hoc artists while they were peacefully decorating the pavement in a touristic neighbourhood. Now the volunteers are being prosecuted with vandalism.
But we still do not know their identity or how many of them are out decorating. All we know is that now we look at colourful patches of pavements while running our errands, instead of the sad and ugly cracked pavements.



 According to Cvetanoski, a lot has improved in the region over the last 15 years. The era during which journalists were targeted and killed is long passed, but the media is still dogged by censorship and political divides. In fact, journalists are regularly threatened and vilified by political elites, often denounced as foreign mercenaries, spies and traitors. Cvetanoski reports that this has led to “physical threats, the atmosphere of impunity, media ownership and also verbal attacks amongst the journalists themselves”. He notes that techniques pressuring journalists have changed from “blatant physical assaults to more subtle ones”.
According to Cvetanoski, a lot has improved in the region over the last 15 years. The era during which journalists were targeted and killed is long passed, but the media is still dogged by censorship and political divides. In fact, journalists are regularly threatened and vilified by political elites, often denounced as foreign mercenaries, spies and traitors. Cvetanoski reports that this has led to “physical threats, the atmosphere of impunity, media ownership and also verbal attacks amongst the journalists themselves”. He notes that techniques pressuring journalists have changed from “blatant physical assaults to more subtle ones”. As MMF illustrates, journalists in all three countries have to deal with constant pressure from authorities and various degrees of censorship. In 2016, 42 incidents were reported in Hungary, 21 in Romania and 7 in Bulgaria.
As MMF illustrates, journalists in all three countries have to deal with constant pressure from authorities and various degrees of censorship. In 2016, 42 incidents were reported in Hungary, 21 in Romania and 7 in Bulgaria. A Dutch national based in Belgrade, Serbia and the Netherlands are Nazar’s natural beats, and she also monitors media freedom in the nearby Balkan states of Slovenia and Kosovo.
A Dutch national based in Belgrade, Serbia and the Netherlands are Nazar’s natural beats, and she also monitors media freedom in the nearby Balkan states of Slovenia and Kosovo. 



